初诊急性心肌梗死患者血清N末端脑钠肽前体及D-二聚体水平与预后的关系研究
2020-12-23王新宙贾艳静
王新宙 贾艳静

【摘要】 目的 探討初诊急性心肌梗死患者血清N末端脑钠肽前体(NT-proBNP)及D-二聚体(D-Dimer)水平与预后的关系。方法 选取80例初诊急性心肌梗死患者作为观察组, 同时选择同期的80例体检健康者作为健康对照组。比较两组受试者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平, 观察组不同心功能分级患者、不同冠状动脉造影情况患者、是否发生心血管事件患者、死亡与存活患者的D-Dimer、NT-pro BNP水平。结果 观察组患者D-Dimer为(513.72±55.67)mg/ml、NT-proBNP为(2749.62±449.51)ng/L均高于健康对照组的(127.67±32.43)mg/ml、NT-proBNP(462.36±134.57)ng/L, 两组数据经检验均符合正态分布, 且方差齐, 差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。观察组Ⅰ级患者D-Dimer水平(512.73±11.47)mg/ml、NT-proBNP为(2217.16±317.52)ng/L, 均最低;Ⅳ级患者D-Dimer(579.31±26.42)mg/ml、NT-proBNP(2752.27±367.42)ng/L, 均最高。随着心功能分级的增加, 患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP的水平也随之增高, 差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。观察组冠状动脉单支病变患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平最低, 分别为(473.61±16.72)mg/ml、(2181.73±289.39)ng/L, 冠状动脉三支病变患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平最高, 分别为(576.65±26.57)mg/ml、(2779.32±396.43)ng/L, 随着患者患病支数增加, 患者的D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平越高, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。观察组未发生心血管事件的患者D-Dimer为(426.57±31.12)mg/ml、NT-proBNP为(2153.31±416.27)ng/L均低于发生心血管事件患者的(562.71±51.53)mg/ml、(2799.87±452.13)ng/L, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。观察组死亡患者D-Dimer为(962.71±142.61)mg/ml、NT-proBNP为(9239.21±1452.47)ng/L均高于存活患者的(502.56±97.72) mg/ml、(2353.31±506.97)ng/L, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 D-Dimer与NT-proBNP在急性心肌梗死患者的诊断中有着良性的指导作用, 随着患者疾病程度的加重, D-Dimer、NT-proBNP的水平也在随之升高, 同时患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP的水平越高, 患者的预后也就越差, 在临床中对于D-Dimer、NT-proBNP的水平应引起重视。
【关键词】 急性心肌梗死;N末端脑钠肽前体;D-二聚体;预后
DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2020.31.003
Study on the correlation between serum N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide and D-Dimer levels and prognosis in patients with newly diagnosed acute myocardial infarction WANG Xin-zhou, JIA Yan-jing. Linfen Vocational and Technical College, Linfen 041000, China
【Abstract】 Objective To discuss the correlation between serum N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and D-Dimer levels and prognosis in patients with newly diagnosed acute myocardial infarction. Methods There were 80 patients with newly diagnosed acute myocardial infarction selected as the observation group, and 80 healthy subjects during the same period as the healthy control group. Comparison was made on levels of D-Dimer and NT-proBNP between the two groups, the levels of D-Dimer and NT-proBNP in patients with different cardiac function classifications, patients with different coronary angiography conditions, patients with cardiovascular events, death and surviving patients in the observation group. Results D-Dimer (513.72±55.67) mg/ml and NT-proBNP (2759.62±449.51) ng/L of the observation group were higher than (127.67±32.43) mg/ml and (462.36±134.57) ng/L of healthy control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). In the observation group, the levels of D-Dimer and NT-proBNP in grade Ⅰ patients were (512.73±11.47) mg/ml and (2217.16±317.52) ng/L, which were the lowest; D-Dimer level and NT-proBNP level of grade Ⅳ patients were (579.31±26.42) mg/ml and (2742.27±367.42) ng/L, which were the highest. With the increase of cardiac function classification, the levels of D-Dimer and NT-proBNP were also increased, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). In the observation group, the levels of D-Dimer and NT-proBNP in patients with single-vessel coronary artery disease were the lowest, which were (473.61±16.72) mg/ml and (2181.73±289.39) ng/L, respectively. The levels of D-Dimer and NT-proBNP in patients with three-vessel coronary artery disease were the highest, which were (576.65±26.57) mg/ml and (2779.32±396.43) ng/L, respectively. With the increase of the number of diseased vessel, the higher the level of D-Dimer and NT-proBNP, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). In the observation group, D-Dimer and NT-proBNP of patients without cardiovascular events were (426.57±31.12) mg/ml and (2153.31±416.27) ng/L, which were lower than those of patients with cardiovascular events (562.71±51.53) mg/ml, (2799.87±452.13) ng/L, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05); D-Dimer (962.71±142.61) mg/ml and NT-proBNP (9239.21±1452.47) ng/L of dead patients were higher than those of surviving patients (502.56±97.72) mg/ml and (2353.31±506.97) ng/L, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion D-Dimer and NT-proBNP have a benign guiding role in the diagnosis of patients with acute myocardial infarction. With the aggravation of the disease, the levels of D-Dimer and NT-proBNP are also increasing. At the same time, the higher the level of D-Dimer and NT-proBNP, the worse the prognosis of patients. Attention should be paid to the levels of D-Dimer and NT-proBNP in clinical practice.
【Key words】 Acute myocardial infarction; N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; D-Dimer; Prognosis
急性心肌梗死是临床常见的心内科急危重疾病[1]。现阶段急性心肌梗死的诊断多凭借肌钙蛋白的升高与心电图的改变来确定, 所以如何提高急性心肌梗死患者的诊断效率, 同时对患者预后情况的评估成为现阶段的研究重点[2]。为了探讨初诊急性心肌梗死患者血清N末端脑钠肽及D-二聚体水平与预后的关系, 作者选取本院2019年2月~2020年2月门诊收治的80例初诊急性心肌梗死患者, 同时选择同期的健康体检者80例, 进行临床观察, 现将结果报告如下。
1 资料与方法
1. 1 一般资料 选取本院2019年2月~2020年2月门诊收治的80例初诊急性心肌梗死患者作为观察组, 同时选择同期的80例体检健康者作为健康对照组。观察组中男42例, 女38例;平均年龄(57.57±12.86)岁;单支病变27例, 双支病变29例, 三支病变24例;心功能分级:Ⅰ级23例, Ⅱ级26例, Ⅲ级15例, Ⅳ级16例。健康对照组中男40例, 女40例;平均年龄(58.03±13.12)岁。两组一般资料比较, 差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05), 具有可比性。所有研究对象及家属均同意参加本次研究且经伦理委员会批准。
1. 2 方法 所有患者在入院后空腹状态下采取静脉血液, 健康体检者与门诊直接采集, 4℃的温度条件下静止放置1 h, 转速为3000 r/min离心15 min, 收集上层血清, NT-proBNP水平采用全自动电化学发光免疫分析仪(Thermo Fisher Scientific)进行检测, 阳性参考值为≥2000 ng/L。D-Dimer采用免疫荧光法检测, 阳性参考值为≥200 mg/ml[3]。
1. 3 观察指标 比较两组受试者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平, 观察组不同心功能分级患者、不同冠状动脉造影情况患者、是否发生心血管事件患者、死亡与存活患者的D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平。
1. 4 统计学方法 采用SPSS22.0统计学软件处理数据。计量资料以均数±标准差( x-±s)表示, 采用t检验;计数资料以率(%)表示, 采用χ2检验。P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2. 1 两组受试者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平比较 观察组患者D-Dimer为(513.72±55.67)mg/ml、NT-proBNP为(2749.62±449.51)ng/L均高于健康对照组的(127.67±32.43)mg/ml、NT-proBNP(462.36±134.57)ng/L, 两组数据经检验均符合正态分布, 且方差齐, 差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
2. 2 观察组不同心功能分级患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平比较 Ⅰ级患者D-Dimer水平(512.73±11.47)mg/ml、NT-proBNP为(2217.16±317.52)ng/L, 均最低;Ⅳ级患者D-Dimer(579.31±26.42) mg/ml、NT-proBNP(2752.27±367.42)ng/L, 均最高。随着心功能分级的增加, 患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP的水平也随之增高, 差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表1。
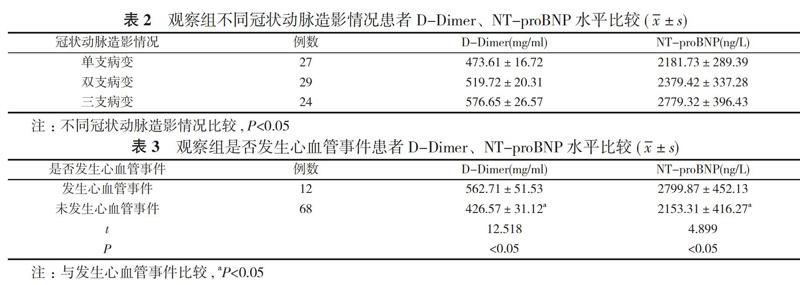
2. 3 观察组不同冠状动脉造影情况患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平比较 冠状动脉单支病变患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平最低, 分别为(473.61±16.72)mg/ml、(2181.73±289.39)ng/L, 冠状动脉三支病变患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平最高, 分别为(576.65±26.57)mg/ml、(2779.32±396.43)ng/L, 随着患者患病支数增加, 患者的D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平越高, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表2。
2. 4 观察组是否发生心血管事件患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平比较 未发生心血管事件的患者有68例,D-Dimer为(426.57±31.12)mg/ml、NT-proBNP为(2153.31±416.27)ng/L, 发生心血管事件患者有12例, D-Dimer為(562.71±51.53)mg/ml、NT-proBNP为(2799.87±452.13)ng/L, 发生心血管事件患者的D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平均明显高于未发生心血管事件的患者, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表3。
2. 5 观察组死亡与存活患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平比较 死亡患者有4例, D-Dimer为(962.71±142.61)mg/ml、NT-proBNP为(9239.21±1452.47)ng/L;存活患者有76例, D-Dimer为(502.56±97.72) mg/ml、NT-proBNP为(2353.31±506.97)ng/L, 死亡患者的D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平明显高于存活患者, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
3 讨论
急性心肌梗死是临床中致残率高, 致死率高的急危重疾病。D-Dimer是纤维蛋白的降解产物, 当D-Dimer水平升高, 在临床中多反映出体内存在高凝状态和继发性的纤维蛋白溶解亢进, 临床中D-Dimer的浓度多作为血栓性疾病的重要参考指标[3]。本文研究结果提示, 观察组患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP均高于健康对照组, 差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。观察组Ⅰ级患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平均最低;Ⅳ级患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平均最高。随着心功能分级的增加, 患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP的水平也随之增高, 差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。观察组冠状动脉单支病变患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平最低, 冠状动脉三支病变患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平最高, 随着患者患病支数增加, 患者的D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平越高, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。观察组未发生心血管事件的患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平均低于发生心血管事件患者, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。观察组死亡患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP均高于存活患者, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。说明了D-Dimer与NT-proBNP水平在急性心肌梗死患者的诊断中有着重要的参考作用, 对于患者的治疗也有着重要的指导作用, 同时可以对急性心肌梗死患者的预后有着良性的指导作用。
郭建萍等[4]研究表明, 急性心肌梗死患者的D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平随着疾病的严重程度增加, 这与本研究的结果相似, 说明了D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平在急性心肌梗死患者的诊断中有着良性的指导作用, 同时对于患者的预后情况也有着良性指导作用, 患者的血清指标越高, 患者的疾病严重程度越高, 同时患者发生心血管疾病的概率就越高。温宗玉等[5]研究表明, 在急性心肌梗死患者中, 患者的D-Dimer水平相对于健康组来说, 有着明显的升高, 同时患者的D-Dimer水平越高, 患者死亡情况与心脑血管意外的发生情况就越高, 说明了D-Dimer在急性心肌梗死的诊断中有着良性的指导作用。宋冰等[6]研究表明, NT-proBNP的水平在诊断急性心肌梗死中有着重要的参考作用, 同时可以判断患者预后情况。亦有多项研究表明, D-Dimer、NT-proBNP的水平对于急性心肌梗死的诊断有着重要的参考作用, 同时对于患者的预后情况有着重要的参考作用, D-Dimer、NT-proBNP的水平越高, 患者的预后情况就越差, 同时D-Dimer、NT-proBNP水平越高, 患者心血管意外的发生情况越高, 对患者的身心健康带来了不利的影响, 所以对于D-Dimer、NT-pro BNP水平应当得到重视。
综上所述, D-Dimer与NT-proBNP在急性心肌梗死患者的诊断中有着良性的指导作用, 随着患者疾病程度的加重, D-Dimer、NT-proBNP的水平也在随之升高, 同时患者D-Dimer、NT-proBNP的水平越高, 患者的预后也就越差, 在临床中对于D-Dimer、NT-proBNP的水平应引起重视。
参考文献
[1] 安铁峰, 王文科, 赵宁. 急性心肌梗死患者血脑钠肽、D-二聚体、纤维蛋白原、血糖水平对预后的影响. 内科急危重症杂志, 2017, 5(2):54-59.
[2] 王禺, 李秀娥, 赵曼, 等. D-二聚体联合N-末端前体脑钠肽对急性脑梗死早期诊断的价值及预后的相关性. 神经损伤与功能重建, 2017, 4(12):580.
[3] 王彩玲, 郑君平, 李淑钰. 血浆cTnI、D-二聚体检测在急性 心肌梗死、急性肺栓塞所致胸痛病因中的应用. 心脑血管病防治, 2018, 18(6):509-510, 515.
[4] 郭建萍, 王华. 初诊急性心梗患者血清N末端脑钠肽及D-二聚体水平與预后的相关性研究. 实验与检验医学, 2020, 38(3):561-563.
[5] 温宗玉, 于彤彤, 武佳科. D-二聚体对急性非ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者预后的预测价值. 中国现代医学杂志, 2019, 29(7):86-91.
[6] 宋冰, 方孝美, 倪慧群. 急性心肌梗死患者基质金属蛋白酶3及N末端脑钠肽前体水平检测结果分析. 预防医学, 2016, 28(11):1184-1186.
[收稿日期:2020-08-12]
