基于Wells评分和网络宣教的分级护理预防腹腔镜胆囊切除术后静脉血栓栓塞症的临床研究
2020-11-09高玲李炳芹张承丽王玉涛
高玲 李炳芹 张承丽 王玉涛

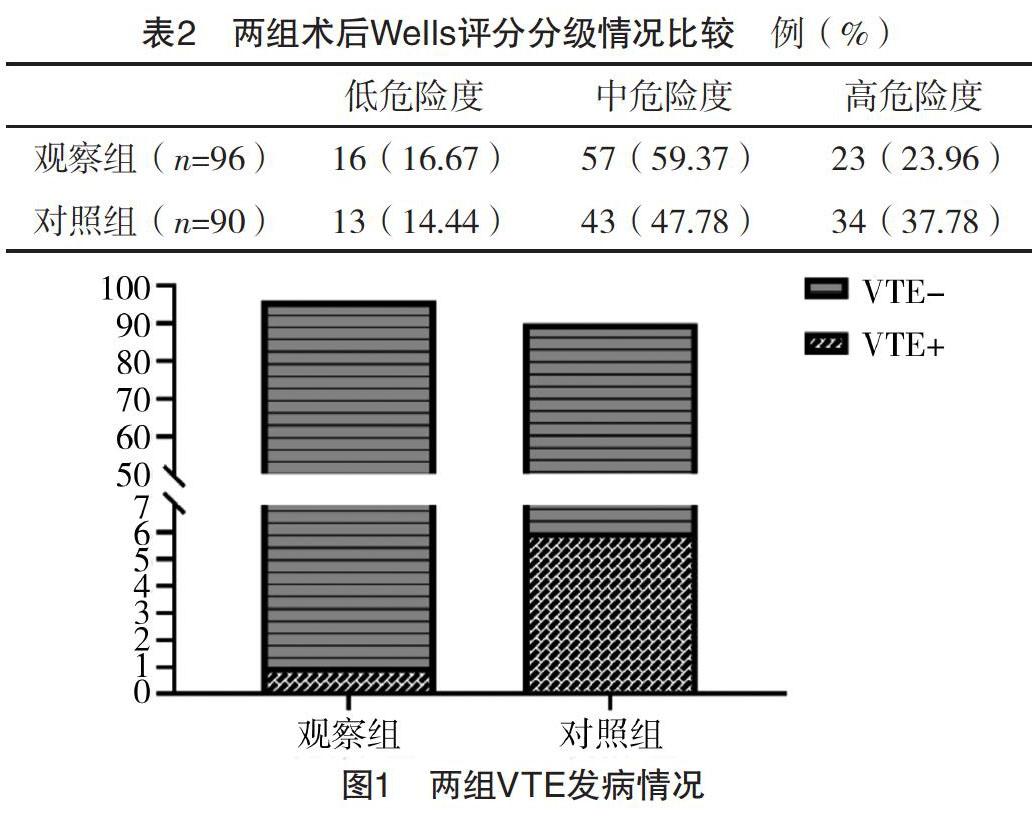
【摘要】 目的:探讨基于Wells评分和网络宣教的分级护理预防腹腔镜胆囊切除术后静脉血栓栓塞症的效果。方法:选取2014年10月-2018年12月于济南市中医医院与利津县明集中心卫生院進行腹腔镜胆囊切除术(laparoscopic cholecystectomy,LC)治疗的患者186例,按护理方法不同分为对照组(n=90)与观察组(n=96)。对照组给予常规护理,观察组给予基于Wells评分和网络宣教的分级护理。比较两组术后Wells评分分级、VTE发生情况及对VTE相关知识的掌握情况。结果:对照组高危险度者比例高于观察组(P<0.05)。观察组VTE发生率为1.04%低于对照组的6.67%(P<0.05)。观察组VTE相关知识掌握评分高于对照组(P<0.05)。结论:基于Wells评分和网络宣教的分级护理措施能够有效提高患者及家属对VTE危害和预防方法相关知识的掌握度,降低LC术后患者VTE发病风险。
【关键词】 腹腔镜胆囊切除术 静脉血栓栓塞症 Wells评分 网络宣教
[Abstract] Objective: To investigate the effect of grading nursing based on the Wells score and network education in preventing venous thromboembolism after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Method: A total of 186 patients treated with laparoscopic cholecystectomy (LC) in Jinan Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Mingji Central Hospital of Lijin County in Dongying from October 2014 to December 2018 were selected. According to different nursing methods, they were divided into control group (n=90) and observation group (n=96). The control group was given routine nursing, while the observation group was given grading nursing based on the Wells score and network education. The Wells score grading, VTE occurrence and mastery of VTE related knowledge were compared between the two groups. Result: The proportion of high risk patients in the control group was higher than that in the observation group (P<0.05). The incidence of VTE in the observation group was 1.04% lower than 6.67% in the control group (P<0.05). The mastery of VTE related knowledge scores in the observation group was higher than that in the control group (P<0.05). Conclusion: The grading nursing based on the Wells score and network education can effectively improve the knowledge of VTE hazards and prevention methods of patients and their families, and reduce the risk of VTE in patients after LC.
[Key words] Laparoscopic cholecystectomy Venous thromboembolism Wells score Network education
First-authors address: Mingji Central Hospital of Lijin County in Dongying, Lijin 257400, China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2020.23.027
静脉血栓栓塞症(venous thromboembolism,VTE)是常见的血管疾病,主要包括深静脉血栓形成(deep vein thrombosis,DVT)和肺栓塞(pulmonary embolism,PE)[1]。主要表现为静脉血液不正常凝结成块,部分或完全堵塞静脉管腔,导致静脉血液回流障碍,诱发肢体肿胀、浅静脉扩张、皮肤温度升高等症状,严重者可致人死亡。手术创伤、麻醉、卧床、恶性肿瘤等是VTE的高危因素。随着腹腔镜技术的快速发展和培训进修学习的日益便捷,腹腔镜胆囊切除术(laparoscopic cholecystectomy,LC)迅速在各级医疗机构普及。由于腹腔镜手术体位、麻醉、CO2气腹等多种应激因素影响,术后患者VTE的预防成为外科医务人员关注的重点问题[2]。本研究对186例行LC治疗的患者临床资料进行回顾性分析,探讨基于Wells评分和网络宣教的分级护理预防腹腔镜胆囊切除术后VTE的效果,旨在探索更为安全、有效的预防VTE的护理方法。
Wells评分表于1995年由Wells教授等人编制,包含了10个条目,根据累计得分将患者发生VTE风险分为3个等级,因其对VTE预测的有效性而广泛应用于临床[9-11]。Wells评分级可以协助医务工作者快速制定分级护理干预措施,降低VTE的风险,或在确诊VTE后,及早采取相应的措施,降低VTE远期并发症发生率[12-14]。在LC术后患者中应用Wells评分分级作为预防VTE护理措施的指导原则,是护理模式的一种新的尝试。
护理宣教在诊疗过程中意义重大。赵飞燕等[15]研究发现,患者的文化程度、是否接受宣教等因素显著影响患者的抗凝药物服药依从性。随着移动通信技术的发展,人们获取信息的方式也越来越便捷、多样。网络宣教是一种新型宣教方式,借助网络和移动智能设备,护理人员可以及时、全面、形象地开展宣教工作,不必拘泥于时间地点,患者及家属也可反复学习,生动的教学内容也更有助于受众理解[16-17]。本研究结果显示,观察组VTE相关知识知识掌握评分高于对照组(P<0.05)。表明接受网络宣教的患者及家属更容易掌握VTE相关知识。
综上所述,基于Wells评分和网络宣教的分级护理能够有效提高患者及家属对VTE危害和预防方法的认知度,降低LC术后患者VTE发病风险。本研究尚存在不足之处,如随访时间较短,对于迟发性VTE缺乏随访数据等,无法评价基于Wells评分和网络宣教的分级护理对VTE的远期预防效果。更全面、准确、有效地VTE预防护理措施有待临床工作者进一步探寻。
参考文献
[1] Kunutsor S K,M?kikallio T H,Seidu S,et al.Physical activity and risk of venous thromboembolism:systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies[J].Eur J Epidemiol,2019,34(11):431-442.
[2] Stein P D,Matta F,Sabra M J.Pulmonary embolism and deep venous thrombosis following laparoscopic cholecystectomy[J].Clin Appl Thromb Hemost,2014,20(3):233-237.
[3]邱燕碧,罗秀霞,羅志兰.妇产科术后预防深静脉血栓栓塞症护理的临床研究[J].中国医学创新,2016,13(13):86-89.
[4] Maíllo C L,Martín E,López J,et al.Effect of pneumoperitoneum on venous hemodynamics during laparoscopic cholecystectomy.Influence of patients age and time of surgery[J].Med Clin(Barc),2003,120(9):330-334.
[5] Gundogdu R H,Oduncu M,Bozkirli B O,et al.Does thromboprophylaxis cause bleeding after laparoscopic cholecystectomy?[J].Bratisl Lek Listy,2017,118(3):156-159.
[6] Henry M L,Abdul-Sultan A,Walker A J,et al.Duration and Magnitude of Postoperative Risk of Venous Thromboembolism after Cholecystectomy:A Population-Based Cohort Study[J].Dig Surg,2019,37(1):1-7.
[7] Milic D J,Pejcic V D,Zivic S S,et al.Coagulation status and the presence of postoperative deep vein thrombosis in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy[J].Surg Endosc,2007,21(9):1588-1592.
[8]温薇,曾国华,余芳,等.分级预防护理在骨科大手术患者深静脉血栓形成中的应用效果[J].中国医学创新,2019,16(36):105-108.
[9] Wells P S,Hirsh J,Anderson D R,et al.Accuracy of clinical assessment of deep-vein thrombosis[J].Lancet,1995,345(8961):1326-1330.
[10] Wells P S,Ginsberg J S,Anderson D R,et al.Use of a clinical model for safe management of patients with suspected pulmonary embolism[J].Ann Intern Med,1998,129(12):997-1005.
[11] van Es N,Kraaijpoel N,Klok F A,et al.The original and simplified Wells rules and age-adjusted D-dimer testing to rule out pulmonary embolism:an individual patient data meta-analysis[J].J Thromb Haemost,2017,15(4):678-684.
[12] Modi S,Deisler R,Gozel K, et al.Wells criteria for DVT is a reliable clinical tool to assess the risk of deep venous thrombosis in trauma patients[J].World J Emerg Surg,2016,11(1):24.
[13] Gaitini D,Khoury R,Israelit S, et al.Sparing ultrasound in emergency department patients with suspected deep vein thrombosis by using clinical scores and D-dimer testing[J].J Clin Ultrasound,2016,44(4):231-239.
[14]阮小贞,何琳.Wells量表和修正的Geneva评分对肺栓塞的预测价值分析[J].中国医学创新,2018,15(24):106-109.
[15]赵飞燕,崔英,肖树芹.肺血栓栓塞症患者华法林抗凝治疗的知识、态度及行为的调查分析[J].中华护理杂志,2016,51(12):1451-1455.
[16]汪小冬,徐莺,何艳娟,等.提升动静脉内瘘患者功能锻炼执行率的品管圈实践[J].护理学报,2016,23(15):9-11.
[17]吁佳,杨菊莲.微信平台健康教育对口服阿片类镇痛药物中晚期癌痛患者自我效能感和治疗依从性的影响[J].中国医学创新,2019,16(12):150-153.
(收稿日期:2020-01-19) (本文编辑:田婧)
