基于ResNet与BiLSTM的心电QRS波群检测方法
2021-03-12黄毅孙为军王丹雷伍贤美袁永浩
黄毅 孙为军 王丹雷 伍贤美 袁永浩
开发设计
基于ResNet与BiLSTM的心电QRS波群检测方法
黄毅 孙为军 王丹雷 伍贤美 袁永浩
(广东工业大学,广东 广州 510006)
为快速准确地检测出心电信号中的QRS波群,提出一种基于残差网络(ResNet)与双向长短期记忆网络(BiLSTM)的深度学习模型—ResBiLSTM,检测QRS波群的起始点和终点。实验结果表明:相比于传统的QRS波群检测方法,ResBiLSTM提高了检测效率,且具有较强的鲁棒性,能够准确检测不同形态的QRS波群。
心电信号;QRS波群;残差网络;双向长短期记忆网络
0 引言
QRS波群是心电信号最显著和最重要的特征[1],通过检测QRS波群可以获取用于诊断的生物信息,如心率和呼吸信号[2]可用于心跳分类[3]等。目前,QRS波群检测方法较多,传统的QRS波群检测方法有小波变换法[4-6]、希尔伯特变换法[7]和向量变换法[8]等。但这些检测方法存在提取特征过于依赖经验、模型参数固定和变换域计算量大等问题,导致检测算法鲁棒性差、效率低。
近年来,深度学习在计算机视觉和语音识别等领域应用广泛。卷积神经网络和循环神经网络也逐渐应用于心电信号QRS波群的特征提取和检测定位,这些神经网络可实现端到端的QRS波群检测,解决了传统检测方法模型参数固定和变换域计算量大等问题。XIANG等[9]搭建两级一维卷积神经网络模型,在MIT-BIH心率失常数据库中获得的灵敏度和阳性预测值分别为99.77%和99.91%。YUEN等[10]搭建CNN-LSTM神经网络模型,在MIT-BIH噪声压力数据库和欧洲ST-T噪声压力数据库中都取得较好的QRS波群定位结果。CAI等[11]提出2种基于多拓展卷积块的神经网络模型,在MIT-BIH心率失常数据库中获得最高灵敏度和最高阳性预测值分别是99.95%和99.97%。虽然这些深度学习模型的QRS波群定位精度较高,但没有检测QRS波群的起始点和终点,无法通过这些模型计算QRS波群宽度。而QRS波群宽度是心电图临床医学诊断的重要参数,常被用作心律失常的诊断依据。
本文提出一种基于残差网络(residual network, ResNet)与双向长短期记忆网络(bidirectional long short-term memory, BiLSTM)的心电QRS波群起始点和终点检测方法。该方法通过构建ResBiLSTM进行QRS波群的特征提取和检测,实现端到端的QRS波群检测,从而提高QRS波群的检测效率。
1 数据处理
1.1 QT数据库
QT数据库[13]共有105条15 min的双导联心电信号记录,每条心电信号记录由1个头文件、1个信号文件和9个注释文件组成,采样频率为250 Hz。其中,record.q1c注释文件对信号文件中的3623个QRS波群做了标记。MARTÍNEZ等[6]、DI MARCO等[14]、BOTE等[15]和王大雄等[16]在record.q1c文件标记QRS波群数据上做QRS波群起始点和终点的检测。record.pu0注释文件对信号文件中222026个QRS波群做了标记。本文在record.pu0文件标记QRS波群数据上做QRS波群起始点和终点的检测,并从QT数据集中选择92条心电信号记录,其中64条用来训练模型,剩下28条用来测试模型。
1.2 去噪
在心电信号QRS波群起始点和终点检测过程中,去除噪声是关键一步。如果直接将带有基线漂移、高频肌电干扰等噪声的心电信号输入ResBiLSTM模型,受这些噪声干扰的模型无法准确学习QRS波群的有效特征,从而导致模型检测QRS波群起始点和终点的准确率下降。目前,一般采用带通滤波器[17]或小波变换[18-19]去除心电信号噪声。本文采用基于带通巴特沃斯滤波器的前向后向滤波器[20]去除基线漂移和高频肌电干扰噪声。心电信号Sel30去噪前图和去噪后图分别如图1、图2所示。
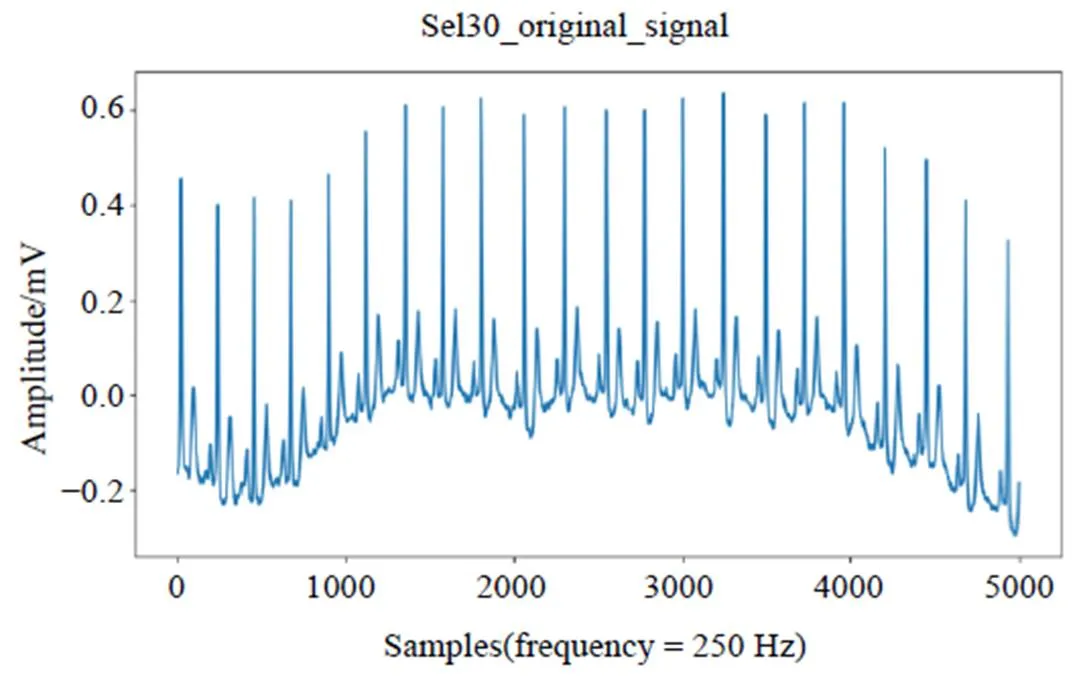
图1 sel30去噪前
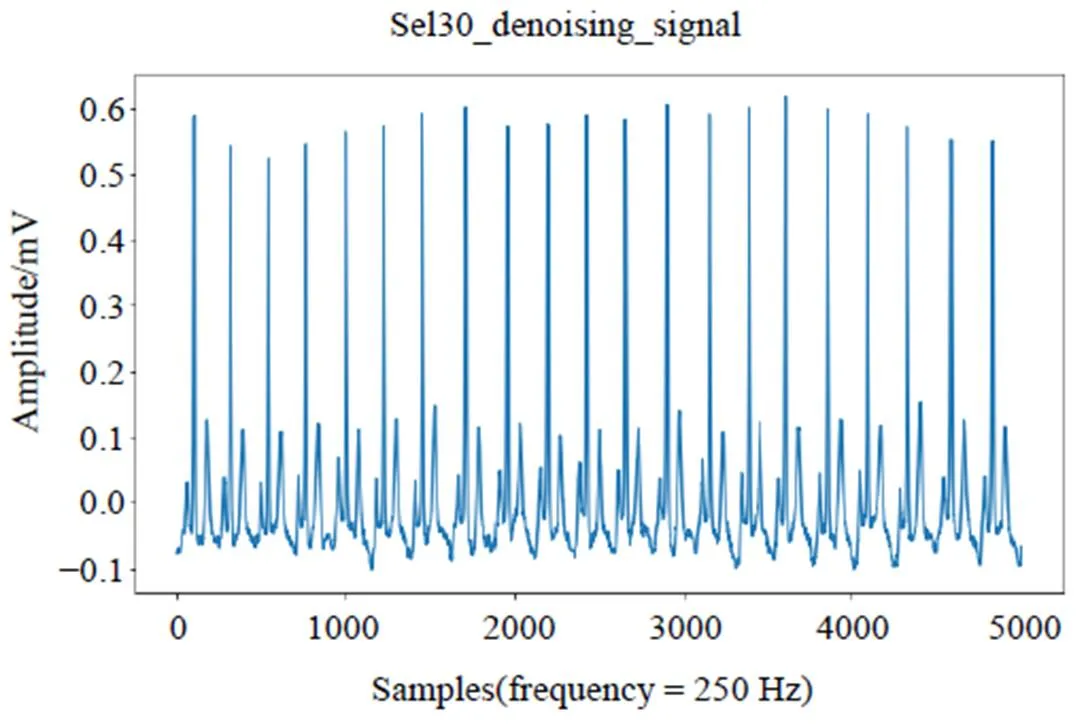
图2 Sel30去噪后
1.3 切片数据


QRS波群标签编码后,其图形是一条幅度为1的脉冲波形,脉冲波形的上升沿和下降沿位置分别对应QRS波群的起始点和终点。心电信号Sele0210的QRS波群标签编码图如图3所示。
图3 Sele0210的QRS波群标签编码
2 方法
受2015年HEK提出的ResNet[12]结构启发,本文采用一维卷积神经网络构建4层残差网络模块;再结合一维卷积层,双向长短期记忆网络和全连接层构建ResBiLSTM模型用来检测QRS波群起始点和终点,模型结构如图4所示。
ResBiLSTM模型的第一层一维卷积层有4个卷积核,卷积核大小为11×1,激活函数是LeakyReLU。4层残差网络模块里的一维卷积层有4个卷积核,卷积核大小为21×1,激活函数是LeakyReLU。BiLSTM层有128个神经元,激活函数是ReLU。全连接层有2个神经元,激活函数是Softmax。ResBiLSTM模型训练时,选择Adam作为训练优化器,设置学习率为10-3,训练60个epoch,批量数据大小为128条切片数据。


最终模型得到采样点属于QRS波群的预测概率值是一条幅度为1的脉冲波形,脉冲波形的上升沿和下降沿位置就是QRS波群起始点和终点的检测位置。
3 实验和结果分析
为验证本文提出的基于ResNet和BiLSTM的心电QRS波群起始点和终点检测方法的有效性,用测试集数据测试ResBiLSTM模型。在QRS波群起始点和终点的检测过程中,查找模型检测的QRS波群起始点和终点附近150 ms[21]内是否存在对应注释QRS波群的起始点和终点。
QRS波群基点包括起始点和终点,评估其检测方法有4个指标:敏感度()、阳性预测值()、QRS波群基点位置的平均误差()和QRS波群基点位置误差标准差()。表示所有正样本有多少被模型判为正样本;表示模型判为正的所有样本中有多少是真正的正样本;±反映QRS波群基点的位置误差数据分布。这4个指标可以通过式(3)~式(6)计算。

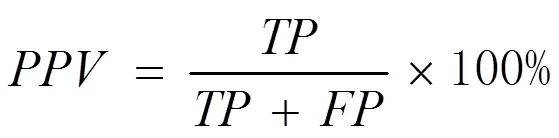
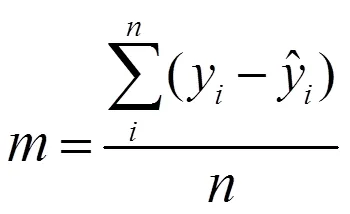
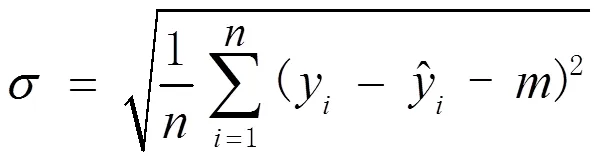
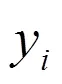
QRS波群起始点和终点检测如图5所示。图5中的(a)图、(b)图和(c)图都是由上下子图组成,其中上子图是QRS波群标签图,下子图是QRS波群检测图。

图5 (a) Sel808的正常QRS波群起始点和终点检测
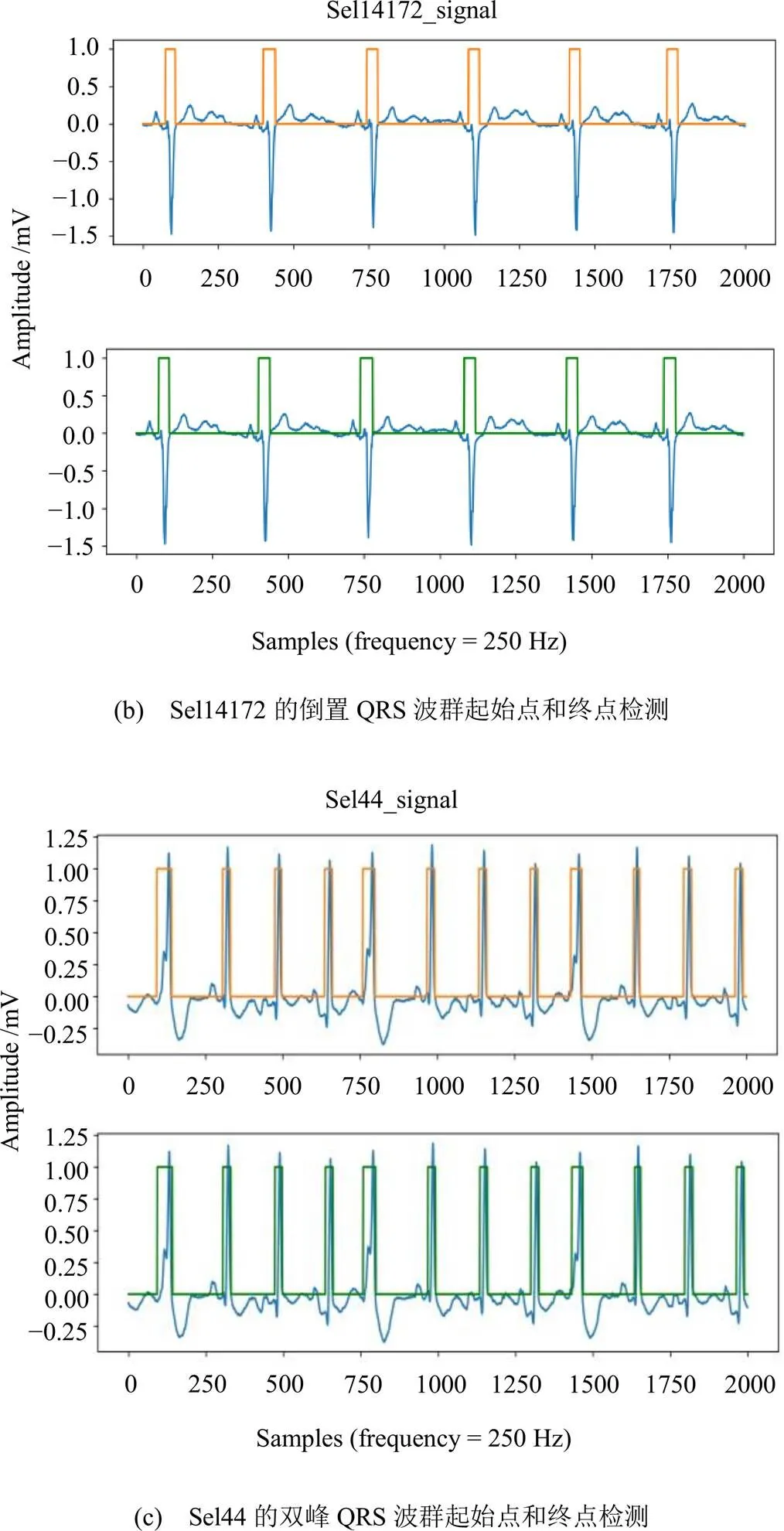
图5 QRS波群起始点和终点检测
由图5可知:本文提出方法能准确检测正常QRS波群,倒置QRS波群和双峰QRS波群。
在QT数据集上,本文提出的基于ResNet与BiLSTM的心电QRS波群起始点和终点检测方法与其他检测方法比较结果如表1所示。
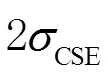
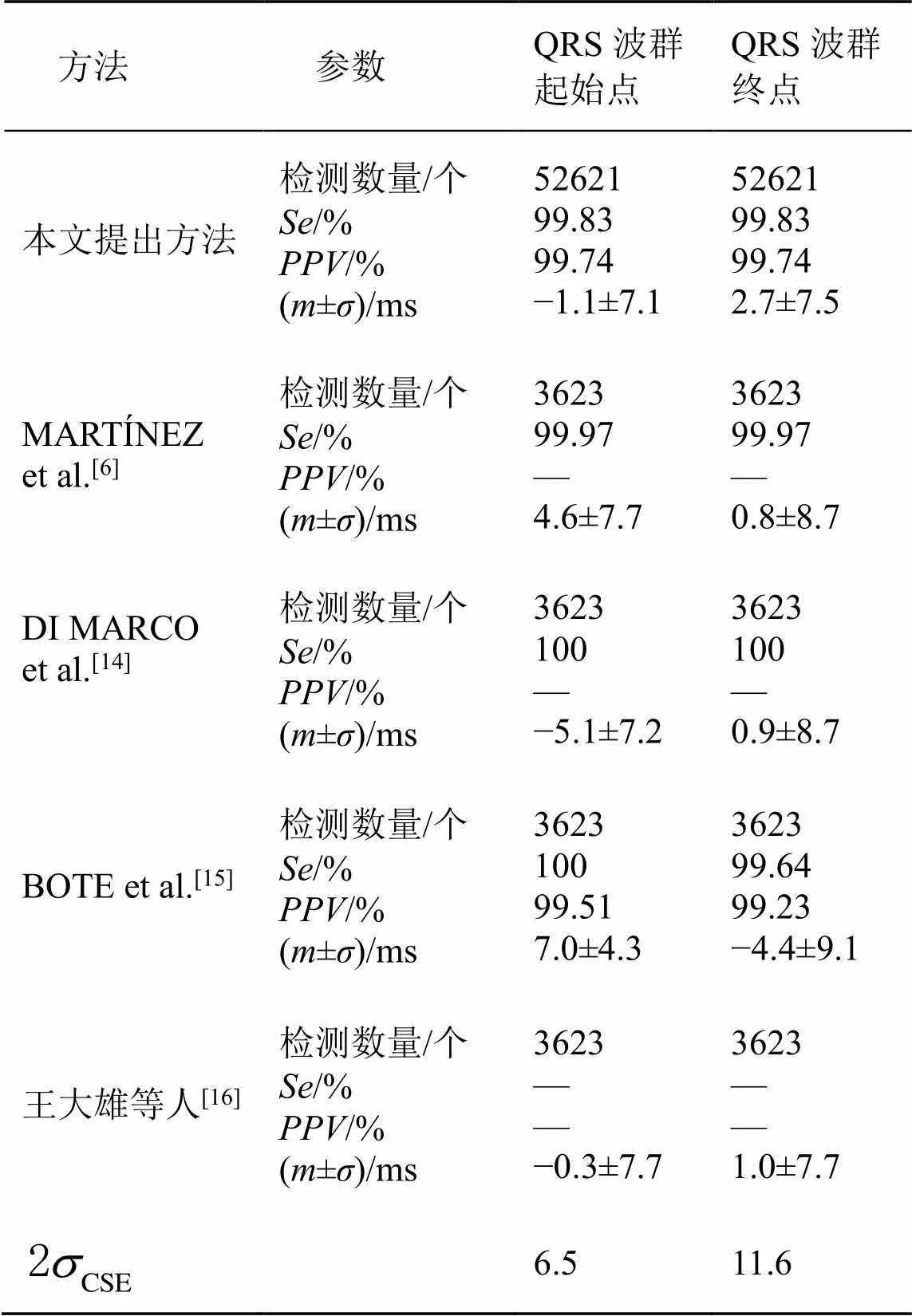
表1 不同QRS波群起始点和终点检测方法的比较结果
4 结语
本文提出一种基于ResNet与BiLSTM的心电QRS波群起始点和终点检测方法,解决了传统QRS波群检测方法存在提取特征过于依赖经验、模型参数固定和变换域计算量大等问题,具有检测效率高、鲁棒性强等特点,适用于实时的QRS波群检测。
[1] SHARMA T, SHARMA K. QRS complex detection in ECG signals using locally adaptive weighted total variation denoising[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2017,87: 187-199.
[2]LANGLEY P, BOWERS E J, MURRAY A. Principal component analysis as a tool for analyzing beat-to-beat changes in ECG features: application to ECG-derived respiration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,2010,57(4):821-829.
[3] BANERJEE S, MITRA M. Application of cross wavelet transform for ECG pattern analysis and classification[J].IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement,2014,63(2): 326-333.
[4] LI C , ZHENG C,TAI C. Detection of ECG characteristic points using wavelet transforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 1995, 42(1):21-28.
[5] SAHAMBI J S, TANDON S N, BHATT R K P. Using wavelet transforms for ECG characterization. An on-line digital signal processing system[J]. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine, 1997, 16(1):77-83.
[6] MARTÍNEZ J P, ALMEIDA R, OLMOS S, et al. A wavelet-based ECG delineator: evaluation on standard databases[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2004, 51(4): 570-581.
[7] BENITEZ D, GAYDECKI P A, ZAIDI A, et al. The use of the Hilbert transform in ECG signal analysis[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2001, 31(5): 399-406.
[8] MARTINEZ A, ALCARAZ R, RIETA J J. Automatic electrocardiogram delineator based on the phasor transform of single lead recordings[C]//2010 Computing in Cardiology. IEEE, 2010: 987-990.
[9] XIANG Y , LIN Z , MENG J . Automatic QRS complex detection using two-level convolutional neural network[J]. Biomedical Engineering Online, 2018, 17(1):13.
[10] YUEN B, DONG X, LU T. Inter-patient CNN-LSTM for QRS complex detection in noisy ECG signals[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 169359-169370.
[11] CAI W , HU D . QRS complex detection using novel deep learning neural networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2020 (99):1-1.
[12] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2016: 770-778.
[13] LAGUNA P, MARK R G, GOLDBERG A, et al. A database for evaluation of algorithms for measurement of QT and other waveform intervals in the ECG[C]//Computers in cardiology 1997. IEEE, 1997: 673-676.
[14] DI MARCO L Y, CHIARI L. A wavelet-based ECG delineation algorithm for 32-bit integer online processing[J]. Biomedical Engineering Online, 2011, 10(1): 23.
[15] BOTE J M, RECAS J, RINCÓN F, et al. A modular low-complexity ECG delineation algorithm for real-time embedded systems[J]. IEEE journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2018, 22(2): 429-441.
[16] 王大雄,蒋云良,徐耕,等.基于LS估计检测QRS波群宽度[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2010,29(3):321-325.
[17] PAN J, TOMPKINS W J. A real-time QRS detection algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 1985,32(3): 230-236.
[18] KADAMBE S, MURRAY R, BOUDREAUX-BARTELS G F. Wavelet transform-based QRS complex detector[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 1999, 46(7): 838-848.
[19] ELHANINE M, ABDELMOUNIM E, HADDADI R, et al. Electrocardiogram signal denoising using descrete wavelet transform[C]// 2014 International Conference on Multimedia Computing and Systems(ICMCS).IEEE, 2014.
[20] GUSTAFSSON F. Determining the initial states in forward-backward filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1996, 44(4): 988-992.
[21] Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation. Testing and reporting performance results of cardiac rhythm and ST segment measurement algorithms[R]. ANSI/AAMI EC38, 1998, 1998.
[22] CSE Working Party. Recommendations for measurement standards in quantitative electrocardiography[J]. European Heart Journal, 1985, 6(10): 815-825.
QRS Complexes Detection Method of Electrocardiogram Signal Based on ResNet and BiLSTM
Huang Yi Sun Weijun Wang Danlei Wu Xianmei Yuan Yonghao
(Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, China)
In order to detect QRS complexes quickly and accurately, a deep learning model based on residual network (ResNet) and bidirectional long short-term memory network (BiLSTM) is proposed and the model is ResBiLSTM. The ResBiLSTM can detect the start and end points of QRS complexes. The experimental results show that compared with the traditional QRS complexes detection methods, ResBiLSTM not only improves the detection efficiency, but also has strong robustness ,which can accurately detect different forms of QRS complexes.
electrocardiogram; QRS complexes; residual network; bidirectional long short-term memory
TN911.7; TP183
A
1674-2605(2021)01-0005-06
10.3969/j.issn.1674-2605.2021.01.005
黄毅,男,1993年生,硕士研究生,主要研究方向:深度学习,模式识别,生物信号处理。E-mail:1216621782@qq.com
