Mechanism of therapeutic effects of Huangbo on ureteral stones based on network pharmacology
2021-01-04WenXiaoYuNingSunFangYuanXiaoHuaPei
Wen-Xiao Yu, Ning Sun, Fang Yuan, Xiao-Hua Pei
1.Beijing First Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Department of Urology, Beijing 100026 2.Beijing First Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Beijing 100026
3.Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100026, China
Keywords:Network pharmacology Huangbo Ureteral stones Mechanism
ABSTRACT Objective: To analyze the effective chemical components and action targets of Phellodendron chinense, and to study the mechanism of Phellodendron chinense in treating ureteral stones. Methods: Search the potential chemical active substances of Phellodendron chinense and target proteins acting on the human body through the TCMSP database, and use the genomic annotation database platform (Genecards) to predict the target of ureteral stones, and use the uniprot database Query the corresponding gene names, build a network diagram of "drugdisease-target" with the help of Cytoscape (3.7.2) software, build a protein interaction network through the String database platform, and then use the Bioconductor platform and R language GO Enrichment analysis and KEGG enrichment analysis. Results: Through screening, a total of 36 effective chemical constituents of Phellodendron chinense, 8 key chemical constituents related to ureteral calculi, and 20 common targets of Phellodendron-ureteral calculi were obtained. The core genes of PPI were FOS, CXCL8, IL6, SERPINE1, VEGFA, EGF, NOS3, SPP1, CCL2, CCND1, EGFR, HMOX1, IL10, CDKN1A, CRP; obtained 36 GO biological processes, and 14 KEGG related signaling pathways, including HIF-1 signaling pathway, FoxO signaling pathway , EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance, endocrine resistance, viral protein interaction with cytokines and cytokine receptors, calcium signaling pathway, p53 signaling pathway, ErbB signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, Ras signaling pathway. Conclusion: Phellodendron can achieve the effect of treating ureteral calculi through multiple targets and multiple ways, which provides a theoretical basis for the future extraction of effective components to treat ureteral calculi.
1. Introduction
Ureteral stones are a very common clinical urinary stones, the main symptoms are pain and hematuria. Modern medicine believes that urine factors, urinary system, individual reasons are related to the external environment. A large number of basic studies have confirmed that hypercalcemia is the main risk factor for the formation of ureteral stones. When the content of calcium, oxalic acid, uric acid and other substances in the urine caused by hypercalcemia leads to supersaturation of the urine, it provides for the formation of stones The environment; secondly, urinary tract infections, obstructions and other factors have also become the cause of ureteral calculi; anatomically, three ureteral stenosis often become places where stones stay [1-4]. Modern medicine treatment of ureteral calculi mainly includes the use of tramadol drugs to relieve pain, scopolamine and other drugs to relieve ureteral flat muscle spasm, and diuretics and other drugs to promote the discharge of stones [5-7]. In recent years, the above-mentioned methods have been rarely used, and the clinical method is more impact treatment, but this method has obvious contraindications, such as acute urinary tract infections, pregnant women and distal urinary tract infections, and other patients are forbidden to use, and pain may occur 1. Consequences of increased hematuria [8,9].
Chinese medicine believes that the occurrence of ureteral stones is mainly due to the accumulation of spicy and fat products in the body, resulting in dampness and heat stagnation. Its pathogenesis is mainly blamed on the kidney, kidney deficiency, gasification, or long-term dampness and heat. Stone blocks the urinary tract [10-12]. As stated in "The Theory of Diseases and Diseases": "Gonorrhea is a disease, the kidney is weak and the bladder is hot. The kidney qi is ventilated to the yin, yin, and water flows down. The bladder is the body of the fluid, the kidney is the number of urine, the bladder Heat is astringent under the water, counts and astringent, and the astringency is not pronounced, so it is said to be drenched, its appearance is more and less urine, the lower abdomen string is urgent, the pain is caused by the umbilical cord. , Injecting the bladder with heat and humidity, which leads to unfavorable gasification of the bladder, so bladder irritation appears. The method of clearing away heat and dampness is often used clinically to play a role in diuresis and diarrhoea. A large number of drugs such as cork, Shiwei, and psyllium are used to clear scorching dampness and heat, and the effect is quite good [13-15]. In clinical practice, the prescriptions of the Huangbai formula, such as Zhibai Nioshao Pai Pai Decoction, are widely used in clinic, and satisfactory results have been obtained. There are many chemical constituents in Phellodendron amurense, and there are few studies on its active ingredients and molecular mechanisms. This study is based on network pharmacology to study the effective chemical constituents and targets of Phellodendron amurensis in the treatment of ureteral calculi, with a view to exploring the mechanism of Phellodendron aureides in treating ureteral calculi.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Screening of key chemical components of Phellodendron chinense
Retrieve all the active ingredients of Phellodendron chinense through TCMSP, http://lsp.nwu.edu.cn/index.php, collect 140 compounds in total, and then take oral bioavailability (OB) 30%, drug similarity (DL)≥ 0.18 to screen the pharmacokinetics of the compound, where OB refers to the relative amount and rate of drug absorption into the blood circulation after oral administration; DL reflects the specific function of the compound The similarity between the group and the known drugs is of great significance to the evaluation of the activity of traditional Chinese medicine chemical components.
2.2 Screening the target of Phellodendron-ureteral stones
Use TCMSP database to search for target information of key chemical components of Phellodendron chinense, and query the human gene name corresponding to the target through uniprot database (https://www.uniprot.org/), and then through Genecards database (https: // www.genecards.org/), OMIM database (https://www.omim.org/) screened protein target genes of ureteral calculi to map to get drug-disease target genes.
2.3 Network visualization of drugs-key chemical components-disease targets
In order to study the mechanism of Phellodendron in the treatment of ureteral stones, this study imported the common chemical components and common protein target genes of Phellodendronureteral stones into Cytoscape 3.7.2 software for visual processing. The form is presented. In this network diagram, key compounds and targets are represented by nodes, and the interaction between nodes is represented by edges.
2.4 PPI network construction
PPI is a network of interactions between proteins. Import the common target genes of Phellodendron and ureteral stones into the String database (https://string-db.org/Version 10.5), select the research species as human (Homo sapiens), get the protein interaction network, and set the protein relationship score It is 0.4 and hides the free protein that appears. The blue line represents the evidence of gene co-evolution, the red line represents the evidence of gene fusion, and the yellow line represents the evidence of text mining. Download the PPI protein interaction diagram and filter the top 15 The core gene of the PPI network.
2.5 GO (gene ontology) enrichment analysis and KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) enrichment analysis
Use the Bioconductor database (http://bioconductor.org/bioc Lite.R) to query the gene ID of a drug-disease target gene Use R language to install the relevant installation package of Bioconductor platform, set pvalue = 0.05, qvalue = 0.05 to perform GO enrichment analysis and KEGG enrichment analysis, output the results and draw barplot histogram.
3. Results
3.1 Screening of chemical constituents in Phellodendron amurense
A total of 140 effective chemical constituents of Coptis chinensis were obtained through the TCMSP database, and then screened by OB ≥30% and DL≥ 0.18 criteria to obtain 36 key compounds of Phellodendron chinense, see Table 1 for details.

Table 1 Effective chemical components of Phellodendron amurense after screening
3.2 Drug-disease target prediction
Query the target information of effective compounds of Phellodendron chinense through TCMSP database, and annotate gene ID through Uniprot. Search the target genes of ureteral stones through Genecards and OMIM database, enter "Ureteral stones", get a total of 207 genes with a correlation score greater than 5, map the target genes of Phellodendron and ureteral stones, and get the common Phellodendron-ureteral stones There are 20 targets in total, and a venn diagram is drawn through R language (see Figure 1).
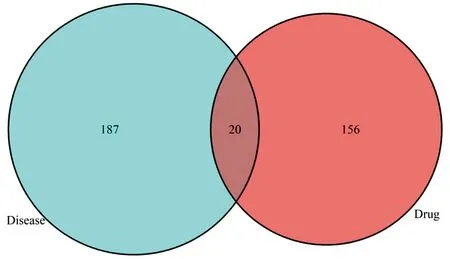
Figure 1: Huangbai-ureteral stones target gene matching
3.3 Construction of drug-key chemical components-disease network
The Cytoscape 3.7.2 software was used to visualize the drugkey compound-disease-target gene network, which recorded the key compounds of Phellodendron corresponding to the common target, and finally obtained a total of 8 key chemical components of Phellodendron-ureteral stones, which were the original Opioid, hydrogenated berberine, quercetin, stigmasterol, dehydrotanshinone II A, β-sitosterol, isocogenine, carvedine. The common target genes of Phellodendron-ureteral stones are CHRM3, CHRM4, ADRA1A, ADRA1D, EGFR, VEGFA, CCND1, FOS, CDKN1A, IL10, EGF, IL6, HMOX1, CCL2, CXCL8, NOS3, SERPINE1, CRP, SPP1, IGF2 . (Figure 2).

Figure2: Huangbai Drugs-Key Chemical Components and Target Networks for ureteral stones Action
3.4 PPI protein interaction network analysis
The 20 target genes shared by Phellodendron and ureteral stones were imported into the String database platform to study the species selection of humans, obtain protein interaction relationships, screen protein relationships with scores> 0.4, and draw a network diagram of protein interaction relationships (Figure 3). The network includes 20 nodes and 110 edges, and the interaction proteins with scores ≥0.98 are EGFR-EGF, CDKN1A-CCND1, IL10-IL6, IL10-CXCL8, IL10-CCL2, VEGFA-NOS3, VEGFA-EGF, IL6- CXCL8, VEGFA-SERPINE1, IL6-FOS, IL6-CCL2, VEGFA-IGF2, CXCL8-CCL2. The interaction between these proteins is very important in the network. By calculating the number of connection nodes of each gene, the first 15 PPI core genes are found, which are FOS, CXCL8, IL6, SERPINE1, VEGFA, EGF, NOS3, SPP1, CCL2 , CCND1, EGFR, HMOX1, IL10, CDKN1A, CRP. These are the core genes of Phellodendron in the treatment of ureteral stones. As shown in Figure 3, Figure 4.
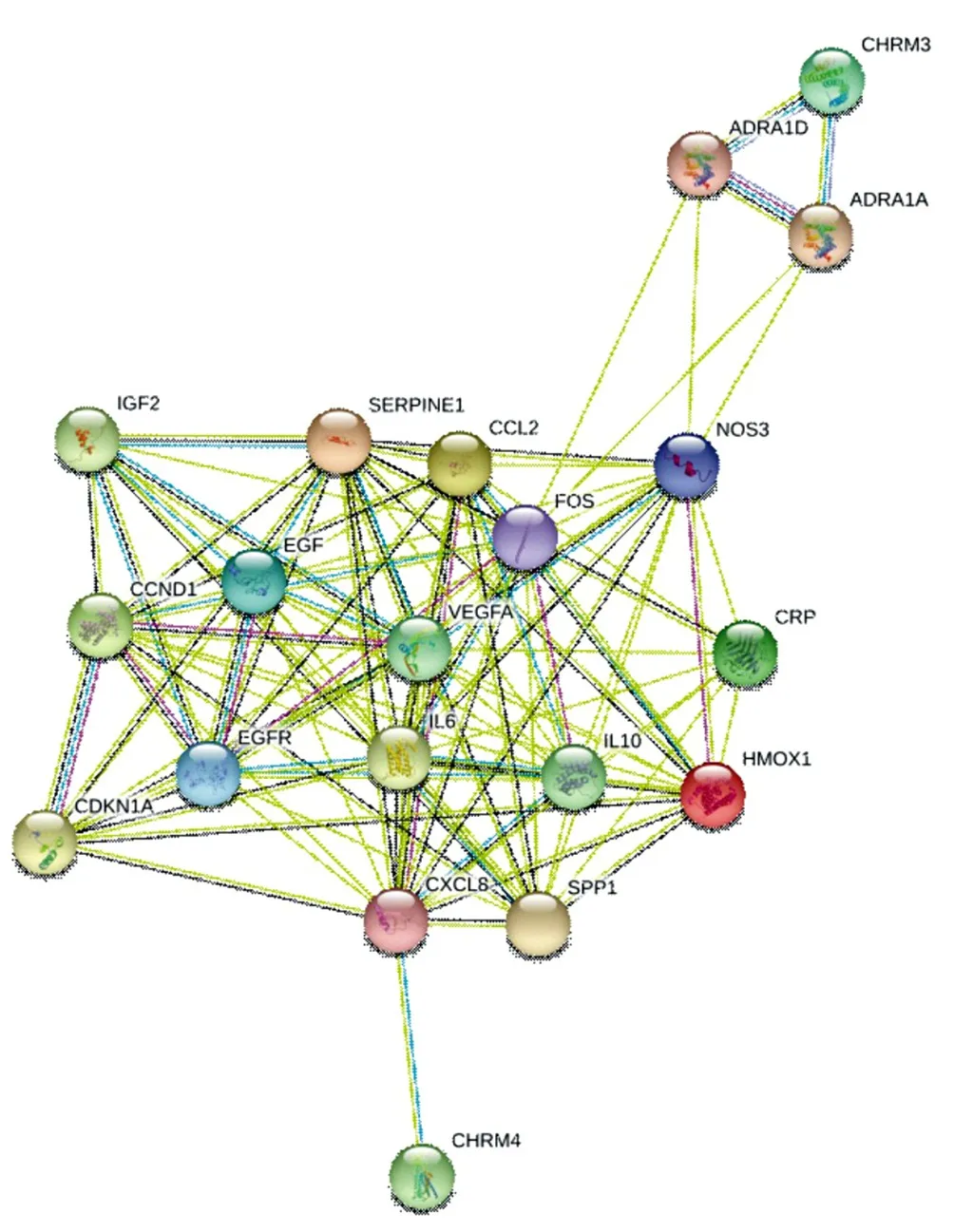
Figure3: PPI protein interaction network
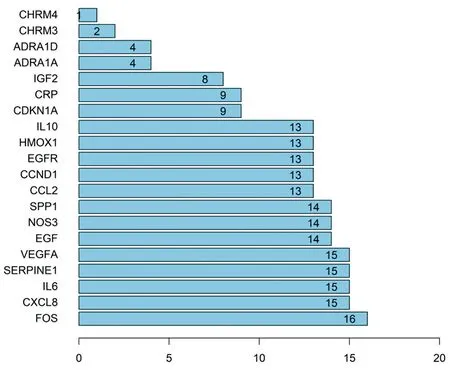
Figure4: PPI core genes
3.5 GO function enrichment analysis
GO enrichment analysis results showed that a total of 36 GO biological processes were obtained, and the top biological functions mainly include receptor ligand activity (8 targets VEGFA / IL10 / EGF / IL6 / CCL2 / CXCL8 / SPP1 / IGF2) , Cytokine activity (6 targets VEGFA / IL10 / IL6 / CCL2 / CXCL8 / SPP1), G proteincoupled amine receptor activity (4 targets CHRM3 / CHRM4 / ADRA1A / ADRA1D), growth factor activity (5 Target VEGFA / IL10 / EGF / IL6 / IGF2), cytokine receptor binding (5 target VEGFA / IL10 / IL6 / CCL2 / CXCL8), growth factor receptor binding (4 target VEGFA / IL10 / EGF / IL6), protein kinase modulator activity (4 targets CCND1 / CDKN1A / EGF / IGF2), kinase modulation activity (4 targets CCND1 / CDKN1A / EGF / IGF2), protein kinase activator activity (3 targets CDKN1A / EGF / IGF2), kinase activator activity (3 targets CDKN1A / EGF / IGF2). As shown in Figure 5. It shows that Phellodendron may play a role in treating ureteral calculi through various biological regulation processes.
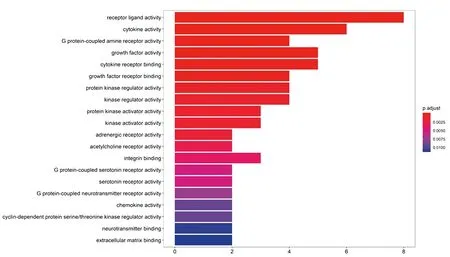
Figure5: Enrichment analysis of huangbai-ureteral stones key target by GO biological process
3.6 KEGG pathway enrichment analysis
KEGG pathway enrichment analysis results show that Phellodendron chinense has 14 key gene target pathways for the treatment of ureteral stones. The main pathways involve HIF-1 signaling pathway, FoxO signaling pathway, EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance, and endocrine Resistance, interaction of viral proteins with cytokines and cytokine receptors, calcium signaling pathway, p53 signaling pathway, ErbB signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, Ras signaling pathway. As shown in Figure 6.

Figure6: Enrichment analysis of KEGG metabolic pathway for huangbaiureteral stones key target
4. Discussion
Phellodendron is a class of dicotyledonous plants, Rutaceae, and is the dry bark of the yellow bark tree. It is mainly produced in Sichuan, Yungui and other places. It has a bitter taste and coldness, and it returns to the kidney and bladder channels. Effect. "Clinical Handbook of Commonly Used Traditional Chinese Medicines" records: "Huangbai bitter cold settlement, clearing heat and dampness, strong fire detoxification, return to the kidney, bladder meridian, longer than clearing scorched damp heat." Ureteral stones are not clearly recorded in ancient Chinese medicine, and their diagnosis and treatment are based on Chinese medicine "Shilin", in the treatment of Shilin, most medical practitioners use cork for compatibility, and the effect is quite good [16-18].
The results of this study show that key compounds in Phellodendron amurense can affect the occurrence and development of ureteral stones through multiple target genes and signaling pathways. In this study, eight key chemical constituents of Phellodendron chinense for ureteral calculi were retrieved, including pro-opiodine, hydrogenated berberine, quercetin, stigmasterol, dehydrotanshinone II A, β-sitosterol, and isocopa Alkaline, Carvedine. Pro-opioids are also known as dianthramycin and corydine. They are insoluble in water and have analgesic, antispasmodic, antiasthmatic, and cough suppressing properties. In the treatment of ureteral calculi, proopioids exert their antispasmodic, The effect of relaxing smooth muscles is also anti-arrhythmic, anti-platelet aggregation, improving microvascular circulation and anti-tumor. In its application, proopioids are often used as antibacterial agents, smooth muscle relaxants, choleretic drugs and sedatives [ 19,20]. Quercetin is a flavonoid compound widely distributed in nature. Various compounds contain quercetin. Related literature indicates that quercetin can reduce the tension of intestinal and bronchial smooth muscles, thereby exerting antispasmodic effects; Studies on the mechanism of drug analgesia indicate that quercetin has a certain inhibitory effect on neuropathic pain, and the analgesic effect on pain caused by local inflammation is related to the blocking of pro-inflammatory factors [21,22]. Stigmasterol is a typical representative of phytosterols, which account for a large proportion in the extraction of various plants and vegetable oils. Foreign studies have indicated that stigmasterol can inhibit the degradation of various inflammatory mediators and matrices, it can stimulate the proliferation of the reticuloendothelial system and strengthen The ability of macrophages to play an antiinflammatory role, this function is particularly important in the treatment of ureteral stones [23]. β-sitosterol is also one of the phytosterols, which has cholesterol lowering, cough suppressing, expectorant and tumor suppressing functions, and has the function of repairing tissues. It is widely used in hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis and chronic bronchus The treatment of inflammation [24]. Isocopaine is also present in the poppy shell, which has the analgesic effect and smooth muscle relaxation of the poppy shell [25]. In this study, through the PPI protein interaction analysis, 15 PPI core genes were obtained, namely FOS, CXCL8, IL6, SERPINE1, VEGFA, EGF, NOS3, SPP1, CCL2, CCND1, EGFR, HMOX1, IL10, CDKN1A, CRP. These are the core genes of Phellodendron in the treatment of ureteral stones.
In order to study the role of targets in gene functions and signaling pathways, GO biological function enrichment analysis was performed in this study, and it was found that the above PPI core genes can pass receptor ligand activity, cytokine activity, G protein-coupled amine receptor activity , Growth factor activity, cytokine receptor binding, growth factor receptor binding, protein kinase modulator activity, kinase modulation activity, protein kinase activator activity, kinase activator activity and other pathways play a role in the treatment of ureteral stones. KEGG pathway enrichment analysis results showed that the main gene-enriched pathways of Phellodendron chinense for ureteral calculi involved HIF-1 signaling pathway, FoxO signaling pathway, EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance, endocrine resistance, viral proteins and cytokines and Cytokine receptor interaction, calcium signaling pathway, p53 signaling pathway, ErbB signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, Ras signaling pathway. The HIF-1 signaling pathway plays an important intermediary role in hypoxia signal transduction, and participates in the body's regulation of target genes reflected by hypoxia, thereby prompting the body to produce complex physiological and pathological responses to hypoxia stimulation [26]. The MAPK signaling pathway brings together signal transduction pathways such as cell proliferation, stress, differentiation, transformation, and apoptosis, and is involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, and canceration [27]. The p53 signaling pathway is closely related to cell cycle, abnormal cell proliferation, repairing damaged DNA, etc. [28].
In summary, this study described the relationship between the main active components and target genes of Phellodendri phellodendron and ureteral calculi through the network pharmacology method, and analyzed the complex of multi-component, multi-target and multi-pathway of Phellodendron in the treatment of ureteral calculi The mechanism of action laid the foundation for more in-depth experiments and provided a theoretical basis for the future extraction of active ingredients from Phellodendron chinense to treat ureteral stones.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Molecular mechanism of Turmeric in the treatment of liver cancer based on network pharmacology
- Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
- Therapeutic efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine compound in the treatment of membranous nephropathy: A systematic review and metaanalysis
- Correlation between CT dynamic enhanced scanning parameters and serum tumor markers before and after radiofrequency ablation in patients with lung cancer
- Effects of fumigation and washing with Shujin Huoluo decoction combined with Duhuo Parasitic decoction on TIMP-1 and PON1 levels in KOA patients
- The effect of Xuebijing on burn patients and its effect on pain and wound healing
