Effects of Boron Application on Growth and Quality of Flue-cured Tobacco NC297 under Different Potassium Supply Levels
2022-01-12XIEXinqiaoLIXiangweiTIANYutianYANGJizhouHUBaowenLUOLihuaLIJiazhiZHANGKunlan
XIE Xin-qiao, LI Xiang-wei, TIAN Yu-tian, YANG Ji-zhou, HU Bao-wen, LUO Li-hua, LI Jia-zhi,ZHANG Kun-lan
Hongta Tobacco (Group) Co., Ltd., Yuxi 653100, PRC
Abstract In order to provide reference for high quality tobacco producion, this experiment adopted a randomized block design in a field plot, and analyzed the effects of boron fertilizer on the growth, development on comprehensive quality of flue-cured tobacco by using mathematical statistics methods such as multiple comparison with NC297 as test material. The results showed that: spraying boron fertilizer on flue-cured tobacco leaves can promote the growth of flue-cured tobacco NC297 to a certain extent, effectively reduce the total particulate matter and tar content of tobacco, and play a positive role in regulating the total sugar, reducing sugar, nicotine and potassium content of flue-cured tobacco; the comprehensive quality of NC297 was the best when boron was applied at medium potassium level(K2B1).
Key words Flue-cured tobacco NC297; Boron; Potassium; Quality
1. Introduction
Boron is one of the essential trace elements for the growth and development of flue-cured tobacco. It plays a very important role in regulating the physiological functions of flue-cured tobacco at different growth stages. Boron is involved in protein metabolism, substance transport, alkaloid synthesis as well as the transformation related to calcium, potassium and other main elements, thus affecting the growth and development of tobacco leaves, and the yield and quality of tobacco leaves. Boron enters tobacco plant in the form of BO, participates in the synthesis of uracil and chlorophyll, and affects carbohydrate transportation and protein metabolism. Too much or too little boron will affect the growth and development of tobacco, which will cause physiological dysfunction of tobacco, resulting in poor growth and disease resistance of tobacco. When the available boron content in soil is 0.5~1.0 mg/kg, it is beneficial to plant growth;while when it is more than 1.0 mg/kg, toxic effects will occur. Applying proper amount of boron can promote the growth and development of flue-cured tobacco, improve its botanical characters, increase pigment content, increase photosynthetic intensity and transpiration rate, and increase yield, quality of tobacco. The content of boron in high-quality fluecured tobacco leaves in China generally ranges from 10 mg/kg to 40 mg/kg.
Tobacco is a potassium-loving crop. Potassium also plays an important role in increasing leaf size,leaf yield, single leaf weight and leaf color. And it can improve the quality of tobacco by affecting biochemical process of tobacco. Biochemical process have a decisive influence on the synthesis and accumulation of chemical components such as nicotine, organic acids and amino acids.NC297 has outstanding characteristics of sweet aroma, with high concentration, of low irritant and comfortable aftertaste, which is favored by cigarette industry enterprises and can meet the differentiated demand of high-grade cigarettes for raw materials.A randomized block design in a field plot with tobacco NC297 as material was adopted to explore the effects of boron application on the growth, development and quality of flue-cured tobacco under different potassium supply levels, so as to lay a foundation for the study of boron and potassium interaction mechanism in flue-cured tobacco, and find out the reasonable boron potassium fertilizer proportion for high quality tobacco production.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental materials
Tobacco NC297 provided by tobacco company in Yuxi was used as test flue-cured tobacco.
2.2. Experimental site
Experiment was conducted in Qinghe Village Committee of Branch River Town, Eshan County,Yuxi City with an altitude of 1 320 m. The tested soil was paddy soil, formerly used as rape soil. The chemical properties of tested soil were shown in Table 1.

Table 1 Physical and chemical properties of test soil
2.3. Experimental design
In the experiment, three levels of potassium were set. K1: low level of potassium fertilizer(KO), 9 kg/667m; K2: medium level of potassium fertilizer (KO), 15 kg/667m; K3: high level of potassium fertilizer (KO), 21 kg/667m. In each level of potassium fertilizer, applying boron fertilizer or applying water with a total of 6 treatments was set.B1: applying boron fertilizer on leaf surface; B0:applying water on leaf surface. Random block design was adopted in the experiment. The row spacing was 120 cm×60 cm, there were 50 plants in each plot, there were three replicates in each treatment with a total of 900 plants. Guard rows were set around the test area.
In the experiment, 6 kg/667mof pure nitrogen was applied, ammonium nitrate (35% N), superphosphate (16% PO), potassium sulfate (50% KO),sodium borate (18% boron) were used as nitrogen fertilizer, phosphorus fertilizer, potassium fertilizer and boron fertilizer, respectively. Nitrogen fertilizer was applied with 60% concentration as basal fertilizer and 40% as topdressing; potassium fertilizer was applied with 40% concentration as basal fertilizer and 60% as topdressing; phosphorus fertilizer was applied with all as basal fertilizer. Topdressing should be applied in three times within 25 d after transplanting.Boron fertilizer was sprayed on the leaf surface of the whole plant with a concentration of 0.5%. It was sprayed 3 times at the resettling growth stage and vigorous growth stage respectively, and the upper,middle and lower leaves were sprayed once before roasting, respectively. Field management was carried out according to Yuxi high quality tobacco production technical specifications.
2.4. Testing items and methods
2.4.1. Investigation of agronomic characters
After the normal growth and development of tobacco plants were capped, 10 representative tobacco plants were selected for each treatment, and the tobacco leaves were marked. According to the YC/T 142—1998standard, the height, stem girth,effective leaf number and other agronomic characters of tobacco plants were measured and recorded.
2.4.2. Routine chemical components and sensory quality of primary flue-cured tobacco
The tobacco leaves in the different position were marked. The representative samples were selected to be divided into two halves along the main veins after mature picking and roasting. One half was used to determine the total sugar, reducing sugar, nicotine and other chemical indexes of primary cured tobacco leaves, and the other half was used for sensory evaluation. The chemical components was determined in the Tobacco Engineering Laboratory, College of Tobacco Science, Yunnan Agricultural University according to Tobacco Chemistry edited by WANG Rui-xin. Sensory evaluation was completed by the technology center of Hongta Group.
2.4.3. Analysis of smoke characteristics of monomer cigarette
The C3F grade of tobacco samples were taken from the middle leaves and made into cut tobacco according to the standard of cigarette processing, and then filled in the cigarette tube with a specification of (60 mm+24 mm) × 24.9 mm, ventilation rate of 30.3%, cigarette paper air permeability of 39 CU,and filter draw resistance of 616 Pa. The cut tobacco weight of single cigarette was 0.78 g. After filling, all the cigarette was balanced in a temperature and humidity chamber with a temperature of (22±1) ℃ and a relative humidity of (60±3) % for 48 h. Sample treatment,rolling, analysis and determination were completed by technology center of China Tobacco Yunnan according to the standard of GB/T19609-2004.
2.5. Data processing
Excel and SPSS 19.0 were used for statistical analysis.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. The agronomic characters of NC297 in the different treatments
As shown in Table 2, there were no significant differences in plant height, effective leaf number and stem girth among all treatments, whereas there were significant differences in maximum leaf length,maximum leaf width and maximum leaf area among all treatments. Of which, K3B1 had the maximum leaf length, leaf width and leaf area, which were 58.1 cm,25.0 cm and 1 456.3 cmrespectively. Moreover, the maximum leaf length and leaf area in the K3B1 were significantly higher than those in the other treatments.Under spraying boron fertilizer, the maximum leaf length, leaf width and leaf area of tobacco plant increased continuously with the increase of potassium level. At high level of potassium, the maximum leaf length and leaf area in the treatment with boron fertilizer (K3B1) were significantly higher than that in the treatment without boron fertilizer (K3B0);while at medium or low level of potassium fertilizer,the difference between the treatment with spraying boron fertilizer and no spraying boron fertilizer was not significant, whereas the treatment with spraying boron fertilizer also had a certain effect on promoting growth. The results showed that spraying boron fertilizer on leaf surface could effectively improve the agronomic characters of tobacco plant under the test soil condition, and the effect was most obvious at high level of potassium.
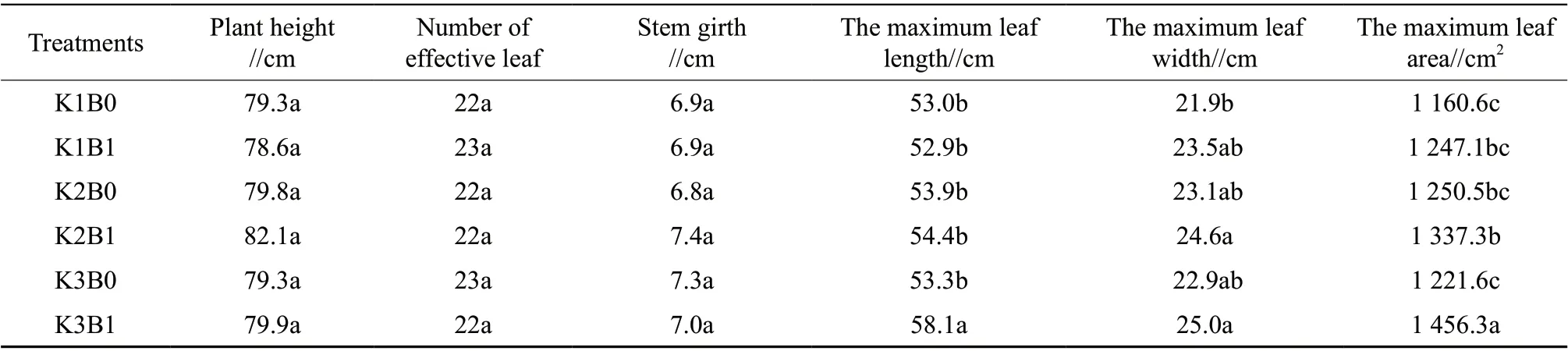
Table 2 Effects of spraying boron fertilizer on the agronomic characters of NC297 under different potassium supply levels
3.2. Main chemical components in middle leaves of primary flue-cured tobacco in different treatments
As shown in Table 3, at low level of potassium,compared with the K1B0, the chemical components contents in the K1B1 were significantly different. The contents of total sugar, reducing sugar and KO were increased by 2.57%, 10.87% and 11.61%, respectively,while the contents of nicotine and total nitrogen, the difference between the content of total sugar and reducing sugar were decreased by 20.57%, 4.49% and 30.68%. At medium level of potassium, compared with the K2B0, the chemical components contents except total nitrogen and KO in the K2B1 were significantly different. The contents of total sugar and reducing sugar were decreased by 3.16% and 8.21%,respectively, while the difference of two sugars and nicotine were increased. Spraying boron fertilizer had little effects on the contents of total nitrogen and KO.At high level of potassium, compared with the K3B0,the chemical components contents except KO in the K3B1 were significantly different. The contents of nicotine and total nitrogen increased. On the whole,the chemical components contents in the K2B1 was more harmonious, which meet the requirements of high quality tobacco leaves.

Table 3 Effects of spraying boron fertilizer on the chemical components of NC297 under different potassium supply levels
3.3. Sensory quality in middle leaves of primary flue-cured tobacco in the different treatments
As shown in Table 4, K2B1 had the best sensory quality, that was, it had the highest score, up to 88.The characters of K2B1 was fresh-sweetness aroma highlight, supplemented by burnt sweet, baking aroma, medium concentration of aroma amount, gentle aroma, comfortable and suitable taste. The sensory quality at low level of potassium was basically equal to that at high level of potassium. Compared with the tobacco leaves sprayed with water, samples which were sprayed with boron fertilizer had good quality and performance in sweetness aroma and richness.The burnt aroma of tobacco leaves sprayed with boron fertilizer increased with the increase of potassium level.In conclusion, K2B1 had the best sensory quality.
3.4. Smoke characteristics of middle leaves in the different treatments
As shown in Table 5, At the same level of potassium, the total particulate matter, measured tar content and nicotine content of smoke in the treatment with boron fertilizer were significantly different from those in the control, and the total particulate matter decreased, indicating that boron fertilizer could decrease the total particulate matter of smoke.At medium and low level of potassium, compared with the control, the measured tar content of smoke in the treatment with boron fertilizer decreased by 20.45% and 10.48%, respectively. While at high level of potassium, compared with the control, the measured tar content of smoke in the treatment with boron fertilizer increased. However, on the whole, themeasured tar contents of smoke at medium and high level of potassium were lower than that at low level of potassium. Spraying boron fertilizer and medium or high level of potassium was conducive to decreasing nicotine content, while spraying boron fertilizer and low level of potassium had no significant effect on the nicotine content. Focusing on tar and harmful reduction, spraying boron and potassium fertilizer was beneficial to improving the safety of tobacco,especially spraying boron fertilizer and medium level of potassium was more beneficial to reduce the tar content of tobacco.

Table 4 Effects of spraying boron fertilizer on the sensory quality of NC297 under different potassium supply levels
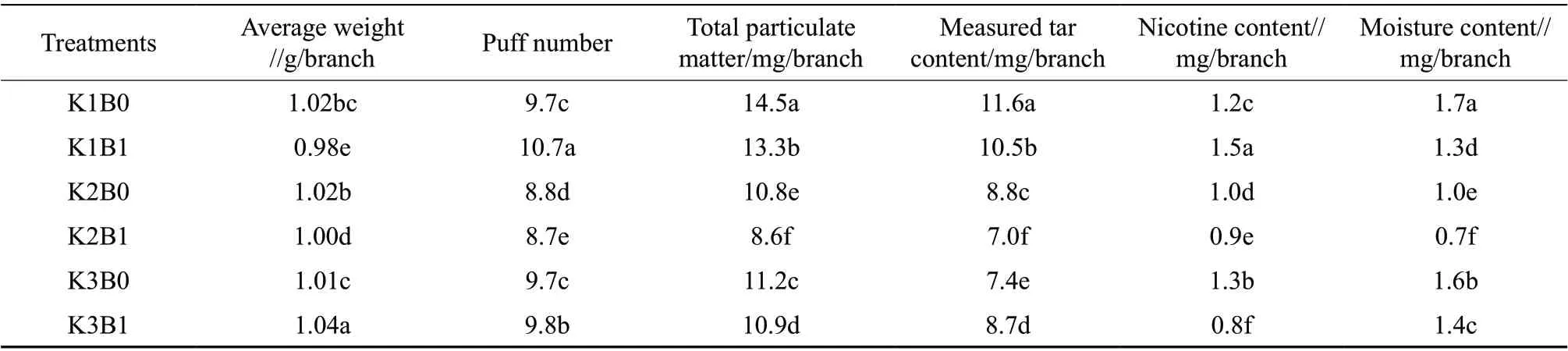
Table 5 Effects of spraying boron fertilizer on smoke index characteristics of NC297 under different potassium supply levels
4. Discussion
The results showed that under spraying boron fertizer, the maximum leaf length, leaf width and leaf area of tobacco plant increased continuously with the increase of potassium level. At high level of potassium, the maximum leaf length and leaf area in the treatment with boron fertilizer (K3B1) were significantly higher than that in the treatment without boron fertilizer (K3B0); while at medium or low level of potassium fertilizer, the difference between the treatment with spraying boron fertilizer and no spraying boron fertilizer was not significant, whereas the treatment with spraying boron fertilizer also had a certain effect on promoting growth.
Potassium, known as the "quality element"of tobacco leaves, can significantly improve the combustion property of tobacco leaves, as well as improve the aroma quality, aroma amount, taste and quality. The results showed that the content of potassium significantly increased after spraying boron fertilizer, indicating that spraying boron fertilizer could improve the adsorption of potassium by NC297, which was consistent with the results of previous studies.Moreover, spraying boron fertilizer effectively increased the contents of total sugar, and reducing sugar of tobacco NC297 decreased the content of nicotine and protein, improved the coordination of chemical components, indicating that spraying boron fertilizer had a positive effect on the regulation of sugar content, potassium content and nicotine content in tobacco leaves. Of which, spraying boron fertilizer combined with medium level of potassium had the best harmonious chemical components
K2B1 had the best sensory quality. Compared with the tobacco leaves sprayed with water, samples which were sprayed with boron fertilizer had good quality and performance in sweetness aroma and richness, and the burnt aroma amount of tobacco leaves sprayed with boron fertilizer increased with the increase of potassium level. Spraying boron fertilizer had a positive effect on the reduction of total particulate matter and that combined with medium level of potassium was more beneficial to reducing the content of tar and nicotine. It indicated that spraying boron fertilizer was conducive to improving the quality of flue-cured tobacco, which was consistent with previous studies.
5. Conclusion
Spraying boron fertilizer on the leaf surface of flue-cured tobacco could promote the growth of tobacco NC297, effectively regulate the contents of total sugar, reducing sugar, nicotine and KO to make the chemical indexes of tobacco leaves more close to the requirements of high quality tobacco leaves,effectively reduce the content of total particulate matter and tar, and improve the smoking safety of tobacco. Spraying boron fertilizer combined with medium level of potassium (K2B1) had the optimal comprehensive quality.
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Screening of an Antagonistic Strain of Phytophthora nicotianae and Its Application Potential
- Characterization of Specific Spoilage Bacteria and Volatile Flavor Compounds of Flavored Crayfish
- Protective Effect of Immaturue Bitter Orange (Citrus aurantium L.) Flavonoids Extracts on PC12 Cell Injury Induced by 6-Hydroxydopamine
- Efficient Extraction of Tea Saponin from Tea Seed Meals by 60Co γ-Irradiation
- Community Characteristics of Cardamine in Brassicaceae
- Effects of 4 Types of Remediation Agents on Reducing Cd Contents in Soil and Rice on Cd-contaminated Farmland
