B超定位一步扩张法建立经皮肾通道在肾结石患者治疗中的应用研究
2020-09-02吴兆春曾会勇韩巧军徐汉新陈溯邱锦新游嘉琨
吴兆春 曾会勇 韩巧军 徐汉新 陈溯 邱锦新 游嘉琨
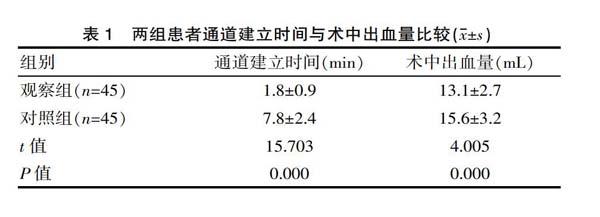
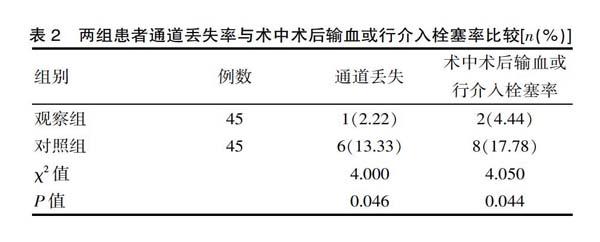
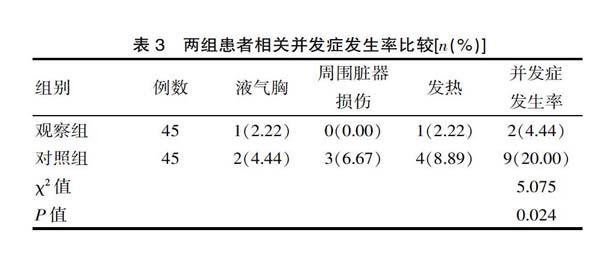
[摘要] 目的 探討分析B超定位一步扩张法建立经皮肾通道在肾结石患者治疗中的应用效果。方法 便利选取2019年1—8月期间该医院收治的90例经皮肾镜取石术治疗肾结石患者作为研究对象,采用随机数字分组为观察组(n=45例)与对照组(n=45例)。观察组患者采用B超定位一步扩张法(F18/F20)建立经皮肾通道;对照组患者采用传统序列扩张法(F6-F20)建立经皮肾通道。比较两组患者通道建立时间、术中出血量、通道丢失率、术中术后输血或行介入栓塞率、相关并发症发生率之间的差异。结果 观察组患者的通道建立时间(1.8±0.9)min明显短于对照组(7.8±2.4)min,术中出血量(13.1±2.7)mL明显低于对照组(15.6±3.2)mL,差异有统计学意义(t=15.703、4.005,P<0.05);观察组通道丢失率2.22%与术中术后输血或行介入栓塞率4.44%明显低于对照组的13.33%与17.78%,差异有统计学意义(χ2=4.000、4.050,P<0.05),观察组相关并发症发生率4.44%明显低于对照组的20.00%,差异有统计学意义(χ2=5.075,P<0.05)。结论 B超定位一步扩张法建立经皮肾通道在肾结石患者治疗中,能够显著缩短通道建立时间,减少术中出血量,降低通道丢失率、术中术后输血或行介入栓塞率及相关并发症发生率,效果确切,安全性高。
[关键词] B超定位;一步扩张法;经皮肾通道;肾结石
[中图分类号] R692.4 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-0742(2020)06(a)-0094-03
Application of One-step Expansion of B-ultrasound to Establish Percutaneous Renal Channel in the Treatment of Patients with Kidney Stones
WU Zhao-chun, ZENG Hui-yong, HAN Qiao-jun, XU Han-xin, CHEN Su, QIU Jin-xin, YOU Jia-kun
Department of Surgery, Qingxi Hospital, Dongguan, Guangdong Province, 523660 China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the application of one-step expansion of B-ultrasound to establish percutaneous renal channels in the treatment of patients with kidney stones. Methods Ninety patients who underwent percutaneous nephrolithotomy for kidney stones treated in the author's hospital from January to August 2019 were convenient selected as the research subjects. Random numbers were divided into observation group (n=45 cases) and control group (n=45 cases). Patients in the observation group used the B-mode localized one-step expansion method (F18/F20) to establish percutaneous renal channels; patients in the control group used the traditional sequence expansion method (F6-F20) to establish percutaneous renal channels. The differences between the two groups of patients in terms of channel establishment time, intraoperative blood loss, channel loss rate, intraoperative and postoperative blood transfusion or interventional embolization rate, and related complications were compared. Results The channel establishment time (1.8±0.9)min in the observation group was significantly shorter than that in the control group (7.8±2.4)min. The intraoperative blood loss (13.1± 2.7) mLwas significantly lower than that in the control group (15.6±3.2)mL. There was a difference. Statistical significance(t=15.703, 4.005, P<0.05); the channel loss rate in the observation group was 2.22% and the rate of blood transfusion or interventional embolization during the operation was 4.44%, which was significantly lower than the control group's 13.33% and 17.78%(χ2=4.000, 4.050, P<0.05). The incidence of related complications in the observation group was 4.44%, which was significantly lower than that in the control group, 20.00%. The difference was statistically significant (χ2=5.075, P<0.05). Conclusion The one-step expansion of B-ultrasound to establish percutaneous renal channels can significantly shorten the time of channel establishment, reduce the amount of intraoperative blood loss, reduce the rate of channel loss, the rate of blood transfusion or interventional embolization during surgery, and related complications incidence, with exact effect and high safety.
