基于自适应非线性粒子群算法的光刻光源优化方法
2021-10-18刘俊伯
王 建,刘俊伯,胡 松*
基于自适应非线性粒子群算法的光刻光源优化方法
王 建1,2,刘俊伯1,胡 松1,2*
1中国科学院光电技术研究所,四川 成都 610209;2中国科学院大学,北京 100049
光刻光源优化作为必不可少的分辨率增强技术之一,能够提高先进光刻成像质量。在先进光刻领域,光源优化的收敛效率和优化能力是至关重要的。粒子群优化算法作为一种全局优化算法,自适应控制策略可以提高粒子的全局搜索能力,非线性控制策略可以扩大粒子搜索范围。本文提出一种基于自适应非线性控制策略的粒子群优化算法,将光刻光源优化问题转换成多变量评价函数求解。对简单周期光栅图形和不规则图形进行成像优化仿真,通过粒子群优化算法的全局迭代特性优化光源形貌。利用图形误差(PEs)作为多变量评价函数,对迭代300次的仿真结果进行评价,两种仿真图形的PEs分别降低52.2%和35%。与传统粒子群优化算法和遗传算法相比,该方法不仅能提高成像质量,而且具有更高的收敛效率。
光源优化;光刻;分辨率增强技术;粒子群优化算法

1 引 言
光刻技术作为超大规模集成电路制造必不可少的关键技术。目前,光刻分辨率成为约束集成电路图形临界尺寸的重要因素。根据瑞利准则,波长()和数值孔径(numerical aperture,NA)是决定光刻技术分辨率(resolution)的两个关键因素。缩短曝光波长、扩大数值孔径成为提高光刻分辨率的有效方法。但由于设备温度、装配公差等因素的影响,会导致光刻成像质量下降。此外,当微纳图形特征尺寸小于曝光波长时,受到衍射效应的影响,产生光学邻近效应(optical proximity effect,OPE),造成晶圆表面图形发生畸变。因此,提高光刻成像质量,分辨率增强技术(resolution enhance techniques,RETs)是解决这些负面效应必不可少的手段[1-3]。
传统RETs主要包含离轴照明技术(off-axis illumination technique,OAI)、光学邻近校正技术(optical proximity correction technique,OPC)和相移掩模技术(phase-shift mask technique,PSM)[4]。随着光刻工艺不断发展,传统RETs已无法满足先进节点复杂图形的高成像质量需求,比如,在离轴照明中的各种照明方式,环形、偶极子、四极等。然而,逆光刻技术(inverselithography techniques,ILTs)作为RETs的一种先进方法,被广泛应用到先进光刻成像质量优化领域。其中,在ILTs方法中,基于像素表征的光源优化(source optimization,SO)[5-6]具有灵活度高、易于调制的优势,被应用于精确调制光源强度分布。
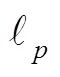
本文提出一种基于自适应非线性控制策略(adaptive nonlinear control strategy,ANCS)的PSO算法优化光刻光源形貌。自适应策略能够降低粒子陷入局部最优的概率,非线性控制策略能够扩大粒子的搜索范围。基于像素的SO模型中,采用光刻胶图形布局与目标图形之间的图形误差作为评价函数,对光源优化结构进行评价。对简单阵列图形与较复杂不规则图形进行仿真。与传统粒子群优化算法及遗传算法对比,ANCS-PSO具有更优越的收敛效率。
2 部分相干成像模型
根据光刻成像理论,光刻成像模型是典型的部分相干成像模型,如图1所示。光刻照明光源经汇聚镜组形成经典科勒照明,均匀入射掩模表面,受掩模透射率影响,产生带有掩模图形频谱信息的衍射光,并入射投影物镜系统。在光刻成像模型中,由于光瞳的低通滤波效应,只有低频衍射光通过投影物镜,在理想焦面形成空间像。光线入射晶面表面与光刻胶发生光化学反应,经过烘烤显影等处理后,特征图形显示在晶圆上。根据瑞利准则,光刻成像系统的极限分辨率为

图1 光刻成像模型
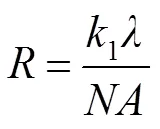
其中:1表示工艺因子。在光刻成像系统中,照明模式与系统光瞳为关于光轴圆对称结构,故光源相干因子()可定义为照明模式圆半径大小(s)与系统光瞳半径大小(p)的比值,即:

在部分相干成像系统中,空间像强度分布可由阿贝成像理论与霍普金斯成像理论计算获得[15]。而根据阿贝成像理论,部分相干成像系统近似等于一系列完全相干成像系统在不同点光源处衍射相干光的叠加。对于光刻光源优化,采用阿贝成像方法,能够降低计算复杂度。在完全相干成像系统中,照明光源为理想点光源,则完全相干成像模型可表示为
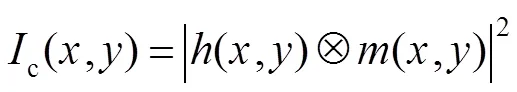





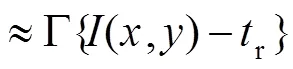


3 光源优化模型
在基于像素的SO模型中,采用一定数量像素点的方式离散光源图形。将搜寻评价函数全局最优解转换成求解多变量函数问题。对于ANCS-PSO模型,优化变量的数量决定计算的复杂度。在光刻成像模型中,光刻光源为关于光轴圆对称结构,可将光源划分为四个相等的部分,如图2所示,为典型环形照明模式。因此,按照笛卡尔坐标系将光源图形划分为四个象限,仅利用第一象限的有效光源像素点作为优化变量,可沿着水平垂直方向反转第一象限像素点分布得到最终光源形貌[17]。out表示环形光源最大半径,in表示环形光源最小半径。

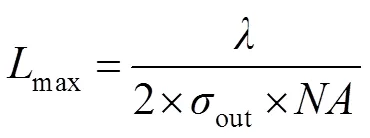
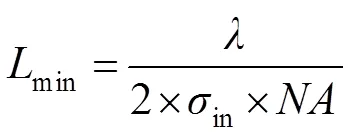
环形照明光源内外半径大小分别为
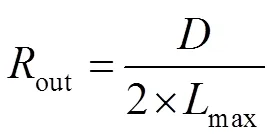
在笛卡尔坐标系中,光源图形中心点位置为
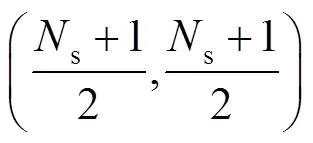


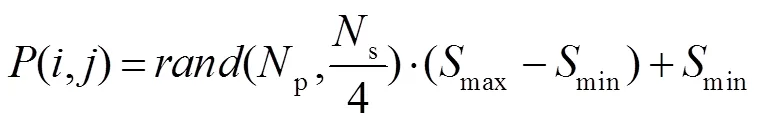



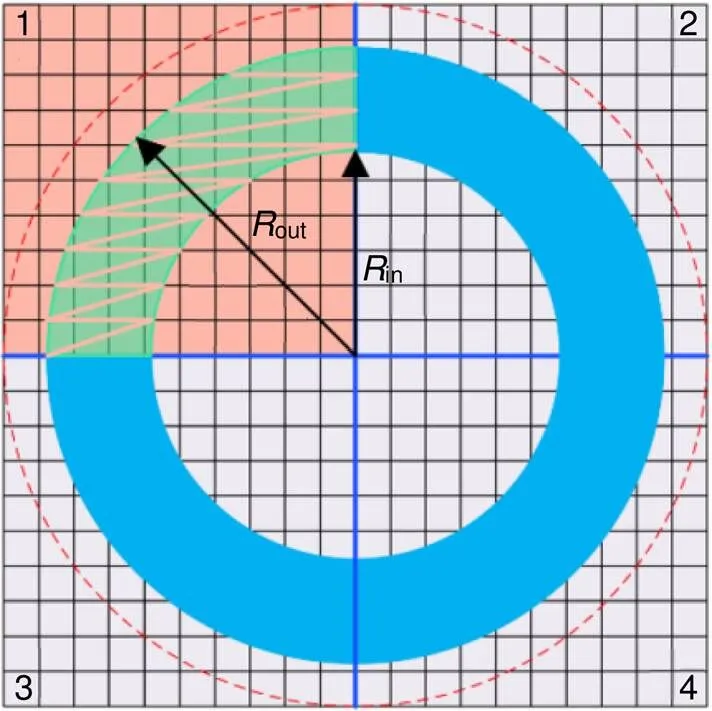
图2 光源表示方式

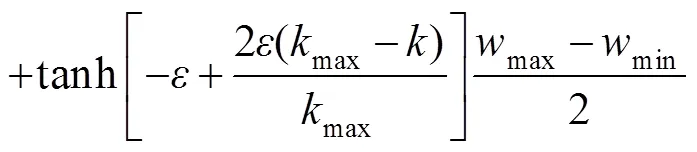
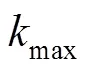
4 仿真结果


图4显示为逆光刻光源优化仿真结果。当目标图形布局类似单周期光栅时(图3(b)),光源模式近似水平方向偶极照明,如图4(a),4(e),4(i)所示。而目标图形布局接近水平方向光栅结构时(图3(c)),照明光源模式近似于垂直方向偶极照明,如图4(c),4(g),4(k)所示。根据优化后的光源形貌,对两种目标图形进行部分相干成像仿真,并通过sigmoid函数(式(5))得到光刻胶图形,分别为图4(b),4(f),4(j)和4(d),4(h),4(l)。与初始PEs相比,三种算法两种成像图形误差值降低,分别为:Pattern 01:52.2%,41.7%,37.4%;Pattern 02:35%,25.3%,25.3%。
图5显示三种优化算法模型收敛曲线效率。经过多次仿真实验,当迭代次数为300次时,收敛曲线已保持稳定状态。两种目标图形的仿真PEs初始值均由相同光源强度分布计算得到,其中有效光源像素点值为随机数。在两种PSO模型中,为了保证仿真结果有效性,其学习因子及惯性权重系数最大最小值相同。此外,在PSO模型中,优化模型计算复杂度与粒子种群个数相关,为保证模型的收敛效率,设置粒子种群p=50。迭代结果显示,ANCS-PSO相比其他两种算法具有更快迭代速度和效率。

图3 (a) 环形光源形貌;(b) 简单阵列图形;(c) 不规则光栅
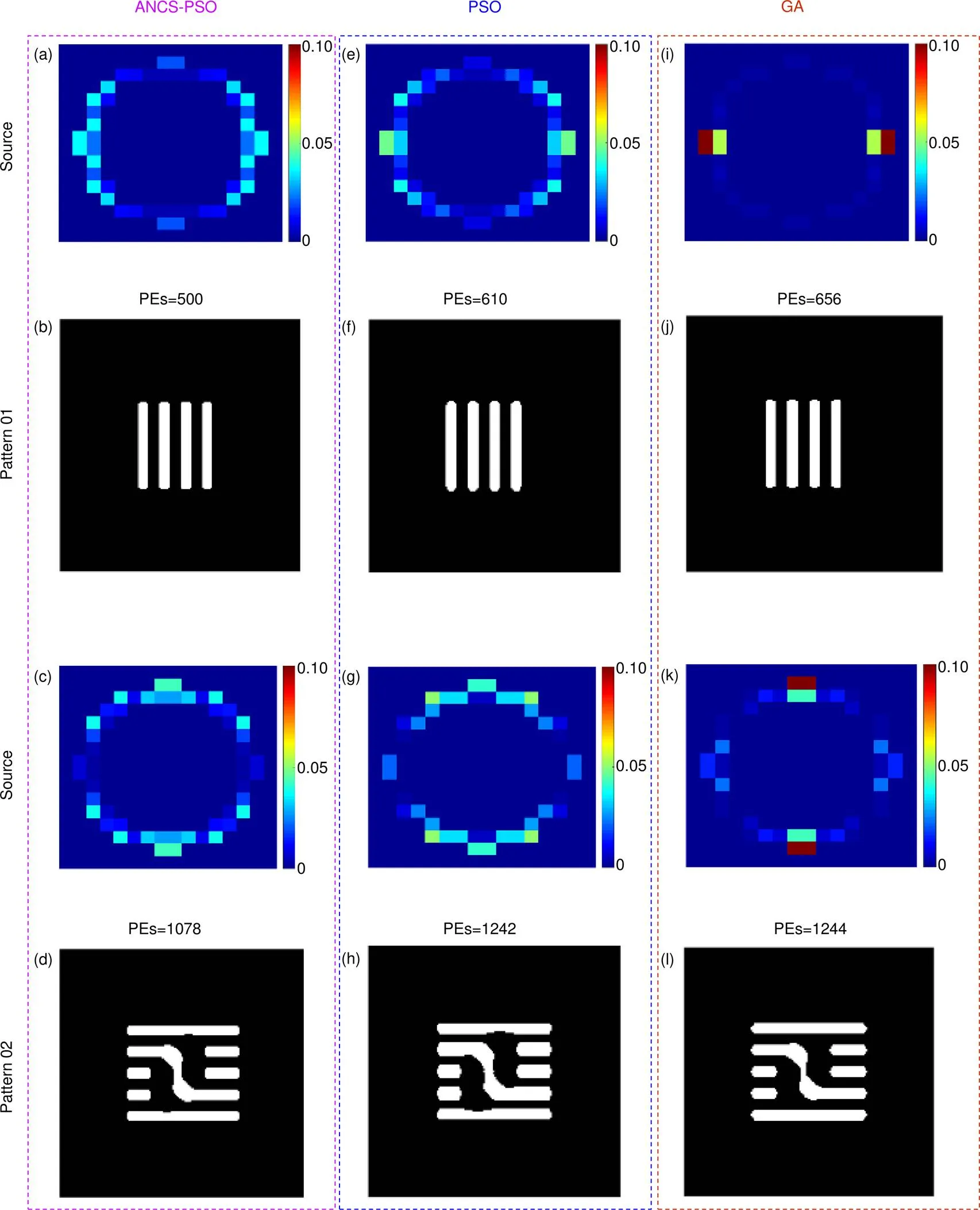
图4 光源优化仿真结果
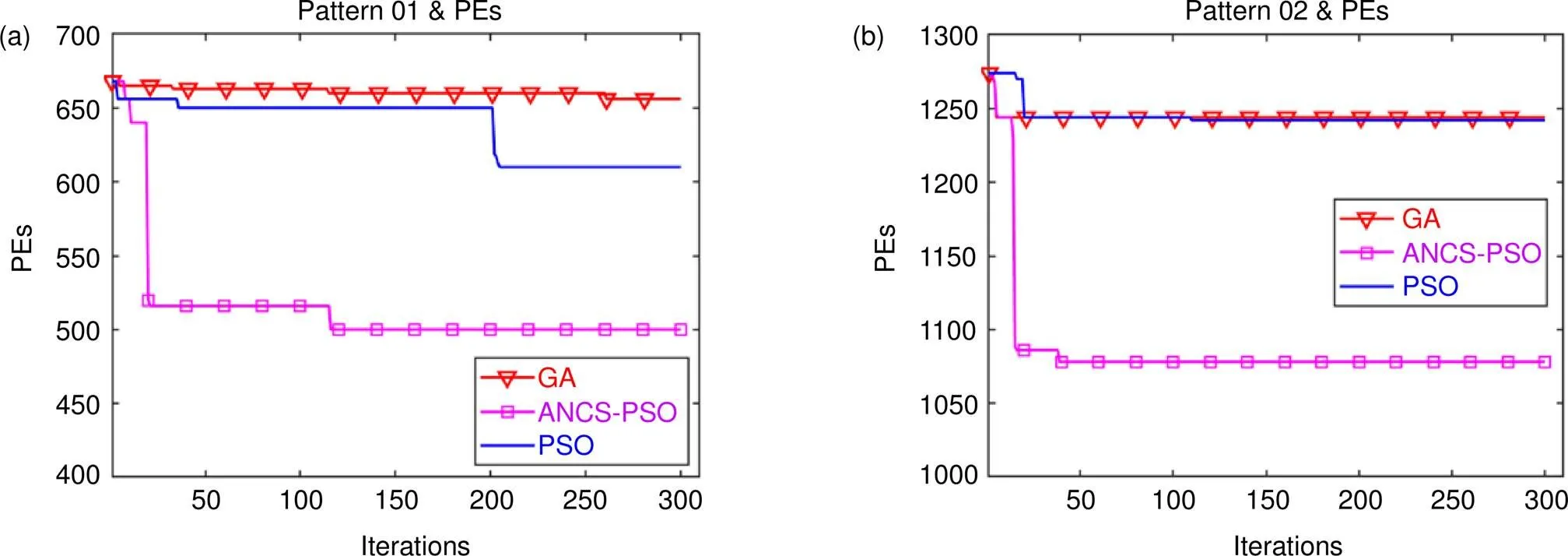
图5 仿真收敛曲线
5 总 结
本文提出了一种改进的PSO算法应用于逆光刻技术的光源优化中,即自适应非线性粒子群优化算法(ANCS-PSO)。通过仿真两种目标图形布局,验证了该算法的有效性。此外,为了验证ANCS-PSO的优越性,与传统粒子群优化算法和遗传算法对比。仿真结果表明,两种仿真图形误差PEs值降低,分别Pattern 01:52.2%,41.7%,37.4%;Pattern 02:35%,25.3%,25.3%,有效地提高光刻成像质量。三种算法仿真结果进行了对比,本文所提方法不仅具有更高的收敛效率,而且在提高光刻成像质量中更具有优势。随着仿真图形复杂度的提高,图形误差降低百分比有所降低,在后续的工作中,将采用多目标函数优化的方式来提高优化表现结果。
[1] Wong A K K.[M]. Bellingham, Washington: SPIE Press, 2001.
[2] Melville D, Rosenbluth A E, Waechter A,. Computational lithography. 2011.
[3] Liebmann L W. Resolution enhancement techniques in optical lithography: It's not just a mask problem[J]., 2001, 4409: 23–32.
[4] Mack C.[M]. Chichester, West Sussex: Wiley, 2007.
[5] Peng Y, Zhang J Y, Wang Y,. High performance source optimization using a gradient-based method in optical lithography[C]//, San Jose, CA, USA, 2010: 108–113.
[6] Rosenbluth A E, Seong N. Global optimization of the illumination distribution to maximize integrated process window[J]., 2006, 6154: 61540H.
[7] Ma X, Arce G R. Pixel-based simultaneous source and mask optimization for resolution enhancement in optical lithography[J]., 2009, 17(7): 5783–5793.
[8] Peng Y, Zhang J Y, Wang Y,. Gradient-based source and mask optimization in optical lithography[J]., 2011, 20(10): 2856–2864.
[9] Jia N N, Lam E Y. Pixelated source mask optimization for process robustness in optical lithography[J]., 2011, 19(20): 19384–19398.
[10] Li J, Lam E Y. Robust source and mask optimization compensating for mask topography effects in computational lithography[J]., 2014, 22(8): 9471–9485.
[11] Shen Y J, Peng F, Zhang Z R. Semi-implicit level set formulation for lithographic source and mask optimization[J]., 2019, 27(21): 29659–29668.
[12] Ma X, Zheng X Q, Arce G R. Fast inverse lithography based on dual-channel model-driven deep learning[J]., 2020, 28(14): 20404–2042.
[13] Ma X, Wang Z Q, Lin H J,. Optimization of lithography source illumination arrays using diffraction subspaces[J]., 2018, 26(4): 3738–3755.
[14] Fühner T, Erdmann A, Farkas R,. Genetic algorithms to improve mask and illumination geometries in lithographic imaging systems[C]//, Coimbra, Portugal, 2004: 208–218.
[15] Born M, Wolf E.[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001.
[16] Saleh B E A, Rabbani M. Simulation of partially coherent imagery in the space and frequency domains and by modal expansion[J]., 1982, 21(15): 2770–2777.
[17] Zhang Z N, Li S K, Wang X Z,. Source mask optimization for extreme-ultraviolet lithography based on thick mask model and social learning particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]., 2021, 29(4): 5448–5465.
Source optimization based on adaptive nonlinear particle swarm method in lithography
Wang Jian1,2, Liu Junbo1, Hu Song1,2*
1Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, Sichuan 610209, China;2University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China

The imaging model of lithography
Overview:With the continuous reduction of critical dimension (CD) of semiconductors, lithography technology has gradually become a key technology in the field of integrated circuit manufacturing. Resolution enhancement technologies (RETs) is to improve the resolution of lithography by modifying the incident angle of the light source and the mask mode under the premise that the wavelength and numerical aperture (NA) remain the same. Due to the influence of experimental conditions, such as temperature, assembly tolerance, and other factors, the aberration is introduced, leading to the deformation of the aerial image. In addition, the optical proximity effect (OPE) will be introduced, if the CD of the pattern is smaller than the illumination wavelength. Therefore, it is very important to solve the above problems to improve the imaging quality and image fidelity. Recently, many researchers have proposed the optimization algorithm based on pixelated representation of illumination source for inverse lithography optimization. This method has not only achieved high modulation and flexibility, but also has great advantages in improving lithography resolution. In this paper, a particle swarm optimization algorithm (PSO) combing with adaptive nonlinear control strategy (ANCS) is proposed to optimize the shape of lithography illumination source based on pixel representation. According to the unique symmetry characteristics of the light source, the light source is characterized by equal separation and dispersion, which can reduce the optimization complexity and improve the iteration efficiency. A simple grating array pattern and a complex and irregular grating array pattern are selected to verify the simulation results, and the pattern errors (PEs) between the photoresist pattern and the ideal pattern are used as the cost function to evaluate the simulation results. The effectiveness of the improved algorithm is verified by simulation of the two grating structures. In order to verify the superiority of ANCS-PSO, it is compared with the traditional particle swarm optimization algorithm and genetic algorithm. The simulation results show that the errors of the two kinds of simulation patterns are reduced by Pattern 01: 52.2%, 41.7%, 37.4%, and Pattern 02: 35 %, 25.3%, 25.3%, respectively, which effectively improves the photoresist image assurance. The comparison of the simulation results of the three algorithms shows that the proposed method not only has higher iteration efficiency, but also has more advantages in improving the quality of lithographic imaging and image fidelity.
Wang J, Liu J B, Hu SSource optimization based on adaptive nonlinear particle swarm method in lithography[J]., 2021, 48(9): 210167; DOI:10.12086/oee.2021.210167
Source optimization based on adaptive nonlinear particle swarm method in lithography
Wang Jian1,2, Liu Junbo1, Hu Song1,2*
1Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, Sichuan 610209, China;2University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
As an essential resolution enhancement technique, source optimization can improve the quality of advanced lithography. In the field of advanced lithography, the convergence efficiency and optimization ability of the source optimization are very important. Particle swarm optimization (PSO) is a global optimization algorithm. The adaptive control strategy can improve the global search ability of particles, and the nonlinear control strategy can expand the search range of particles. In this paper, a PSO algorithm based on adaptive nonlinear control strategy (ANCS) is proposed to solve the problem of source optimization by transforming it into a multivariable evaluation function. The image optimization simulation is carried out with a brief periodic grating image and an irregular image, and the source shape is optimized by the global iteration property of the proposed method. By using the pattern errors (PEs) as a multivariate merit function, the results of 300 iterations are evaluated, and the PEs of the two kinds of simulation patterns are reduced by 52.2% and 35%, respectively. Compared with the traditional PSO algorithm and genetic algorithm, the proposed method not only improves the imaging quality, but also has higher convergence efficiency.
source optimization; lithography; inverse lithography optimization techniques; particle swarm optimization algorithm
王建,刘俊伯,胡松. 基于自适应非线性粒子群算法的光刻光源优化方法[J]. 光电工程,2021,48(9): 210167
Wang J, Liu J B, Hu SSource optimization based on adaptive nonlinear particle swarm method in lithography[J]., 2021, 48(9): 210167
TP391
A
10.12086/oee.2021.210167
2021-05-21;
2021-08-26
国家自然科学基金资助项目(61604154,61875201,61975211,62005287)
王建(1981-),男,博士,副研究员,主要从事微电子装备关键技术的研究。E-mail:wangjian@ioe.ac.cn
胡松(1965-),男,博士,研究员,主要从事微电子装备关键技术的研究。E-mail:husong@ioe.ac.cn
National Natural Science Foundation of China (61604154, 61875201, 61975211, 62005287)
* E-mail: husong@ioe.ac.cn
