脉冲星风云G0.9+0.1的非热辐射特性及能谱演化
2020-06-23方倩朱静萍吴绍华卢方武
方倩,朱静萍,吴绍华,卢方武
脉冲星风云G0.9+0.1的非热辐射特性及能谱演化
方倩,朱静萍,吴绍华,卢方武
(玉溪师范学院 物理与电子工程学院,云南 玉溪 653100)
观测表明,脉冲星风云G0.9+0.1能够辐射出由射电波段延伸至高能伽马射线的光子.建立了一个描述脉冲星风云多波段辐射与动力学演化的理论模型.结合观测数据,数值求解该模型,重建了脉冲星风云G0.9+0.1的多波段辐射谱,并探讨了该星云非热辐射谱的时间演化特性.结果表明,该脉冲星风云的多波段辐射谱随时间的变化具有明显的改变.
脉冲星风云;G0.9+0.1;多波段辐射谱

1 辐射模型
脉冲星风云内部粒子主要来源于中心高速旋转的脉冲星.假设脉冲星风云内部高能粒子主要由正负电对组成,并且均匀分布,则粒子谱的演化方程可描述为
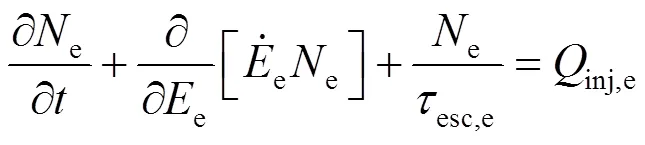



假设脉冲星是一个纯偶极子辐射体,则脉冲星的自转能损功率可表示为


观测表明,脉冲星风云是一个动力学演化系统,也就是其半径和膨胀速度是时间的函数.通常情况,其演化过程可分为3个阶段:自由膨胀阶段、混响阶段和谢多夫-泰勒阶段.本文采用Bucciantini[9]等人于2011年提出的演化理论,则自由膨胀阶段的半径为



由于脉冲星风云中存在着磁场,因此星云内部高能电子在传播的过程中,将受磁场的作用而发生同步辐射,从而产生射电波段至X射线波段的高能光子,采用Zhang[11]等人于2008年给出的辐射理论,则同步辐射光度可表示为

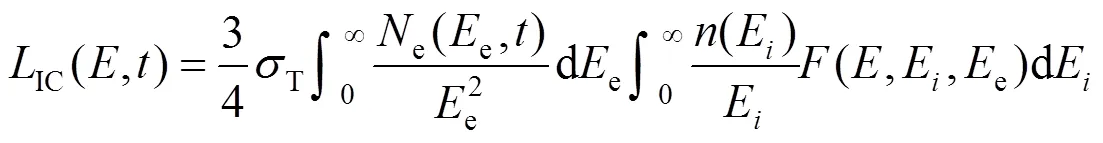
2 模型结果


图1 脉冲星风云G0.9+0.1的能谱拟合结果
由图1可以看出,本文模型可以很好地重建脉冲星风云G0.9+0.1的多波段辐射谱.图形中:Syn表示同步辐射谱,IC-CMB,IC-FIR,IC-NIR,IC-SSC分别表示高能电子与微波背景光子、远红外背景光子、星际光子场和同步辐射光子的逆康普辐射谱,Total表示辐射总谱,Flux表示辐射流量,Energy表示光子的能量.能量范围10-12~10-10MeV的射电波段观测数据点来源于VLA,能量范围10-4~10-1MeV的X射线观测数据(交叉实线)来源于Newton-XMM,能量范围102~105MeV的GeV波段观测数据(虚线)来源于Fermi-LAT,能量范围102~105MeV的TeV波段观测数据点来源于H.E.S.S.由计算结果可以看出,脉冲星风云G0.9+0.1的射电与X射线谱产生于高能电子的同步辐射过程,而高能伽马射线则主要产生于高能电子与远红外和近红外背景光子的逆康普顿散射过程,且同步自康普顿过程对高能伽马射线光子的贡献非常小,可以忽略不计.


图2 脉冲星风云G0.9+0.1的多波段辐射谱随时间的演化
3 结果与讨论
本文基于电子的演化方程、星云的动力学演化和辐射理论,构建了一个描述脉冲星风云多波段辐射的理论模型,并将模型应用于脉冲星风云G0.9+0.1,探讨了该脉冲星风云的能谱辐射特性和动力学演化特性.结果表明,我们的模型能够很好地重建脉冲星风云G0.9+0.1的多波段辐射谱(见图1).由模型结果可知,该脉冲星风云的射电和X射线谱产生于高能电子的同步辐射过程,高能伽马射线产生于高能电子与远红外和近红外背景光子的逆康普顿散射过程.基于能谱重建所得到的参数,还探讨了该脉冲星风云的能谱随时间的演化特性(见图2).由模型结果可知,由于该脉冲星风云具有复杂的动力学演化过程,导致其能谱也会随时间演化变得非常复杂.当然,模型预测出该脉冲星风云能谱在2 000 yr之后的演化情况,还需要观测的进一步检验.
;
[1] CAMILO F,RANSOM S M,GAENSLER B M,et al.Discovery of the Energetic Pulsar J1747-2809 in the Supernova Remnant G0.9+0.1[J].The Astrophysical Journal Letters,2009,700(1):34-38
[2] DUBNER G,GIACANI E,DECOURCHELLE A.High resolution radio study of the pulsar wind nebula within the supernova remnant G0.9+0.1[J].Astronomy and Astrophysics,2008,487(3):1033-1040
[3] PORQUET D,DECOURCHELLE A,WARWICK R S.XMM-Newton spectral analysis of the Pulsar Wind Nebula within the composite SNR G0.9+0.1[J].Astronomy and Astrophysics,2003,401(4):197-203
[4] AHARONIAN F,AKHPERJANIAN A G,AYE K M,et al.Very high energy gamma rays from the composite SNR G 0.9+0.1[J].Astronomy and Astrophysics,2005,432(2):25-29
[5] COLLABORATION H E S S, ABDALLA H, ABRAMOWSKI A, et al.The H E S S Galactic plane survey[J].Astronomy and Astrophysics,2018,612(4):1-61
[6] LERCHE I,SCHLICKEISER R.On the transport and propagation of relativistic electrons in galaxies[J].Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series,1981,47(2):148-160
[7] REN J Y,GAO Q G,LI H Z,et al.Nonthermal Emission and Spectral Evolution Properties of G54.1+0.3[J].Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society,2019,487(3):5781-5787
[8] LI H,CHEN Y,ZHANG L.Lepto-hadronic origin of gamma-rays from the G54.1+0.3 pulsar wind nebula[J].Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society,2010,408(1):80-84
[9] BUCCIANTINI N,ARONS J,Amato E.Modelling spectral evolution of pulsar wind nebulae inside supernova remnants[J].Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society,2011,410(1):381-398
[10] BUCCIANTINI N,BANDIERA R,BLONDIN J M,et al.The effects of spin-down on the structure and evolution of pulsar wind nebulae[J].Astronomy and Astrophysics,2004,422(1):609-619
[11] ZHANG L,CHEN S B,FANG J.Nonthermal Radiation from Pulsar Wind Nebulae[J].The Astrophysical Journal,2008,676(2):1210-1217
[12] FANG J,ZHANG L.Multiband emission from pulsar wind nebulae:a possible injection spectrum[J].Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2010,515(1):20-28
Modelling nonthermal emission and spectral evolution of pulsar wind nebula G0.9+0.1
FANG Qian,ZHU Jingping,WU Shaohua,LU Fangwu
(School of Physics and Electronic Engineering,Yuxi Normal University,Yuxi 653100,China)
The observations indicate that the photons emission from pulsar wind nebula G0.9+0.1 can be ranged from radio to TeV gamma-rays.A theoretical model which includes the multiband photon emission and dynamical evolution of the pulsar wind nebula is presented to investigate non-thermal radiative properties of G0.9+0.1.The calculated results reveal that the observed photon spectral energy distribution can be well reproduced in the framework of our model.According to the parameters obtained from the modelling results of the multiband spectrum, the spectral evolution of G0.9+0.1 is also investigated.The modelling results indicate the non-thermal spectrum of G0.9+0.1 have obvious changes as the increase of time.
pulsar wind nebula;G0.9+0.1;spectral energy distribution
O241.82∶P14
A
10.3969/j.issn.1007-9831.2020.04.011
1007-9831(2020)04-0050-05
2019-11-01
国家自然科学基金青年项目(11803027);云南省高等学校大学生创新创业训练计划项目(2018A12);云南省应用基础研究计划高校联合面上项目(2017FH001-017)
方倩(1996-),女,云南玉溪人,在读本科生.
卢方武(1983-),男,江西九江人,副教授,博士,从事天体物理方面的研究.E-mail:sfweb@yxnu.edu.cn
