Changes of serum β2-MG, Cys C and urine mAlb levels in patients with ureteral calculi before and after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy and their clinical significance
2020-07-04MingShuangLiuWenXueFeng
Ming-Shuang Liu, Wen-Xue Feng
Emergency Department, Chengdu 363 Hospital, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan
Keywords:Ureteral calculi Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy β2-MG CysC Urine mAlb
ABSTRACT Objective: To investigate the changes of serum β2 microglobulin (β2-MG), cystatin C (CysC) and urine microalbumin (mAlb) levels in patients with ureteral calculi before and after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy and their clinical significance. Methods Sixty-eight patients with ureteral calculi admitted to the hospital between June 2018 and June 2019 were selected as the observation group. 35 volunteers who received physical elimination in the hospital during the same period were selected as the control group. Levels of β2-MG, Cys C and urine mAlb in the observation group were compared before and after treatment, and compared with those in the control group. Changes in serum β2-MG, Cys C and urine mAlb levels and renal function indicators [blood urea nitrogen (BUN), serum creatinine (SCr)] in patients with different prognosis in the observation group after treatment were analyzed. The value of serum β2-MG, Cys C and urine mAlb levels in the diagnosis and treatment of ureteral calculi was analyzed with ROC curve. The correlations between serum β2-MG, Cys C and urine mAlb levels and renal function indexes were analyzed. Results Serum β2-MG, Cys C and urine mAlb levels in the observation group before treatment were significantly higher than those in the same group after treatment or those in the control group (P<0.05). Serum β2-MG, Cys C and urine mAlb levels, BUN and SCr in patients with residual stones were significantly higher than those in patients without (P<0.05). ROC curve analysis showed that the sensitivity and the area under the curve of combined detection of serum β2-MG, Cys C and urine mAlb levels for evaluating the curative effect of extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy on ureteral calculi were significantly higher/larger than those of single detection of the three (P<0.05). Partial correlation analysis showed that serum β2-MG, Cys C and urine mAlb levels were positively correlated with BUN and SCr (P<0.05). Conclusion There are obvious changes of serum β2-MG, Cys C and urine mAlb levels in patients with ureteral calculi before and after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. The combined detection of the three indexes is helpful for the early diagnosis of ureteral calculi and the evaluation of renal function after lithotripsy. They can provide reference for protecting renal function in patients with ureteral calculi treated by extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy.
1. Introduction
Ureteral calculus is also known as upper urinary tract calculus. They are common in urology and often occur in middle and middle-aged adults. Common symptoms include lower abdominal pain, hematuria, obstruction, or infection. The causes are closely related to metabolism and infection[1],Diagnosis is made through medical history, physical examination, X-ray, etc. At present, its main purpose in clinical treatment is to relieve pain and protect renal function[2]. In recent years, extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy(ESWL) has become an important treatment method for patients with ureteral calculi due to its advantages such as less trauma, safety and good curative effect[3];However, clinical research has found that for most patients with surgical lithotripsy, the phenomenon of postoperative stones difficult to discharge is still exists, which has caused some patients to suffer from small stones for a long time after surgery, and even had the risk of renal function damage[4];Serum β2 microglobulin (β2-MG) is mainly produced by lymphocytes, and its increased expression level is commonly found in renal hypofunction, immune disorders or malignancies, and is mainly used to identify the source of proteinuria,Cystatin C (CysC) is a newly developed sensitivity index for evaluating renal function. CysC concentration in the blood changes with the change of glomerular filtration rate when renal function is impaired, When the glomerular filtration rate decreases, the concentration of CysC in the blood will increase significantly,urinary microalbumin (mAlb) was originally a sensitive indicator of glomerular microangiopathy in diabetic patients and has recently become an effective marker of kidney damage, Related studies have pointed out that changes in serum β2 microglobulin (β2-MG), cystatin C (CysC), and urine microalbumin (mAlb) levels have a positive role in predicting early renal impairment[5], but currently changes of serum β2-MG, Cys C and urine mAlb in patients with ureteral calculus before and after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy and its clinical significance are still in the preliminary stage of exploration in China, To this end, a clinical controlled study is conducted. The specific results are reported as follows.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 General Information
A total of 68 patients with ureteral calculi received treatment in our hospital from June 2018 to June 2019 (as the observation group) were selected as the subjects,In 68 cases,gender: 46 males and 22 females, aged 30-65 (51.03 ± 3.09) years, stone diameter 1-3 (1.68 ± 0.56) cm, stone location: 41 cases in the upper ureter, 27 cases in the lower ureter. Another 35 volunteers who underwent a health checkup in our hospital during the same period were used as the control group, 22 males and 13 females, aged 31-64 (50.99 ± 3.13) years. Inclusion criteria: ①Diagnosis of ureteral stones was confirmed by X-ray examination after enrollment;②Medicinal drugs were not used before enrollment;③Without complicated liver kidney and other important organ function damage;④Patients signed informed consent forms knowing the content of this study. Exclusion criteria: ① combined with stones in other parts; ② combined with renal and other urinary system diseases; ③ the presence of systemic malignancies; ④ the existence of absolute contraindications to extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy; ⑤ the presence of infectious diseases; ⑥ the existence of severe mental disease; ⑦ combined diabetes, hypertension and kidney disease.
2.2 Methods
①Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy: under the guidance of ESWL-190 color ultrasound (shenzhen huikang), extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy was performed for the patients,the upper and lower ureters were placed in supine and prone positions,with the help of skin,The rubber balloon is coupled to contact with patients,and the focal point is positioned by color ultrasound.,then the shock wave (voltage is 12kv) enters the stone site through the ventral or dorsal of the patient, and the number of each shock waves is 2000-2400 times.②Detection of serum β2-MG, Cys C and urine mAlb levels: 3 ml venous blood and 2mL urine samples were collected from the observation group before,after treatment(3 months after surgery) patients and control group,The serum was separated by conventional centrifugation and kept for test,Serum Cys C expression level was detected by ELISA,Serum level β2-MG was detected by LETIA, and urine mAlb level was detected by immunoturbidimetry.
2.3 Observation indexes and detection judgments
①Comparison of serum β2-MG, Cys C and urine mAlb levels before and after treatment in the observation group and control group;②Serum β2-MG, Cys C, urine mAlb levels and renal function indicators changes of patients with different prognosis after treatment in the observation group, 3 months after treatment, the ureteroscope was used to observe the residual stones of the patients,If small stones were observed under the ureteroscope, the patients were recorded as residuals, and the serum β2-MG, Cys C, and urine mAlb levels were compared between residual and non-residual subjects;At the same time, SMT-100 automatic biochemical analyzer was used to detect urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine (SCr) in patients with different prognosis.(3)The value of serum β2-MG Cys C and urine mAlb in the diagnosis and treatment of ureteral calculi.(4)Correlation analysis between serum β2-MG, Cys C, urine mAlb levels and renal function indexes.
2.4 Statistical analysis
SPSS 20.0 software was used to analyze and process the research data.,Measurement data such as serum β2-MG, Cys C, and urine mAlb levels were indicated by(±s),Serum levels of β2-MG Cys C and urine mAlb in the observation group before and after treatment were compared by repeated measure anova, serum β2-MG, Cys C, and urine mAlb levels between the two groups were compared by independent sample t-value test, ROC curve was used to analyze the value of serum levels of β2-MG Cys C and urine mAlb in the diagnosis and treatment of ureteral calculi,Correlation was analyzed using partial correlation analysis.P<0.05 was considered statistically significant。
3. Results
3.1Changes in serum β2-MG, Cys C and urine mAlb levels in the observation group before and after treatment and in the control group
Serum β2-MG, Cys C and urine mAlb levels in the observation group before treatment were significantly higher than those in the observation group after treatment and in the control group(P<0.05),There were no significant differences in serum levels of β2-MG Cys C and urine mAlb between the observation group and the control group after treatment(P>0.05),see Table 1.
3.2 Changes in serum β2-MG, Cys C, urinary mAlb levels, and renal function indexes of patients with different prognosis after treatment in the observation group
Follow-up data showed that 21 patients had stone residues in the observation group after treatment, 47 patients had no stone residues, and serum β2-MG,Cys C,urine mAlb levels,BUN and SCr in the remaining patients were significantly higher than those without residues,see Table 2.
3.3 The value of serum β2-MG、CysC and urine mAlb levels in the diagnosis and treatment of ureteral calculi
ROC curve analysis indicates that the combined detection of serum β2-MG, Cys C, and urine mAlb levels has a sensitivity of 88.6%,the area under the curve 0.953 was significantly higher than those in single detection,as shown in Figure 1, to evaluate the efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy for ureteral stones with the combined detection of serum β2-MG, Cys C, and urine mAlb levels has a sensitivity of 85.9%, and the area under the curve is 1.000compared with those in single detection,see Figure 2.
Table 1 Changes in levels of serum β2-MG、CysC and urine mAlb in the control group before and after treatment(±s)

Table 1 Changes in levels of serum β2-MG、CysC and urine mAlb in the control group before and after treatment(±s)
Group Time quantum β2-MG(mg/L) CysC(mg/L) Urinary mAlb(mg/L)Observation group before treatment(n=68) 4.89±1.49 1.65±0.26 21.95±2.06 after treatment(n=68) 2.26±1.02 1.01±0.15 8.26±1.58 F value - 144.257 309.132 1890.845 P value - <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 control group (n=35) 2.25±0.90 0.98±0.13 w7.76±1.48 t(Compared with the observation group before treatment)、P - 9.606、0.000 14.327、0.000 36.190、0.000 t(Compared with the observation group before treatment)、P - 0.049、0.961 1.004、0.318 1.554、0.123

Table 2 Changes in serum β2-MG, Cys C, urinary mAlb levels, and renal function indexes of patients with different prognosis after treatment in the observation group.
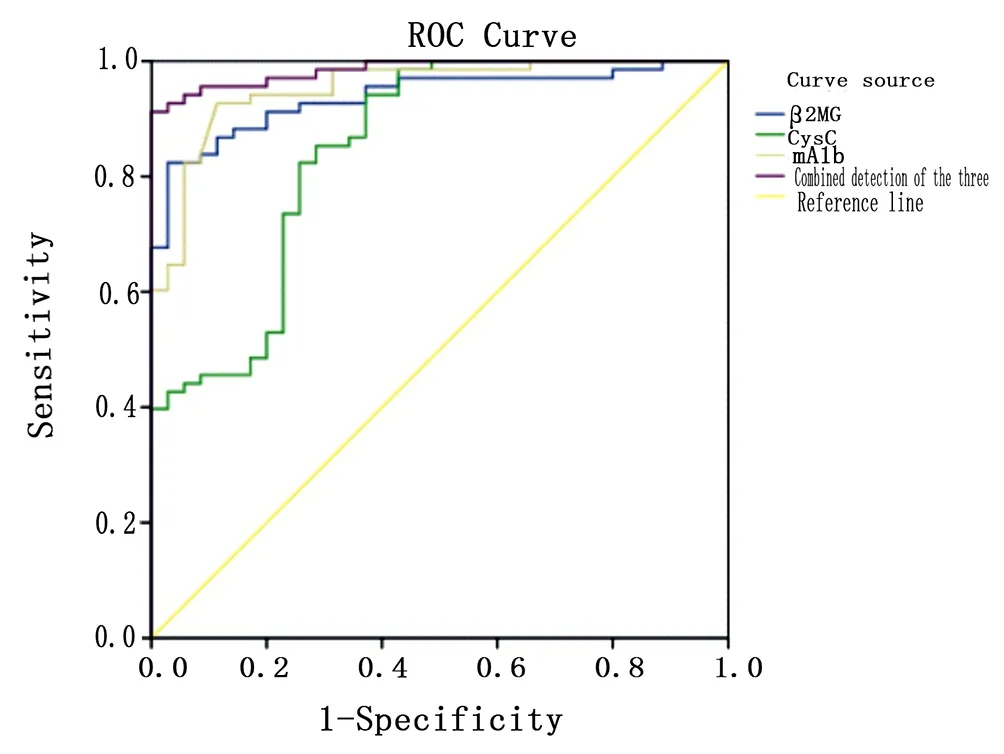
Figure 1:ROC curve of diagnosis of ureteral calculi with serum levels of 2-mg Cys C and urine mAlb

Figure 2:The ROC curve of extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy for ureteral calculi was evaluated by serum level of β2-MG、Cys C and urine mAlb
3.4Correlation analysis of serum β2-MG、Cys C and urinary mAlb levels with renal function indexes
Partial correlation analysis showed that serum β2-MG, Cys C and urine mAlb levels were significantly positively correlated with BUN and SCr (P <0.05), see table 3.
4. Discussion
Ureteral calculus is a common disease in clinical urology. The etiology is related to long-term bad diet habits, which lead to the precipitation and aggregation of cholesterol calculus, calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate and other substances, causing the formation of calculus,The final manifestation is unbearable abdominal pain, hematuria, hydronephrosis, and renal function injuries, etc. [6],according to literature reports, extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy has a clear therapeutic effect on patients with ureteral calculi diameter> 0.5 cm and obvious renal colic, but conservative treatment is ineffective[7],And with the continuous update of extracorporeal lithotriptor and the improvement of medical treatment, extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy has become an effective treatment for many patients with ureteral calculi. Some scholars have confirmed that ureteral stones still have residual stones after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy[8],and residual stones not only affect the therapeutic effect of patients but also damage renal function, affect the prognosis of patients, so actively explore and evaluate the molecular biomarkers for evaluating lithotripsy patients renal function after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy have become the focus of clinical attention.
β2-MG is a single-chain low-molecular-weight protein composed of 100 amino acids. It can participate in the lymphocyte surface recognition, and is closely related to the killer cell receptor,nucleated cells can synthesize β2-MG,The expression level of β2-MG in blood and urine MG has important clinical significance in the diagnosis of various diseases,studies have shown that serum β2-MG has a positive role in early renal function prediction[9-10];Cys C is a low molecular weight non-glycosylated basic low protein,in the body, the generation rate is constant, and the Cys C in the circulation is cleared only by the glomerular filtration,it has been regarded as an effective marker to reflect the changeof glomerular filtration rate. Recent studies have shown that Cys C can be used as an effective indicator for evaluating early renal function[11];urine mALB is also an effective indicator for assessing the renal function of patients, under normal circumstances, there is mALB in urine, once the expression level of mALB in urine is higher than the normal range, it indicates that urine The increase of microalbumin in the fluid often indicates that the kidney's filtration barrier is impaired[12-13]。Renal function of patients will change before and after ureteral calculi undergoing extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy treatment [14],and renal function will also differ in patients with different prognosis after treatment, BUN and SCr are important markers for predicting renal function[15]. Serum β2-MG, Cys C, and urine mAlb levels will be affected by basic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and kidney disease. The subjects included in this study excluded basic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and kidney disease, which were better excluded the influence of other factors on these indicators. In addition, the results of this analysis showed that the serum β2-MG, Cys C, and urine mAlb levels in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group, however, there was no significant difference between the level after treatment and the control group,indicating that the serum β2-MG, Cys C, and urine mAlb levels were significantly abnormal before treatment in patients with ureteral calculus, after treatment with extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy, serum β2-MG, Cys C, and urine mAlb levels could be effectively adjusted. Further research found that serum β2-MG, Cys C, urinary mAlb levels, BUN, and SCr were significantly higher in the observation group patients with residue calculus after treatment than in those without residue calculus, and after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy for ureteral calculus, the renal function improvement of patients with residual stones was not as good as those without residual stones, so the serum β2-MG, Cys C, and urine mAlb levels are relatively higher, and the analysis of this ROC curve suggests that the combined detection of serum β2-MG, Cys C, and urine mAlb levels to evaluate ureteral calculus and its postoperative efficacy, its sensitivity and the area under the curve were significantly higher than those in single detection,Further partial correlation analysis found that serum β2-MG, Cys C, and urine mAlb levels were significantly positively correlated with BUN and SCr, thereby confirming serum β2-MG , Cys C, urinary mAlb levels have important clinical significance for early diagnosis of ureteral stones and assessment of renal function impairment after surgery. Changes in serum β2-MG, Cys C, and urinary mAlb levels of patients before and after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy may be considered as an effective marker for evaluating renal function.
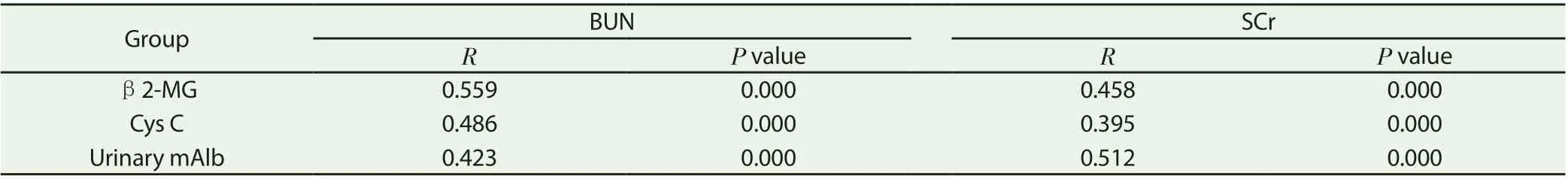
Table 3 Correlation analysis of serum β2-MG、Cys C and urinary mAlb levels with renal function indexes
Based on the above analysis, serum β2-MG, Cys C, and urine mAlb expression levels have clear predictive value in the early diagnosis of ureteral calculi and renal function damage after lithotripsy.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Clinical effect of preventive nursing on the rate of deep vein thrombosis in patients with lung cancer: A meta-analysis
- A network pharmacology approach to explore action mechanisms of Bi xie and Tu fuling for treating gouty arthritis
- Study on the value of parecoxib sodium preemptive analgesia for laparoscopic surgery based on postoperative pain and stress mediator secretion
- Study on the effect of Baiban Ointment on the whole gene expression profile of vulvar sclerosing lichen
- To investigate the effects of butylphthalide on reducing neuronal apoptosis in rats with cerebral infarction by inhibiting the JNK / P38 MAPK signaling pathway
- Study of KAP status and influencing factors of Protective Behaviour on COVID-19 among Hainan Mobile Phone Users
