Property uniformity of thick nickel-based alloy plate for nuclear power steam-generator divider plate
2021-07-20,
,
Baowu Special Metallurgy Co.,Ltd.,Shanghai 200940,China
Abstract: This paper introduces a thick 690 nickel-based alloy plate produced by the former Baosteel Special Steel Co.,Ltd.used as the steam-generator divider plate in the pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant.According to the product characteristics and design requirements of the thick nickel-based alloy plate,multidimensional sampling and testing were conducted to investigate its microstructure and mechanical properties.The results show that all the property indexes of the thick hot-rolled nickel-based alloy plate meet the design requirements,and there is good uniformity in the microstructure and mechanical properties in different dimensions.These findings indicate that China has mastered the core manufacturing technology of thick nickel-based alloy plates for their use as divider plates in nuclear power steam generators.
Key words: nuclear power station; nickel-based alloy; divider plate; thick hot-rolled plate
1 Introduction
The success of nuclear power development and operation around the world as a large-scale appli-cation of power generation has proved that nuclear power is a clean,safe,economical,and mature technology with a strong supply capacity[1].Acceler-ating the construction of nuclear power plants and increasing the proportion of nuclear power used to supply power to China will alleviate the challenges associated with the growth in power and transporta-tion demands while protecting the environment.The development of nuclear power can play a significant role in driving the development of high-tech and equipment manufacturing industries,promoting econom-ic growth,adjusting the energy structure,ensuring energy security,and enabling the implementation of sustainable development strategies[2].
The structural materials used in nuclear power are the basis for localizing key nuclear power equip-ment.As nickel-based alloys have excellent mech-anical properties,high-temperature and corrosion resistance,and other environmentally effective prop-erties,they are widely used in the key components of the nuclear islands in nuclear power plants,in-cluding pressure vessels,steam generators,and voltage stabilizers.The nuclear power steam generator is one of three major pieces of equipment in the nuclear island,the main function of which is transferring the heat generated in the reactor core.The lower-head divider plate is the key component of the steam generator that divides its lower head into two water chambers:the cooling inlet and outlet.Because of its direct contact with the primary circuit coolant,and being subjected to high tem-perature and high pressure,this plate must meet high requirements with respect to its mechanical properties,corrosion resistance,and plate size accuracy[3].At present,third-generation nuclear power technology mainly adopts the ASME SB168 UNS N06690 and RCC-M M4107 NC30Fe alloy(hereinafter referred to as 690 alloy) thick hot-rolled plates,which exhibit excellent comprehensive performance in the manufacture of divider plates[4].Because of their heavy weight,thickness,and width,they are difficult to manufacture and have had to be imported.In addition,with the increased installed capacity of Chinese nuclear power plants,there are higher requirements for the size of alloy plates.For example,the maximum design thickness,length,and width of the thick nickel-based alloy plate for the CAP1400 unit are 80 mm,4 500 mm,and 2 450 mm,respectively.The difficulty in controlling the uniformity of the microstructure and properties increases exponentially with the increases in the plate size.This inevitably generates high require-ments for the smelting control of large ingots,hot-forming process control,heat treatment process control,and manufacturing and processing equip-ment.As such,it is very difficult to manufacture 690 alloy as a divider plate that both meets the plate size requirements and demonstrates comprehensive performance.
In response to the call for the nationally independent construction of third-generation nuclear power technology,the former Baosteel Special Steel Co.,Ltd.(Baosteel Special Steel for short) under-took to manufacture key nickel-based alloy materi-als for nuclear power application in cooperation with domestic nuclear power equipment manufac-turers,designers,and other units after the production line of the special alloy plate and strip was put into operation[5].After exploration and a series of efforts,Baosteel Special Steel has mastered the core manufacturing technology of the thick 690 nickel-based alloy hot-rolled plate.Since 2013,thick nickel-based alloy plates have been successfully manufactured for use as divider plates in the CAP1000,CAP1400,and Hualong No.1 nuclear power steam generators,and have fully replaced imported products.
According to the manufacturing practices of Baosteel Special Steel,in this paper,multidi-mensional sampling and testing of the developed nickel-based alloy plates,i.e.,thick,large,and wide hot-rolled plates,were performed to verify the uniformity of their microstructures and properties.
2 Test materials and sampling methods
In the 690 alloy used in the nuclear power steam-generator divider plate,the C content is not more than 0.030%,and the main elements are Cr,Ni,and Fe.However,the microelements are strictly con-trolled,and their proportions must meet the require-ments listed in Table 1.The design requirements for the purity of the components in the alloy plates used for nuclear power are much higher than those used in conventional products.
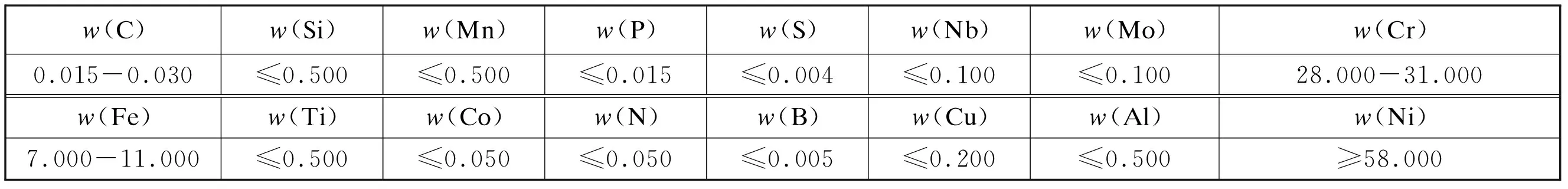
Table 1 Standard requirements for the chemical composition of UNS N06690 alloy %
According to the French RCC-M technical materials specification general rule M140 for nuclear power,a randomly selected thick 690 plate produced by Baosteel Special Steel was subjected to aging by heat treatment and its microstructure and mechanical properties were then analyzed.The dimensions of the thick plate in this experiment were as follows:thickness of 52 mm,width of 1 800 mm,and length of 9 000 mm.The sampling positions were at both ends of the plate,mid-length along the plate,and at one-quarter-width intervals.A total of 15 positions(A-Q) on the plate were tested,as shown in Fig.1.The number of samples corresponding to each sampling position on the test items is listed in Table 2.
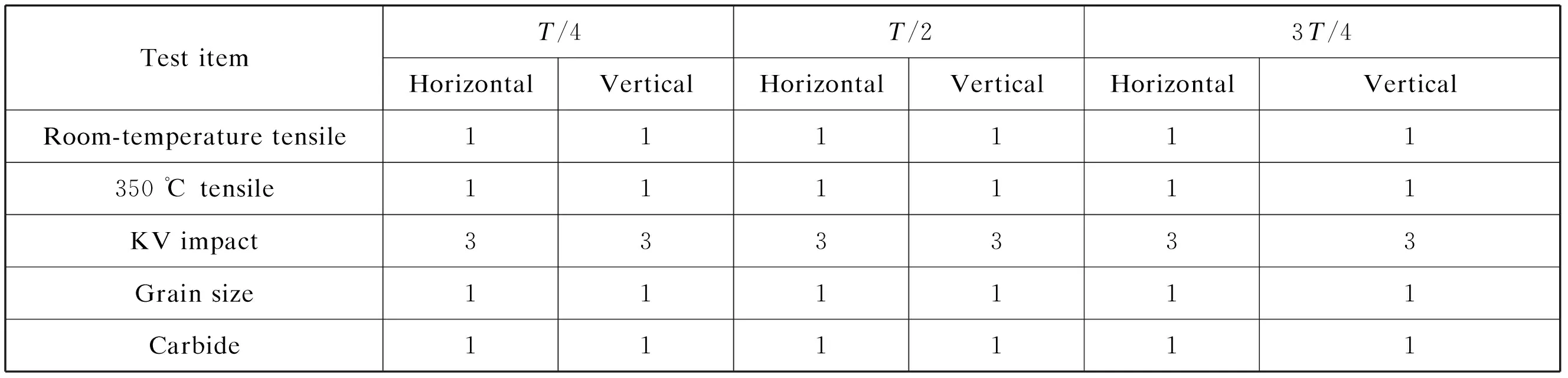
Table 2 Test items,sampling positions,and number of samples on test coupon
3 Test results and analysis
3.1 Microstructural uniformity of thick nickel-based alloy plate
The grain sizes of 15 test coupons were tested with respect to the items listed in Table 2.Table 3 shows the results for a total of 90 grain size tests(standard grain size:3.0-8.0),in which it can be seen that the grain size of the entire thick plate ranged between 7.0-5.0,with a few fine grains of 7.5 grade and a very few coarse grains of 4.5 grade,which fully meet the standard requirements.Typical metallographic photos are shown in Fig.2(positions A,B,and N).Regarding the distribution of carbides shown in Fig.3,the precipitated car-bides were distributed continuously along the grain boundaries,with very few intragranular carbides,which fully meets the technical requirements for the nuclear power steam-generator divider plate.
Based on the above results obtained for the grain size and carbides,excellent microstructural unifor-mity was demonstrated by the thick 690 nickel-based alloy plate developed by Baosteel Special Steel,which fully verifies the degree of uniformity control demonstrated at each key production process.
3.2 Uniformity of mechanical properties of thick nickel-based alloy plate
3.2.1 Statistical results for overall mechanical pro-perties
Table 4 shows the statistical data obtained for the mechanical properties of the plate.At room temperature,the tensile strength range was 625-662 MPa,the yield strength range was 274-307 MPa,the elongation range was 51%-57%,the section shrinkage range was 60%-66%,and the impact energy was 251-302 J.At 350 ℃,the tensile strength range was 524-556 MPa,the yield strength range was 211-239 MPa,the elongation range was 50%-58%,and the section shrinkage range was 63%-67%.Compared with the standard mechanical properties specified in Table 4,based on our multidimensional tests and a large number of samples,it is clear that the mechanical properties of the thick nickel-based alloy plate developed by Baosteel Special Steel meet the design requirements for thick 690 plate.In addition,the mechanical properties measured at room temperature and 350 ℃ are presented as scatter plots in Fig.4,which show that the measured tensile strength,yield strength,and impact energy values are concentrated in narrow ranges,which indicates their good uniformity in the thick plate.
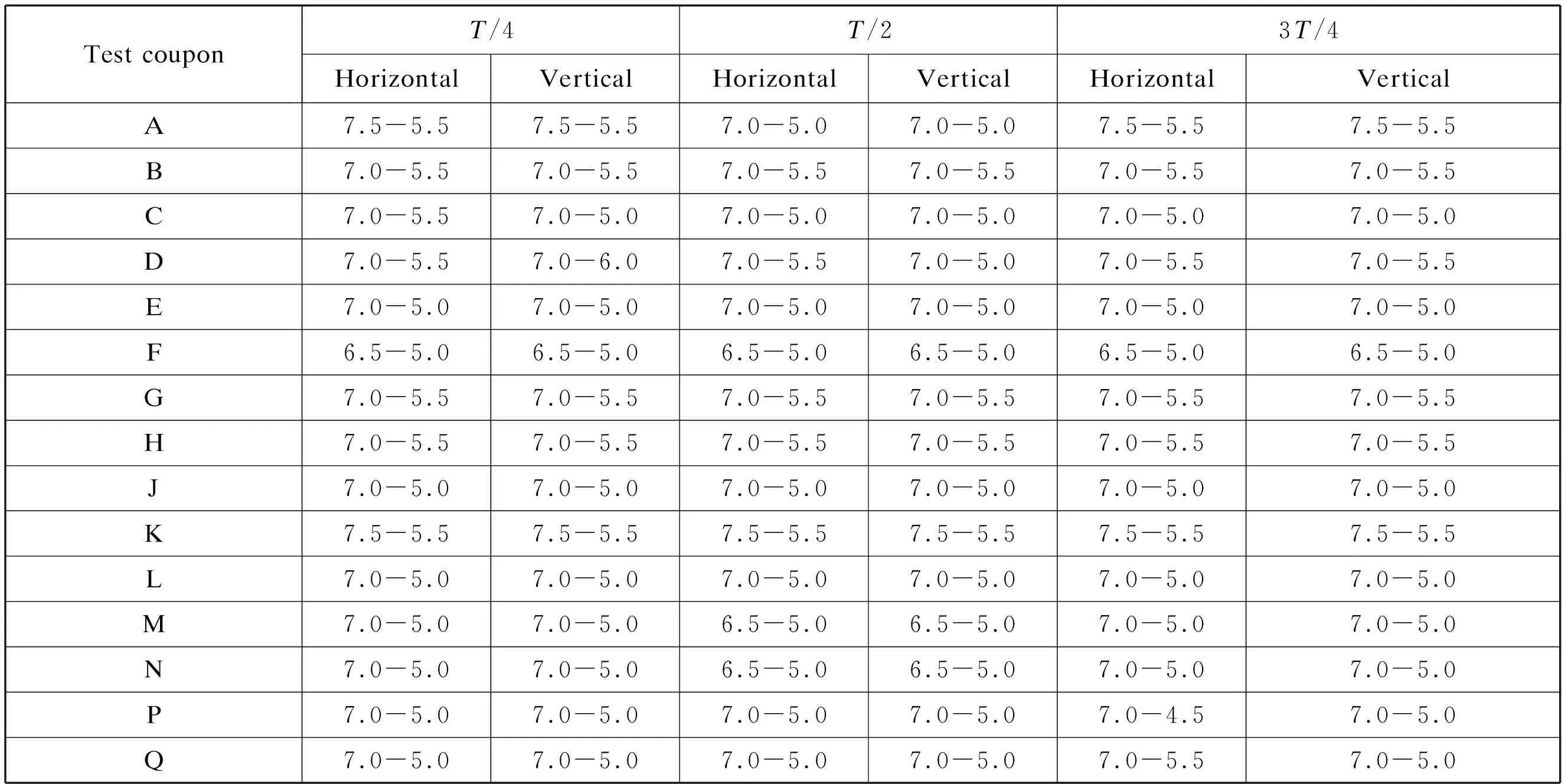
Table 3 Grain sizes at different sampling positions on the thick UNS N06690 plate(solid solution+aging)
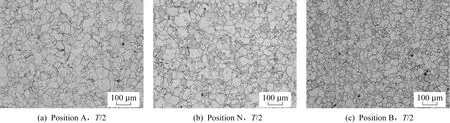
Fig.2 Microstructures of samples at different positions on the thick UNS N06690 plate(solid solution+aging)

Fig.3 Carbide distribution on the thick UNS N06690 plate

Table 4 Statistical test results of the mechanical properties of thick UNS N06690 plate
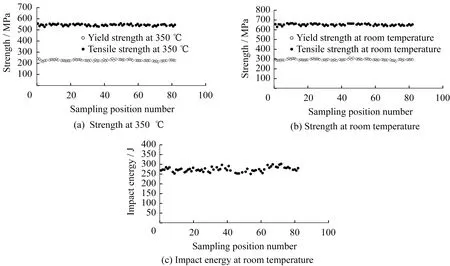
Fig.4 Mechanical properties of thick UNS N06690 plate at room temperature and 350 ℃
3.2.2 Analysis of uniformity of mechanical proper-ties in different dimensions
To verify the uniformity of the mechanical properties of the thick plates in different directions,three groups of dimensions were investigated and com-pared:the length,thickness,and width directions.First,the average values of different directions or locations of each group were compared to chara-cterize the performance differences of different directions or locations of the group.Then the standard deviations of the performance in different directions or locations of each group were compared,and the degree of dispersion in the performance in different directions or locations of each group was obtained.If the difference between the average performance values was small,the standard deviation was smaller,and the uniformity of the performance was better.The specific methods used for comparison are as follows:
Length direction:The performance in three locations on the plate,i.e.,the head,middle,and tail,was compared.As shown in Fig.1,the positions C,A,E,F,and G are at the head;L,M,N,P,and Q are in the middle;and K,J,H,B,and D are at the tail.
Thickness direction:The performance atT/4,T/2,and 3T/4 was compared along the thickness (T) direction of the plate.
Width direction:The performance at the edges on both sides of the plate,i.e.,W/4,W/2,and 3W/4,was compared along its width (W) direction.In Fig.1,side 1 refers to positions C,L,and K;W/4 refers to positions A,M,and J;W/2 refers to posi-tions E,N,and H;3W/4 refers to positions F,P,and B;and side 2 refers to positions G,Q,and D.
The uniformity of the plate was further analyzed by comparing the average and standard deviation values of the room temperature (RT) and 350 ℃ tensile strength and the room temperature impact properties at the different plate locations of the three dimensions.
(1) Length direction
Regarding the uniformity of the mechanical properties in the length direction,as shown in Fig.5,the average values of the mechanical properties at the head,middle,and tail of the plate differed only slightly,with the strength of the tail slightly higher than those of the head and middle(difference of 8-12 MPa),and the impact performance of the tail slightly lower than those of the head and middle(difference of 16 J).According to the definition of standard deviation,the degree of discreteness of the data is determined by the standard deviation when the average values of the compared data group are similar.The greater the standard deviation,the greater the degree of data dispersion in this group;the smaller the standard deviation,the smaller the degree of discreteness of the data.A similar standard deviation value indicates an equivalent degree of discreteness among several groups of data.As the differences in the standard deviation of each performance value in the length direction of the head,middle,and tail groups are less than 3.34,this indicates that the degrees of dispersion of the measured data in these three locations were similar.

Fig.5 Comparison of uniformity of mechanical properties in the length direction of the thick UNS N06690 plate
(2) Thickness direction
Regarding the uniformity of the mechanical properties in the thickness direction,Fig.6 shows the data obtained atT/4,T/2 and 3T/4.The average values of each index measured at these three locations are basically the same.The difference in the strength is only 3-11 MPa,and the difference in the impact perfor-mance is 7 J,which indicates excellent uniformity of the mechanical properties in the thickness direction.The comparison of standard deviations shows that the standard deviation of the tensile properties atT/2 at room temperature is slightly larger than those atT/4 and 3T/4(difference of 5.16),and the stan-dard deviations of the three groups with respect to the other properties are very close(difference range of 0.71-3.65),which indicates equivalent degrees of dispersion in the mechanical property data in the thickness direction.

Fig.6 Comparison of uniformity of mechanical properties in the thickness direction of the thick UNS N06690 plate
(3) Width direction
Fig.7 shows a comparison of the uniformity of the mechanical properties in the width direction,in which the data are divided into five groups accord-ing to their sampling positions,i.e.,side 1,W/4,W/2,3W/4,and side 2.The average values of the five groups show that the data for the mechanical proper-ties are basically the same.The difference in strength was only 3-5 MPa, and the maximum difference of the impact performance was 11 J,which also indicates excellent uniformity of the mechanical properties in the width direction.The comparison of the standard deviation shows that both the yield strength and impact properties exhibit the smallest degree of data disper-sion on both sides(the difference in the standard devia-tions of the yield strength is no more than 5.43,and that of the impact properties is no more than 11.27).The degree of data dispersion for tensile strength at the five locations is also similar(the difference in the standard deviations is no more than 2.58).
The results of the above comparative analysis indicate that the strength at the tail of the plate in the length direction was slightly greater than those at the head and middle,and the impact performance at the tail was slightly lower than those at the head and middle,which is mainly related to the solidification characteristics of the electroslag remelting process.Because the tail of the ingot was in the early stage of solidification,the cooling con-dition was the best,the solidification structure was better,and the tensile strength of the plate was slightly higher,although the difference was only approximately 8-12 MPa.This gap could be narrowed by optimizing the power supply and cooling condi-tions during the early stage of electroslag remelting.In the thickness direction,the performance difference was very small,with the difference in the yield strength only 3-4 MPa,the difference in the tensile strength 11 MPa,and the maximum difference in the impact energy 7 J.In the width direction,the difference in strength was only 3-5 MPa and the maximum dif-ference in the impact energy was 11 J,which is more uniform than those in the length and thickness direc-tions.Overall,the uniformity of the 350 ℃ tensile strength,room-temperature tensile strength,and impact performance in the three dimensions were excellent,which fully verifies that Baosteel Special Steel’s manufacturing technology of the thick 690 plate eliminates the anisotropy of the rolled plate and ensures uniformity in the mechanical properties of the thick plate.
4 Conclusions
(1) The results of tests to determine the microstructure and mechanical properties at different positions of the thick 690 alloy plate for the nuclear power steam generator demonstrate that its properties exceeded the standard requirements by a large margin.The overall uniformity of the microstructure was found to be good,with a grain size range of 7.0-5.0.The distribution of carbides fully met the technical requirements of the nuclear power steam-generator divider plate.
(2) Our analysis of the uniformity of the mechanical properties in different dimensions shows that the mean and standard deviation values of the performance data measured at different locations of the thick plate were very similar,which indicates that the mechanical properties of the thick plate were uniform in each dimension.
(3) The research and analysis results show that Baosteel Special Steel’s thick nickel-based alloy plate products have reached a high level of metallurgical quality,thermal processing,and heat treatment uniformity control.These findings further prove that China has successfully mastered the core manufacturing technology of the thick nickel-based alloy plate for use as a nuclear power steam-generator divider plate,and has realized the capacity for local independent manufacturing.
Acknowledgement
This paper is sponsored by Special Fund for Indus-trial Transformation and Upgrading in Shanghai (No.GYQJ-2018-2-03) and Program of Shanghai Academ-ic/Technology Research Leader(No.17XD1420200).
杂志排行
Baosteel Technical Research的其它文章
- Effect of vanadium on the microstructure and properties of metastable austenitic stainless steel AISI 301LN
- Corrosion behavior of super 13Cr stainless steel in a H2S and CO2 environment
- Improving emulsion odor in cold rolling production
- Evaluation of automatic girth weldability of pipeline in special conditions
- Contributions to Baosteel Technical Research wanted
- Effect of novel surface treatment on corrosion behavior and mechanical properties of a titanium alloy
