Isolation and identification of antimicrobial metabolites from sea anemone-derived fungus Emericella sp. SMA01*
2021-06-15YangYUEHuahuaYURongfengLILinfengHUSongLIURongXINGPengchengLI
Yang YUE , Huahua YU ,2,**, Rongfeng LI ,2, Linfeng HU , Song LIU ,2, Rong’e XING,2,Pengcheng LI ,2,**
1 Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology, Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao 266071, China
2 Laboratory for Marine Drugs and Bioproducts, Pilot Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology,Qingdao 266237, China
3 School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Henan Institute of Science and Technology, Xinxiang 453003, China
Abstract Marine symbiotic fungi represent an intriguing source of discovery of novel secondary metabolites with various biological activities. Sea anemones are benthic marine invertebrates, however, the cultivable symbiotic fungi residing in the sea anemones are paid few attentions compared to those derived from their cnidarian counterparts. Here we show the identification of antimicrobial secondary metabolites from the sea anemone-derived symbiotic fungi. Out of five isolated fungal strains, only the strain SMA01 showed strong antimicrobial activities, which was assigned into the genus Emericella based on the morphological characteristics and the ITS sequencing. Media swift from liquid fermentation to solid rice medium presented little influence on its antibacterial activity. A chemical investigation of the ethyl acetate extract of the Emericella sp. SMA01 led to discovery of the primary antibiotic metabolite phenazine-1-carboxylic acid. The IC50 values of the phenazine-1-carboxylic acid against Phytophthora capsici, Gibberella zeae, and Verticillium dahliae were determined to be 23.26–53.89 μg/mL. To the best of our knowledge, this was the first report of Emericella sp. in sea anemones. The current study may benefit understanding of the defensive chemical interactions between the symbiotic fungi and their host sea anemones.
Keyword: sea anemone; symbiotic fungi; phenazine-1-carboxylic acid; antimicrobial activity
1 INTRODUCTION
Marine invertebrates are increasingly becoming an important source of marine symbiotic fungi. These symbiotic fungi constitute an interesting group of marine fungi since most of them are convinced to be a reservoir of diverse compounds with structural and functional novelty (Bugni and Ireland, 2004; Saleem et al., 2007; Jones et al., 2008). In the past few years,novel secondary metabolites from marine-sourced fungi increased rapidly, more than 600 new compounds reported in 2018 according to theNaturalProductReports(Carroll et al., 2020). The novel compounds from marine-derived fungi are found to possess a variety of biological activities, including antimicrobial, cytotoxic, and radical scavenging activities, but their ecological roles are barely understood. Many studies have proven that some metabolites initially isolated from marine invertebrates are actually produced by their symbiotic microbes(Piel, 2009; Schmidt et al., 2012). In the hostile ocean environments, marine invertebrates always harbor a number of microbial symbionts, which could produce various compounds protecting the host animals from microbial infections or predatory (Schmidt, 2008).Discovery of new antibiotics from the alternative chemical defense strategy represents an important trend in marine natural products.
Sea anemones belong to the phylum Cnidaria, class Anthozoa, subclass Hexacorallia. Sea anemones are benthic marine invertebrates, which possess a soft body and have a sessile lifestyle. Lacking physical protection, they may also utilize the chemical defense strategy to immune themselves from environmental noxious stimuli such as infectious microorganisms(Paul et al., 2007; Schmidt, 2009). Like most other cnidarians, sea anemones produce various biologically active substances ranging from small-molecule natural products to biomacromolecules, such as cytolysins and phospholipases (Rojko et al., 2016;Guillen et al., 2020). The small-molecule natural products from sea anemones cover a variety of structural types, including alkaloids, sterols, terpenes,and so on (Guillen et al., 2020). Living on the bottom of the ocean, sea anemones were also found to form complex interactions with various microorganisms,which were recently proven a great source for antibacterial compounds. In the microbiomes of two investigated sea anemones,BacillusandVibriospecies were found to the dominate bacteria producing antimicrobial substances (León-Palmero et al., 2018).Besides bacteria, fungi derived from sea anemones were good candidates for producing novel antimicrobial secondary metabolites (Yang et al.,2012; Qin et al., 2015). However, compared to other marine invertebrates such as sponges (Bolaños et al.,2015; Calabon et al., 2019), corals (Amend et al.,2012; Zhang et al., 2012) and ascidians (López-Legentil et al., 2015; Chen et al., 2018), sea anemonesassociated fungi are currently less investigated. In the present study, we attempted to isolate and identify the sea anemone-derived fungi and further identified the antimicrobial metabolites against a panel of human bacterial pathogens and plant pathogenic fungi.
2 MATERIAL AND METHOD
2.1 General experimental procedures
NMR spectra were recorded using a 600-(1H) and 150-(13C) MHz Bruker spectrometer with tetramethylsilane (TMS) as the internal standard. UV spectra were determined with a TU-1810 UV-Visible spectroscopy system. Electrospray ionization mass spectroscopy (ESI-MS) was performed on Finnigan Thermo spectrometer. Silica gel (200−300 mesh;Qingdao Haiyang Chemical Co. Ltd., China) and Sephadex LH-20 (GE, U.S.A) were used for column chromatography. TLC was carried out with pre-coated silica gel GF254 plates (Qingdao Haiyang Chemical Co. Ltd., China). Compounds were visualized under UV light or by spraying with H2SO4-EtOH (1:9, v/v)followed by heating.
2.2 Fungal material
Three sea anemone individuals were collected in September 2013 from the First Bathing Beach,Qingdao, China. Isolation of symbiotic fungi were performed as previously described (Yue et al., 2015).Briefly, after sterilization and washing with 75%ethanol and sterile natural seawater, the sea anemone individuals were cut into cubes of 0.5 cm3and immediately placed in plates containing PDA medium(10-g sea salts, 20-g dextrose, 20-g agar powder and 1-L 20% (w/v) potato soup, natural pH). The plates were incubated at 28 °C for 1–3 weeks. Colonies growing around the tissue cubes were picked up for isolating pure strains. And the resultant pure strains were incubated on Wickerham’ medium (3-g yeast extract, 3-g malt extract, 5-g peptone, 10-g glucose in 1-L 75% natural seawater, 18-g agar, pH 7.2–7.4)slants at 4 °C for short-term storage.
2.3 Phylogenetic analysis
DNA extraction procedure of the isolate SMA01 was same as the method reported previously (Yue et al., 2015). The resultant DNA sequences were submitted to NCBI database and compared with other sequences in the BLASTn algorithm. For phylogenetic analysis, 38 similar sequences corresponding to the ITS region were extracted from NCBI database and submitted to MUSCLE for sequence alignment with default parameters, together with SMA01 andPenicilliumexpansum(chosen as the outgroup taxon).In addition, the resultant dataset was further manually edited in MEGA 6.06 and analyzed in PHyML 3.1 using maximum likelihood with a bootstrap analysis of 1 000 replicates. The tree was viewed and edited in Figtree 1.1. Results strongly indicate the isolate SMA01 belonged to the genusEmericella. The ITSrDNA sequence ofisolateEmericellasp. SMA01 was deposited in GenBank under the accession number of KM390915.
2.4 Small-scale fermentation and screening for antibacterial activity
2.4.1 Small-scale fermentation of five sea anemoneassociated fungi
For small-scale fermentation, fungi were cultured for seven days on PDA, and then mycelium-containing plugs (Φ=5 mm) were punched and carefully placed in 1-L flasks containing Liquid Wickerham’s Broth(WMB: 3-g yeast extract, 3-g malt extract, 5-g peptone, 10-g glucose in 1-L 75% natural seawater,pH 7.2–7.4) for fermentation. After 4–6 weeks of cultivation at room temperatures, about 200 mL of ethyl acetate (EtOAc) were added into each flask.Then, the flasks were left closed for 2 days. The liquid cultures were separated from the mycelia by filtration and extracted with EtOAc (3×250 mL). The organic layers were collected and dried over anhydrous MgSO4, then concentrated in vacuo to aff ord 5 EtOAc extracts for screening of antibacterial activity.
2.4.2 Cultivation ofisolate SMA01 in solid rice media
As an alternative way, the isolate SMA01 initially cultivated in liquid WMB media was cultured in solid rice media (RM, containing 100-g rice, 110-mL 100%seawater containing 0.3% peptone). After cultivation for 4–6 weeks at room temperatures, the cultures were crushed mechanically and then extracted with EtOAc(3×500 mL) in an Ultraturrax (JY92-II, Scientz) at 600 W for 2×90 cycles of running for 20 s with an internal of 5 s. The homogenates were subject to filtration with medical gauze and the organic layer was collected. After removing the solvent in vacuo, 3.6-g crude extract was obtained for preliminary isolation.Crude EtOAc Extract (3.6-g gum) was isolated by Vacuum Liquid Column chromatography (VLC, 30 g,230–400 mesh Silica gel 60) with stepwise mobile phase CH2CH2:MeOH from 100:1 to 0:1 to aff ord six fractions, which were further combine into four fractions (Fr.) A–D. To track the antibacterial compounds, the fractions were submitted to screening of antibacterial activity against five bacterial pathogens.
2.5 Large-scale fermentation, extraction and bioassay-guided separation of phenazine-1-carboxylic acid
The isolateEmericellasp. SMA01 was cultivated in 30-L Wickerman’s Medium containing 3-g yeast extract, 3-g malt extract, 5-g peptone, 10-g glucose in 1-L 75% natural seawater, pH 7.2–7.4 for 38 days without shaking. The mycelia and fermentation broths were separated by filtration with 200-mesh plankton net and the filtrate was extracted 3 times with 20-L EtOAc. The organic layers was combined and dehydrated with anhydrous MgSO4. Crude EtOAc extract was obtained as dark gum after concentrated under reduced pressure. The mycelia were excised and extracted three times with 3-L acetone. After removing the solvent, the aqueous layer was extracted twice with equal volume of EtOAc. Two EtOAc extracts from fermentation broth and mycelia were combined because of similar TLC and HPLC pattern observed. Finally, 7.8-g dark brown gum was obtained for further isolation of antimicrobial compounds.
7.8-g crude extracts were subjected to VLC chromatography (80 g, 230–400 mesh Silica gel 60)with stepwise mobile phase Petroleum Ether (PE)-EtOAc (0–100%) and CHCl3-CH3OH (5%–100%) to aff ord fractions Fr.1–14. According to the antibacterial assays using bacterial pathogenStaphylococcusaureusas indicator strain, we found seven fractions Fr.4–Fr.8, Fr.13, Fr.14 possessed significantly antibacterial activity againstS.aureus, of which Fr.5 showed highest antibacterial activity with inhibitory zone of 21.3 mm (Supplementary Fig.S1). Then, Fr.5(185 mg) was subject to VLC column chromatography(30 g, 230–400 mesh Silica gel 60) with increasing polarity of CH2Cl2:MeOH (50:1–0:1) to yield six subfractions. Subfractions Fr.5-3 were subject to repeated LH-20 separation with CH2Cl2:MeOH=1:1 and preparative-TLC (pTLC) with Hexane:CH2Cl2:EtOAc (10:50:1, 0.1% HCOOH) to obtain Compound 2 (3.1 mg, yellow needles,Rf=0.45). Compound 3(4.2 mg) was separated from Fr.3 (inhibitory zone,8 mm) by recrystallization in dichloromethane.Detailed spectral data of compounds 2–3 were presented in the supporting information(Supplementary Figs.S2–S7).
2.6 Antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests
For screening antibacterial compounds from five sea anemone-derived fungi cultivated in WMB media,six bacterial pathogens, and three plant pathogenic fungi deposited in our laboratory was used. They areS.aureus,Bacillussubtilis,Escherichiacoli,Salmonellaenterica,Bacillusanthracis,ClostridiumPerfringens,Glomerellacingulate,Gibberellazeae,andFusariumoxysporum.
For screening antibacterial compounds from RM culture ofisolate Emericella sp. SMA01, five bacterial pathogens purchased from CGMCC including two Gram-positive bacteria (S.aureussubsp.aureusCGMCC 1.879=CMCC 26001,B.subtilissubsp.subtilisCGMCC 1.3382=ATCC 11774), two Gram-negative bacteria (E.coliCGMCC 1.872=CMCC 44568,S.entericasubsp.entericaCGMCC 1.10754=ATCC 19585), and one marine fish pathogens (VibrioParahaemolyticCGMCC 1.1616=ATCC 33847)were used.
Antimicrobial activities of EtOAc extracts,fractions, and pure compounds were performed according to the Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Standards M2-A11 as described previously (Yue et al., 2015). Briefly, the microbial strains for test were recovered from 4 °C and inoculated on Mueller-Hinton Agar (MHA) plates overnight aerobically in a 37 °C incubator. Single colonies were picked up and suspended into Mueller-Hinton Broth, which was adjusted to match the 0.5 Mcfarland standards. Then,the suspensions were evenly spread on MHA plates using cotton swab. The EtOAc extracts from five sea anemone-associated fungi were resolved in 0.5–1.0-mL DMSO. VLC fractions were prepared for antibacterial assays by resolving 100–200-mg fractions in 1.0-mL DMSO. 10–15 μL of EtOAc extracts and 5 μL of fractions or pure compounds were pipetted onto sterile paper disks (5-mm diameter). After removing the DMSO at room temperature, the paper disks were placed on the surface ofindicator medium plates in duplicates.After inoculation for 18 h at 37 °C, the inhibitory activity was determined by measuring the diameter of inhibitory zone (diameter, mm). DMSO was used as negative control. Penicillin G potassium salt (MDBio,Inc, 20 μg/mL in DMSO) and streptomycin sulfate(Sigma, 20 μg/mL in DMSO) were used as positive control, respectively.
2.7 Antifungal assays
Three plant pathogenic fungi,Phytophthoracapsici,VerticilliumdahliaCGMCC 3.375 8,GibberellazeaeCGMCC 3.428 8, were used in this study. Antifungal bioactivity of the compound 2 was conducted according to the method described in literature (Zhang et al., 2013). Briefly, 10.6 mg of compound 2 were dissolved in 2 mL of DMSO, and diluted in 2-fold way, yielding seven concentration gradients. 100 μL of the 2-fold diluted solutions were added into 10 mL ofliquid potato dextrose agar at final concentrations of 0.83–53 μg/mL. Agar plugs containing the fungal mycelia were inoculated onto the center of PDA plates, respectively. Then, the plates were placed in an incubator at 28 °C. 1% (w/w)DMSO was used as a negative control, when the fungal mycelium reached the edges of the control dishes, the antifungal activities were calculated as follows, and the experiments were carried out in triplicates.
Inhibition activity (%)=(1–De/Dc)×100,
whereDe, the diameter of the growth zone in the experimental dish (mm);Dc, the diameter of the growth zone in the control dish (mm).
2.8 Statistical analysis
Results are expressed as mean±S.E.M. The significance of diff erences between the means of diff erent experimental groups was analyzed by Analysis of Variance, followed by Tukey multiple comparisons test build in Graphpad Prism 6.0(GraphPad software, San Diego, CA, USA).P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 RESULT
3.1 Isolation of sea anemone-associated fungi and screening of the antibacterial potential
The sea anemones were collected in the First Bathing Beach of Qingdao and were used to isolate the symbiotic fungi (Fig.1a). In total of five pure fungal isolates were obtained from inner tissues of the sea anemones in PDA plates (Fig.1b). To investigate their antibacterial potential, all 5 isolates were fermented in small scale with liquid Wickerman’s media, and then EtOAc extracts from the liquid cultures were employed to assay the antibacterial activities against a panel of bacterial pathogens by disc diff usion assay. Results are shown in Fig.2a. Of all the test samples, EtOAc extracts from the isolate SMA01 possessed the highest antibacterial activity against all tested pathogens, inhibitory zone ranging from 10 mm to 15 mm (Fig.2a). Moreover, EtOAc extracts from another three isolates showed relatively mild antibacterial activities with average inhibitory zone of 5–10 mm.
To validate the antibacterial potential ofisolate SMA01, we also cultivated this fungal in solid rice media in small scale. The EtOAc extract was obtained after fermentation and used to trace its antibacterial activity. After preliminary isolation by normal phase vacuum liquid chromatography with CH2Cl2:MeOH(100:1–0:1), four subfractions Fr.A–D were obtained from the EtOAc extract and were further assayed for antibacterial activity. Results indicated that subfraction Fr.A, eluted with CH2Cl2:MeOH (100:1–10:1), exhibited significantly antibacterial activity againstVibrioParahaemolytic,StaphylococcusaureusandBacillussubtilis(Fig.2b). While other subfractions except for Fr.B, showed mild inhibitory eff ects against one or two bacterial pathogens. These results indicate that isolate SMA01 is a good candidate for isolation of active secondary metabolites.
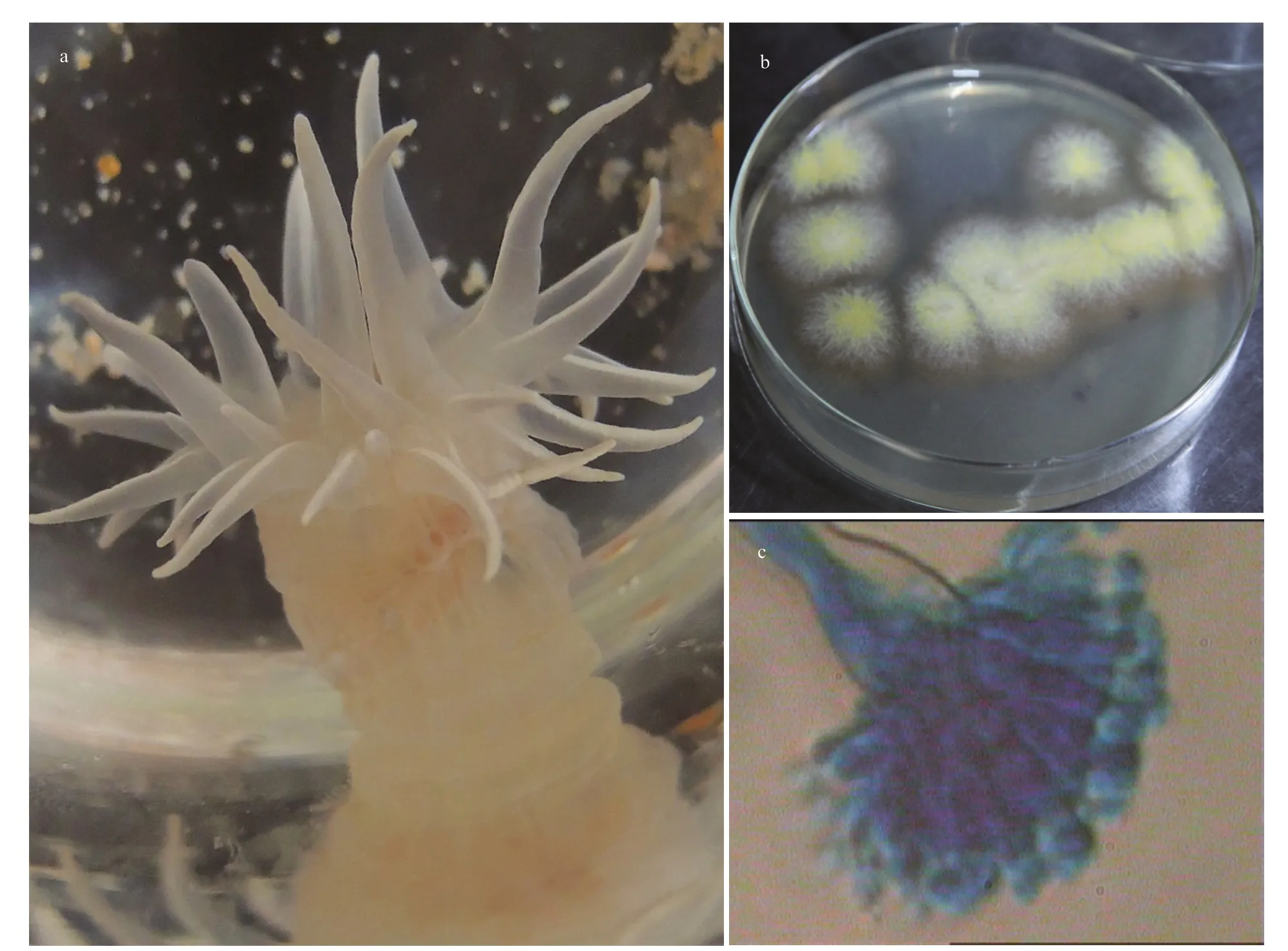
Fig.1 Photos of the sea anemone investigated in this study (a); the strain SMA01 isolated from the inner tissues of the sea anemone host (b); and the microscopic image of characteristic spore produced by the strain SMA01 (40×) (c)
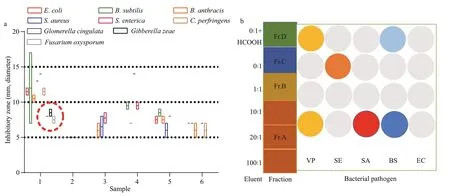
Fig.2 Screening of antimicrobial activities of EtOAc extracts from five sea anemone-derived fungi (a) and subfractions from strain SMA01 (b)

Fig.3 Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree from analysis of 38 similar rDNA-ITS sequences of strain SMA01
3.2 Identification of the sea anemone-derived fungi SMA01
The potential antibiotics-producing isolate SMA01 was further identified by morphology and ITS-rDNA sequencing. One representative stain and its characteristic spore structure are shown in Fig.1b–c.The colonies ofisolate SMA01 on MEA are flat with white aerial mycelium on the edge, and are covered by yellow conidia in the center (Fig.1b). The spore structure is shown in Fig.1c, which indicate that the strain SMA01 may belong to the genusAspergillus.However, the morphological characteristics is not enough to assign the identity of this strain exactly,thus molecular identification based on ITS-rDNA sequencing was performed. A sequence of 482 bp was obtained from the ITS-rDNA region and was submitted to BLASTn for searching similar species in the database. A phylogenetic tree was constructed based on 39 similar ITS-rDNA sequences downloaded from the BLAST results and the results strongly suggest that strain SMA01 belonged to genusEmericella(Fig.3).
3.3 Separation and identification of antibacterial and antifungal compound phenazine-1-carboxylic acid from Emericella sp. SMA01 liquid cultures
The fungal strainEmericellasp. SMA01 was cultivated in liquid WMB media for 38 days at room temperature, and then EtOAc extracts from the liquid cultures was obtained and further isolated by a combination of silica gel column chromatography,Sephadex LH-20 and preparative TLC according to the antibacterial activity against an indicator strainS.aureus. Figure 4 shows the schematic flowchart of isolation of antibacterial Compound 2.
Compound 2 (3.1 mg) was obtained as yellow needles. In the1H NMR spectrum, signals for seven aromatic protons were observed atδH7.21–8.98.Moreover, at downfield, chemical shift corresponding toδH15.55, one singlet changeable proton, probably-OH, was observed.13C NMR highlighted the feather that only twelve aromatic cartons (δC125.06–144.21)existed together with a carbonyl carbon (δC166.04).DEPT 135 revealed seven primary carbons of twelve aromatic cartons existed. According to the NMR data,a carbonyl group and at least one benzene ring were deduced. Further literature survey suggested that the NMR characteristics of compound 2 was in accordance with the known compound phenazine-1-carboxylic acid (Jayatilake et al., 1996). MS analysis of compound 2 affi rmed our deduction that compound 2 was phenazine-1-carboxylic acid withm/z223.05(ESI-MS, [M-H]-).
Compound 3 (4.2 mg) was obtained as white needles. Interpretation of1H and13C NMR data suggested that compound 3 was in accordance with previously reported Ergosta-5,7,22-trien-3β-ol (Wang et al., 2004). Therefore, compound 3 was identified as Ergosta-5,7,22-trien-3β-ol.
Figure 5 shows the antifungal eff ects of phenazine-1-carboxylic acid against three phytopathogenic fungi.Results suggested that phenazine-1-carboxylic acid exhibits significantly antifungal activity below 53 μg/mL. The IC50values againstPhytophthoracapsici,Gibberellazeae(CGMCC 3.428 8) andVerticilliumdahliae(CGMCC 3.375 8) were determined to be 23.26, 30.67, and 53.89 μg/mL, respectively, by the Probit analysis built in SPSS software. Therefore,phenazine-1-carboxylic acid shows the most powerful inhibition against theP.capsici.
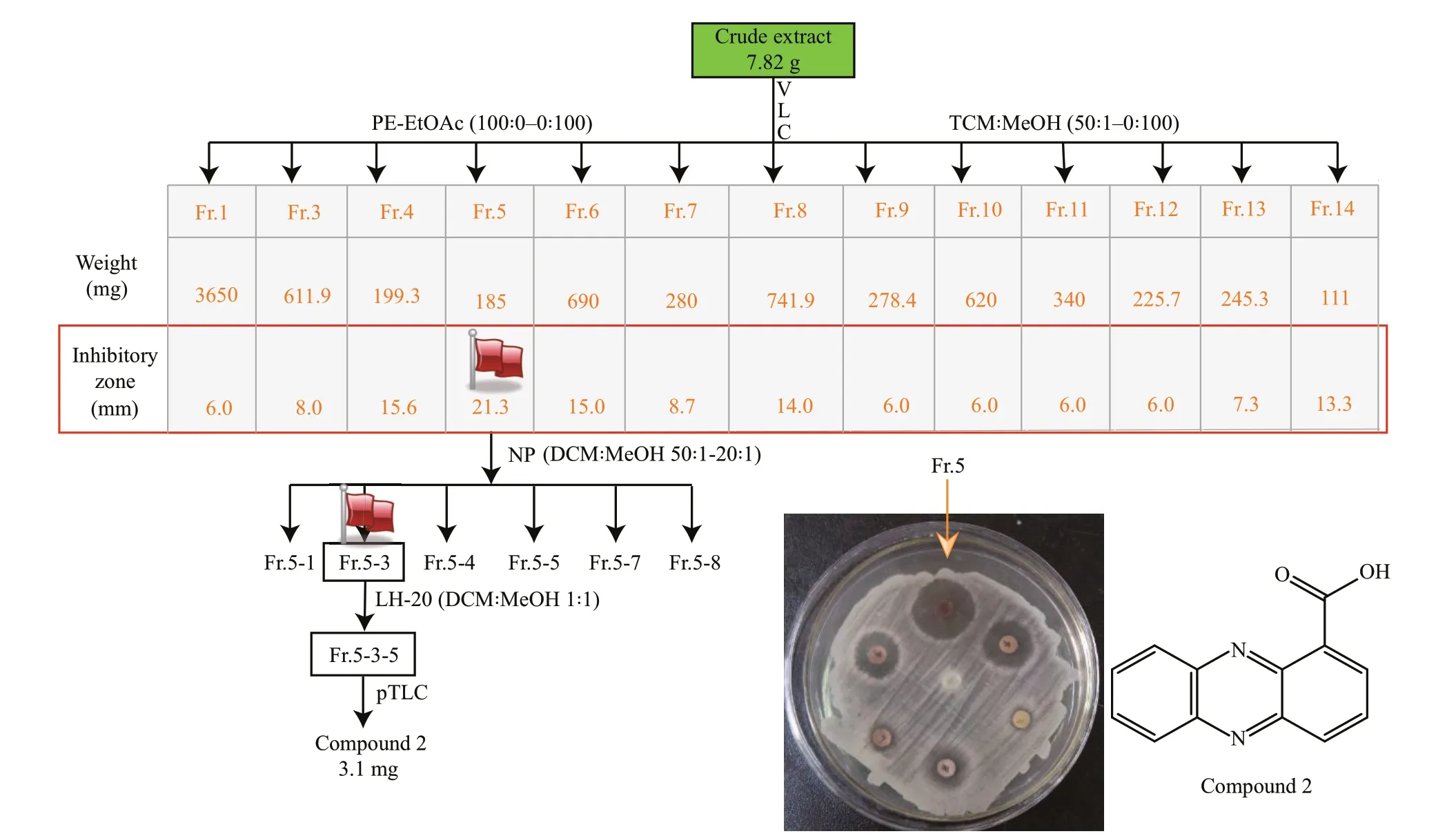
Fig.4 Schematic illustration ofisolation of antimicrobial compound 2 from EtOAc extracts ofliquid cultivation of Emericella sp. SMA01
4 DISCUSSION
Sea anemones were renowned as venomous animals in nature for producing neurotoxic toxins,while their associated fungi were not investigated enough. In this study, 5 sea anemone-associated marine fungi were isolated and assayed for antibacterial activity against a panel of bacterial pathogens. One fungal strain whose metabolites possessed potent antibacterial activity and chemical diversity was found and was further identified asEmericellasp. according to the morphological characteristics and ITS-rDNA sequence. Moreover,bioassay-guided isolation of active metabolites againstS.aureusled to a known antibiotics,phenazine-1-carboxylic acid, in subfraction Fr.5.Importantly, phenazine-1-carboxylic acid was found to inhibit three phytopathogenic fungi with IC50values ranging 23.26 μg/mL to 53.89 μg/mL, which extended our knowledge of the applications of the compound phenazine-1-carboxylic acid.
In 2001, 23 fungal strains isolated sea anemonesAnthopleuraqingdaoenisisPei andA.midoriwere grouped in to six genera, includingRhozopus,Penicillium,Alterinaria,Aspergillus,Dospora,Fusarium, andGliocladium(Liu et al., 2001). Da Silva et al. (2008) reported 110 fungal species within eight genera from sea anemonesPalythoacaribaeorum,P.variabilis, andZoanthussolanderi.Moreover, the culturable fungal diversity of sea anemoneP.haddoniin the South China Sea was demonstrated by identifying 49 independent fungal strains, of which 25 fungal isolates fell into 18 genera(Qin et al., 2015). Recently, sea anemoneAnthopleuraxanthogrammicawas found to harbor phylogenetically diverse fungi of 18 genera, of whichAspergillusdominated (Liu et al., 2020). Of special, the genusEmericellawas not included in above sea anemonederived fungi. The genusEmericellahad been reported previously as plant endophytic fungi (Xu et al., 2013) and in various marine environments such as green alga (Oh et al., 2007), sponge (Malmstrøm et al., 2002), jellyfish (Malmstrøm, 1999), and marine sediments (Fredimoses et al., 2019). To the best of our knowledge, it was the first report ofEmericellasp. in sea anemones.
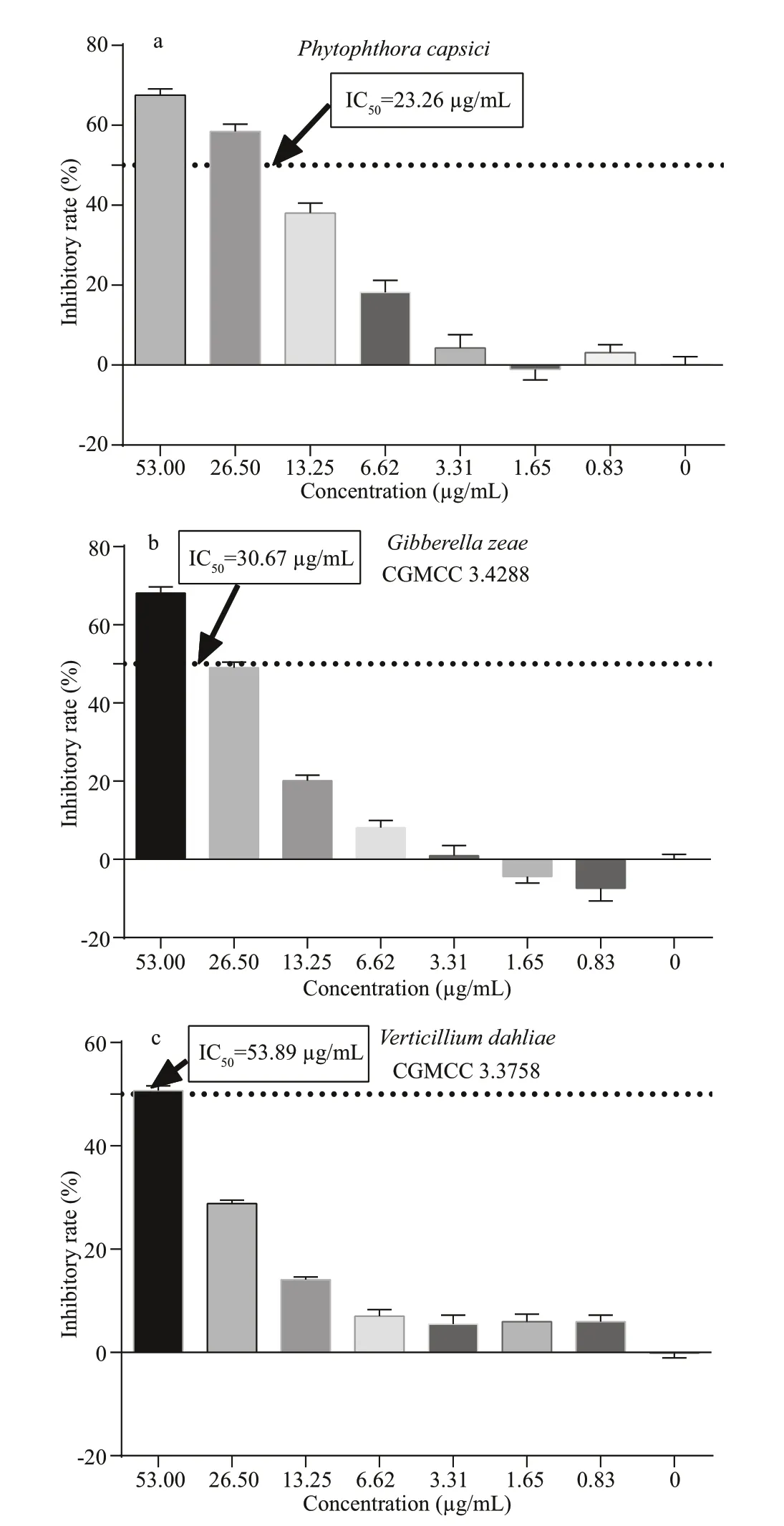
Fig.5 Antifungal activities of phenazine-1-carboxylic acid against three phylopathogenic fungi
Numerous studies have indicated that organic extracts from marine invertebrates-associated microorganisms possessed antibacterial activity. In the case of corals, approximately 20%–70% microbes exhibited considerable antibacterial activity (Shnit-Orland and Kushmaro, 2009; Nithyanand et al.,2011). Investigation on the antibacterial activities of organic extracts from the sea anemone-associated fungi revealed similar phenomenon with coralrelated microorganisms, up to 59% of the culturable fungi possessing antimicrobial activity (Qin et al.,2015; Liu et al., 2020). In this study, all isolated fungal strains exhibited diff erent levels of antibacterial activity, however, onlyEmericellasp.SMA01 showed the strongest inhibitory eff ects against a panel of human bacterial pathogens (Fig.2a).Moreover, the shift from liquid fermentation to solid rice medium presented little influence on the antibacterial activity of theEmericellasp. SMA01,which indicated thatEmericellasp. SMA01 may be a good producer for synthesizing antibacterial secondary metabolites.
Recent years witnessed an increasing evidence of producing novel antimicrobial secondary metabolites by theEmericellaspp. from diff erent source organisms. These novel natural products covered a broad range of structural characteristics from cyclic peptides (Malmstrøm, 1999), polyketides (Pang et al.,2018), to meroterpenoids (Chen et al., 2019; Li et al.,2019). Moderate to potent antimicrobial activities were usually observed against either human bacterial pathogens or plant pathogenic fungi among these metabolites. Noteworthy, emervaridones A fromEmericellasp. TJ29 showed significant inhibition to extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producingE.coliwith an minimum inhibitory concentration value of 2 μg/mL, which was comparable to the clinically used antibiotic amikacin (He et al., 2017). In this study,bioassay-guided isolation led to a known antibiotics,phenazine-1-carboxylic acid, from theEmericellasp.SMA01. Phenazine-1-carboxylic acid was able to inhibit three phytopathogenic fungi with IC50values ranging from 23.26–53.89 μg/mL. Phenazine-1-carboxylic acid is a natural phenazine antibiotics,mainly isolated from plant rhizosphere-symbiotic bacteriaPseudomonasspp. for biocontrol of soilborne microbial pathogens (Thomashow et al., 1990;Mavrodi et al., 2006). Therefore, considering the occurrence of theEmericellaspp. in plants and animals from a terrestrial or marine origin, the antimicrobial metabolites fromEmericellaspp. may play a vital role in protecting the sea anemone hosts from the environmental threat of pathogenic microorganisms. The fungal strainEmericellasp.SMA01 included in this study may have a great potential in developing into a biocontrol agent for prevention of agricultural microbial diseases.
5 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, investigation on the marine-derived fungi led to first isolation and identification of theEmericellasp. SMA01 in sea anemone with broadspectrum antibacterial activity in two diff erent media.Tracing the antibacterial activity of the organic extract allowed identification a known antibiotic phenazine-1-carboxylic acid, which also showed considerable inhibition to three phytopathogenic fungi with IC50values of 23.26–53.89 μg/mL. This study extends our knowledge of sea anemone-associated fungi, and may benefit understanding of the defensive chemical interactions between the symbiotic fungi and their host sea anemones.
6 DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
杂志排行
Journal of Oceanology and Limnology的其它文章
- Steady increase in water clarity in Jiaozhou Bay in the Yellow Sea from 2000 to 2018: Observations from MODIS*
- Phylogenetic diversity and bioactivity of culturable deepsea-derived fungi from Okinawa Trough*
- Allelopathic eff ects of mixotrophic dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea on co-occurring phytoplankton: the significance of nutritional ecology*
- Investigation of the decline of Ulva prolifera in the Subei Shoal and Qingdao based on physiological changes*
- Effi ciency of phosphorus accumulation by plankton,periphyton developed on submerged artificial substrata and metaphyton: in-situ observation in two shallow ponds*
- Petroleum exploitation enriches the sulfonamide resistance gene sul2 in off shore sediments
