To investigate the effects of butylphthalide on reducing neuronal apoptosis in rats with cerebral infarction by inhibiting the JNK / P38 MAPK signaling pathway
2020-07-04YanSunYuanZouQianXueXiaoQinWang
Yan Sun , Yuan Zou✉, Qian Xue , Xiao-Qin Wang
Department of Neurology, the First Affiliated Hospital of North China University,Zhangjiakou City,Hebei Province 075000
Keywords:Cerebral infarction Butylphthalide Nerve cells Infarct size JNK/P38 MAPK signaling pathway
ABSTRACT Objective: To investigate the effects of butylphthalide on reducing neuronal apoptosis in rats with cerebral infarction by inhibiting the JNK / P38 MAPK signaling pathway. Methods: Forty-eight SD male rats were divided into DZ group (control group), CI group (model group) and NBP group (butylphthalide group). Rats in CI group and NBP group were used to establish cerebral infarction models. NBP group used NBP. The solution (80 mg / (kg · d)) was administered orally, and the remaining two groups were administered with the same volume of peanut oil. After 14 consecutive days of treatment, the Zea Longa score was used to evaluate the neurological function of DZ, CI and NBP rats. Scoring, TTC staining was used to observe the cerebral infarction volume of rats in DZ group, CI group and NBP group, HE staining was used to observe the pathological morphology of brain tissue in DZ group, CI group and NBP group. Neuronal apoptosis, Western blot was used to detect the expression of p-JNK and p-p38MAPK in brain tissues of DZ group, CI group and NBP group. Results: The neurological function of the rats in the CI group was higher than that in the DZ group, and the difference was statistically significant (P <0.05). The neurological function score of the rats in the NBP group was reduced compared with the CI group, and the difference was statistically significant (P <0.05). The cerebral infarction volume in the group was 35.56% higher than that in the DZ group, and the difference was statistically significant (P <0.05). The minor infarct volume in the NBP group was 21.59%, which was less than that in the CI group, and the difference was statistically significant (P <0.05). Nerve cells are neatly sorted, with a large number. The gap between blood vessels and interstitial tissue in the CI group is enlarged, the cells are severely contracted, and the neuron structure is incomplete. Compared with the CI group, the NBP group has reduced neuron contraction and increased number; The dead nerve cells were brown. The apoptosis rate of nerve cells in the CI group was 79.65% higher than that in the DZ group was 5.82%. The difference was statistically significant (P <0.05). The nerve cell apoptosis rate in the NBP group was 30.23%. Compared with CI group, the difference was statistically significant (P <0.05); Western blot results showed that p-JNK and p-p38MAPK protein expression in CI group was higher than that in DZ group, and the difference was statistically significant (P <0.05). The levels of p-JNK and p-p38MAPK proteins in the NBP group were lower than those in the CI group. There was statistically significant (P <0.05). Conclusion: Butylphthalide can improve neurological damage, reduce apoptotic nerve cells, and reduce infarct volume in rats with cerebral infarction, which is related to the inhibition of JNK / P38 MAPK pathway expression.
1. Introduction
Cerebral infarction (CI) is a high incidence disease in clinic. It can block cerebral blood flow circulation for many reasons and induce brain neuron apoptosis continuously. Some patients suffer from cerebral blood supply dysfunction and decrease of blood flow due to the circulation of embolic substances into the brain. Due to the continuous improvement of medical level and the increase of aging, the number of patients with cerebral infarction continues to increase. According to big data, there are nearly 2.3 million patients with cerebral infarction every year in China, about 50% of them die, and the life safety of patients can not be guaranteed [2]. Previous literature shows that the traditional medicine treatment of cerebral infarction is mainly through improving hemodynamics to alleviate the disease, but because the body's bearing capacity and other reasons are that the curative effect is general, patients' disease cannot be completely controlled, and the disability rate and death rate are still rising [3].
The main component of NBP is racemic dl-3-n-butylphthalide, which is a successful anti cerebral ischemia drug developed in China. Previous literature shows that NBP can improve the blood-brain barrier, improve the free radicals in blood vessels, reduce ischemiareperfusion, and improve the cerebral hemodynamics [4]. Mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) mainly includes three pathways: JNK, p38 and ERK, which are involved in the expression of various tumors. It is found that cytokines and extracellular stimulators can regulate the expression of MAPKs signal pathway, promote tumor metastasis and participate in the damage of blood-brain barrier [5]. In this paper, the relationship between butylphthalide and JNK / p38 MAPK signal and the effect on neuron apoptosis were studied by establishing cerebral infarction model in rats.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental animals and groups
48 SPF male SD rats, aged 4-5 weeks, were purchased from Beijing Experimental Animal Research Center. The rats weighed 200g-250g and were kept in constant temperature environment for one week. After adapting to the surrounding environment, they were divided into three groups. The rats were compared with the normal rats (duizhao, DZ group) to establish the brain infarction model rats (cerebral) Infarction (CI group) and n-butylphthalide (NBP group) rats after establishing the cerebral infarction model, 16 rats in each group. In accordance with animal ethics regulations, Certificate No.: Jingdong Zi 01-3054
2.2 Main instruments and reagents
Ding Bentai (p-p38MAPK), p-JNK antibody (American Abcam), HE staining kit, TUNEL Kit (Shanghai Shenglong), Goat anti rabbit IgG two antibody (American Abcam), gel electrophoresis and electrophoretic instrument (Beijing Zping Technology Co., Ltd.).
2.3 Establishment of animal model
The rats in CI group and NBP group were fixed in supine position for 12h before operation. The rats were anesthetized in abdominal cavity with 6% chloral hydrate. The rats were opened in the middle of the neck, the skin and fascia were exposed and cut, and the common carotid artery of the rats was found. A small cut was made at the right common artery nearest to the heart with scissors, from which the thread bolt was inserted into the common artery until the resistance was obvious In the DZ group, normal saline was injected into the tail vein, only the skull was exposed, and no other treatment was done [6].
2.4 Intervention methods
NBP group: the NBP and peanut oil were diluted into a 7g / L solution, and the NBP solution of 70 mg / (kg · d) was administered to the stomach on the first day after modeling, and the other two groups were administered with 70 mg / (kg · d) peanut oil for 14 days.
2.5 Neurological score
After 14 days of continuous gavage, the limbs of the three groups of rats were observed, and tail lifting and suspension test was conducted. The rats without spasm and unconsciousness were included in the neurological score. Zea longa scoring standard was selected for neurological function, see Table 1 for details.

Table 1 neurological scoring criteria
2.6 TTC staining to observe the percentage of cerebral infarction volume in rats
The three groups of rats were killed after 14 days of continuous gavage. The brain tissues of the rats were taken out in a sterile state and stored in an environment of - 80 ℃. After 5 minutes, the frontal pole with a thickness of 2 mm was stored in a 1% TTC solution. The normal brain tissue was red and the infarct tissue was white. The professional image analysis software processed and analyzed the image to calculate the percentage of cerebral infarction volume.
2.7 HE staining
After the rats were killed, a small amount of brain tissue was extracted, fixed with formaldehyde, dehydrated with 85 °medical alcohol, transparent with diphenyl, embedded in paraffin, overnight, stained with he, and observed the pathological changes of brain tissue with microscope according to the instructions
2.8 TUNEL method to detect the apoptosis of brain cells in each group
TUNEL staining was used to detect the apoptosis of brain cells in three groups of rats. Each section randomly selected 5 fields of vision which were not cross repeated and observed under high power optical microscope, the brown granules appeared as apoptosis. The apoptotic rate of cardiomyocytes is calculated by dividing the number of apoptotic cells by the total number of cells and multiplying by 100%.
2.9 Western blot to detect the protein levels of p-JNK and P-P38MAPK
The brain tissues of the three groups were added to the lysate and centrifuged at 4 ℃ for 30 minutes. BCA protein assay kit (Pierce) was used to detect the total protein concentration. After SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, the samples were transferred to PVDF membrane and incubated overnight at 4 ℃ with anti-p-jnk, P-P38MAPK and GAPDH antibodies. After washing, the samples were incubated with horseradish peroxidase conjugated two antibodies for 60min. After cooling, the protein expressions of p-JNK and P-P38MAPK were calculated. The data were processed by nuance analysis software, exposed by ECL, and photographed.
2.10 Statistical methods
In this paper, spss22.0 software was used to analyze the data. Nerve function, neuron apoptosis, infarct volume, p-JNK and p-p38 protein groups in DZ group, CI group and NBP group were compared with each other by t-test. Single factor analysis was used between the groups. Standard deviation of addition and subtraction (±s) was used to calculate the data. P < 0.05 indicated that the difference was statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1 Comparison of nerve function among three groups of rats
The scores of neurological function (3.49 ± 0.47) and (1.53 ± 0.56) in CI group and NBP group were higher than those in DZ group (0.00 ± 0.00). The difference was statistically significant (tcivsdz = 27.9, tnbpvsdz = 10.93, P < 0.05). The difference was statistically significant (t = 10.72, P < 0.05). See Figure 1

Figure 1 Comparison of nerve function in three groups of rats (compared with DZ group * P <0.05; compared with CI group #P <0.05)

Table 1 Comparison of nerve function in three groups of rats
3.2 Volume comparison of cerebral infarction in three groups
The volume of cerebral infarction in CI group and NBP group was (32.51 ± 4.17)% and (19.44 ± 2.39)% higher than that in DZ group (0.00 ± 0.00)%, the difference was statistically significant (tcivsdz = 31.18; tnbpvsdz = 32.54p < 0.05), NBP group was less than CI group, the difference was statistically significant (t = 10.88, P < 0.05), as shown in Figure 2

Figure 2 Comparison of cerebral infarction volume in three groups of rats (compared with DZ group * P <0.05; compared with CI group #P <0.05)

Table 2 Comparison of cerebral infarction volume in three groups of rats
3.3 Pathological analysis of brain tissue in three groups of rats
In DZ group, the nerve cells were arranged orderly with a large number. In CI group, the gap between blood vessels and brain interstitium was enlarged, the cell pyknosis was serious, and the neuron structure was incomplete. In NBP group, compared with CI group, the neuron pyknosis was reduced and the number was increased, as shown in Figure 3

Figure 3 Pathological analysis of brain tissue in three groups of rats (× 200)
3.4 TUNEL method for the detection of neuronal apoptosis in three groups of rats
The apoptosis rate of neurons in CI group and NBP group was (70.48 ± 8.11)% and (34.26 ± 4.81)% respectively, which was higher than that in DZ group (3.50 ± 0.61)%, the difference was statistically significant (tcivsdz = 32.94; tnbpvsdz = 25.38, P < 0.05), NBP group was less than CI group, the difference was statistically significant (t =, 15.37, P < 0.05), as shown in Figure 5 Figure 5 Comparison of neuronal apoptosis rates in three groups of rats (compared with DZ group*P <0.05; compared with CI group#P <0.05)

Figure 4 Neuron apoptosis in three groups of rats (×200)
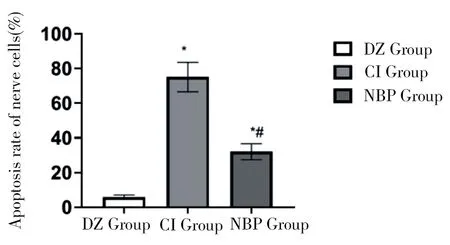
Figure 7 Comparison of the protein expression levels of p-JNK and p-p38MAPK in the brain tissues of the three groups of rats (compared with DZ group * P <0.05; compared with CI group #P <0.05)

Table 3 Apoptosis rates of three groups of rats
3.5 Western blot to detect the effect of butylphthalide on the protein levels of p-JNK and P-P38MAPK in three groups of rats
Western blot showed that the expression of p-JNK in CI group and NBP group was (1.25 ± 0.45), (0.75 ± 0.16) higher than that in DZ group (0.32 ± 0.11), the difference was statistically significant (tcivsdz = 8.030; tnbpvsdz = 8.585, P < 0.05), NBP group was less than CI group, the difference was statistically significant (t = 4.188, P < 0.05); P-P38MAPK in CI group and NBP group The protein expression was (2.47 ± 0.22), (1.46 ± 0.18) higher than that of DZ group (0.87 ± 0.12), the difference was statistically significant (tcivsdz = 25.54; tnbpvsdz = 10.91, P < 0.05), NBP group was less than CI group, the difference was statistically significant (t = 14.21, P < 0.05), as shown in Figure 6-7.

Figure 6 Protein levels of p-JNK and p-p38MAPK in brain tissue of three groups of rats

Table4 Comparison of the protein expression levels of p-JNK and p-p38MAPK in the brain tissues of the three groups of rats
4. Discussion
Cerebral infarction is a brain disease caused by oxygen deficiency in brain tissue for a long time. At present, it has been found that JNK / p38 MAPK signaling pathway is closely related to cerebral infarction, which is involved in the regulation of neuronal differentiation and apoptosis in the pathological process of cerebral infarction, as well as other brain diseases [7]. The key to the treatment of cerebral infarction is to prevent ischemia-reperfusion. At present, drug pretreatment is used to reduce the irreversible damage of nerve cells and protect brain tissue. When drug treatment is used for cerebral ischemia, the area of ischemic focus can be reduced [8]. In this study, the JNK / p38 MAPK signal pathway and neuronal apoptosis were observed by butylphthalide gavage in the cerebral infarction model. The results are as follows.
In this study, we found that the neurological deficit of CI group was the most serious, compared with CI group, NBP group reduced the neurological damage. Compared with CI group, NBP group had the largest cerebral infarct volume, which indicated that butylphthalide could reduce the infarct area and improve the neurological damage of cerebral infarction. P38 MAPK and JNK are one of the downstream factors of MAPK signal. A large number of studies have found that JNK / p38 MAPK signal is closely related to the occurrence and development of cerebral infarction. When cerebral infarction occurs in the body, the blood flow of cerebral vessels is impaired. The activated JNK / p38 MAPK signal induces neurological dysfunction by regulating a variety of signals, mainly including inflammatory factors and nitric oxide, which will aggravate the brain at the same time Necrosis appeared in the tissue of the partial perfusion area, forming the ischemic area and worsening the condition [9]. A large number of clinical studies have found that butylphthalide can reduce the expression of inflammation by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes, reducing the content of calcium ions in cells, and JNK / p38 MAPK signaling pathway can differentiate a large number of inflammatory factors, indicating that butylphthalide has the function of repairing nerves and can inhibit the activation of JNK / p38 MAPK signaling pathway, which is similar to the results of Yang Shen et al [10-11]. T Chen Yumei et al. [12] found that butylphthalide has the function of protecting brain mitochondria, increasing cerebral microcirculation, strengthening energy metabolism, reducing infarct volume of CI patients, reducing JNK / p38 MAPK signal in platelets through seizure, so as to improve prognosis.
The results of HE staining showed that the number of neurons in CI group was decreased and pyknosis was serious, while that in NBP group was increased and pyknosis was improved. The results of TUNEL showed that the apoptosis of neurons in CI group increased, compared with CI group, the apoptosis of neurons in NBP group decreased. JNK / p38 MAPK signal can aggravate neurons and worsen the condition of patients with infarction. Liu Yongliang et al. [13] confirmed that butylphthalide can reduce platelet aggregation, inhibit JNK / p38 MAPK signal activation, and improve the condition of cerebral infarction, which is similar to the results of Zhang Huikai et al. [14].
In this study, we found that the expression of p-JNK and p-p38 MAPK protein increased in CI group compared with DZ group, and p-JNK and p-p38 MAPK protein decreased in NBP group compared with CI group
The expression of p-JNK and p-p38 MAPK in brain tissue. P-JNK can apoptosis nerve cells in many ways. After brain infarction rats were treated with butylphthalide, the number of nerve cells increased. It is related to the decrease of JNK signal related receptors and a variety of death receptors that lead to apoptosis, which is consistent with the results of Hui Lei [15-16]. Wang Yingyi et al. [11.17] found that p-p38 MAPK was involved in the process of cerebral infarction injury. After p-p38 MAPK was activated, it could regulate the release of Li-6 and other inflammatory factors, and aggravate the condition of cerebral infarction. Butylphthalide can reduce platelet activation, inhibit p-p38 MAPK to regulate the release of inflammation, and reduce neuronal apoptosis, which may be one of the mechanisms of butylphthalide in the treatment of cerebral infarction [18].
To sum up, butylphthalide can improve the nerve injury and reduce the infarct volume in rats with cerebral infarction, which is related to the inhibition of JNK / p38 MAPK pathway expression.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Clinical effect of preventive nursing on the rate of deep vein thrombosis in patients with lung cancer: A meta-analysis
- A network pharmacology approach to explore action mechanisms of Bi xie and Tu fuling for treating gouty arthritis
- Study on the value of parecoxib sodium preemptive analgesia for laparoscopic surgery based on postoperative pain and stress mediator secretion
- Changes of serum β2-MG, Cys C and urine mAlb levels in patients with ureteral calculi before and after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy and their clinical significance
- Study on the effect of Baiban Ointment on the whole gene expression profile of vulvar sclerosing lichen
- Study of KAP status and influencing factors of Protective Behaviour on COVID-19 among Hainan Mobile Phone Users
