Systematic review on ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging for prenatal diagnosis of placenta accreta
2021-09-14LUOShuyingFURandiXUANRongrongJINWei
LUO Shuying ,FU Randi* ,XUAN Rongrong ,JIN Wei
(1.Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science,Ningbo University,Ningbo 315211,China;2.Affiliated Hospital of Medical School of Ningbo University,Ningbo 315020,China)
Abstract:This study evaluates the functionalities of ultrasound (US) and magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) in the diagnosis of placenta accreta (PA).In this paper,we provide a comprehensive overview of the recent research efforts on prenatal diagnosis of PA with US and MRI and look forward to future research directions in this field.We first summarize and analyze the performance of PA in US and MRI images and compare their diagnostic functions,reaching a conclusion that there is no significant difference in diagnostic accuracy between the two.US imaging is still the main instrument for screening.As an auxiliary means,MRI,on the other hand,shows great advantages in identifying the topography and depth of PA as well as describing the posterior wall of placenta.Based on the work aforementioned,we address some potential challenges,the new research direction and development trend.The application of machine learning combined with radiomics in the diagnosis of PA is also probed.It is believed that this study is of great significance in the sense of system accuracy improvement and applicability,and offers valuable reference for early-stage R&D in the relevant industry.
Key words:placenta accreta;ultrasound;magnetic resonance imaging;prenatal diagnosis;radiomics
1 Introduction
Placenta accreta (PA) includes various types of abnormal placenta whose chorionic villi directly attach or invade the myometrium.Pathologically,PA is divided into the following three subtypes according to the depth of invasion of placental villi into myometrium (Fig.1):placenta accreta,the placental villi are embedded in uterine myometrium,and the boundary between the placenta and uterus is not clear;placenta increta,the placental villi invade the myometrium but not to the serous layer of uterus;and placenta percreta,the placental villous tissue penetrates the uterine serosa and invades the bladder,rectum and other adjacent tissues and organs.PA lacks typical clinical manifestations in prenatal delivery.The general clinical manifestations after delivery are as follows:placenta delivery is incomplete,maternal appearance is rough,or more than 30 minutes after delivery,placenta cannot be separated from the uterine wall and needs to be removed by hand,some of which are difficult to peel off by hand,or it is found that the adhesion between placenta and uterine myometrium is close and there is no gap.
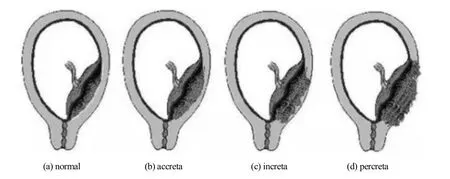
Fig.1 Normal placenta and three subtypes of placenta accreta
The prevalence rate of PA is high.The literature[1]suggest a higher prevalence of about 1 in 500 deliveries.PA is an important factor causing perinatal hemorrhage and postpartum hysterectomy,and it is also the main cause of high maternal mortality,among which placenta previa (PP) and previous cesarean delivery (CD) are the two most important risk factors.According to a survey[2],up to 38% of postpartum hysterectomies are related to PA.In 2014,the rate of CD in China was as high as 34.9%[3].In the United States,the rate of CD in the past 30 years has increased to 20%.In particular,the rate of repeated CD has increased,resulting in a significant increase in the risk of PA[4-5].Among them,uterine malformation,previous uterine surgery,dilatation curettage and myomectomy are additional but relatively secondary risk factors.Advanced maternal age are an independent risk factor,and when women are older than 35 years old,the risk of PA increases by 3.2 times.
Identification and management of PA is a clinical and diagnostic challenge being encountered with increasing frequency.Clinicians should be aware of the clinical issues and risk factors,while radiologists with imaging protocol and findings associated with it to facilitate optimal case management.At present,ultrasound (US) imaging is the main screening method for PA,routine ultrasound examinations in early pregnancy provides an ideal opportunity for diagnosis,while magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide information about the depth of placental infiltration and describe the posterior wall of placenta more clearly,so MRI is increasingly used in patients with uncertain US or limited placental evaluation.Clinicians should understand the clinical problems,risk factors and imaging findings related to PA to promote the best case management.
The existing relevant reviews mainly present the comparison of the performance of US and MRI in diagnosing PA,and few relevant review articles report the future direction of prenatal PA diagnosis.In this paper,we not only discuss the application of US and MRI in the prenatal diagnosis of PA and some challenges encountered,but also present the current state of development in the diagnosis of PA using artificial intelligence (AI) and radiomics technology.
2 Prenatal diagnosis
PA is one of the serious obstetrical complications.As shown in Table 1,with the increase in the number of CD,the incidence of PP with PA and the need for hysterectomy will increase[6].

Table 1 Rates of PA,PP and hysterectomy by number of previous CD[6]
Therefore,timely and accurate prenatal diagnosis is critical to guide clinicians to make early plans and improve maternal pregnancy outcome.At present,US and MRI are the two most important imaging methods for prenatal diagnosis of PA.The following will introduce US and MRI in PA diagnosis in detail.
2.1 US for the diagnosis of PA
In the US prenatal diagnosis of PA,traditional transabdominal gray-scale ultrasound is the earliest method used to diagnose PA.Recently,color and power Doppler ultrasound,transvaginal ultrasound and threedimensional ultrasound have gradually been used in clinical practice.Color and power Doppler ultrasound can show a large number of thickened blood vessels crossing the placenta and uterine wall,so it can further verify the sonographic characteristics of gray-scale ultrasound.
US imaging is used as the primary modality for prenatal diagnosis of PA and is conducted especially in the second or third trimesters of pregnancy;however,early diagnosis during the first trimester has been reported.The US is proven to help detect 50%-80% of cases and its sensitivity and specificity were 83%(95% confidence interval (CI):77%-88%) and 95%(95% CI:93%-96%),respectively[7].Most patients will undergo US at 18-20 weeks of pregnancy inspection,which provides an ideal opportunity to screen for the disease.
Since US imaging is susceptible to operator experience,in order to reduce errors caused by subjectivity in the diagnostic process,ensuring that all operators use the same description for the same signal,the European Working Group on Abnormally Invasive Placenta (EW-AIP) recently proposed a standardized description and name (shown in Table 2) for all US signs used for the prenatal diagnosis of PA[8-9].

Table 2 The standardized definition (EW-AIP suggestions) of US signs of PA
Recently,it has been suggested that cesarean scar pregnancy (CSP) represents a precursor of one of thedifferent grades of PA.The following studies have the same findings.Comstock et al[10]analyzed US images of 7 pregnant women with PA and found that the location of the gestational sac in the lower part of the uterine cavity during early pregnancy may be the US manifestation of PA in early pregnancy.D’Antonio et al[11]found that 91.4% of PA patients had at least one first-trimester US sign suggesting PA,and 82.4% of their US features were low implantation of the gestational sac,which would significantly increase the risk of PA.Calì et al[12-13]showed that the relationship between the gestational sac of the CSP,previous cesarean scar and anterior uterine wall thickness can be used to predict not only the evolution of the CSPs towards placenta increta and percreta,but also the clinical outcome of these women.
In the middle and late stages,real-time gray scale and color Doppler ultrasound were used for imaging[14].Research[15]has found that color and power Doppler ultrasound can help to find PA,but it does not improve the accuracy of PA diagnosis compared with traditional gray-scale ultrasound.For patients with suspected lower uterine diseases,transvaginal Doppler ultrasound has unique advantages.It can better display the PP and show the relationship between the lower edge of the placenta and the internal cervix,thereby improving the diagnostic accuracy rate of low position PA.Some scholars also believe that color Doppler and power Doppler have high specificity in the diagnosis of PA,especially in the diagnosis of invasive depth[16].In a study using Doppler,the diagnostic sensitivity was 82%,while the positive predictive value was 87%[17].O’Brien et al[18]reported 55 cases of prenatal diagnosis in 109 pregnant women.According to the results of the meta-analysis[19],among the different US signs the presence of abnormal vasculature on color Doppler ultra sound has the best combination of sensitivity (90.74%) and specificity(87.68%),and that abnormality of the uterus-bladder interface has the best specificity (99.75%) for the prediction of invasive placentation.The presence of placental lacunae and loss of the clear space between the placenta and myometrium does not perform as well.Some researchers have shown that prenatal diagnosis of PP with PA is easier.Literature[20]studied the examination data of 108 pregnant women with PP and the sensitivity and specificity of the US in the diagnosis of PA were 89.5% and 91.0%,respectively.Threeimensional ultrasound can directly display images of blood vessels with cluttered branches,and its diagnostic sensitivity and specificity are 97% and 92%,respectively[21].However,the post-processing of threedimensional images may bring artifacts,leading to certain limitations in the application of threedimensional ultrasound.Therefore,three-dimensional ultrasound cannot diagnose PA alone,but it can be used as a better supplementary method for prenatal diagnosis of PA.
Considering,when people at high risk of PA are found clinically (such as a history of uterine surgery and PP),US is an effective method to detect PA.The US is low in cost,noninvasive,easy to perform,and reproducible.At present,the US is often used clinically as the first diagnostic method for the diagnosis of PA.However,US diagnosis of PA is susceptible to many factors,including PA location,depth,inspection timing,and examiner experience,etc.When the placenta is located on the posterior wall of the uterus,the diagnostic result is unreliable and there is almost no relevant report about the accurate assessment of PA depth by US.
2.2 MRI for the diagnosis of PA
As a new method for prenatal diagnosis of PA,MRI has attracted more attention in recent years.Due to the many advantages of US,it is difficult for MRI to be a screening tool for PA;however,MRI can clearly show the uterine-placental contact surface.When the US diagnosis is unclear or the placenta is located on the posterior wall of the uterus,MRI examination can be selected.
A recent study[22]showed that MRI is significantly better than the US in predicting invasive placental staging,and it also concluded that any patient suspected of having invasive placenta by the US should undergo further MRI to best evaluate and guide surgical management and adopt appropriate delivery procedures to improve pregnancy outcomes.Although there are a large number of studies on the accuracy of MRI and US in the diagnosis of PA,it is considered that MRI is only an auxiliary diagnostic tool,and there is no significant difference in diagnostic accuracy compared with US[7,23].However,MRI is valuable in the diagnosis of suspected placental adhesion in the posterior wall of the uterus,ambiguity in the US,or whether PP is associated with PA.
The MRI signs of PA are mainly focused on the changes of morphology and signal intensity.At present,there is no unified standard for the diagnosis of MRI signs of PA.According to the study of references[24-25],we can get the main signs of PA on MR images as shown in Table 3.
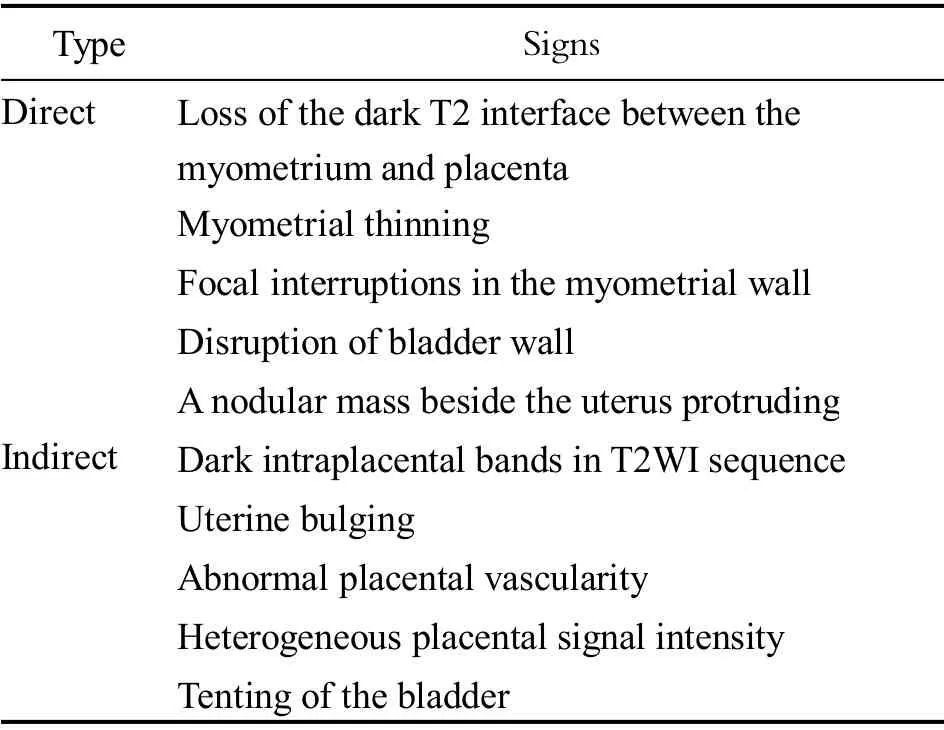
Table 3 MRI signs of PA
The following are the studies on the direct signs of MRI in the diagnosis of PA.Bour et al[26]believe that the loss of uterine-placental interface is the most sensitive sign of PA,which can occur in any subtype.Ueno et al[27]detected muscular thinning in 80% of patients without PA,and the study[23]has shown that this sign often seems to be associated with normal pregnancy,especially in the third trimester of pregnancy,because the fetus is larger and the false positive rate of this sign is higher,which cannot effectively diagnose PA.In the recent literature[23],focal interruption of myometrial wall has shown 79.2%-97.2% sensitivity and 50.4%-90.4% specificity.Bladder wall disruption and parauterine nodular mass are usually PA,which is the most serious type of PA with low incidence,poor prognosis and high maternal mortality;it often occurs in the posterior superior wall of the bladder,showing low signal intensity,interrupted continuity of the bladder wall,local nodular protruding,and its specificity is high[28].
The following are the studies on the indirect signs of MRI in the diagnosis of PA.T2 dark bands correlate with areas of intraplacental infarcts or hemorrhage.Lim et al[29]considered that the presence of T2 dark bands in the placenta may indicate bleeding,which is the most specific sign for the diagnosis of PA,and the volume of dark bands is related to the degree of implantation,and its sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of PA are 70.9%-95.6% and 55.6%-84.0%,respectively[23].Derman et al[30]think that heterogeneous placental signal intensity is a subjective sign as it may depend on the presence of T2 dark bands and at the gestational age of the placenta,which cannot be used as a diagnostic criterion,and normal placenta can also show obvious heterogeneity.Uterine bulging often indicates that for serious PA,meta-analysis[23]shows that the sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of PA are 60.3%-90.4%and 76.2%-96.4%,respectively.It is worth noting that,this bulging is due to the ‘mass effect’ of the placenta on the myometrium and may occur anywhere along the cesarean section scar,distorting the normal pear-shaped gravid uterus,which is thinner inferiorly and wider superiorly.Abnormal placental vessels are the focus of current research.Derman et al[30]propose the sign of abnormal placental vascular disorder for the first time,which is not only helpful for the diagnosis of PA,but also related to the depth of PA,which mainly reflects the pathological changes of vascular remodeling and terineplacental neovascularization caused by the trophoblast invasion during PA.Chen et al[31]classified the abnormal vessels of placenta and considered that the increase in placental bulge and bridging vessels and the increase in uterine serous vessels were the most valuable signs for the diagnosis in placental penetration and were related to the increase of bleeding after cesarean section.
In short,when PA is suspected on the US but the depth of invasion cannot be confirmed,further MRI examination can be performed.However,there is no clear standard for MRI diagnosis of PA and it is relatively expensive.What kind of manifestation is a specific sign of PA,and which sequence can be used to improve the sensitivity of diagnosing PA and the accuracy of classification need to be further studied.
3 Comparison of US and MRI in the prenatal diagnosis of PA
US imaging is the most commonly used imaging modality for the diagnosis of PA.When its diagnosis is uncertain,MRI is used as a supplementary means of examination,which makes the extra effectiveness of the MRI obtained to assist the diagnosis of PA in addition to the information provided by US.Einerson et al[32]have shown that MRI as an ultrasound-assisted means of diagnosing PA often leads to over-diagnosis or under-diagnosis,illustrating that MRI dose not provide additional value for clinicians.Satija et al[33]conducted a prospective study,thirty patients at risk of PA underwent both color Doppler ultrasound and MRI and eight cases of PA were identified.US had a sensitivity of 87.5%(95% CI,47.3%-99.6%) and a specificity of 86.4%(95% CI,65.1%-97.1%) and MRI had a sensitivity of 75.0% (95% CI,34.9%-96.8%) and a specificity of 77.3% (95% CI,54.6%-92.2%).Therefore,when comparing the diagnostic performance of US and MRI,MRI should be used as the main tool for the diagnosis of high-risk groups,or MRI scan should be performed without knowing the US and pathological results.And it is concluded that US and MRI have fairly good sensitivity for prenatal diagnosis of PA;however,specificity does not appear to be as good as reported in other studies.Although US imaging has been proved to have high prediction accuracy,once US tests suspect invasive placenta and a resection is planned,further assessment may be needed,such as understanding the topography of placental invasion,which will help surgeons perform the operation more smoothly.However,there is no large-scale study on the role of the US in evaluating placental invasion of the depth and topography.According to meta-analysis[23,34],MRI has good performance in evaluating the depth of placental invasion (sensitivity,92.9% (95% CI,72.8%-99.5%);specificity,97.6% (95% CI,87.1%-99.9%);diagnostic odds ratio (DOR),44.2 (95% CI,1.95-1 001.00)) and the topography (sensitivity,99.6% (95% CI,98.4%-100.0%);specificity,95.0% (95% CI,83.1%-99.4%);DOR,803(95% CI,9.0-71 411.0)),where especially,the latter plays an important role in planning hysterectomy.This shows that although both US and MRI have good performance in diagnosing PA,only MRI can describe the topography and predict the depth of invasion more accurately.There were several studies in which MRI and US were conducted on the same at-risk population and in which the radiologists reading the scans were blinded to both the US findings and the final diagnosis.When stratifying the analysis only on these studies MRI showed a sensitivity of 92.9% (95% CI,82.4%-97.3%),a specificity of 93.5% (95% CI,82.2%-97.8%),DOR of 186.0 (95% CI,40.0-864.5).US showed a sensitivity of 87.8% (95% CI,75.8%-94.3%),specificity of 96.3%(95% CI,74.4%-99.6%),and DOR of 189.2 (95% CI,15.8-2 269.0) (Table 4).
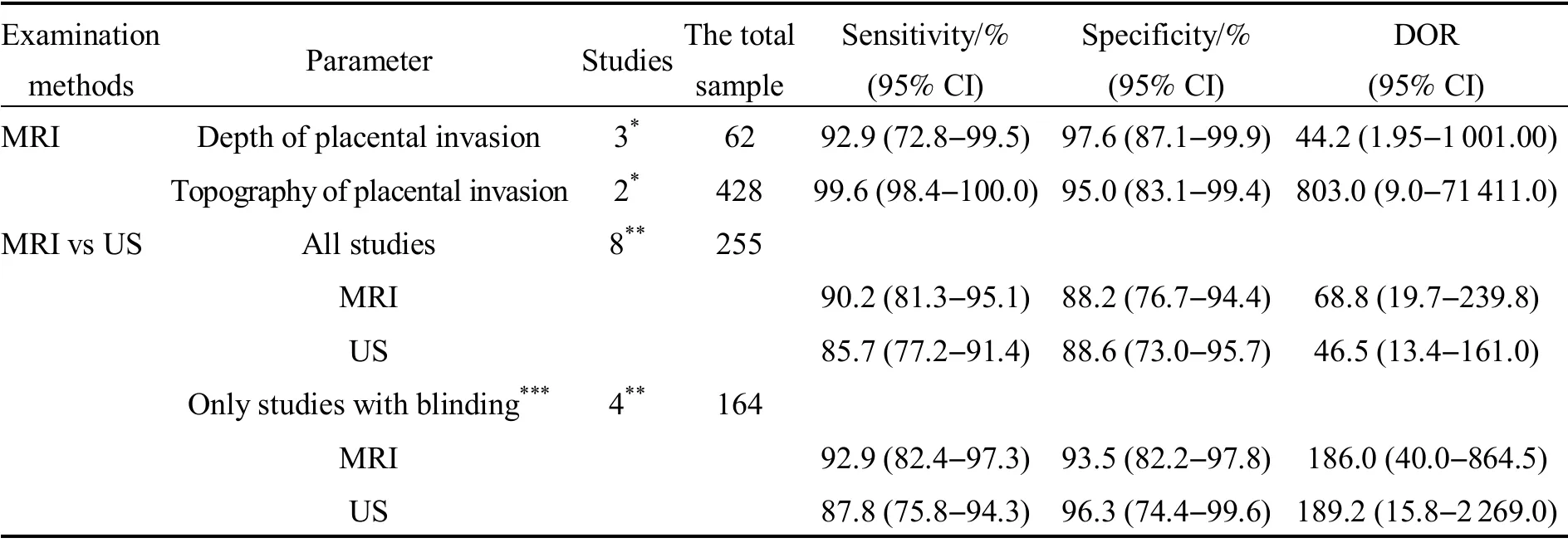
Table 4 Summary estimates of sensitivity,specificity of MRI for degree and topography of placental invasion and for comparison between MRI and US for detection of PA[23]
Both modalities have complementary roles,and in the case of an indeterminate finding on one imaging modality,the other modality can be used to obtain a diagnosis.US remains the first major modality for the prenatal diagnosis of PA,and MRI is reserved for the cases in which US is inconclusive.In short,in future studies,in order to evaluate the true accuracy of MRI and US in the diagnosis of PA,it should be conducted in a large and clear population,simultaneously,MRI and US should be the main examination tools and report independently of each other.There is no significant difference between US and MRI in the diagnosis of PA,but if hysterectomy is planned and lateral invasion is suspected by the US,MRI should be considered toevaluate the depth and topography of placental invasion,which will help adjust surgical methods and predict perioperative complications.In the future,it is necessary to combine the US and MRI for prenatal diagnosis of PA to further improve the accuracy of diagnosis results.
4 Challenges and directions
Although imaging is the best investigation modality available for prenatal identification of invasive placenta,the sensitivity and specificity are not 100%.For example,the ability of the US to detect PA depends on several factors,such as the experience of the operator,the gestational age at the time of the assessment,the number of US signs needed to determine scan abnormalities,and the degree of placental invasion;with the increase in gestational weeks,the myometrium becomes thinner and the placental signal is heterogeneous,the signs of PA on MR images become increasingly difficult to evaluate,relying more on the experience of radiologists[35].In cases of false-negative prenatal diagnosis,the surgeon performing the CD will use a low transverse uterine incision and this may lead to massive intraoperative hemorrhage,even before the fetus is delivered.By contrast,a false-positive diagnosis of PA will lead to an unnecessary midline vertical skin incision and a fundal uterine incision,thus increasing the risk of intraoperative and postoperative complications and the risk of PA disorders and uterine rupture in subsequent pregnancies[9,36].
Recently,with the rapid development of AI,an increasing number of fields begin using AI technology to conduct research work.The medical fields also paid attention to the great achievements of AI in the field of image processing,and began to use AI for academic research.In addition,with the rise of radiomics,the effective combination of the two can greatly improve the efficiency and accuracy of prenatal diagnosis.Radiomics,an emerging and relatively new research field,refers to extracting semi-quantitative or quantitative features from medical images with the goal of developing predictive or prognostic models.In the near future,it is expected to be a critical component for integrating image-derived information used for personalized treatment.The conventional radiomics workflow is typically based on extracting predesigned features (also referred to as handcrafted or engineered features) from a segmented region of interest (ROI).Nevertheless,recent advancements in deep learning have inspired trends toward deep-learning-based radiomics (DLRs)[37-38].DLR is a fully automatic diagnostic system which has more advantages than conventional radiomics,such as no need to manually segment ROI.Now,an increasing number of studies have been applying AI technology,combined with radiomics and clinical factors,to diagnose diseases.Radiomics that can quantify high-dimensional features that are invisible to the naked eye show great potential in the field of accurate medicine,most of which are used in the field of oncology[39-40].Radiomics provides us with a quantitative method to reflect the heterogeneity of tissue or tumor.Compared with the subjective evaluation,radiomics is more stable.The use of radiomics to evaluate PA has only recently appeared,and the current research is still relatively rare.Siauve[41]agreed that texture analysis (TA) combined with machine learning (ML) is a new viewpoint for placental evaluation using MRI data in the future.TA provides a quantitative analysis of heterogeneity through the quantification of gray-level patterns and pixel interrelationships within an image,and the textural features for each image are extracted from several matrices.ML and AI identify the most relevant textural features and can be used to construct an optimal model to facilitate diagnosis.
Chen et al[42]quantified placental heterogeneity on T2-weighted MRI images and extracted texture features,proved the potential role of TA in helping diagnose PA on MRI.In 2019,Romeo et al[43]used texture features derived from MRI and combined with many ML models to predict the existence of PA in patients with PP.The results showed thatk-nearest neighbors with the lowest number of features (n=26) obtained the highest accuracy(98.1%),precision (98.7%),sensitivity (97.5%) and specificity (98.7%).Sun et al[44]developed a pipeline including textural features and automated ML for prenatal prediction of invasive placentation after 24 weeks of gestational age.According to LoG filtering and TA,abnormal placentas can be distinguished by their heterogeneous appearance and normal maturation,with the accuracy (95.2%),sensitivity (100.0%),and specificity(88.5%).The prediction of CD hysterectomy in people with high-risk PA using the texture features of MRI data showed that the prediction is significantly related to the pathological outcome[45].Wu et al[46]extracted radiomics features from T2-weighted images and established nomogram to predict postpartum hemorrhage combined with clinical information.The experimental results show that the model is effective in predicting the risk of postpartum hemorrhage and performed better in patients without PP than in patients with PP,with area under curve (AUC) of 0.832 compared with 0.815,sensitivity of 97.6% compared with 97.2% in the validation cohort.
It can be seen that the above studies mainly apply the traditional radiomics research process and are all applied to MRI.At present,the application of US images combined with AI and radiomics in the diagnosis of PA is relatively rare,which also provides a new idea for our future research.It can effectively use the new technology to study the diagnosis of PA.On the one hand,it can improve the efficiency and accuracy of diagnosis.On the other hand,it can improve the robustness of the diagnostic results and make the results more objective.
The above results show that the application of radiomics and AI in the diagnosis and prediction of PA has great potential.This will also become the focus and area of difficulty of our research in the future.
5 Conclusion
The prevalence of PA is still increasing,and PP and previous CD are still the most important risk factors for PA.Prenatal screening can effectively reduce the morbidity and mortality of pregnant women.The US is relatively economical and easy to implement,and it can be examined and reexamined in all periods of pregnancy,and it should still be the first choice for the diagnosis of PA.MRI can be used to locate the abnormal placenta better and determine the degree of PA because it is not affected by maternal weight and placental position and can be used to assist and supplement the diagnosis of suspected placenta after US screening when it is difficult to diagnose.In summary,either kind of imaging examination method has limitations.It is impossible to diagnose every case of PA completely and accurately.Both examination methods should be integrated to complement each other and provide more diagnostic basis for clinically devising correct treatment plans.
In the future,the diagnosis of PA will not just be limited to using US and MRI only,but will be combined with AI and radiomics to better judge it.As mentioned in the previous section,this will improve the efficiency and accuracy of the diagnosis,and at the same time make the diagnosis more objective.
