Two Metal-Organic Frameworks Built from 2,2′-Dimethyl-4,4′-biphenyldicarboxylic Acid
2021-05-16HEXinZHANGShunLinXIAOTianYuZHUDunRu86003
HE Xin ZHANG Shun-Lin XIAO Tian-Yu ZHU Dun-Ru*,,( 86)( 003)
Abstract:Two metal-organic frameworks(MOFs),[Ni(μ2-H2O)(L)(DMF)(H2O)]·0.5H2O(1)and[Cd2.5(L)(trz)3(H2O)2]·2.5DMF(2)(L=2,2′-dimethyl-4,4′-biphenyldicarboxylic acid,DMF=N,N-dimethylformamide,Htrz=1,2,4-triazole),have been synthesized and characterized by FT-IR,thermogravimetric analysis(TGA),powder and single crystal X-ray diffraction.MOF 1 crystallizes in monoclinic system with a space group P21/c.Niion adopts an elongated[NiO6]octahedron as a 4-connected node and is linked by μ2-H2O and L2-ligands to generate a 2D sql topological network.MOF 2 crystallizes in monoclinic system with a space group C2/m and contains three crystallographically different Cd ions.Each Cd ion shows a distorted octahedral geometry and three Cd ions are connected by trzco-ligands in a μ1,2,4-bridging mode to form a 2D kgd layer with(3,6)topology in the ab plane.These layers are further pillared by the L2-ligands along the c axis to produce a binodal(4,8)-connected 3D flu framework.The TGA showed that 1 and 2 were stable below 390 and 230℃,respectively.CCDC:2042076,1;2042077,2.
Keywords:metal-organic frameworks;2,2′-dimethyl-4,4′-biphenyldicarboxylic acid;crystal structure;topology
0 Introduction
Metal-organic frameworks(MOFs)have attracted intense attention not only for their versatile topological structures but also for their promising applications in gas separation,catalysis,proton conductivity and photoluminescence sensor[1-4].Owing to their rich coordination modes as bridging ligands and the hard-base O-atom donors,multicarboxylic acids have been widely used as organic ligands for the build of MOFs[5-7].During the past decade,we have been particularly interested in synthesizing MOFs via substituted 4,4′-biphenyldicarboxylic acid (BPDC)because introduction of different substitutes into the biphenyl ring can finely tune the structures and properties of the resulting MOF materials[8-20].However,to our knowledge,MOFs constructed directly from 2,2′-dimethyl-BPDC acid(H2L)have been less reported up to now[21-31].Recently,by using H2L to bind with acis-[InO4(μ2-OH)2]octahedron,we have successfully synthesized a novel chiral 3D indium-based MOF,[In(μ2-OH)L]·3H2O·2DMA(DMA=N,N-dimethylacetamide),which shows an unprecedented 4-connectedumytopology[32].As a continuation of our investigation on the H2L ligand,we report here the syntheses of two new MOFs,[Ni(μ2-H2O)(L)(DMF)(H2O)]·0.5H2O(1)and[Cd2.5(L)(trz)3(H2O)2]·2.5DMF(2)(DMF=N,N-dimethylformamide,Htrz=1,2,4-triazole).Their single crystal structures and thermal stabilities were also investigated.
1 Experimental
1.1 Chemicals and general methods
2,2′-Dimethyl-4,4′-biphenyldicarboxylic acid(H2L)was prepared according to the reported method[33-34].All the other chemicals and solvents purchased were of analytical grade and used without further purification.Elemental analysis was performed by a Thermo Finnigan Flash 1112A elemental analyzer.FT-IR spectrum(4 000~400 cm-1)was recorded on a Nicolet 380 FT-IR instrument(KBr discs).Thermogravimetric analysis(TGA)was carried out on a NETZSCH STA 449C thermal analyzer under nitrogen atmosphere at a scan rate of 10℃·min-1.Powder X-ray diffraction(PXRD)data were collected on a Bruker D8 ADVANCE diffractometer using CuKαradiation(λ=0.154 06 nm)at 40 kV and 40 mA in the range of 5°~50°.
1.2 Syntheses of MOFs 1 and 2
A mixture of Ni(NO3)2·6H2O(0.011 6 g,0.04 mmol),H2L(0.010 8 g,0.04 mmol),DMF(2 m L)and H2O(1 mL)was heated in a 25 mL capacity stainlesssteel reactor lined with Teflon at 100℃for 72 h and then cooled down to room temperature.Green block crystals of 1 were obtained in 79% yield based on H2L.Anal.Calcd.for C19H24NNiO7.5(%):C,51.27;H,5.44;N,3.15.Found(%):C,51.43;H,5.21;N,3.31.FT-IR(KBr discs,cm-1):3 377(m,b),2 975(w),2 927(w),1 656(s),1 530(s),1 410(vs),1 007(m),777(s).
A mixture of Cd(NO3)2·4H2O(0.038 6 g,0.125 mmol),1,2,4-triazole(0.010 4 g,0.15 mmol),H2L(0.013 5 g,0.05 mmol),DMF(2 mL)and H2O(1 mL)was heated in a 25 mL capacity stainless-steel reactor lined with Teflon at 80℃for 72 h and then cooled down to room temperature.Colorless block crystals of 2 were obtained in 75% yield based on H2L.Anal.Calcd.for C29.5H38.5Cd2.5N11.5O8.5(%):C,36.48;H,4.00;N,16.59 Found(%):C,36.32;H,4.13;N,16.46.FT-IR(KBr discs,cm-1):3 408(m,b),3 130(m),2 923(w),1 654(m),1 581(s),1 503(vs),1 411(s),1 384(s),1 282(m),1 158(s),1 065(m),990(m),665(s).
1.3 Crystal structure determination
Suitable single crystals of 1 and 2 were selected for lattice parameter determination and collection of intensity data on a Bruker SMART APEX Ⅱ CCD diffractometer with a graphite-monochromated MoKα(λ=0.071 073 nm)radiation using aφ-ωscan mode at 296(2)K.Multi-scan absorption corrections were applied to all intensity data using SADABS.The structures were solved by direct methods and refined onF2by full-matrix least squares procedures using SHELXTL software[35].All non-hydrogen atoms were refined with anisotropic displacement parameters,and all hydrogen atoms were calculated and refined as riding modes except water molecules.The O2W of 2 was disordered over two positions and refined with an occupancy factor of 0.30(3)for O2W and 0.20(3)for O2WA.In the refinements of 2, the SQUEEZE routine[36]in PLATON[37]was used to include the contribution of disordered solvent molecules in the structure factors in the least-squares refinement.The solvent-accessible volume(1.802 nm3)in the unit cell of 2 was identified,with a total electron count of 197 electrons.They corresponded reasonably to two and a half DMF molecules with an electron count of 100 in the unit cell of 2 and withZ=2.The crystallographic data of 1 and 2 are listed in Table 1,and the selected bond lengths and angles are provided in Table 2.
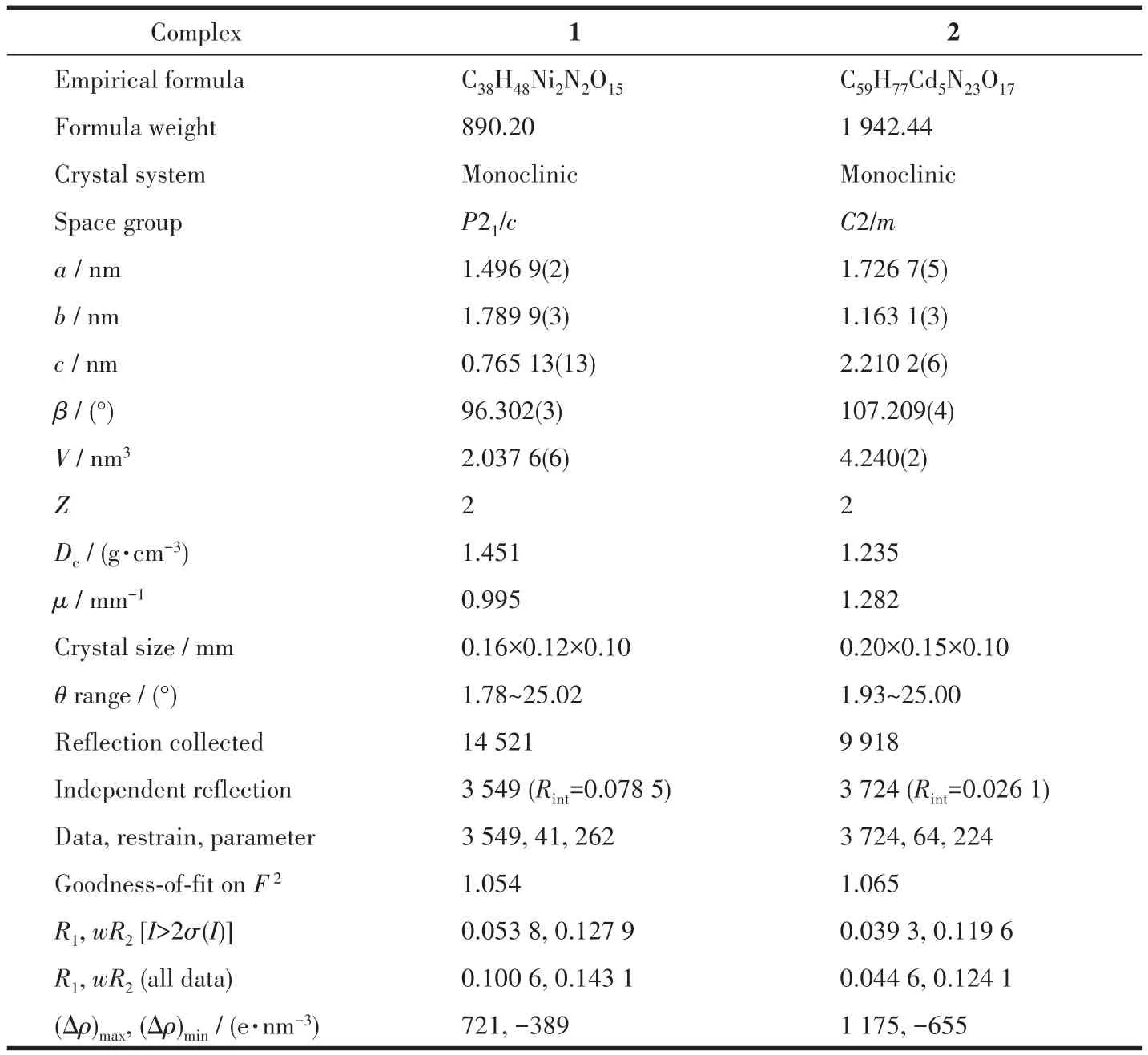
Table 1 Crystal data and structure refinement for 1 and 2

Table 2 Selected bond distances(nm)and angles(°)for 1 and 2

Continued Table 2
CCDC:2042076,1;2042077,2.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Crystal structure analysis
The X-ray crystallographic study reveals that 1 crystallizes in the monoclinic space groupP21/c.The asymmetric unit of 1 consists of one Niion,one L2-ligand,one coordinated DMF molecule,two coordinated H2O molecules,and a half lattice H2O molecule(Fig.1).
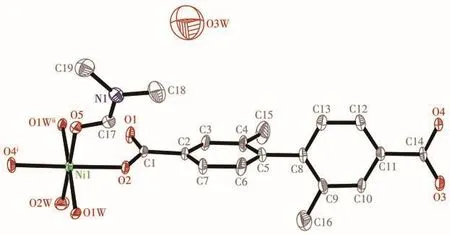
Fig.1 ORTEP drawing of asymmetric unit of 1 with 50% thermal ellipsoids probability
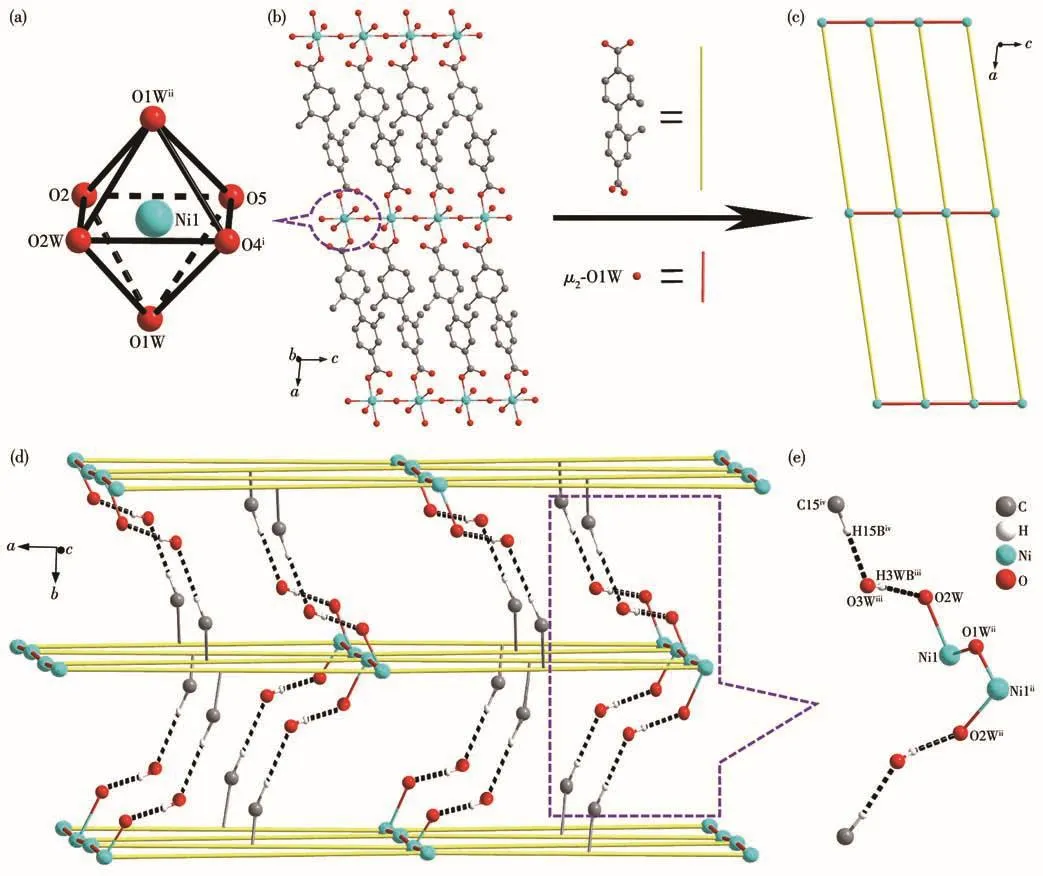
Fig.2 (a)Coordination environment of Niion in 1;(b)2D layer consisting of[NiO6]octahedron and L2-ligands with H atoms and solvent molecules omitted for clarity;(c)2D sql topological network,with the L2-ligand simplified as a line;(d)3D hydrogen-bonded supramolecular framework;(e)Ow—H…O and C—H…Ow hydrogen bonds between the 2D layers
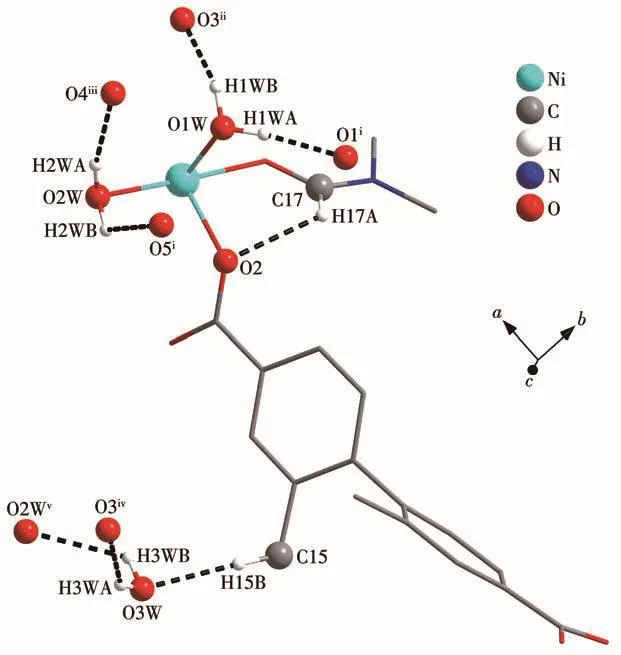
Fig.3 Hydrogen bonding interactions in 1
The single-crystal structural analysis indicates that 2 crystallizes in the monoclinicC2/mspace group.Its asymmetric unit is composed of three crystallographically distinct Cdions(the occupancy factors for Cd1,Cd2and Cd3 are0.25,0.5 and 0.5,respectively),a half of L2-ligand,two 1,2,4-triazolate anions(N1-trzand N4-trz-with an occupancy factor of 0.5 and 1.0,respectively)and two coordinated H2O molecules(both O1W and O2W with an occupancy factor of 0.5)(Fig.4).
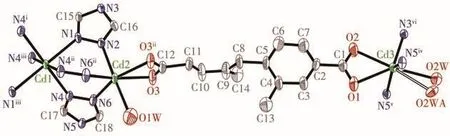
Fig.4 ORTEP drawing of asymmetric unit of 2 with 50% thermal ellipsoids probability
The Cd1 atom is six-coordinated by the nitrogen atoms(N1 and N4)from six different trz-anions to form a nearly perfect[Cd1N6]octahedron with a CSM value of 0.01(Fig.5)[38].However,both Cd2 and Cd3 atoms adopt a distorted octahedral[CdN3O3]geometry coordi-nated by three nitrogen atoms from three different trzanions,one bidentate chelating carboxylate group and one terminal H2O molecule(Fig.5).Their CSM data are 2.75 and 8.22 for Cd2 and Cd3,respectively.The Cd—O(0.236 1(4)~0.250 3(13)nm)and Cd—N(0.225 0(3)~0.237 0(3)nm)bond lengths are in good agreement with the related Cd-MOFs(Table 2)[8,11,19].
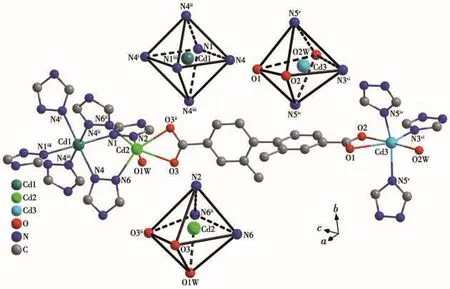
Fig.5 Coordination environment of the Cdions in 2
Each trz-co-ligand links three Cdcations(Cd1,Cd2 and Cd3)in aμ1,2,4-bridging mode(Fig.6a).Especially,each Cd1 atom connects two neighboring Cd2 atoms by six trz-co-ligands in aμ1,2-bridging mode to form a trinuclear[Cd1(μ1,2-trz)6(Cd2)2]cluster(Cd3)with a Cd1…Cd2 distance of 0.392 9(2)nm(Fig.6a,Table 2).Then each trinuclear Cd3cluster are linked to six adjacent Cd3 atoms by six trz-co-ligands in aμ4-bridging mode to produce a 2D Cd-triazolate layer in theabplane.If the Cd3 atom is considered as a 3-connected node,while the trinuclear Cd3cluster as a 6-connected node(Fig.6a),the Cd-triazolate layer can be simplified as a binodal(3,6)-connectedkgdtopology with the Schläfli symbol(43)2(46·66·83)(Fig.6b).These 2Dkgdlayers are further pillared by the L2-ligands along thecaxis to generate a complicated 3D framework(Fig.6c).If the L2-ligand can be treated topologically as a linear connector,the final structure of 2 is a binodal(4,8)-connectedflutopology with the Schläfli symbol(412·612·84)(46)2(Fig.6d),which is rarely observed in the Cd-MOFs[39-40].

Table 3 Hydrogen-bonding parameters of 1
2.2 IR spectra
In the IR spectra of 1 and 2,the asymmetric or symmetric stretching vibrations of the carboxylate groups were observed around 1 530 or 1 410 cm-1for 1 and 1 503 or 1 411 cm-1for 2,respectively[8,32].The absence of very strong absorption bands around 1 700 cm-1confirms the complete deprotonation of the carboxyl group of the H2L during the reactions.The bands at 3 377 and 3 408 cm-1are assigned to O—H stretching vibrations of H2O molecules in 1 and 2,respectively.The peaks at 1 656 and 1 654 cm-1can be attributed to the—C=O stretching bands of DMF molecules in 1 and 2,respectively[12].The typical stretching vibration peaks of methyl groups were 2 927 cm-1for 1 and 2 923 cm-1for 2,respectively[32].These features are in good agreement with the results of their single-crystal X-ray diffraction.
2.3 PXRD and TGA
The PXRD patterns of 1 and 2 and their simulated ones are depicted in Fig.7.The experimental patterns were in good agreement with the simulated ones from X-ray single crystal data,showing the high phase purity of the bulk products.

Fig.7 PXRD patterns of 1 and 2
TGA curves of 1 and 2 are shown in Fig.8.For 1,the weight loss of 22.7% between 30 and 295℃can be assigned to the removal of one DMF molecule,one terminal water and a half lattice water molecule(Calcd.22.5%).For 2,the weight loss of 22.3% between 30 and 180℃was observed due to the loss of two and a half DMF molecules and two coordinated water molecules(Calcd.22.5%).
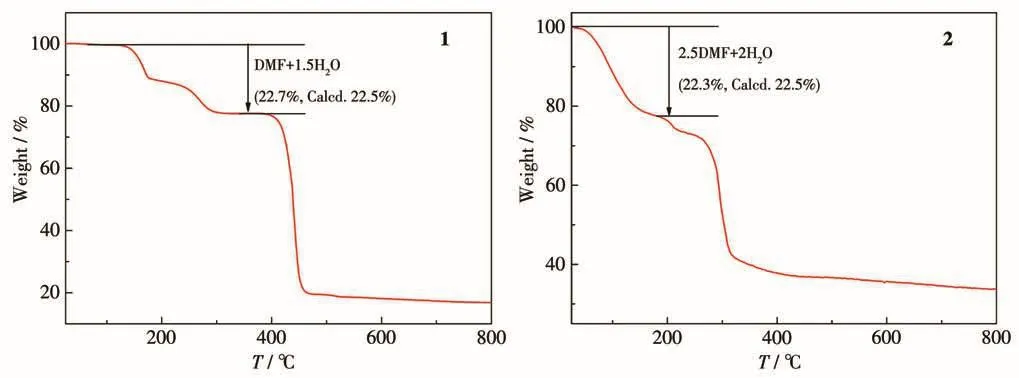
Fig.8 TGA curves for 1 and 2
3 Conclusions
Two novel MOFs 1 and 2 with 2,2′-dimethyl-4,4′-biphenyldicarboxylic acid have been synthesized and characterized by elemental analyses,IR,PXRD,TGA and X-ray crystal structure analysis.X-ray crystallo-graphic analysis shows that 1 is a 2Dsqltopological network,while 2 shows a binodal(4,8)-connected 3Dfluframework.
