经皮射频消融术与腹腔镜肝癌切除术治疗小肝癌的临床效果比较
2020-07-04谭立业汪晶肖阳夏玲洋
谭立业 汪晶 肖阳 夏玲洋

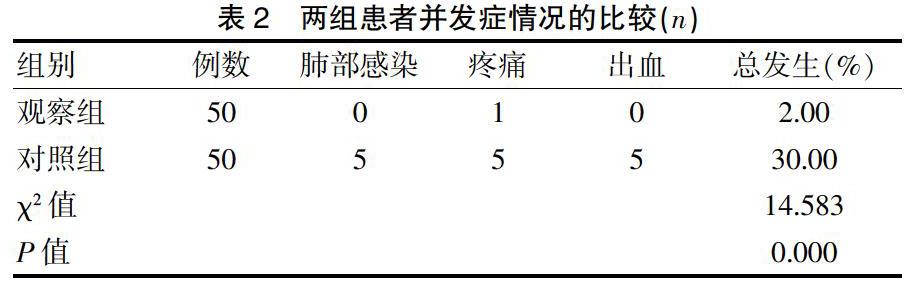

[摘要]目的 比較经皮射频消融术与腹腔镜肝癌切除术治疗小肝癌的临床效果。方法 选取2016年2月~2018年2月我院收治的100例小肝癌患者作为研究对象,按照入院顺序方法分为观察组(50例)与对照组(50例)。观察组采用经皮射频消融术治疗方法,对照组采用腹腔镜肝癌切除术治疗方法。比较两组的肝功能指标、并发症情况、生存时间和无瘤生存时间。结果 观察组治疗后的丙氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT)、天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)水平低于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组的并发症总发生率低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组的生存时间和无瘤生存时间长于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 经皮射频消融术治疗小肝癌效果显著,且能够降低其并发症发生率,延长患者生存时间,改善患者肝功能。
[关键词]经皮射频消融术;腹腔镜肝癌切除术;小肝癌;临床效果
[中图分类号] R735.7 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-4721(2020)5(b)-0096-03
Comparison of clinical effects between percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and laparoscopic liver cancer resection in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma
TAN Li-ye1 WANG Jing2 XIAO Yang1 XIA Ling-yang3▲
1. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Mudanjiang Medical University, Heilongjiang Province, Mudanjiang 157000, China; 2. Department of Cardiology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Mudanjiang Medical University, Heilongjiang Province, Mudanjiang 157000, China; 3. Department of Neurosurgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Mudanjiang Medical University, Heilongjiang Province, Mudanjiang 157000, China
[Abstract] Objective To compare the clinical effect of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and laparoscopic liver cancer resection in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. Methods A total of 100 patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma admitted to our hospital from February 2016 to February 2018 were selected as study objects. They were divided into the observation group (n=50) and the control group (n=50) according to the order of admission. In the observation group, percutaneous radiofrequency ablation was used, while in the control group, laparoscopic liver resection was adopted. Liver function indexes, complications, survival time, and tumor-free survival time were compared between the two groups. Results The levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) in the observation group after treatment were lower than those in the control group, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The total incidence of complications in the observation group was lower than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The survival time and tumor-free survival time of the observation group were longer than those of the control group, with statistical differences (P<0.05). Conclusion Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation is effective in treating small hepatocellular carcinoma, and can reduce the incidence of complications, prolong the survival time of patients, and improve liver function.
