具有双参数扰动的Holling II捕食-食饵模型分析
2021-03-05魏宁,李梅
魏 宁,李 梅
具有双参数扰动的Holling II捕食-食饵模型分析
*魏 宁,李 梅
(南京财经大学应用数学学院,江苏,南京 210023)
针对一类具有双参数扰动的Holling II随机捕食-食饵模型的一些动力学性质问题,利用随机微分方程的一些基本理论和不等式技巧,证明了该系统的正解的存在性和唯一性,随机最终有界性,一致Hölder连续性和随机持久性,并给出了该系统灭绝的充分性条件。最后,通过数值模拟直观表现种群在双参数扰动下的数量变化,并与理论结果一致。
双参数扰动; 捕食-食饵模型; 随机最终有界; 随机持久性; 灭绝
0 引言
种群间的相互作用关系是生态学中重要的现象之一,其中捕食与食饵之间的关系是生态学界和生物数学界研究的一个重要课题,近年来,对捕食-食饵模型的动力学行为的研究受到了广泛关注[1-5]。然而,在生态系统中,种群不可避免地会受到环境噪声的干扰,从而导致模型系统中涉及的出生率、死亡率等其他参数或多或少地出现随机波动的现象。因此,为了使模型更贴近实际,许多学者用随机扰动来表示环境波动对种群的影响,并引入到确定性模型中。Mao和Sabais[6]研究了一类经典Lotka–Volterra随机互惠模型,考虑了环境噪声对种内和种间相互作用系数的影响; Li X[7],Li M[8]和刘思润等[9]针对不同的种群模型,探究了环境噪声对种群增长率的影响。文献[10]考虑了环境波动对内禀增长率和死亡率的影响,提到了下列带有随机扰动项的Holling II捕食者-食饵模型:



进而建立了下列带有双参数扰动的随机模型:


1 存在唯一性和随机最终有界性
系统的全局正解的存在唯一性对研究种群模型长时间的动力学行为具有重要作用,本节首先证明模型(2)具有唯一的全局正解,从而可进一步分析其他的渐进性质。

系统解的有界性表示种群系统的合理性,接下来,本节证明了模型(2)的解是随机最终有界的。

利用Young’s不等式:

因此,
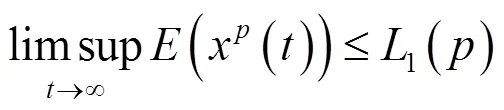
同理可得:


2 一致Hölder连续性和随机持久性
在种群动力学系统中,探究种群系统的一致Hölder连续性和随机持久性对农业、林业、自然资源和珍稀动物的保护,利用和管理具有重要意义, 是研究种群动力学行为的重要课题之一。因此,本节先后讨论了模型(2)的正解的一致Hölder连续性和随机持久性。
证明:式(2)的第一个方程可以转换为下面的随机积分方程:

由定理2,式(3)和离散Hölder不等式[13],可得:
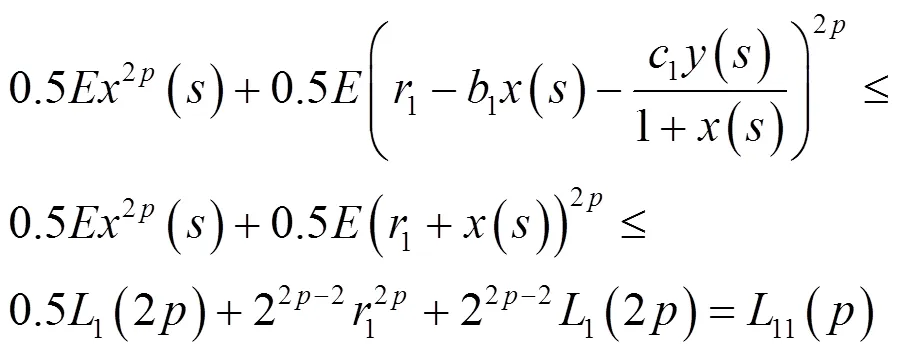
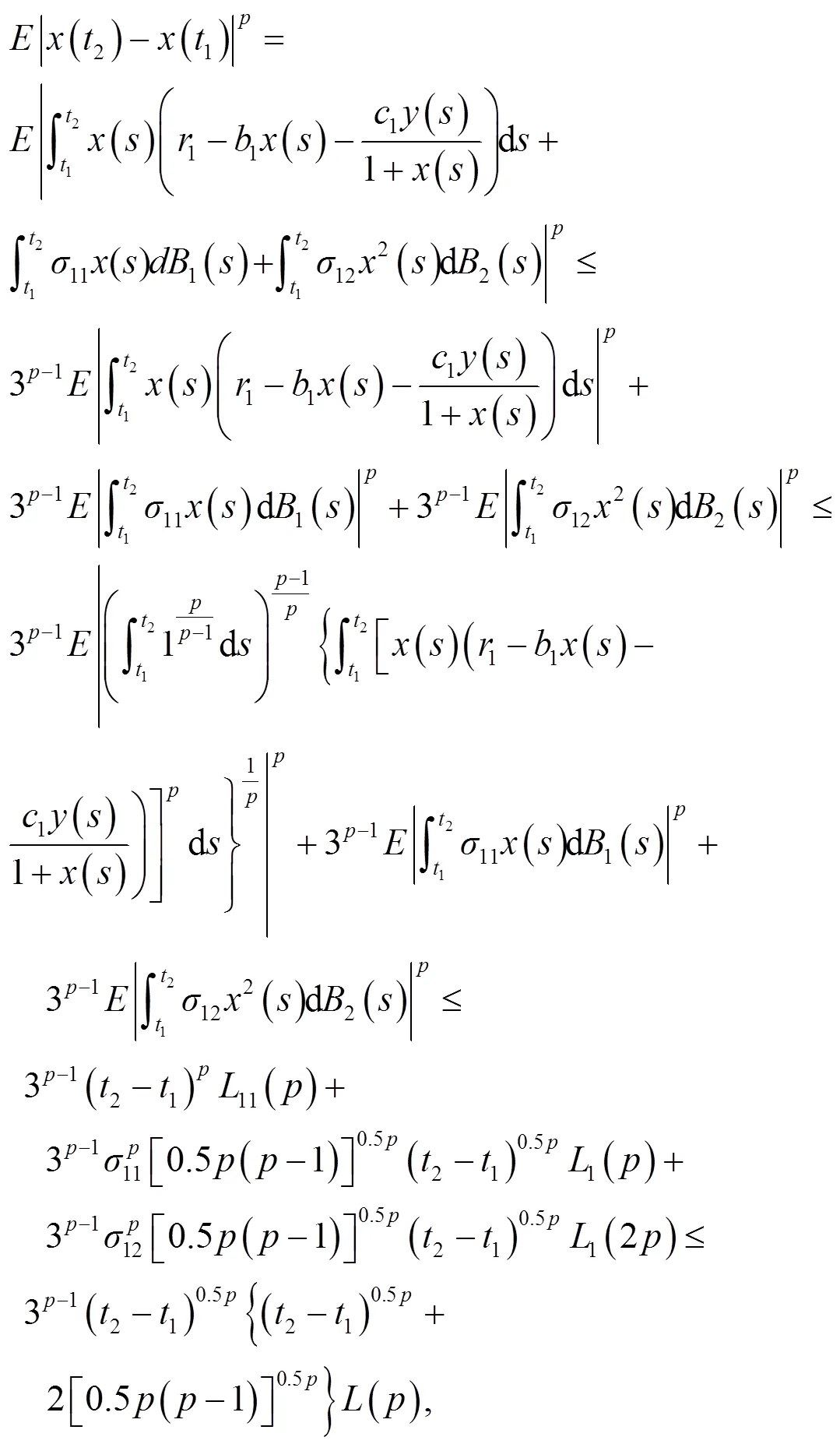
定理4模型(2)是随机持久的。

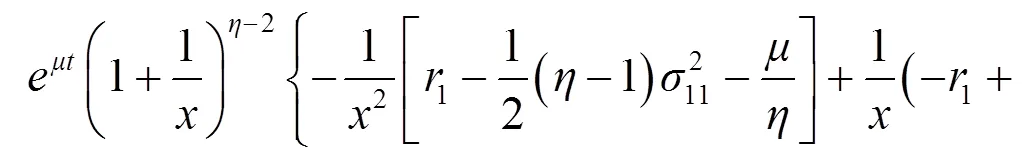
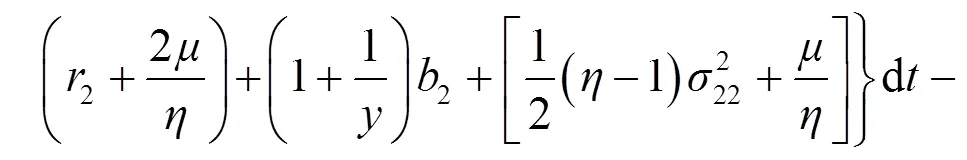

其中

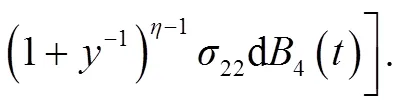
因此
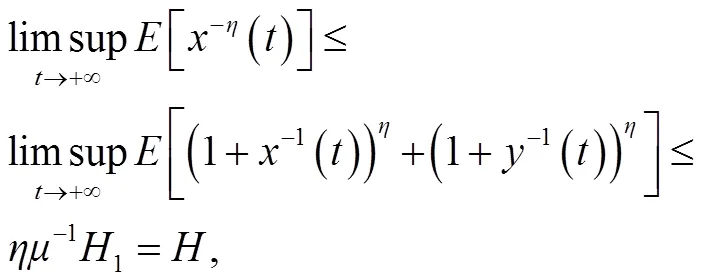
同理可得:

则
那么,
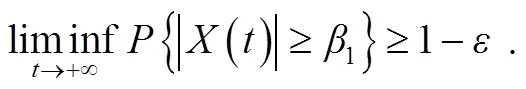
,
由随机持久性的定义[13]即可得证本定理成立。
3 种群灭绝的条件
本节给出模型(2)中种群灭绝的充分性条件。
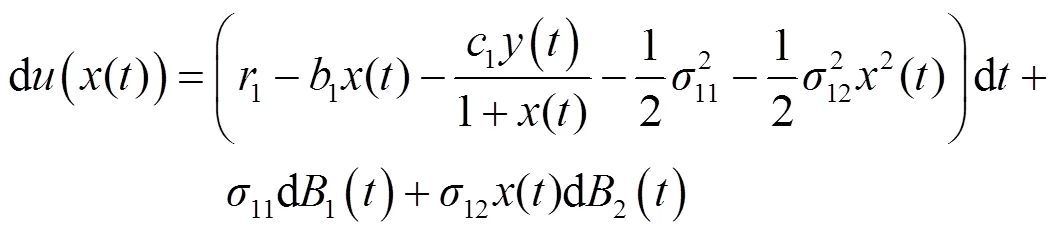


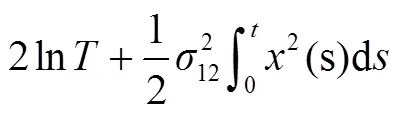
将式(7)代入式(6)可得:


4 数值模拟


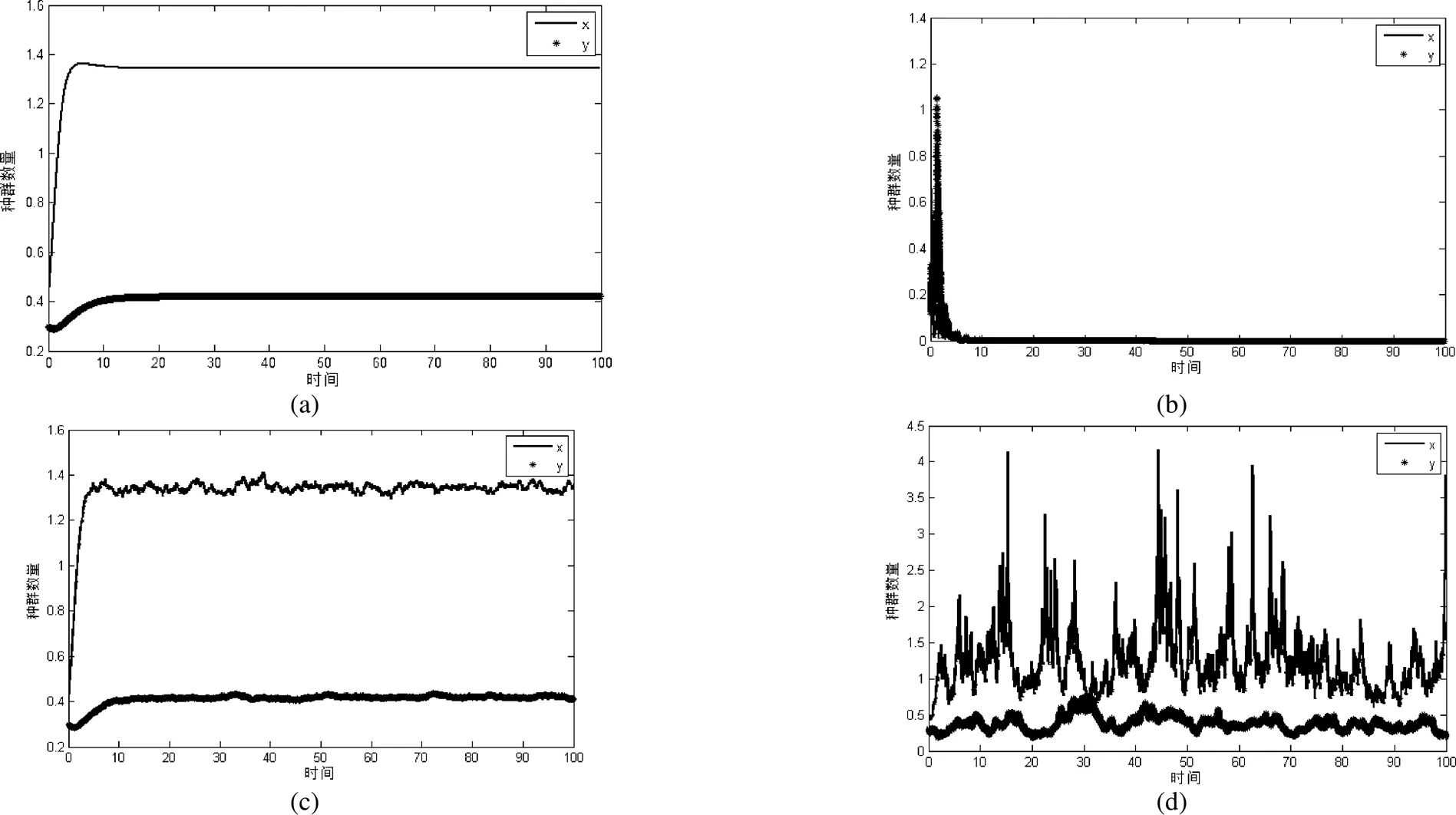
图1 种群的数量变化
[1] Yang J, Tang S. Holling type II predator-prey model with nonlinear pulse as state-dependent feedback control [J]. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2016, 291(1): 225-241.
[2] Raw S N, Mishra P, Kumar R, et al. Complex behavior of prey-predator system exhibiting group defense: A mathematical modeling study [J]. Chaos Solitons & Fractals, 2017, 100: 74-90.
[3] Zhang B, Wang H, Lv G. Exponential extinction of a stochastic predator-prey model with Allee effect [J]. Physica A Statal Mechanics & Its Applications, 2018, 507: 192-204.
[4] Chen M X, Wu R C, Liu B, et al.Pattern selection in a predator-prey model with Michaelis-Menten type nonlinear predator harvesting[J]. Ecological Complexity, 2018, 36: 239-249.
[5] Liu Q, Jiang D, Hayat T, et al. Stationary distribution of a regime-switching predator-prey model with anti-predator behaviour and higher-order perturbations [J]. Physica A: Statal Mechanics and its Applications, 2019, 515: 199-210.
[6] Mao X, Sabais S, Renshaw E. Asymptotic behavior of stochastic Lotka-Volterra model [J]. J. Math. Anal, 2003, 287: 141-156.
[7] Li X, Jiang D, Mao X. Population dynamical behavior of Lotka-Volterra system under regime switching [J]. Journal of Computational & Applied Mathematics,2009,232(2): 427-448.
[8] Li M, Gao J H, Sun C F, et al. Analysis of A Mutualism Model with Stochastic Perturbations [J]. Int. J. Biomath, 2015(8): Article ID 1550072
[9] 刘思润,吕敬亮.一类随机互惠模型的渐进性质[J]. 黑龙江大学自然科学学报, 2016, 33(2): 162-169.
[10] Liu Q, Zu L, Jiang D. Dynamics of stochastic predator- prey models with Holling II functional response [J]. Communications in Nonlinear ence & Numerical Simulation, 2016, 37(1): 62-76.
[11] Liu Q, Jiang D, Shi N, et al. Stochastic mutualism model with Lévy jumps [J]. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat, 2017, 43(1): 78-90.
[12] Friedman A. Stochastic Differential Equations and Their Applications [M]. New York: Academic Press, 1976: 98-125.
[13] Mao X. Stochastic Differential Equations and Applications [M]. Chichester : Horwood Publishing Limited,1997.
[14] Luo J W, Li M, Liu K, et al. Analysis of a mutualism model with time-related coefficients in a stochastic environment [J]. International Journal of Biomathematics, 2020, 11(3): 1-20.
[15] Karatzas I, Shreve S E. Brownian Motion and Stochastic Calculus [M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1991: 53-55.
[16] 赵爱民, 赵晓丹, 刘桂荣. 一类随机互惠种群模型的渐近行为[J]. 山西大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 42(02): 6-11.
[17] Higham D J. An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations [J], SIAM Rev, 2001, 43(3): 525-546.
ANALYSIS OF HOLLING II PREDATOR-PREY MODEL WITH TWO PARAMETERS PERTURBATION
*WEI Ning, LI Mei
(School of Applied Mathematics, Nanjing University of Finance & Economics, Nanjing, Jiangsu 210023, China)
In terms of some dynamics properties questions of Holling II stochastic predator-prey model with two parameters perturbation, through some theories of stochastic differential equations and inequalities, the existence and uniqueness of the positive solution, stochastically ultimate boundedness, uniformly Hölder-continuous and stochastic permanence of the system were proved. Moreover, the sufficient conditions for the system to be extinct were given. Finally, the quantitative change of the population under two parameters perturbation was showed, which was consistent with the theoretical results.
two parameters perturbation; predator-prey model; stochastically ultimate boundedness; stochastic permanence; extinction
O175.13/O29
A
10.3969/j.issn.1674-8085.2021.01.001
1674-8085(2021)01-0001-06
2020-09-25;
2020-11-03
国家自然科学基金项目(11601225)
*魏 宁(1997-),女,河南安阳人,硕士生,主要从事生物数学研究(E-mail: wn1097128722@163.com);
李 梅(1966-),女,江苏兴化人,教授,博士,主要从事生物数学研究(E-mail: 9120021078@nufe.edu.cn).
