IS-LM Model Based Analysis on the Role of China’s Financial Policy for Supporting Agriculture
2021-04-08XiejunCHENG
Xiejun CHENG
Business School of Jiangsu Second Normal University, Nanjing 210013, China
Abstract The "three rural" issues have always been an important and prominent issue in China’s economy and society. The "No. 1 Document" of the central government of China over the years has all stressed this field. The state has also undertaken various economic policies to increase the income of rural residents, support agricultural development, and improve rural infrastructure construction. Among the various policies, financial support for agriculture is a frequently used macroeconomic policy. Based on the IS-LM model, this paper analyzed the effects of financial policy for supporting agriculture on the IS-LM model, discussed the specific role of the financial policy, in order to provide a certain reference for the government to better use financial policy to support the agriculture.
Key words IS-LM model, Financial support for agriculture, Crowding out effect
1 Introduction
TheIS
-LM
model, which stands for "investment-savings" (IS
) and "liquidity preference-money supply" (LM
) is a Keynesian macroeconomic model. It is generally used to discuss the relationship between national output and interest rates in macroeconomics, and then analyze the effects of macroeconomic policies on the model, that is, how to affect national output and interest rates. Existing literature mostly studies the effect of financial policy on abstract product markets, while there are relatively few specific financial policy tools and specific product markets. The agricultural product market is not only an important part of the product market, but also related to the realization of national strategic goals such as agricultural development and farmers’ income increase. In the context of rural revitalization and urban-rural integration, it is worth studying the role of financial support for agriculture, a specific financial policy tool, on the agricultural product market, that is, how to act on theIS
-LM
model.2 IS-LM model of the three-sector economy
Theoretically, theIS
-LM
model represents the relationship between national output and interest rates when the product market and the money market are in equilibrium at the same time. The product market and the money market are at the same time equilibrium is an ideal state, which is represented on the image as the intersection of theIS
curve and theLM
curve.For the convenience of analysis, we assume that there is no foreign sector, theIS
curve equation for a three-sector economy is:
(1)
TheLM
curve is only related to the central bank’s money supply, income level, market rate, and price level. The equation is: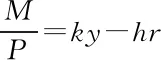
(2)
Combining equations (1) and (2), we can obtain theIS
-LM
model:
etc
. All these are constants. Based on this, we focused analyzing the effects of financial expenditure on agriculture as part of the government transfer payment on the agricultural product market.3 Analysis of the effects of financial support for agriculture on the IS-LM model
Financial support for agriculture is part of the transfer payment in financial policy. According to theIS
curve equation, increasing fiscal expenditure on agriculture can shift theIS
curve to the right. With theLM
curve unchanged, the output of agricultural products will increase, that is, the income of rural residents will increase.Assuming that the initial equilibrium point between the agricultural product market and the currency market isE
, in order to increase the output of agricultural products and increase the income of rural residents, the government increases the financial expenditure on agriculture to move theIS
curve fromIS
toIS
. Then, the new equilibrium point isE
, and the equilibrium income of rural residents increased fromy
toy
. Compared with theE
point, theE
point not only increases the income level, but also the interest rate level, fromr
tor
. Therefore, the expansion of the financial policy to support agriculture has increased the income level of rural residents and the level of market interest rates.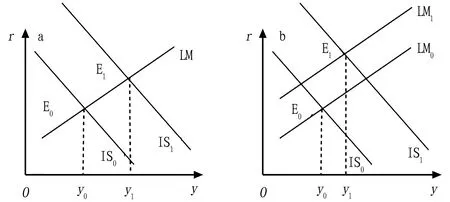
Fig.1 Expenditure effect of financial support for agriculture
Without considering the impact of rising interest rates on the currency market, the effect of financial expenditure on agriculture isy
y
in Fig.1(a). Considering the increase in the market interest rate due to the increase in financial expenditure on agriculture, which leads to changes in the money market, it is found that the effect of the same financial expenditure on agriculture isy
y
in Fig.1(b), which is significantly worse than in Fig.1(a). This is because when the interest rate rises in the money market, the demand for money falls. When the money supply remains unchanged, theLM
curve shifts to the upper left, resulting in the new equilibrium point not being theE
point in Fig.1(a), but theE
point in Fig.1(b). This phenomenon is generally referred to as the "crowding out effect", that is, the increase in government expenditure leads to a decline in social consumption or investment.From the comparison of Fig.1 (a) and (b), we can find that while increasing financial expenditures on agriculture to increase rural residents’ income, attention should be paid to controlling the "crowding effect", otherwise the effect of the policy will be greatly reduced. In other words, the financial expenditure policy on agriculture has two effects. One is the output effect, increasing financial expenditure on agriculture will increase income. The other is the crowding-out effect. The decline in investment caused by the increase in interest rates will lead to a decline in income.
4 Analysis of the effect of financial expenditure on agriculture in increasing the income of rural residents
Financial expenditure on agriculture is a tool for the change of government revenue and expenditure, which mainly acts on theIS
curve. The greater the increase in rural residents’ income caused by the same amount of financial expenditure on agriculture, the better the effect, otherwise, the effect is worse.4.1 Analysis of the relationship between the effect of financial expenditure on agriculture and the
curve
Here, assuming that the slope of theLM
curve remains unchanged, that is, the nature of the money market is stable, and the characteristics of its supply and demand need not be discussed. The effect of financial revenue on agricultural expenditure mainly depends on theIS
curve, that is, the characteristics of supply and demand in the agricultural product market.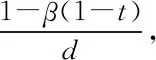

Fig.2 Effect of financial expenditure on agriculture and slope of the IS curve
4.2 Analysis of the relationship between the effect of financial expenditure on agriculture and the
curve
Here, assuming that the slope of theIS
curve remains unchanged, that is, the nature of the product market is stable, and the characteristics of its supply and demand need not be discussed. The effect of financial revenue on agricultural expenditure mainly depends on theLM
curve, that is, the characteristics of supply and demand in the money market.In the three-sector economy, the slope of theLM
curve isk
/h
, wherek
is the currency transaction demand coefficient andh
is the currency speculative demand coefficient. According to theory of Keynesian economics, the currency transaction demand coefficient is considered to be stable, so the slope of theLM
curve depends onh
. The larger theh
, the smaller the slope of theLM
curve, the smaller the increase in interest rates caused by the increase in money demand, the less the investment decreases, and the less income decreases, and the better the financial expenditure on agriculture, as shown in Fig.3.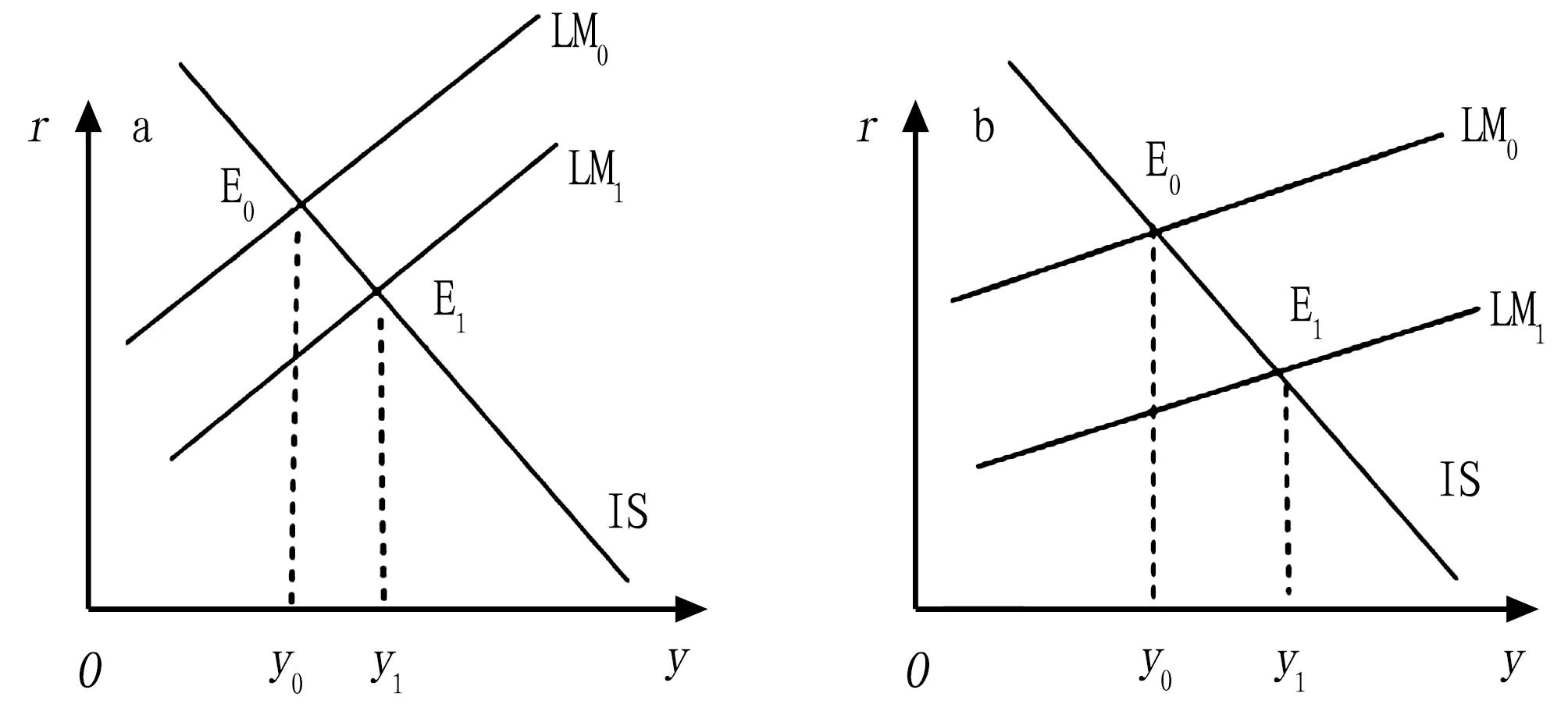
Fig.3 Effect of financial expenditure on agriculture and slope of the LM curve
Simply speaking, the increase in financial expenditure on agriculture will increase the income of rural residents through the multiplier effect, thereby increasing the demand for money. When the money supply remains unchanged (which can be understood as the central bank has no time to increase the money supply), the interest rate rises. A decline in investment leads to a decline in income; a decline in income reduces the demand for money, a decline in interest rates, and an increase in investment, which leads to an increase in income.... The above process is repeated until the currency market and the agricultural product market form a new equilibrium. Ultimately, the increase of income of rural residents from financial expenditure on agriculture depends on the slopes of theIS
curve and theLM
curve.5 Recommendations for giving full play to the role of financial expenditure on agriculture
Through the discussion of the mechanism of financial expenditure on agriculture, the financial expenditure on agriculture has a positive effect on increasing the income of rural residents, but its role is restricted by some factors. In order to better bring into play the income increase effect of this policy, we came up with the following recommendations.
(i) It is recommended to continue to implement the policy of financial supply for agriculture and increase it year by year according to a certain proportion. At present, the income gap between urban and rural residents is still very large. According to the development goal of "common prosperity" in the "14Five-Year Plan", it is practical and effective to vigorously promote the increase of rural residents’ income, truly narrow the income gap between urban and rural areas, and increase financial support for "agriculture, rural areas and farmers".
(ii) It is recommended to establish a high-level construction mechanism for rural public infrastructure to provide a basis for the effect of financial expenditure on agriculture. Financial expenditure on agriculture requires a good hardware environment to play a better role. Relatively weak infrastructure such as roads, communications, education, and medical care in rural areas have largely affected the effects of policies. For example, the financial expenditure on agriculture to support the export of agricultural products may be affected by traffic conditions and fail to achieve the expected goals. Therefore, it is necessary to continuously improve the rural public infrastructure and realize the equalization of urban and rural public services.
(iii) It is recommended to reduce the interest rate sensitivity of rural investment and reduce the "crowding out effect" in rural areas. Governments at all levels should adopt targeted policies for rural areas, preferential interest rates for enterprises investing in the "three rural" fields, encourage more enterprises to engage in production and investment related to "three rural" fields, and strengthen the policy effect of financial expenditure on agriculture.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Ecological Investigation and Ecological Security Assessment of Xizhijiang River Basin in Huizhou City of Guangdong Province
- Molecular Cloning and Bioinformatics Analysis of araC Gene of Vibrio alginolyticus
- Occurrence Regularity and Integrated Control Technology of Canker in Citrus
- Activation Effect of Hydrochemical Energy in Regenerative Agriculture on Nutrients of Arsenic Sandstone
- Prediction and Protection of Cultivated Land in China
- Emergy Estimation of the Main Forest Biomass in Shangri-La, Tibetan Area of Yunnan Province
