Discussion on application of food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine in prevention prescriptions for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
2020-07-23YiFanChenYanLiPingJiangYaLuWenYanPengZengQiaoZouYuRongKong
Yi-Fan Chen, Yan Li, Ping Jiang, Ya-Lu Wen, Yan-Peng Zeng, Qiao Zou, Yu-Rong Kong
Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT
The outbreak of novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) poses a serious threat to the health and life of our people and the world. In January 30, 2020, it was listed as an Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) by World Health Organization (WHO) and was defined as “pandemic” on March 11, 2020 [1]. The novel coronavirus pneumonia diagnosis and treatment plan [2] has been published and revised by the National Health Committee. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an important part of the diagnosis and treatment plan, and plays an important role in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. Units at all levels across the country have also launched TCM prevention prescriptions for COVID-19, in which “both food and traditional Chinese medicine materials according to tradition” (referred to as “foodmedicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine”) are mostly selected, reflecting the characteristics and advantages of simplicity, convenience, effectiveness and low cost of TCM. Therefore, through the analysis of the application of food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine in the prevention prescription, it is expected to provide certain reference value for its clinical and daily use and the research and development of related products.
1. Analysis on the application of various substances in prevention prescriptions of government agencies, medical institutions and clinical experts
1.1 Source of TCM preventive prescriptions and the application of various substances
In this study, 172 TCM prevention prescriptions for COVID-19 were included, and the regions where the prevention prescriptions were issued were all over 26 provinces and autonomous regions in China. It can be seen that the sources of prevention prescriptions were widely distributed, among which Shandong, Henan, Beijing and other places paid much attention to the application of prevention prescriptions and explained in more detail (Table 1).

Tab1 Geographical distribution and proportion of prescriptions included
According to the relevant list issued by national health departments, the substances used in 172 prescriptions can be divided into four categories: food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine (Class A), traditional Chinese medicinal that can be used for health food (Class B), tradional Chinese medicinal that cannot be used for health food (Class C), and common food (Class D). The quantity and frequency of various substances are shown in Table 2.
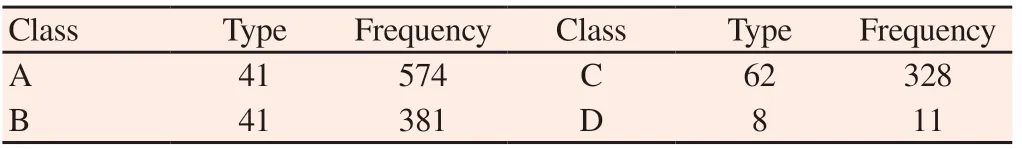
Tab2 Distribution of quantity and frequency of various substances
It can be seen from table 2 that there are many kinds of foodmedicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine in the prevention prescriptions, including honeysuckle, liquorice, agastache, tangerine peel, fresh reed root and perilla and so on. Table 3 lists the food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine with frequency≥10.

Tab3 Dosage and frequency of food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine

Tab4 Dosage and frequency of food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine used in different age groups
Ward method was used to cluster analysis of food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine with frequency≥10, which were mainly divided into five categories: (1) chrysanthemum, mulberry leaf, poria cocos, coix seed, ginger, jujube, mint, platycodon grandiflorum and fresh reed root; (2) perilla and tangerine peel; (3) honeysuckle; (4) agastache; (5) liquorice. Among them, the first category can be divided into three categories: (1) chrysanthemum, mulberry leaf and mint; (2) poria cocos, coix seed, ginger and jujube; (3) platycodon grandiflorum and fresh reed root. As shown in Figure 1.
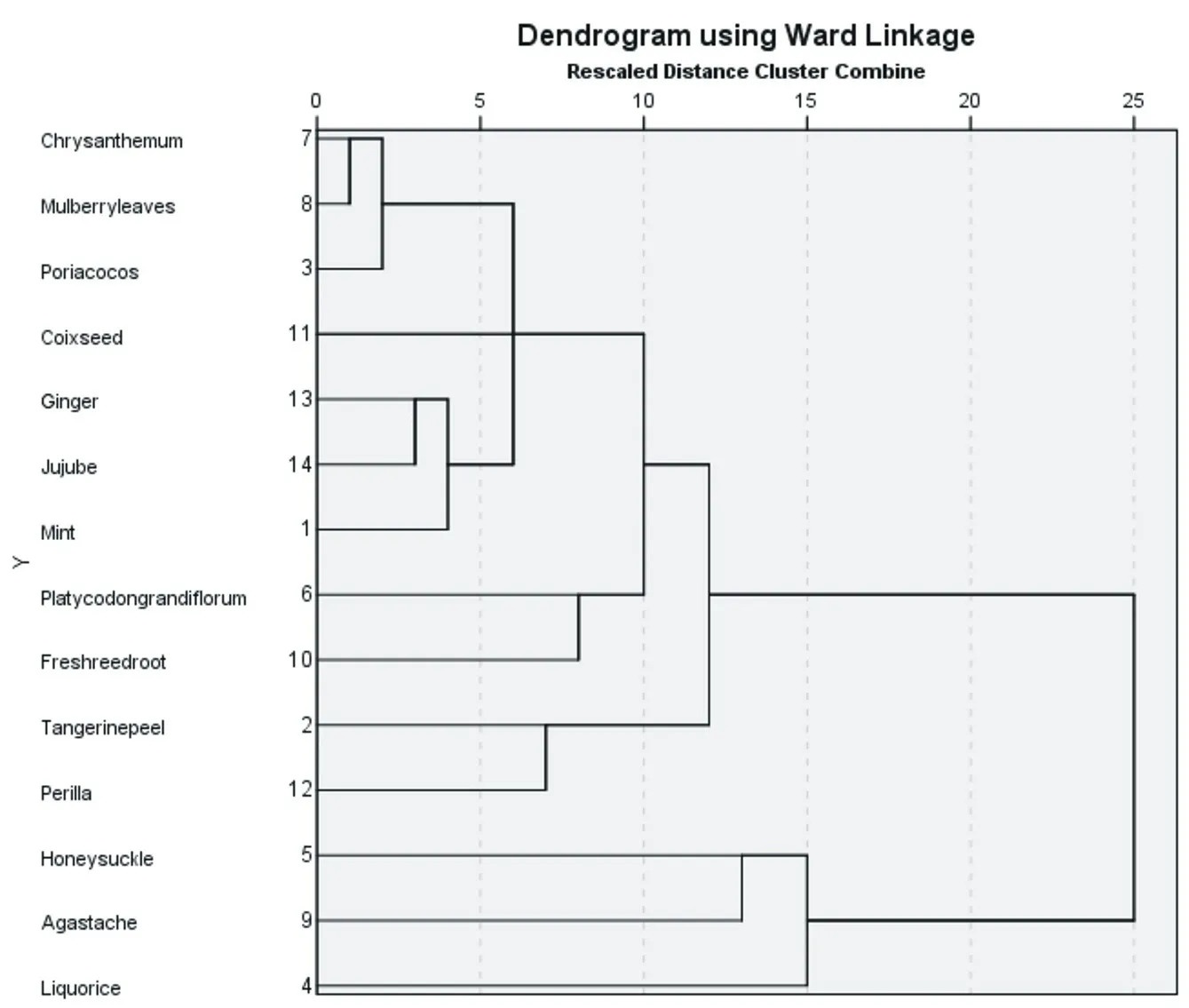
Fig.Clustering results of main food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine
1.2 Application of food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine in prevention prescriptions of different age groups
There are 75 prevention prescriptions for the general population (including those described in the original text as adults, ordinary people, strong people, healthy people and people without special instructions). Substances with frequency≥10 are listed in Table 4. There are 16 prevention prescriptions for children, substances with frequency≥3 are listed in Table 4. There are 5 prevention prescriptions for the elderly, substances with frequency≥2 are listed in Table 4.
1.3 Application of food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine in prevention prescriptions for special population
Special population includes pregnant women, patients with chronic basic diseases and susceptible population. Among them, the susceptible population includes close contacts, medical workers in epidemic areas, returnees from Wuhan. Table 5 lists the application of food and drug substances with frequency≥2.
2. Theory of TCM and modern pharmacology analysis of common food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine in preventive prescriptions
2.1 Analysis of common food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine in preventive prescriptions of TCM
As early as 2000 years ago, Inner Canon of Huangdi put forward the idea of “preventive treatment of disease” which emphasized that the occurrence of diseases is closely related to “vital Qi” and “evil Qi”. After that, it gradually formed the idea of “prevention before disease onset, preventing disease from exacerbating, prevention after recovering” to prevent epidemic diseases, and produced many effective prevention prescriptions which contain many food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine. COVID-19 belongs to the category of epidemic diseases in traditional Chinese medicine. The main pathological characteristics of the disease are dampness, toxin, blood stasis and deficiency because of suffering “epidemic Qi”. It is very important to carry out prevention work because of its sudden onset, complex changes and strong infectivity.
According to the statistical analysis of the frequency of various substances in the COVID-19 prevention prescriptions, the foodmedicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine with higher frequency mainly include honeysuckle, liquorice, agastache, orange peel, fresh reed root, perilla. The cluster analysis results show that honeysuckle, agastache and liquorice belong to the same category. Honeysuckle tastes sweet with cold nature, which can clear away heat and detoxification, evacuate wind-heat, and mainly treat exogenous wind-heat and febrile disease. It is often used as the monarch medicine, and represents a kind of prevention formula mainly for clearing heat. Huoxiang has hot and warm nature, is an essential medicine for removing dampness by means of aromatics. It is mostly used for the exterior syndrome of summer-heat and damp and the beginning of damp-warm syndrome. It is also often used as a monarch medicine, which represents a kind of prevention formula based on warming and resolving. Liquorice has a sweet and gentle nature, which is known as “illustrious elders of a country”. It is often used as an assistant in various prevention formulas, which has the functions of nourishing the spleen and Qi, clearing away heat and toxin, eliminating phlegm and relieving cough. Perilla and tangerine peel are in one categories. Perilla can dispel cold, move Qi and stomach, and tangerine peel can regulate qi and strengthen spleen, dry dampness and phlegm, both of which are used together to play the effect of invigorating spleen and stomach and regulating qi and dampness. Chrysanthemum, mulberry leaf, poria cocos, coix seed, ginger, jujube, mint, platycodon grandiflorum and fresh reed root are the other categories, among which, chrysanthemum, mulberry leaf and mint are the first category. Mulberry leaf and chrysanthemum are sweet, cool and light, supplemented by mint, which can help to evacuate the upper Jiao wind heat. Poria cocos, coix seed, ginger and red date are the second category, which has the function of promoting the transportation of the middle Jiao. Platycodon grandiflorum and fresh reed root are the third category, which can clear the heat, generate the fluid and promote the lung phlegm. Therefore, the above commonly used food-medicine homologous traditional Chinesemedicine mainly embody the concept of “strengthening the vital Qi, nourishing Yin” and the thought of “removing pathogenic factors” such as clearing away heat, removing dampness and detoxification, which are important ways of “preventive treatment of disease”.

Tab5 Frequency of food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine used for special population
2.2 Modern pharmacology analysis of common foodmedicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine in preventive prescriptions
The main components of the food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine used in the prevention prescriptions mostly include organic acids, flavonoids, phenolic acids, polysaccharides and volatile oil, which play anti-virus, anti-oxidation and regulation roles by inhibiting the replication of virus, preventing the release of virus from infected cells, reducing the production of active oxygen, improving the ability of scavenging free radicals, activating mononuclear phagocytic system and other mechanisms. The immune function of the body is similar to the concept of protecting the body’s vital Qi by “strengthening the body and eliminating pathogenic factors” in traditional Chinese medicine.
Previous studies have found that chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid contained in honeysuckle can be used as neuraminidase inhibitors of influenza virus, blocking the release of H1N1 / H3N2 virus from infected cells, and have a strong ability to scavenge free radicals [3-7]. Honeysuckle polysaccharide and honeysuckle flavone can respectively increase the content of hemolysin antibody, IL-2, the activity of serum immune enzyme and lymphoid organ antioxidative activities in rats, which play good roles in immunoregulation [8-9]. Glycyrrhizic acid, the main component of Glycyrrhiza, has a significant inhibitory effect on SARS CoV [10-11], and the latest research has confirmed that glycyrrhizic acid may be a potential anti-COVID-19 compound [12].
Patchouli alcohol is the main component of patchouli, which can play an anti influenza role by regulating RLH signal pathway [13] and combining with influenza virus neuraminidase protein [14], and by activating mononuclear phagocytic system, it can enhance humoral immunity and inhibit cell immunity at the same time [15]. In addition, peppermint polysaccharide in peppermint also has antiviral effect, and has strong inhibitory effect on respiratory syncytial virus [16]. The polysaccharides in tangerine peel [17], reed root [18], poria cocos [19] and mulberry leaf [20] and flavonoids in perilla [21] all have good scavenging ability to DPPH and hydroxyl radicals, and the polyphenols in perilla can effectively increase the expression level of antioxidant enzyme mRNA and protein in endothelial cells [22], while the water extract of fresh reed root can enhance the phagocytic ability of the reticuloendothelial system and the activity of NK cells in immunocompromised mice to improve the immune function [23-24]. In addition, platycodon grandiflorum and coix seed can regulate the immune function, platycodon D can stimulate the secretion of lymphocyte IL-2, IL-4 and macrophage TNF-α, IL-12 to enhance the immunoregulatory activity [25]; coix seed oil can significantly enhance the proliferation ability of spleen lymphocyte and the immunoregulatory function of delayed allergy [26].
3. Discussion
Food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine embodies the concept of “medicine and food homology” in traditional Chinese medicine. The theory of “medicine to dispel, food to follow” is explained in detail in Wuchangzhengdalun, Suwen. There are also many “medicine and food dual-use” materials in the monographs of Materia Medica in the past dynasties, whose efficacy can be divided into two aspects: food therapy and food health-preserving [27]. In recent years, food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine have been gradually respected and valued because of their functions of strengthening the body and removing pathogenic factors. The health departments has also revised The List of Substances That Are both Food and Traditional Chinese Medicine According to Traditional for many times to clarify and regulate such substances. In the COVID-19 Traditional Chinese Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment Handbook written by Wang Qi Academician and others [28], the Chinese medicine prescriptions for preventing novel coronavirus pneumonia has been divided into “medicine and food homologous prescription” and “non medicine and food homologous prescription”. Beijing, Heilongjiang and Henan have also developed COVID-19 preventive prescriptions all composed of food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine, which has been applied more widely.
The main food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine used in the prevention prescriptions for COVID-19 mainly have the effects of clearing away heat and detoxification, eliminating dampness and regulating Qi, nourishing yin and promoting body fluid. For the general population with strong body, more prevention prescriptions are also made with amomum tsao-ko, almonds. Amomum tsao-ko has hot and warm nature and turns over to spleen, stomach channels, which can eliminate dampness, warm middle-jiao, intercept malaria and remove phlegm. Almonds has bitter and tepid nature, which can descend Qi, relieve cough and asthma. The two can strengthen the effect of regulating Qi and resolving dampness to resist external pathogenic factors according to the pathogenic characteristics of damp evil in COVID-19. In the prevention prescriptions for children, we pay attention to the use of lophatherum gracile. “Children have pure Yang”, and “liver is often surplus, spleen is often insufficient, kidney is often deficient; heart is often surplus, lung is often insufficient; Yang is often surplus, Yin is often insufficient”. Therefore, lophatherum gracile which has sweet and slight cold nature, turns over to heart, stomach and small intestine channels, and has the effect of clearing heat, eliminating fidgety and thirst, diuresis and drenching, is suitable for children's prevention. In addition, the elderly “Tiangui are exhausted, essence is little, kidney is weak, body is extremely”, so in the prevention prescriptions, more attention is paid to strengthening: those who have deficiency of Yin can choose lilium brownii which can nourish yin and moisten dryness, which can nourish but not be greasy, tonify but not be dry; those who have deficiency of spleen and stomach Yang can use rhizoma zingiberis which is the main medicine of warm meddle-jiao to disperse cold, warm lung and resolve retained fluid, and can use jujube which is sweet and warm to tonify middle-jiao, nourish Qi and blood, and calm nerves. TCM holds that “Vital Qi stored inside, evil cannot be done.” In the prevention prescriptions for the elderly, more attention should be paid to invigorating the viscera, supporting the healthy Qi to resist the exogenous evil.
In the prevention prescriptions of special population, the patients with high blood sugar or diabetes often have the foundation of phlegm and dampness, depression and heat, who burning Qi and Yin. Therefore, the food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine mostly choose coix seed, poria cocos, pueraria lobata and other substances which have sweet, cool and gentle nature. Coix seed, poria cocos can invigorate the spleen and Qi, promoting water and moisture, resolving turbid and heat, while pueraria lobata can promote fluid to quench thirst, which are suitable for this kind of population. In addition, the patients with high blood pressure or hypertension often have the characteristics of Yin deficiency and Yang hyperactivity. Therefore, mulberry leaves, chrysanthemum can be selected to calm the liver and clear the heat, accompanied by Chinese olive to benefit the pharynx and promote fluid, so as to achieve the function of nourishing yin and Yang, which is more suitable for the prevention of related basic diseases. However, it is also necessary to recognize that although some food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicines have high safety, they still need to be used appropriately in combination with our own characteristics for disease prevention. For example, for those who are wet and full, we should pay attention to the use of Glycyrrhiza and others with sweet and slow nature; for those who are physically deficient and cold, we should be careful to use the heat clearing and detoxifying substances such as honeysuckle and reed root; for those who are Yin deficient and dry and hot, we should not overuse the moistening substances such as agastache, tangerine peel and coix seed. In addition, modern research on the safety of foodmedicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine has been further strengthened. Pharmacological research has found that menthol has certain hepatorenal toxicity, and the active metabolites of perillaldehyde and perilla acid also have cytotoxic components [29]. Therefore, especially for children, the elderly and patients with basic diseases, it is more recommended to use food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine and related prevention methods carefully under the guidance of doctors.
To sum up, as an important part of the prescription of COVID-19 prevention, the food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine embodies the characteristics of disease prevention and epidemic resistance of “treating disease before disease” in TCM, and often changes according to different regional environment and different age stages. From the perspective of modern pharmacology, most of them have the function of “strengthening the body” such as anti-oxidation and regulating immunity, and the effect of “removing pathogenic factors” such as inhibiting virus activity, because they contain flavonoids, polysaccharides and abundant trace elements. Therefore, combining the theory of traditional Chinese medicine and western medicine, this paper makes an in-depth analysis of the commonly used food-medicine homologous traditional Chinese medicine in the prevention prescriptions, which can provide some inspiration and reference for the prevention and treatment of related diseases and the application of daily health care.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- miR-146a-3p targeted RELB to regulate cytokine secretion in endothelial cells of atherosclerotic mice
- Expression and mechanism of miR-122 in rats with acute myocardial infarction
- The influence of vitamin D3 on airway inflammation and osteopontin expression in cough variant asthma rats
- Differential expression and function prediction of miRNAs in Hepatocellular carcinoma based on bioinformatics
- LINC01614 expression in gastric cancer and its prognostic value based on bioinformatics analyses
- The effect of plasma uric acid on oxidative stress in ankylosing spondylitis by Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway
