LINC01614 expression in gastric cancer and its prognostic value based on bioinformatics analyses
2020-07-23HuiJieWuJingYuanZhouSongDaChenLingYuZhuJiaHaoLiangAiQunLiu
Hui-Jie Wu, Jing-Yuan Zhou, Song-Da Chen, Ling-Yu Zhu, Jia-Hao Liang, Ai-Qun Liu✉
1. Department of Endoscopy Center, Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital, Nanning, Guangxi, 530021
2. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital, Nanning, Guangxi, 530021
Keywords:
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
According to global cancer statistics in 2018, Gastric cancer (GC) is the fifth most frequently diagnosed tumor and the top three tumorrelated causes of death [1]. In China, the incidence and mortality of gastric cancer are common cancer in men and women [2]. Although the diagnostic technology of GC, especially endoscopic diagnosis of early GC, continues to improve, and the treatment methods are gradually enriched, the morbidity and mortality of GC are still not optimistic [3]. Therefore, it is very important to seek for biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of GC.
Long non-coding RNA (LncRNA) is related to the development of cancer. LncRNA has been proved that it regulates the expression of various molecules through lots of mechanisms to interfere with cell homeostasis and affect cell survival, differentiation, invasion, metastasis and genomic stability [4]. LncRNA can also interact with miRNA and mRNA to participate in the molecular and biological processes of diseases [5]. More and more studies have found that LncRNA plays a role in GC [6][7]. Now, many studies have shown that LncRNA can be used as a biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of GC [8]. However, the role and mechanism of LINC01614 in GC is still unclear. In this study, PCR and bioinformatics analyses were conducted to analyze the expression of LINC01614 in GC and predict its relationship with clinicopathological features and prognosis, so as to explore its potential mechanism.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
Tissue samples were collected from 30 patients who were diagnosed GC and accept tumor resection from Guangxi medical university cancer hospital from January 2014 to December 2015. 30 samples of GC tissue and its paired adjacent normal tissue specimens (more than 5cm away from the cancer tissue) were collected. Human GC cell lines SGC-7901, MGC-803 and human normal gastric epithelial cell line GES-1 were preserved in laboratory. DMEM medium, fetal bovine serum, and PBS were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific. RNAiso, PrimeScript RT reagent kit with gDNA Eraser, and RT-PCR detection kit (TB Green Premix Ex Taq ™ II) were purchased from TAKARA (Beijing) co., LTD. Nanodrop One was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA, reverse transcription instrument (t-100) from bio-rad, USA, and fluorescence quantitative gene amplification instrument (qTOWER 3G) from analytik jena, Germany.
2.2 Total RNA extraction
GES-1, SGC-7901 and MGC-803 were cultured in DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin streptomycin at 37 ℃ and 5% CO2. When the cells grew to a confluence of 80% ~ 90% (about 2.5 106), the medium was discarded, the cells were washed with PBS for 3 times. Add 1 mL TRIzol, shake the cell softly, and the cells were lysed. After the cells were fully lysed, they were transferred to 1.5 mL EP tubes and left at room temperature for 5 min. Remove the tissue from the liquid nitrogen, weigh the 0.5 g tissue into the 1.5 mL EP tube with 1 mL TRIzol, and put the EP tube into the pre-cooled tissue grinder for grinding until the tissue is not visible. Subsequently, RNA was extracted according to the instructions in TAKARA's product specifications, and the purity and concentration of RNA were detected by Nanodrop One.
2.3 Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR)
2 μL cells and tissues RNA were used to synthesize cDNA through reverse transcription system. The cDNA was stored at -20 ℃ according to the instructions. The primers sequences are as follow β-actin: 5’-CTGGAACGGTGAAGGTGACA-3’ and5’-CGGCCACATTGTGAACTTTG-3’. LINC01614: 5'-AACCAAGAGCGAAGCCAAGA-3’and 5'-GCTTGGACACAGACCCTAGC-3'. The primers above were purchased from Tsingke biotechnology co., LTD, Beijing. And the amplification conditions were 95 ℃ 15 s, 60 ℃ 10 s, 72 ℃ 20 s, and 42 cycles. Experiment was repeated for 3 times, 2- Ct was used to measure the relative expression of genes in the tissues and cells.
2.4 Data processing
TCGA biolinks package was used to download GC and adjacent normal tissue RNA-Seq data on TCGA (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov). The inclusion criteria are as follows: 1) diagnosed as stomach cancer; 2) complete RNA-Seq data; 3) complete record of prognosis information. At the same time, we search keywords, "Gastric cancer", "Homo sapiens" and "LncRNA”, on GEO database website (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) and download related GC tissue LncRNA expression profile chip dataset: GSE95667, the data sets include 6 cases of GC tissue and paired adjacent normal tissues.
2.5 Analyses of LINC01614 expression and GC occurrence, clinicopathological features and prognosis
The RNA-Seq of 27 pairs of GC tissue and adjacent normal tissues were extracted from TCGA-STAD and used to analyze the expression of LINC01614 in GC tissues and adjacent normal tissues. Then, the expression of LINC01614 extracted from 368 patients’ RNA-Seq data were ranked from high to low, and the samples were divided into high expression group and low expression group by the median value of LINC01614. Subsequently, the correlation between high and low expression of LINC01614 and clinical stage, pathological characteristics was analyzed. The "Survival" package from R Bioconductor was used to analyze the relationship between the expression level of LINC01614 and Overall Survival (OS) of patients.
2.6 Gene enrichment analysis
By using RNA-Seq data, GO and KEGG enrichment analyses were used to predict the potential mRNA associated with LINC01614. By using the "clusterProfiler" package, GO and KEGG signaling pathway enrichment of protein-coding RNA related to LINC01614 expression were performed to predict the potential role of LINC01614 in gastric cancer and the pathways it involved.
2.7 Statistical analysis
SPSS 23.0 and R were used for data analysis. Date were presented as mean±SD and median. Wilcoxon test was used to compare PCR results and sequencing data between GC and adjacent normal tissues. The cell samples were analyzed by ANOVA. χ2test was used to compare qualitative variables. Mann-whitney U test was used to further analyze the relationship between the expression of LINC01614 and the clinicopathological characteristics of patients. Kaplan-Meier method was used to plot the curve, and log-rank test was used to analyze the relationship between the expression of LINC01614 and OS in patients with GC. Meanwhile, Cox regression was used to calculate the Hazard ratio (HR) and 95% Confidence interval (CI). P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1 The expression of LINC01614 in gastric cancer tissues and GC lines
After qRT-PCR, the median expression levels of LINC01614 in gastric cancer tissues and paired normal tissue was 3.325 and 1.018, respectively. And the expression of LINC01614 in gastric cancer tissues was significantly increased, P < 0.005 (figure 1A). In gastric cell lines, the relative expression level of LINC01614 in normal gastric epithelial cell line GES-1 was 1.044±0.370, human GC cell line SGC-7901 was 3.855±0.440, and MGC-803 was 11.475±1.382. The expression level of LINC01614 in SGC-7901 was significantly higher than that of human normal gastric epithelial cell line GES-1 (P < 0.05, see figure 1B). Similarly, compared with GES-1, the expression level of LINC01614 in MGC-803 was significantly upregulated (P < 0.0001, see figure 1B).
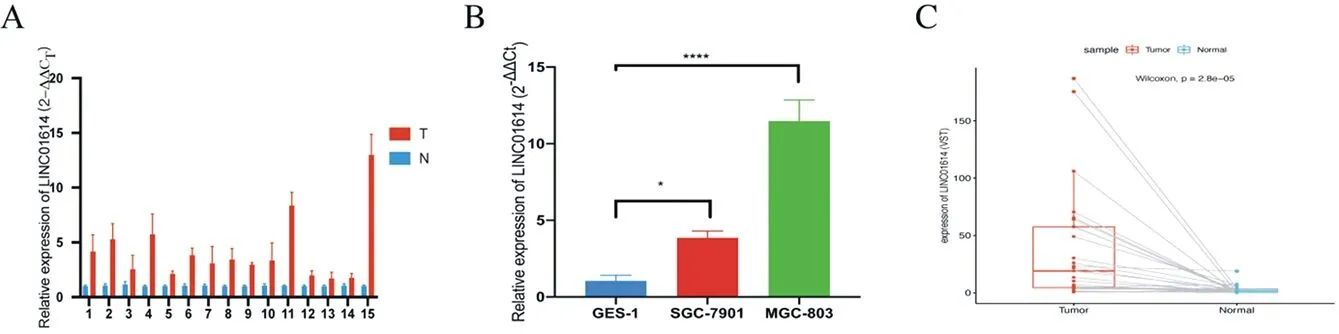
Fig.1 Relative expression of LINC01614 in gastric cancer tissue and paired adjacent normal tissue and gastric cell line. *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001.
3.2 The expression of LINC01614 in GC tissue and adjacent normal tissue in TCGA-STAD
According to the analysis of TCGA-STAD dataset, LINC01614 increased in GC tissue compared with adjacent normal tissue, with the median expressions of 19.060 and 1.622, respectively (P < 0.001), as shown in figure 1C. At the same time, GSE95667 obtained from GEO showed that relative expression of LINC01614 in GC tissues was significantly increased compared with adjacent normal tissues (log2FC=1.953, P < 0.05).
3.3 Correlation between LINC01614 expression level and clinicopathological characteristics of GC patients
In this study, patients were divided into high expression group and low expression group by the median of LINC01614 expression. According to the analysis, the expression of LINC01614 was not correlated with the age (P = 0.251), gender (P = 0.353), Lauren type (P = 0.950), tumor location (P = 0.0696), and cancer stage (P = 0.0696) of the patients with GC, but was correlated with histological grade (P = 0.0177) and residual tumor (P = 0.0218). Among the patients with higher grade G3, 61/143 (42.7%) were in the LINC01614 low-expression group, while 121/215 (56.3%) were in the high-expression group. While the number of patients with higher grade residual cancer, in low expression group was 136/293 (46.4%), and in high expression group was 32/49 (65.3%). The results are shown in table 1. According to the results of χ2test, the correlation of expression of LINC01614 and histological grading, residual tumor in patients were further analyzed. The results of mann-whitney U test showed that LINC01614 differs in different histological grades and residual tumor. The median expression of LINC01614 with G1+G2 and G3 LINC01614 was 3.866 and 4.652, respectively. Meanwhile, among patients with R0 or R1+R2+RX, the expression of LINC01614 was also different, with median values of 4.314 and 5.816, respectively. The differences were statistically significant, as shown in Fig.2.
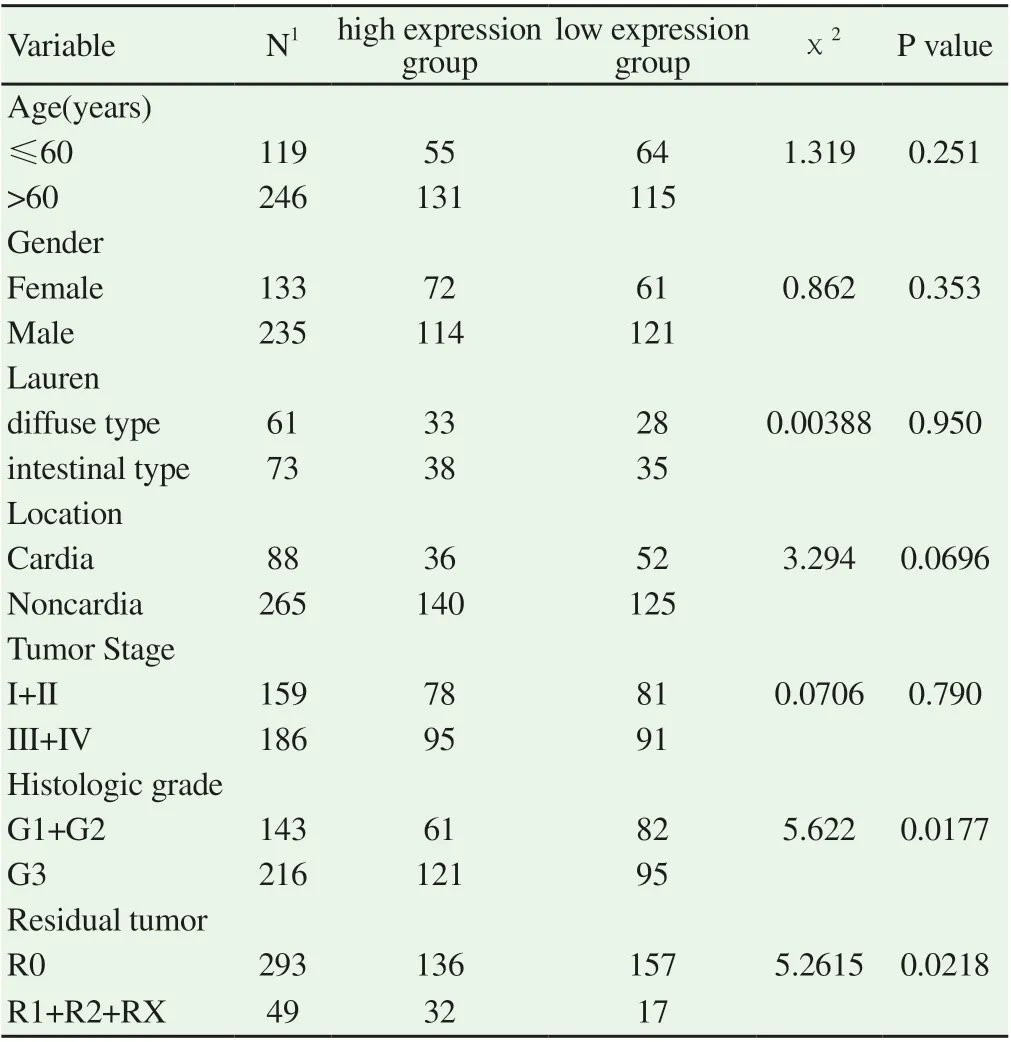
Table1 Analysis of LINC01614 expression and clinical parameter
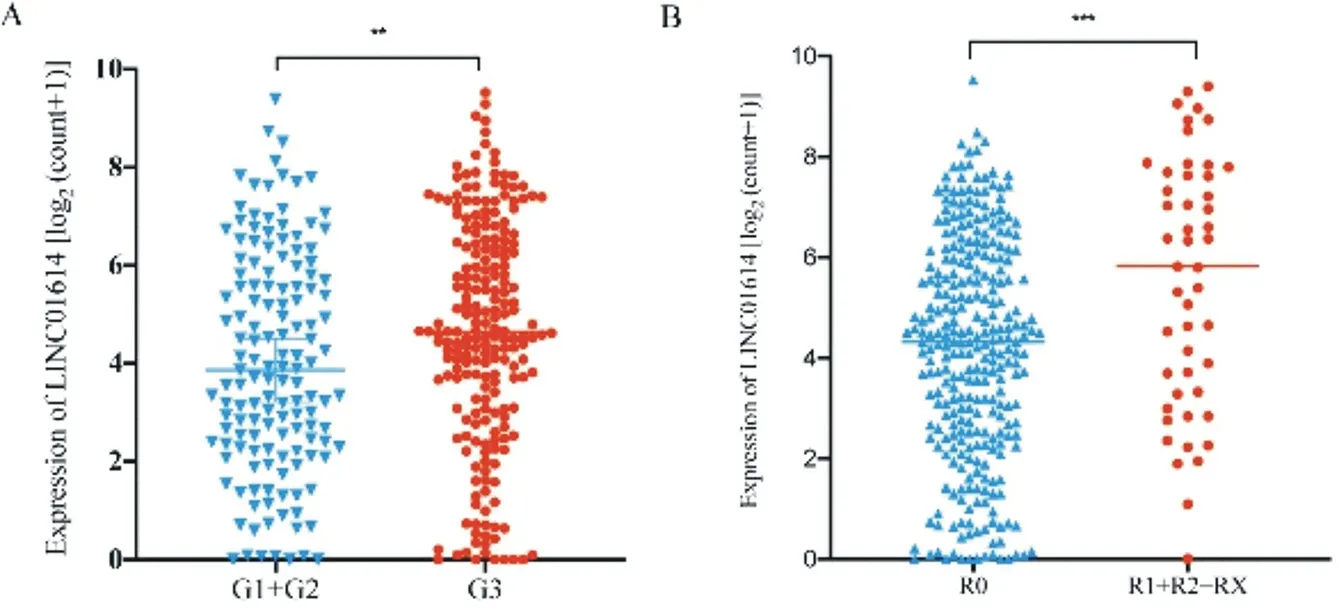
Fig.2 Analysis of expression of LINC01614 and clinical feature
3.4 The relationship between the expression level of LINC01614 and OS in patients with GC
In order to further explore the relationship between LINC01614 and OS in patients with GC, we took the median expression value of LINC01614 as the threshold and divide the patients into high expression (n=182) and low expression (n=186) groups. Then, the survival curve was drawn according to the data. The results showed that the mean survival time of the high-expression and lowexpression group was 1306.635 and 1907.243 days, respectively. And the median survival time was 158.968 and 206.878 days, respectively. According to Kaplan-Meier analysis results, the OS of the patients in low-expression group was better than that in high- expression group (HR = 1.520, 95%ci: 1.094 ~ 2.110), as shown in figure 3.
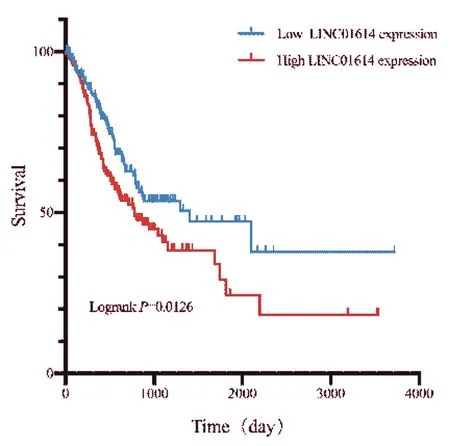
Fig.3 Kaplan-Meier survival curves for OS in GC patients based on LINC01614 expression
3.5 Enrichment analyses
According to the results of the potentially targeted mRNA enrichment analysis of LINC01614, we found that in the GO analysis which composed of Biological Process (BP), Cellular component (CC) and Molecular Function (MF), the potentially targeted mRNA enriched in extracellular matrix, neutrophil activation, growth factor binding and other cancer-related pathways (P<0.05), as shown in figure 4A-C. While in KEGG analysis, the result showed that it was enriched in proven pathways enroll in GC development, including PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, Cell cycle, TGF-β signaling pathway (P<0.05), as shown in figure 4.
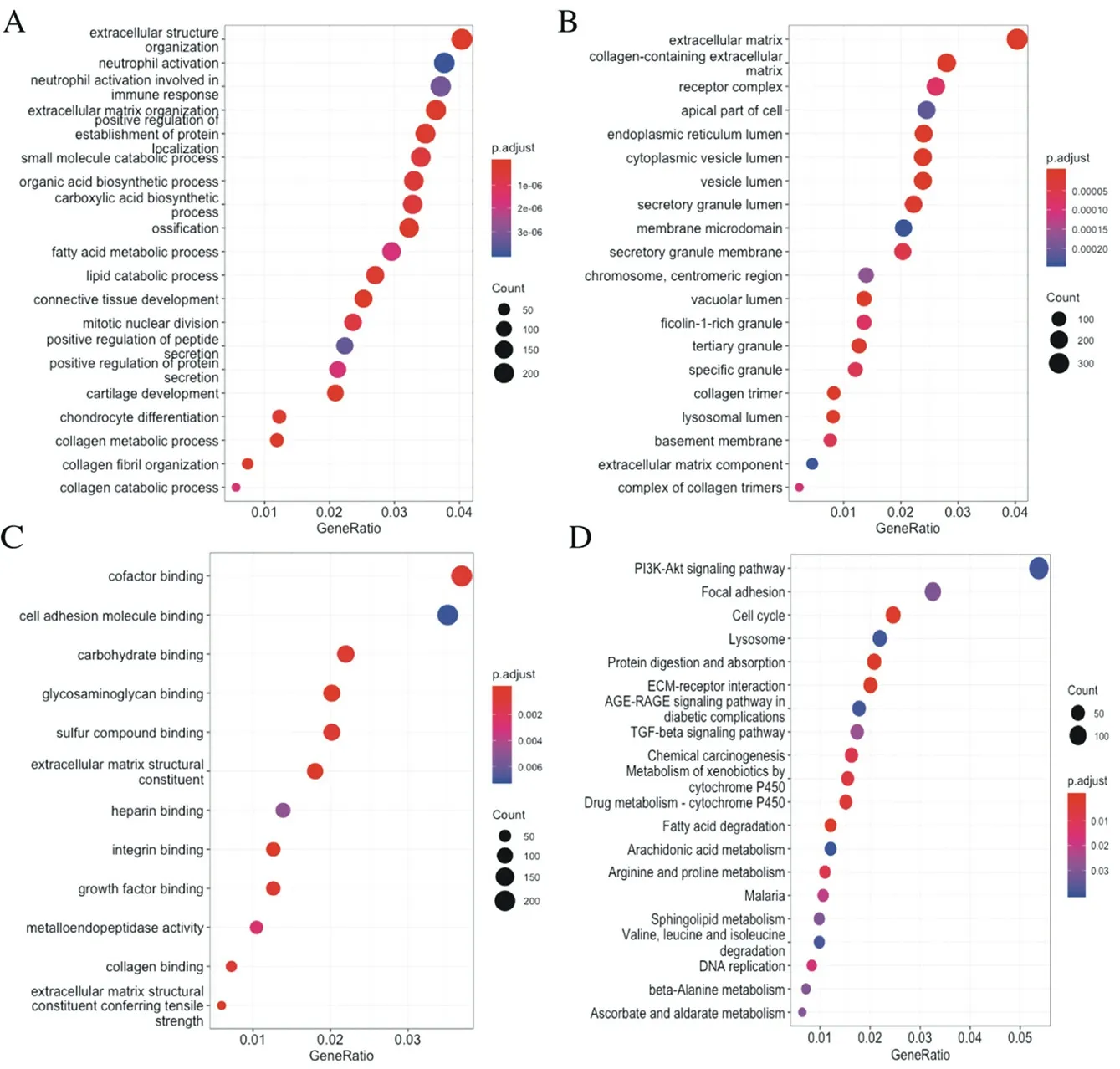
Fig.4 Enriched pathway in LINC01614-related genes
4. Discussion
With the development of sequencing technology, the structure and function of non-coding RNA have been elucidated gradually. LncRNAs are transcripts which mostly do not translated into proteins and are more than 200nt [9]. LncRNA plays a role in the development of cancer by interacting with DNA, chromatin, signaling and regulatory proteins, and a variety of cellular RNA [10]. ZHANG et al. found that LncRNA HOXC-AS3 can promote the development of GC through the interaction with YBX1 [11]. XU[12] et al. found that PVT1 promoted the invasion and metastasis of GC cells through FOXM1-mediated pathway. ZHENG et al. [13] found that KRT19P3 can regulate COPS7A-mediated NF-κB pathway to inhibit tumor growth and metastasis. These studies indicate that LncRNA can play an important role in the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis prediction of GC, providing a new idea for the accurate treatment and prognosis diagnosis of GC. Similarly, LINC01614 has been found involved in the development of multiple malignancies. LIU et al. [14] found that LINC01614 was involved in the development of lung adenocarcinoma by inhibiting miR-217 to promote the expression of FOXP1. SUN et al. [15] also confirmed the correlation between LINC01614 and lung cancer. LINC01614 was significantly upregulated in non-small cell lung cancer, and its expression level was correlated with the prognosis of patients [16]. Similar results have been found in breast cancer, LINC01614 has been confirmed to be an adverse prognostic marker in breast cancer and is associated with HR + / HER2 + molecular subtypes, and it is regulated by TGF-β and FAK signals [17]. These results suggest that LINC01614 is closely related to the occurrence and development of cancer.
In this study, qRT-PCR showed that the expression of LINC01614 was increased in GC tissues and GC cell lines. At the same time, the analysis results of TCGA database and GEO dataset GSE95667 suggested that the expression of LINC01614 was significantly different in the paired GC tissues and adjacent normal tissues, the results was consistent with the experimental results. Through further bioinformatics analyses, the high expression of LINC01614 was associated with higher histological grade and residual tumor. According to the results of survival analysis, the OS time of GC patients in the group with high expression of LINC01614 was shorter than that in the group with low expression of LINC01614. The results of the pathway enrichment analyses also suggested that LINC01614 may involve in a variety of pathways including the occurrence and development of GC.
In summary, LINC01614 related with the occurrence and development of GC and may be a potential prognostic marker. And we will do more research including analyzing clinical sample and interfere LINC01614 expression in GC cell lines so as to explore the role of LINC01614 in GC.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Network pharmacological study of Qingfei Paidu Decoction intervening on cytokine storm mechanism of COVID-19
- Study on the Potential Mechanism of Drug Pair "Honeysuckle-Astragalus" on COVID-19 based on Network Pharmacology
- Observation on clinical application effect of ankle rehabilitation robot
- Meta-analysis of the relationship between post-stroke depression and the risk of mortality
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy of combined traditional Chinese and western medicine in the treatment of granulomatous mastitis
- The effect of plasma uric acid on oxidative stress in ankylosing spondylitis by Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway
