加速康复外科策略对复发性胆道结石患者腹腔镜手术后应激状态的影响
2021-11-04邓晓春
邓晓春
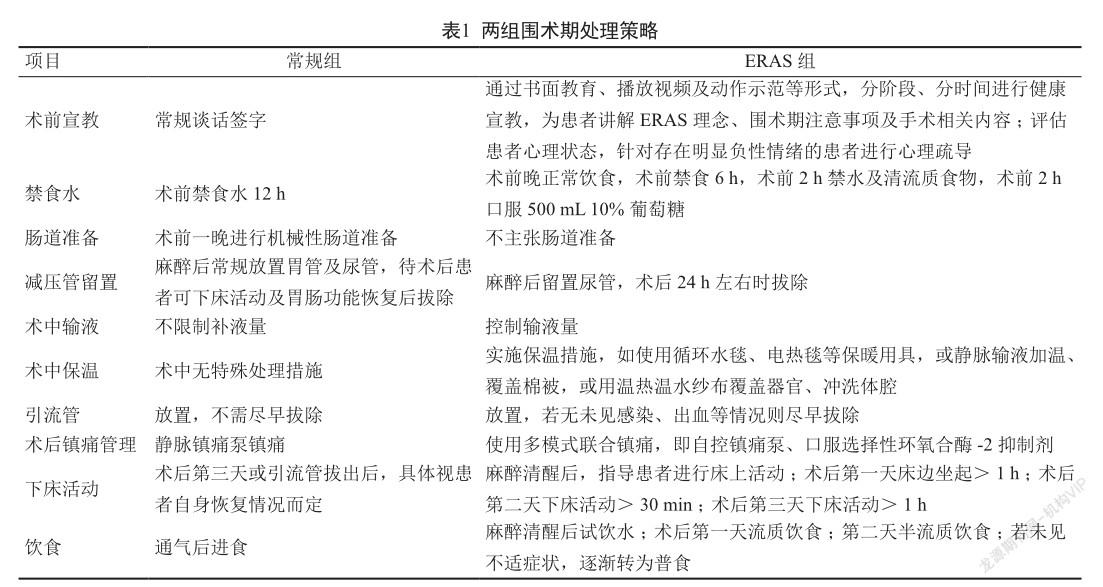


摘 要 目的:評价加速康复外科策略(enhanced recovery after surgery,ERAS)对复发性胆道结石患者腹腔镜手术后应激状态的影响。方法:选择2018年6月至2020年7月于江西省抚州市南城县人民医院接受腹腔镜手术的复发性胆道结石患者96例,按照随机数表法分成两组各48例。常规组接受常规围术期干预,ERAS组在围术期实施ERAS干预。采用视觉模拟评估量表(VAS)评估疼痛程度,应激反应问卷(SRQ)评估心理应激反应情况,比较两组围术期指标、心理应激、生理应激指标及术后并发症。结果:ERAS组引流管拔除时间、术后进食时间、排气时间及术后住院时间均比常规组短(P<0.05)。ERAS组术后48 h SRQ量表各维度评分、VAS评分、血清血管紧张素-2(ANG-2)、肾素(PRA)、醛固酮(ALD)水平均比常规组低(均P<0.05)。ERAS组术后并发症发生率为6.25%,与常规组的12.50%相比差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论:ERAS理念用于复发性胆道结石患者腹腔镜手术可加快术后康复进程,降低围术期心理、生理应激。
关键词 复发性胆道结石;腹腔镜手术;加速康复外科策略;应激状态
中图分类号:R657.4 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1006-1533(2021)20-0020-04
Effect of accelerated rehabilitation surgery strategy on the stress state of patients with recurrent biliary calculi after laparoscopic surgery
DENG Xiaochun(The Second Department of Surgery of Nancheng County Peoples Hospital, Fuzhou City, Jiangxi Province 244700, China)
ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate the effect of accelerated rehabilitation surgery strategy on stress state of patients with recurrent biliary calculi after laparoscopic surgery. Methods: Ninety-six patients with recurrent biliary calculi who underwent laparoscopic surgery in Nancheng County Peoples Hospital, Fuzhou City, Jiangxi Province from June 2018 to July 2020 were selected, and according to the random number table method, divided into two groups with 48 cases each. The routine group received routine perioperative intervention, and the accelerated rehabilitation surgery strategy group received accelerated rehabilitation surgery strategy intervention during perioperative period. The visual analogue assessment scale(VAS) was used to assess the degree of pain, the stress response questionnaire(SRQ) was used to assess the psychological stress response, and the perioperative indicators, psychological stress, physiological stress indicators and postoperative complications were compared between the two groups. Results: The drainage tube extraction time, postoperative eating time, exhaust time and postoperative hospital stay in the accelerated rehabilitation surgery strategy group were shorter than those in routine group(P<0.05); the SRQ scale scores, VAS scores, serum angiotensin-2(ANG-2), renin and aldosterone(ALD) levels in the accelerated rehabilitation surgery strategy group were lower than those in the routine group at 48 h after surgery(all P<0.05) . The postoperative complication rate in the accelerated rehabilitation surgery strategy group was 6.25%, which was not statistically different from 12.50% in the routine group(P>0.05). Conclusion: The concept of accelerated rehabilitation surgery strategy for laparoscopic surgery in patients with recurrent biliary calculi can speed up the postoperative recovery process and reduce perioperative psychological and physical stress.
