Numerical simulation of super-continuum laser propagation in turbulent atmosphere∗
2021-03-19YaQianLi李雅倩WenYueZhu朱文越andXianMeiQian钱仙妹
Ya-Qian Li(李雅倩), Wen-Yue Zhu(朱文越), and Xian-Mei Qian(钱仙妹),†
1Key Laboratory of Atmospheric Optics,Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics,HFIPS,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Hefei 230031,China
2Science Island Branch of Graduate School,University of Science and Technology of China,Hefei 230026,China
3Advanced Laser Technology Laboratory of Anhui Province,Hefei 230037,China
Keywords: super-continuum laser source,pump laser source,numerical simulation,atmospheric propagation properties
1. Introduction
High brightness and wide spectrum are the advantages of super-continuum laser sources,[1-6]which are widely used in laser engineering applications, such as laser remote sensing,free-space optical communication, hyper-spectral light detection and ranging (LIDAR) and laser guidance.[7-10]It is believed that the distortions of atmospheric turbulence can lead beam spreading, beam wandering, and scintillation to have significant negative influence on practical applications due to random variation in the refractive index of the atmosphere.Therefore,comprehensive researches of the propagation characteristics of super-continuum (SC) laser sources in atmospheric turbulence are most important for the practical applications of super-continuum.
So far,the more mature technology is based on the spectral absorption characteristics of SC laser to study its applications in the detection of atmospheric composition.[11-13]Nevertheless, the characteristics of SC laser propagating through the atmosphere are rarely studied. On the assumption that the beam qualities of different wavelength components of SC laser are identical,Li et al. (2010)[14]numerically studied the influence of turbulence on the Strehl ratio of SC laser. The results showed that the Strehl ratio of SC laser is greatly affected by atmospheric turbulence. The effect, especially, on its shortwave components is more serious. Four years later, taking into account the atmospheric refraction,extinction,and turbulence, Wu et al. (2014)[15]numerically calculated the beam width and propagation efficiency of SC laser source in a slant path through the turbulent atmosphere. Then,Kang(2015)[16]experimentally measured the centroid drift of SC laser source after propagating for 1 km. The results revealed that beam wandering of the SC laser is the same as that of the monochromatic laser,in other words,the horizontal drift is smaller than the vertical one. However, to the best of our knowledge, theoretical analysis or experimental studies on other turbulent effects of SC laser sources (e.g., instantaneous scintillation effects)has not been conducted before.Furthermore,the universal law of the influence of turbulence on propagation characteristics of SC laser is not clear at all.
On the one hand, most of theoretical researches on the propagation of laser sources in turbulence are only applicable to weak turbulence conditions because of the assumption of small perturbations. On the other hand, uncontrollable experimental conditions make it so difficult to obtain an ensemble average. Recently,numerical simulation method has become an important way to investigate the laser propagation in turbulent atmosphere. In this paper, according to the propagation theory of partially coherent beams, based on the Maxwell equation and atmospheric radiance transfer equations,the characteristics of beam spreading,beam wander and intensity scintillation of SC laser sources are analyzed by using the multiple phase screen method. Difference in propagation property between SC laser source and their pump laser source is also discussed.
2. Numerical simulation approach
We use a superposition of narrow-band spectral components to simulate the super-continuum spectrum.[17]According to the atmospheric radiation transmission theories of partially coherent beams,the superposition of propagation results of each narrowband spectral component is taken as the ultimate total value of SC laser at the receiver.
Based on the parabolic approximation and the Maxwell equation,the optical field E in turbulence satisfies





where F and F−1are the Fourier transform and the inverse Fourier transform,respectively,and r is the position vector on the phase screen. By using the phase screen transfer method,we can obtain the final optical field E(r,L,λ) on the objective plane. Thus,the total intensity distribution of SC laser at propagation distance z=L can be written as

where I(r,L,λ) is the intensity distribution of each spectral component at propagation distance z=L,T(λ,L)is the transmittance, ν(λz) is the attenuation factor, and [λ1,λ2] is the spectral range of SC laser source.
The SC laser is a special kind of partially coherent beam.Analytically,its partial coherence can be described by the coherence parameter of a partially coherent beam. As proposed in many publications, the partial coherence can be modeled by the random phase screen assumed to be ζ(x,y;t), which changes randomly with time. Thus, the initial optical field of a partially coherent beam can be expressed as
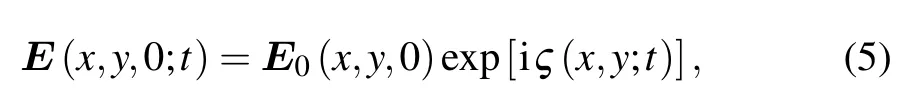
where E0(x,y,0) is the initial optical field of a homologous fully coherent beam. For illustration purpose, we discuss the spatially partially coherent GSM beam which is an analytically tractable model where the spatial coherence function is Gaussian.[22]
The random phase can be modeled as[23]
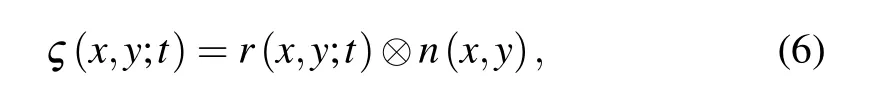
where ⊗indicates a spatial convolution, r(x,y;t) is the spatially uncorrelated random signal with an average 0 and a standard deviation σr, n(x,y) is a Gaussian distribution function with standard deviation σn

thus from Eqs.(6)and(7), the transmittance auto-correlation function can be obtained to be


lateral correlation radius lcdetermines the spectral degree of source coherence and it can be expressed as

For a completely coherent beam, lctends to infinity, and with the degradation of lc, the degree of source coherence degrades. In our study, we assume that the coherent degree of each wavelength component of the whole super-continuum spectrum is identical.
3. Numerical simulation results and analysis
The normalization spectrum distribution of the SC laser is shown in Fig.1, and its spectrum covers the range from 450 nm to 2000 nm.The pump laser we choose is a monochromatic partially(spatial)coherent beam,and its emission aperture is the same as that of the SC laser,i.e.,D0=50 mm. The wavelength of the pump laser is 1064 nm. The atmospheric model used here is the mid-latitude summer and a rural aerosol model with 23-km visibility.
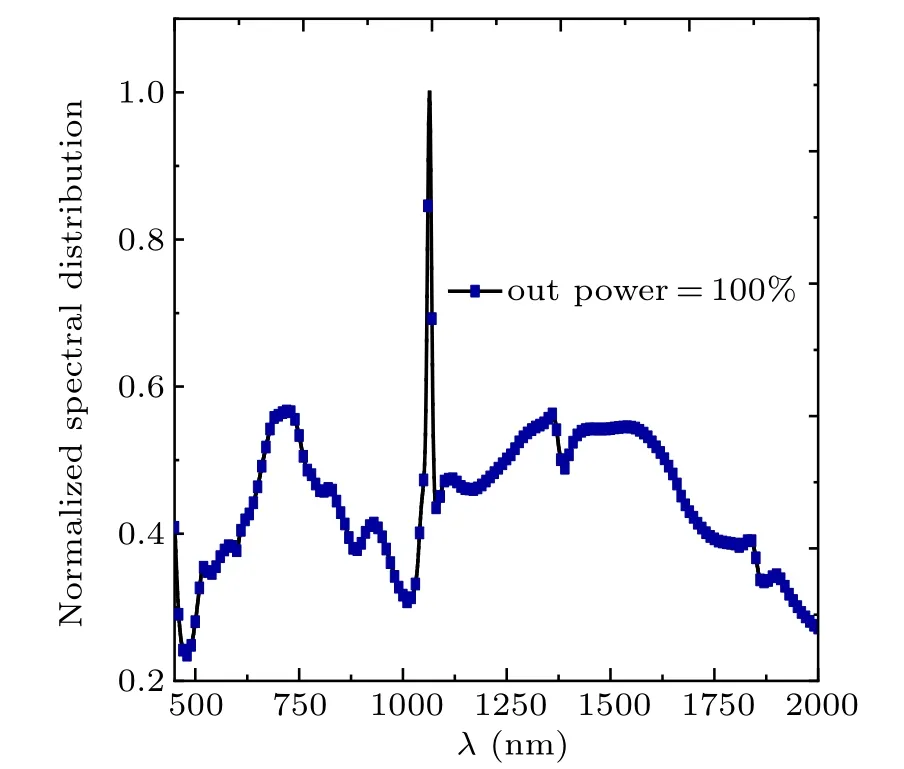
Fig.1. Normalization spectrum distribution of super-continuum source(450 nm-200 nm).

Fig.2. Variations of atmospheric transmittance with wavelength for different propagation distances in turbulence.
Figure 2 shows the curves of atmospheric transmittance versus wavelength λ at different propagation distances. In this paper, we use the wavelength segmentation method to simulate the super-continuum spectrum. Considering these factors such as the spectral distribution of SC laser, the atmospheric transmittance of each spectral segment, and the influences of different wavelengths on the propagation characteristics of a laser beam. For the band with stable transmittance, we set the wavelength interval Δλ =20 nm, while in the band with the unstable change, we set Δλ =1 nm. In a turbulent atmosphere,we assume that during the period that atmospheric turbulence has changed once, the random phase screen ζ(x,y;t)has changed K times, where K is the relative modulation frequency of random phase screen to turbulence frequency, in this paper, the relative modulation frequency is chosen to be K =10. A kolmogorov power-law spectrum is assumed, and the propagation paths involved in this paper are all horizontal paths. Every calculated point in the following figures is the statistic average result of 300 simulation realizations.
3.1. Beam spreading effect
The beam spreading of the SC laser is different from that of a monochromatic partially (spatial) coherent laser. In this part, we study the characteristics of beam spreading of SC laser source propagation in turbulent atmosphere,and discuss the differences in beam spreading between SC laser source and their pump laser source.
The effective beam radius in a particular z plane can be written as[24]

where I(x,y,z)=|E(x,y,z)|2is the total intensity distribution,(xc,yc)is the position coordinate of the beam centroid,and ρ is the distance far from the beam centroid at plane z.

Fig.3. Variations of effective beam radius with propagation distance of SC laser sources and pump laser sources for different source correlation lengths.

Fig.4. Variations of relative beam spreading versus propagation distance of SC laser sources and pump laser sources for different source correlation lengths.
In some sense,relative beam spreading is an appropriate parameter to reflect to what extent a beam is affected by atmospheric turbulence. We divide the effective beam radius in turbulence wtby the effective beam radius in free space wfto obtain the relative beam spreading wt/wf. Figure 4 shows the curves of relative beam spreading of SC laser source to pump laser source versus propagation distance L for different source correlation lengths. It can be observed that as the source correlation length increases, relative beam spreading increases along the whole propagation path. Under the same condition of source correlation length, the relative beam spreading of the SC laser is a little lower than that of the pump laser at small value of L. As the propagation distance increases, the difference tends to be obvious. It means that the relative beam spreading of the SC laser is more insensitive to the turbulence atmosphere than that of the pump laser. Therefore,the optical field of the SC laser is less distorted than that of the pump laser due to turbulent effects, and SC laser sources can be utilized to improve the performance of laser engineering.

Fig.5. Curves of (a) effective beam radius and (b) relative beam spreading versus of SC laser sources and pump laser sources over 1-kmpropagation distance in turbulence.

3.2. Beam wandering effect
To the best of our knowledge, the beam wander reflects the change in spatial position with time. Turbulence scales that are much large with respect to the beam size cause the beam to tilt and thereby to deflect,resulting in beam wandering. In general,we use the variation of beam centroid position to describe the beam wandering effect,and the beam centroid can be expressed as[25]
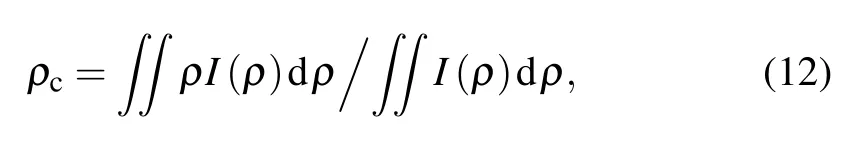
where I(ρ) is the intensity distribution. Then we can obtain the root-mean-square(RMS)value of σρof the wandering of beam centroid to be


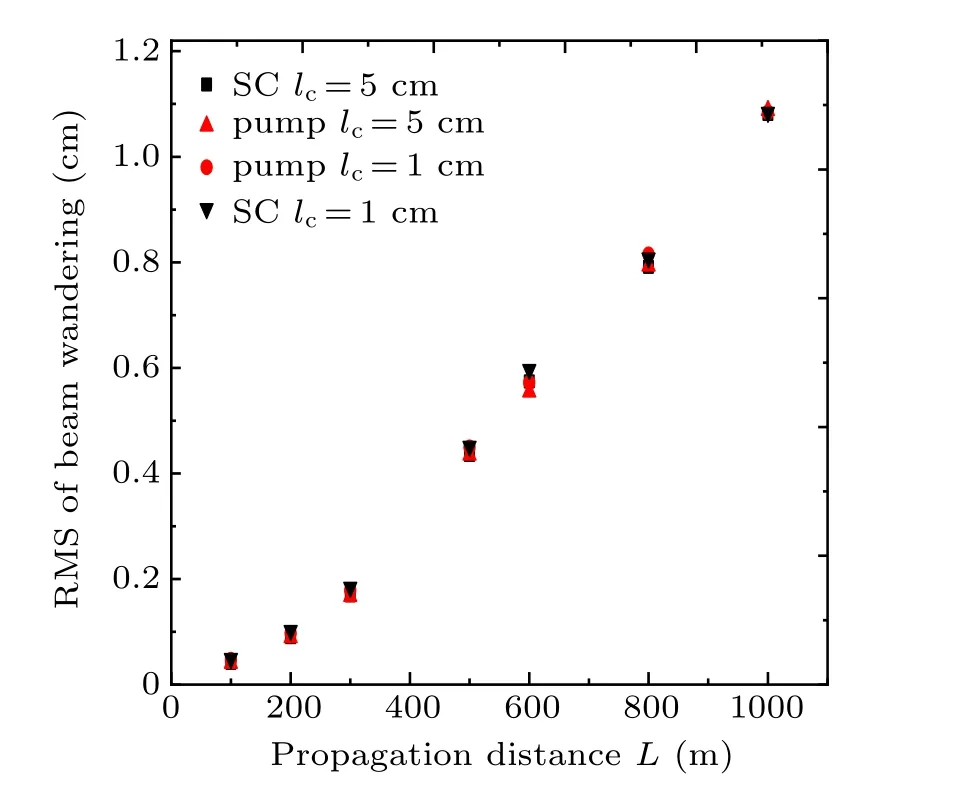
Fig.6. RMS values of beam wandering σρ versus propagation distance L of SC laser sources and pump laser sources versus propagation distance L for different cases.

Fig.7. RMS values of beam wandering σρ versus C2n of SC laser sources and pump laser sources for different cases.
3.3. Intensity scintillation effect



Fig.8. Variations of scintillation index with propagation distance L of SC laser sources and pump laser sources at off-axis distance r=4 cm.

Fig.9. Variations of scintillation indexwith turbulence strength C2n of SC laser sources and pump laser sources at off-axis distance r=4 cm.


Fig.10. Variations of(a)scintillation index and(b)aperture smoothing factor A(D)with aperture radius of receiver of SC laser sources and pump laser sources at r=0 cm.

4. Conclusions and perspectives
In this paper,we study the characteristics of beam spreading, beam wandering, and intensity scintillation of supercontinuum laser sources in turbulent atmosphere by using numerical simulation method,and analyze the difference in propagation property between the SC laser and its pump laser. The results show that the propagation characteristics of the SC laser are similar to those of the pump laser.The degradation of source coherence degree may cause the relative beam spreading and scintillation index to decrease at different propagation distances or different turbulence strengths. The beam wandering is insensitive to the variation of the degree of source coherence. Additionally,the beam wandering of the SC laser is almost the same as that of the pump laser. Therefore,from the point of view of beam wandering,the SC laser has no advantage over the pump laser. There is no need to consider the beam wandering seriously for selecting a laser source from between the SC laser and its pump laser. Unlike beam wandering,under the same condition of source correlation length,the beam spreading and intensity scintillation of the SC laser are less affected by the turbulence than those of the pump laser.This may be one of the most important properties of the SC laser which could be utilized to improve the performance of laser engineering. This property can be used to improve the signal-to-noise ratio and reduce the bit error rate of light communication.
Finally,we analyze the difference in intensity scintillation aperture averaging effect between SC laser and pump laser.It is found that under the same condition, although the pump laser can bring about a bigger aperture average, the SC laser has a lower scintillation index,which may be caused by the additional influence of the multiple wavelength homogenization effects of the SC laser.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Nonlocal advantage of quantum coherence in a dephasing channel with memory∗
- New DDSCR structure with high holding voltage for robust ESD applications∗
- Nonlinear photoncurrent in transition metal dichalcogenide with warping term under illuminating of light∗
- Modeling and analysis of car-following behavior considering backward-looking effect∗
- DFT study of solvation of Li+/Na+in fluoroethylene carbonate/vinylene carbonate/ethylene sulfite solvents for lithium/sodium-based battery∗
- Multi-layer structures including zigzag sculptured thin films for corrosion protection of AISI 304 stainless steel∗
