一种并行加速改进的快速相位解包裹算法
2021-01-08饶长辉高国庆周璐春
龙 潇,鲍 华,饶长辉,高国庆,周璐春
一种并行加速改进的快速相位解包裹算法
龙 潇1,2,3,鲍 华1,2*,饶长辉1,2,高国庆1,2,周璐春1,2
1中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室,四川 成都 610209;2中国科学院光电技术研究所,四川 成都 610209;3中国科学院大学,北京 100049
针对Miguel等人提出的质量图引导相位解包裹算法中串行运算效率较低的缺点,构造了一种多个低可靠度区块并行合并的改进算法。在满足原始算法设计思想的前提下,对解包裹路径进行重新定义,并根据原始算法的解包裹路径非连续的特性,构建了一种低可靠度区块乱序合并的策略,使得多个低可靠度区块的合并任务可以同时进行。改进算法采用多线程软件架构,主线程负责循环遍历未处理的区块,子线程接收待处理的区块执行合并任务。实验结果表明,改进方法与原始算法的处理结果完全一致,而并行改进策略可有效利用计算机多核资源,使得相位解包裹算法的运行效率提高了50%以上。
相位解包裹;质量引导;路径相关;并行计算;相位测量

1 引 言
在相位测量技术中,直接获取的相位通常为被折叠进[-p,p)区间的包裹相位图,当相位的变化范围超过2p时会出现跳变,形成条纹图案[1]。将包裹相位恢复为连续相位的相位展开技术作为相位测量中不可缺少的关键技术,已广泛应用于自适应光学[2]、散斑干涉成像[3]、核磁共振成像[4]、光栅条纹投影测量[5]以及干涉合成孔径雷达[6]等多个领域。
近年来国内外科研工作者针对解包裹算法做出了大量研究,已经提出了许多相位展开算法。这些算法主要可以分为两类[7]:1) 最小范数算法,2) 路径跟踪算法。
最小范数算法是一种全局算法,将解包裹转化为对全图的目标函数求最小值的过程[8],当目标函数使用1范数时,称为最小费用流算法[9];当目标函数使用2范数时,称为最小二乘算法[10],对二维相位解包裹通常使用最小二乘算法。全局算法通常计算量较大,因此出现了对图像分区域并行计算再对处理后的区域进行展开的方法[11],是计算速度与鲁棒性的折衷。
路径跟踪算法的思想是选择合适的解包路径,避免受噪声影响大的区域产生的误差随着路径不断传递。路径的选择主要分为枝切法[6]、最小不连续算法[12]和质量图引导法[13],枝切法寻找包裹图像中会出现解包错误的残差点并形成枝切线,在最后单独进行解包。枝切法计算速度较快,但枝切线出现封闭环时无法正确解包裹。最小不连续算法将差异大于p的相邻像素称为一个不连续,在整个包裹相位中循环搜索不连续区域并展开,使图像的不连续最小,循环搜索使最小不连续算法执行效率较低。质量引导路径算法生成描述相位质量高低的质量图作为引导,优先对高质量像素点解包,使低质量区域产生的误差不会被传播,因此具有较好的抗噪性能。
质量引导路径算法中,Miguel等人[14]提出的快速相位解包裹算法高效准确且具有较强的抗噪鲁棒性,但其串行的计算方式效率较低,对于如自适应光学、干涉法测量等实时性强的任务需要进一步提速。针对上述问题,本文对Miguel等人提出的解包裹算法进行改进,提出了一种低可靠度区块乱序并行合并的策略,改进算法与原始算法的处理结果完全一致,而解包裹算法的运行效率得到了显著提升。
2 原始相位解包裹算法原理
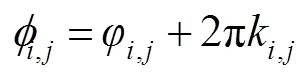
式中:为整数,对于的矩阵有,。
质量导引路径算法的关键在于找到包裹相位图中的平缓区域。将解包路径设置在高可靠度像素之间,避免算法在噪声较大和相位阶跃处进行解包从而导致解包产生误差并传播至图像其他区域。


其中:

定义像素的可靠度为

则可靠度值越大表示像素越可靠。
定义、为水平、竖直方向上两相邻像素间的连接(称为边),则边的可靠度为
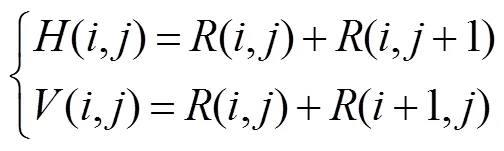
初始化每个像素自成一组,对水平和竖直两方向全部边按照可靠度排序。Miguel算法的相位展开路径从可靠度最大边开始以降序遍历所有边,每条边的解包规则为:若边连接的两像素属于同一组则顺序执行下一边;若边连接的两像素属于不同组,计算它们间的2p跳变大小,像素数少的组内所有像素点均加减该跳变值,使此边连接的两像素间大于p的差异被消去,此后像素数少的组整体并入像素数多的组,并继续顺序执行下一边。
Miguel算法以串行的方式严格按照可靠度降序处理所有边,即使下一边与当前边的所属组不包含重复的像素点,也需要将已完成的处理结果作为下一边的处理方式的判断依据,这种设计方法使算法的执行效率较低。
3 多线程并行改进方法
Miguel算法的核心思想是以最大可靠度的公共边作为两个相邻组的解包路径,当相邻组合并为一组后,它们原有的其他公共边便不再执行,避免了对低可靠度边进行合并,从而降低解包误差。分析Miguel算法的执行流程可知,原始算法为串行运算,运行中同时最多只有一条边解包,在处理高分辨率包裹相位时存在耗时较长的问题,对实时性要求较高的任务,需要对此算法进行并行加速。另一方面,Miguel算法在解包过程中存在大量的逻辑分支判断,不适用于GPU协处理器加速,因此本文选择多核CPU硬件平台,采用多线程任务协同的程序设计方法,使用主线程进行任务分发和逻辑判断,子线程执行合并任务的并行模式。
本文改进算法的思想如图2所示,在图2(a)所示的4´4包裹图像中,所有边已按照可靠度排序为1至24。Miguel算法需要24次合并操作顺序执行,如图2(a)所示,其中绿色边为有效合并边,白色边表示相邻像素已属于同一组,数字代表合并时的循环次数;而本文的改进策略是并行执行低可靠度边中互不影响的合并任务,如图2(b)所示,相同颜色的边代表在一个循环内完成判断与合并,其中数字代表合并时的循环次数,仅有颜色的边表示相邻像素已属于同一组。改进后合并操作减少为15次,并且每次循环可同时执行多个合并任务,仅需要6次循环即可完成。
根据Miguel算法的合并规则可知,对串行算法中的有效执行边乱序执行,解包裹结果不变,仅存在因基准点不同而整体差异整数个2p,若对解包裹结果进行减均值处理则可得到相同结果。改进相位解包裹算法的关键在于主线程找到有效执行边中互不影响、可同时执行解包的边,并交由多子线程同时完成合并。

图2 改进算法的目的。(a) 顺序执行合并操作; (b)并行执行合并操作

图3 并行改进算法流程图

图4 邻域模型示意图
Miguel算法从高可靠度到低可靠度的执行顺序使组与组之间通过最大可靠度的公共边进行合并,若改变执行顺序,则执行边一定为两相邻组中至少一组的最大可靠度边。根据此规律,本文提出的并行化流程图如图3所示,主线程循环遍历未处理边,检查其所属的两个组,若其中一组在本循环中首次出现,则此边为该组的最大可靠度边,属于有效执行边,具体策略如下:对每个组增加一个“空闲/执行/等待”标志,空闲状态表示该组在此轮循环中可以与非执行态的组发起合并任务;执行状态表示该组已进入任务队列,将在子线程内执行完成后置为等待态;等待状态表示该组等待空闲态的组发起合并任务,主线程按可靠度从大到小循环遍历每一条边,并根据此标志判断任务是否分发。
主线程的遍历规则为:
1) 两点属于同一组,丢弃此边;
2) 两个组都空闲,将这两组的标志设为执行,分发此边;
3) 组1等待,组2空闲,将这两组的标志设为执行,分发此边;
4) 组1执行,组2空闲,将组2设为等待,跳过此边;
5) 组1执行,组2执行或等待,跳过此边;
6) 两个组都等待,跳过此边;
7) 主线程进入下一循环时,处于“等待”态的组变为“空闲”态。
本文将组看成宏观意义上的点,组与组之间的有效边为公共边中可靠度最大的一条边,则包裹图像可由如图4中所示的三种邻域模型进行描述,其中4条边按照可靠度排序为1至4。邻域模型中每个像素亦可表示一个邻域模型。
以图4中的三种邻域模型为例,解包顺序如图5所示。
第一种模型,如图4(a):第一次循环,边1执行,边2跳过,边3执行,边4跳过;第二次循环,边2执行,边4跳过;第三次循环边4成为内部边。执行顺序为(1,3)→(2)。
第二种模型,如图4(b):第一次循环,边1执行,边2、3、4跳过;第二次循环,边2执行,边3、4跳过。第三次循环,边3执行,边4跳过;第四次循环边4成为内部边。执行顺序(1)→(2)→(3)。
第三种模型,如图4(c):第一次循环,边1、2执行,边3、4跳过;第二次循环,边3执行,边4跳过;第三次循环边4成为内部边。执行顺序(1,2)→(3)。
4 算法仿真
为检验本文提出的低可靠度区块乱序合并策略的有效性,实验使用标准C++进行编程实现。实验环境为Windows 10,Qt5.13.2,编译器MSVC2017 64 bit,处理器Intel Core i5-8250U,8 GB RAM。
实验数据采用两幅包裹图像进行算法验证。原始连续相位图为随机系数的前36阶泽尼克组合像差和前105阶泽尼克组合像差,叠加噪声为均值为0,标准差0.5的高斯白噪声,图像分辨率为1024´1024,有效数据为圆域孔径。
图6(a)为前36阶泽尼克组合像差,经过叠加高斯白噪声与相位折叠得到图6(b)的包裹图像。图6(c)为原算法解包裹结果,图6(d)为改进算法解包裹结果,两者面形完全一致。

图5 邻域模型的解包流程示意图
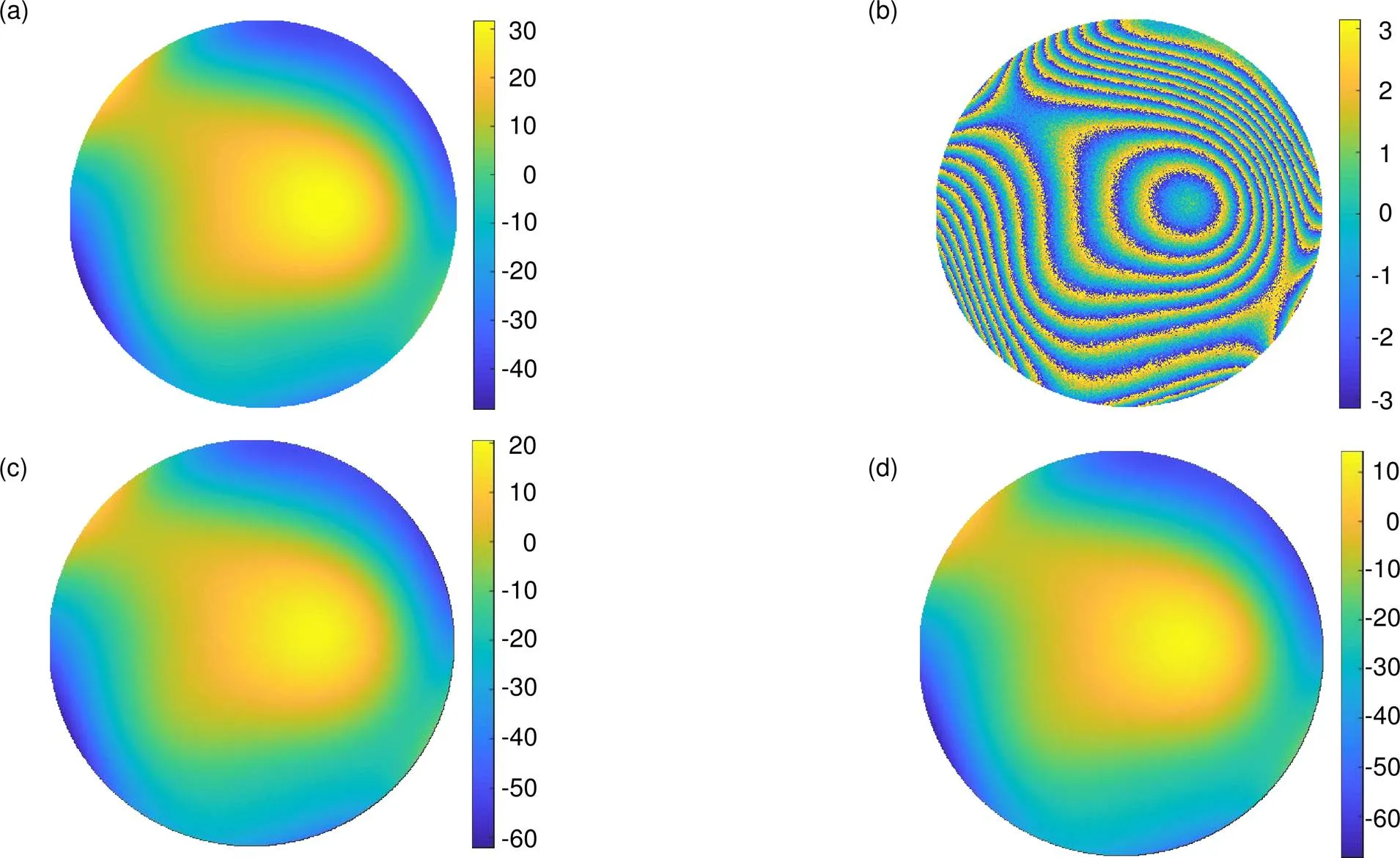
图6 对低阶像差解包效果。(a) 组合像差;(b) 包裹图像;(c) 原算法解包裹结果;(d) 改进算法解包裹结果

图7 对高阶像差解包效果。(a) 组合像差;(b) 包裹图像;(c) 原算法解包裹结果;(d) 改进算法解包裹结果

图8 解包裹过程中的分组示意图。(a) 原算法;(b) 改进算法
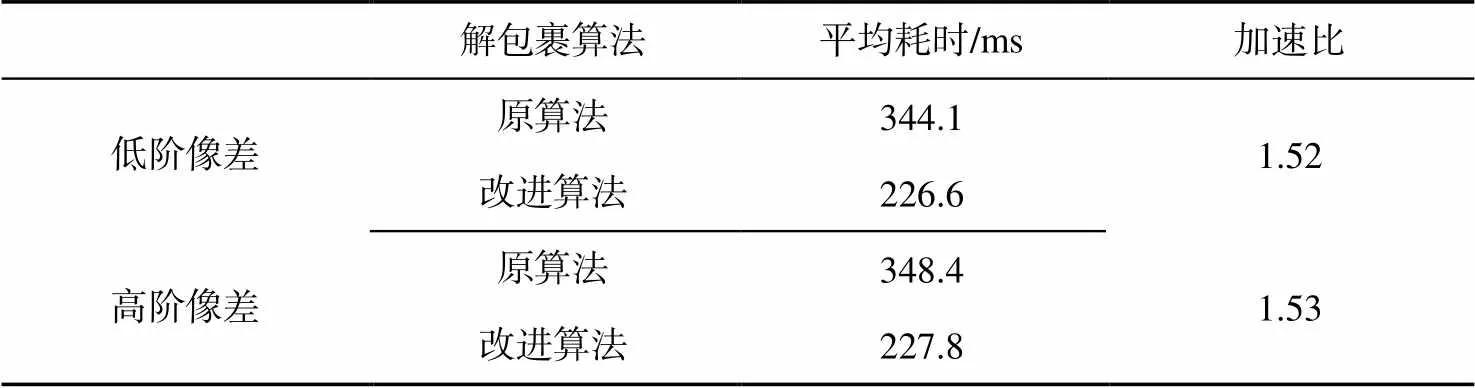
表1 两种算法的耗时比较
图7(a)为前105阶泽尼克组合像差,经过叠加高斯白噪声与相位折叠得到图7(b)的包裹图像。图7(c)为原算法解包裹结果,图7(d)为改进算法解包裹结果,两者面形完全一致。
本文对两种1024´1024分辨率的组合像差进行20次实验,统计原方法和改进算法的执行时间。两种方法的对比如表1所示。
分析改进算法和原始算法的执行过程,以不同颜色代表像素所属的不同组,截取两种方法在解包裹过程中的分组图,可以看出原算法趋向于一个组吞并周围的点,而改进算法适当提前了可靠度较低的边的执行顺序,均匀地使每个像素点与邻近的像素合并成组,从而达到了并行加速的目的。
实验最后分析了在不同大小的包裹相位下,改进算法与原算法的平均耗时比较,比较结果如图9所示。
在不同的包裹图像中,改进算法均达到了提速的效果,但与改进算法的理论加速存在一定差距。分析其原因有两点:一是在算法后期,可同时执行的边太少,算法退化为串行算法;二是前期小区块间的合并造成后续合并任务的运算量增大,降低了计算效率。通过大量仿真实验,结合本文实验平台CPU调度开销,本文提出的算法的最优线程数为4。
5 结 论
本文针对Miguel等人提出的相位解包裹算法,提出了一种基于低可靠度区块乱序合并的改进策略,使之可以并行计算。改进算法与原算法进行对比,仿真实验表明,改进算法达到了降低原算法耗时并且不影响解包裹结果的目的,证实了改进策略正确有效。目前改进算法的加速比与计算机的核心数存在一定差距,是否可以进一步提高并行化效率或利用空余计算能力提高算法精度,是下一步研究工作的重点。
[1] Fornaro G, Franceschetti G, Lanari R,. Robust phase-unwrapping techniques: a comparison[J]., 1996, 13(12): 2355–2366.
[2] Bao H, Rao C H, Tian Y,. Research progress on adaptive optical image post reconstruction[J]., 2018, 45(3): 170730. 鲍华, 饶长辉, 田雨, 等. 自适应光学图像事后重建技术研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2018, 45(3): 170730.
[3] Wu S J, Yang J, Pan S Y,. Dynamic deformation measurement of discontinuous surfaces using digital speckle pattern interferometry and spatiotemporal three-dimensional phase unwrapping[J]., 2018, 47(2): 0212002. 吴思进, 杨靖, 潘思阳, 等. 数字散斑干涉术和时空三维相位解包裹用于非连续表面动态变形测量[J]. 光子学报, 2018, 47(2): 0212002.
[4] Chavez S, Xiang Q S, An L. Understanding phase maps in MRI: a new cutline phase unwrapping method[J]., 2002, 21(8): 966–977.
[5] Yuan H X, Li J L, Luo P,. Image restoration for blurred fringes of rail profile 3D online measurement based on PMP[J]., 2017, 44(7): 695‒700. 袁宏翔, 李金龙, 罗鹏, 等. 基于PMP的钢轨三维形貌在线测量模糊条纹复原[J]. 光电工程, 2017, 44(7): 695–700.
[6] Goldstein R M, Zebker H A, Werner C L. Satellite radar interferometry: two-dimensional phase unwrapping[J]., 1988, 23(4): 713–720.
[7] Wang Y H, Chen W J, Zhong S M,. Research progress in phase unwrapping technology and its applications[J]., 2018, 37(12): 1–7, 16. 王永红, 陈维杰, 钟诗民, 等. 相位解包裹技术及应用研究进展[J]. 测控技术, 2018, 37(12): 1–7, 16.
[8] Qian XF, Zhang Y A, Li X Y,. Phase unwrapping algorithm based on mask and least-squares iteration[J]., 2010, 30(2): 440–444. 钱晓凡, 张永安, 李新宇, 等. 基于掩膜和最小二乘迭代的相位解包裹方法[J]. 光学学报, 2010, 30(2): 440–444.
[9] Costantini M. A novel phase unwrapping method based on network programming[J]., 1998, 36(3): 813–821.
[10] Guo Y, Chen X T, Zhang T. Robust phase unwrapping algorithm based on least squares[J]., 2014, 63: 25–29.
[11] Huang K M, Yamada T. Phase unwrapping by regions using least-squares approach[J]., 1998, 37(11): 2965–2970.
[12] Flynn T J. Two-dimensional phase unwrapping with minimum weighted discontinuity[J]., 1997, 14(10): 2692–2701.
[13] Xu W, Cumming I. A region-growing algorithm for InSAR phase unwrapping[J]., 1999, 37(1): 124–134.
[14] Herráez M A, Burton D R, Lalor M J,. Fast two-dimensional phase-unwrapping algorithm based on sorting by reliability following a noncontinuous path[J]., 2002, 41(35): 7437–7444.
Improved fast phase unwrapping algorithm based on parallel acceleration
Long Xiao1,2,3, Bao Hua1,2*, Rao Changhui1,2, Gao Guoqing1,2, Zhou Luchun1,2
1Key Laboratory of Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, Sichuan 610209, China;2Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, Sichuan 610209, China;3University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China

(a) Group diagram of original algorithm; (b) Group diagram of parallel algorithm
Overview:In the phase measurement technology, the phase directly obtained is usually folded into a range of wavelengths, so that the phase pattern appears as a stripe pattern. Generally, this stripe pattern is not the final result required for phase measurement. There is a phase unwrapping operation needed to obtain a continuous phase map.
The main problem facing by the phase unwrapping algorithms is how to balance the robustness and the computational efficiency. At present, there have been a lot of researches on unwrapping algorithms. They are mainly divided into two categories, including the minimum norm method and the path tracking method. The minimum norm algorithm is a global algorithm that transforms the process of phase expansion into a process of minimizing an objective function of the full graph. In the least norm method, the least squares algorithm is a commonly used unwrapping algorithm for two-dimensional phase wrapping images. Because global algorithms usually need a large amount of calculations, they require high computing power. The idea of the path tracking algorithm is to choose a suitable path for expansion, so as to avoid that the areas affected by noise appear prematurely in the path and cause errors and continue to be transmitted along the path. Quality map guidance algorithm is a common type of path tracking algorithm. This algorithm first generates a quality map describing the impact of noise. The quality map guides the unwrapping path through high-quality areas, so that the errors generated in low-quality areas will not be propagated. Thus, quality map guidance algorithm has good noise immunity.
The quality map-guided unwrapping algorithm proposed by Miguel needs a small amount of calculations and has strong noise immunity, but its serial calculation method has low operating efficiency. To solve this problem, an improved algorithm for parallel merging of multiple low-reliability blocks is proposed. Under the condition that the original algorithm design idea is satisfied, the unwrapping path is redefined as the largest reliable edge of the block. In addition, based on the non-continuous characteristic of the unwrapping path of the original algorithm, a low-reliability block out-of-order merging strategy is proposed to make multiple merging tasks can be performed simultaneously. The improved algorithm uses a multi-threaded software architecture. The main thread is responsible for looping through the unprocessed blocks to check whether they meet the requirements of merging, and the child threads receive and perform the merge tasks. The experimental results show that the improved method is completely consistent with the processing results of the original algorithm, and the parallel improvement strategy can effectively use the computer's multi-core resources, so that the operational efficiency of the phase unwrapping algorithm is improved by more than 50%.
Citation: Long X, Bao H, Rao C H,. Improved fast phase unwrapping algorithm based on parallel acceleration[J]., 2020,47(12): 200111
* E-mail: hbao@ioe.ac.cn
Improved fast phase unwrapping algorithm based on parallel acceleration
Long Xiao1,2,3, Bao Hua1,2*, Rao Changhui1,2, Gao Guoqing1,2, Zhou Luchun1,2
1Key Laboratory of Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, Sichuan 610209, China;2Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, Sichuan 610209, China;3University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Aiming at the shortcoming of low serial operational efficiency in the quality-map-guided phase-unwrapping algorithm proposed by Miguel, an improved algorithm for parallel merging of multiple low-reliability blocks is proposed. Under the condition that the original algorithm design idea is satisfied, the unwrapping path is redefined as the largest reliable edge of the block. In addition, based on the non-continuous characteristic of the unwrapping path of the original algorithm, a low-reliability block out-of-order merging strategy is proposed to make multiple merging tasks can be performed simultaneously. The improved algorithm uses a multi-threaded software architecture. The main thread is responsible for looping through the unprocessed blocks to check whether they meet the requirements of merging, and the child threads receive and perform the merge tasks. The experimental results show that the improved method is completely consistent with the processing results of the original algorithm, and the parallel improvement strategy can effectively use the computer's multi-core resources, so that the operational efficiency of the phase unwrapping algorithm is improved by more than 50%.
phase unwrapping; quality guidance; path dependent; parallel computing; phase measurement
National Natural Science Foundation of China (11727805)
10.12086/oee.2020.200111
TP391;TN29
A
龙潇,鲍华,饶长辉,等. 一种并行加速改进的快速相位解包裹算法[J]. 光电工程,2020,47(12): 200111
: Long X, Bao H, Rao C H,Improved fast phase unwrapping algorithm based on parallel acceleration[J]., 2020, 47(12): 200111
2020-04-02;
2020-05-27
国家自然科学基金资助项目(11727805)
龙潇(1994-),男,硕士,主要从事相位差波前测量技术的研究。E-mail:836868760@qq.com
鲍华(1981-),男,博士,副研究员,主要研究自适应光学图像事后处理及相位差法波前探测。E-mail:hbao@ioe.ac.cn
