A finite-time 3D guidance law based on fixed-time convergence disturbance observer
2020-06-11FengYANGGuangqingXIA
Feng YANG, Guangqing XIA
a State Key Laboratory of Structural Analysis for Industrial Equipment, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China
b Key Laboratory of Advanced Technology for Aerospace Vehicles of Liaoning Province, Dalian University of Technology,Dalian 116024, China
c School of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China
KEYWORDS Disturbance;Finite-time stability;Fixed-time stability;Guidance law;Observer
Abstract In order to achieve accurate interception of high-speed maneuvering targets, this paper presents a relative Line-of-Sight (LOS) velocity based finite-time three-dimensional guidance law design framework, and discusses the application of fixed-time convergence disturbance observer in this framework.Firstly,a simple Lyapunov function is provided to show that the coupled terms in the relative kinematics can be ignored in the proposed guidance law design framework.Secondly,the realizations of several classical guidance laws are analyzed with the proposed framework,including TPN guidance law, finite-time Input-to-State Stability (ISS) guidance law, and sliding mode guidance law.Thirdly,fixed-time convergence disturbance observers are introduced to design the composite finite-time 3D guidance law,and Lyapunov method is employed to show the stability of the guidance system.Numerical simulations with different scenarios show that the proposed generalized guidance law performs high interception accuracy.
1. Introduction
The developments of the high-tech flight technology have greatly increased the performance of the advanced target,e.g.hypersonic flight technology improves the target’s velocity feature and range maneuverability, and spiraling reentry warhead and unmanned aerial vehicle possess strong maneuverability. The interceptor is no longer dominant in speed and maneuverability, which makes the accurate interception of the advanced target to be a challenging task. Although traditional Proportional Navigation(PN)guidance law and its variants are popular for their simple structure and convenient implementation, guidance laws of PN-type could not satisfy the requirements for interception of the advanced target. To this end, researchers are devoting themselves to handle the guidance problem via modern control methods, so that the advanced target can be accurately intercepted within finite time, such as sliding mode guidance law,1,2disturbance obser-
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2020.01.001 1000-9361 © 2020 Production and hosting by Elsevier Ltd. on behalf of Chinese Society of Aeronautics and Astronautics.
This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).ver based composite guidance law,3,4and finite-time Input-to-State Stability (ISS) based guidance law.5
First of all, since the practical interception engagement takes place in 3D space, it is necessary to carry out the study on 3D guidance law design. On the basis of vector operation,researchers presented very elegant PN-type 3D guidance laws,which are normally in the form of Coriolis type acceleration,for example, 3D PPN guidance law,63D realistic TPN guidance law,7and unified 3D PN-type guidance law.8However,the PN-type guidance laws are incapable of active target maneuver rejection. H∞control based 3D guidance law9and ISS approach based guidance law10ensure that the guidance errors asymptotically converge to a neighborhood of zero.However, the design procedure of H∞guidance law is very sophisticated, and high gain is indeed required by the ISS based guidance law to maintain the interception accuracy.Recently, Zhou and his team find out a generalized approach to design nonlinear robust 3D guidance law,1,11,12by which most 2D guidance laws can be directly extended to the 3D case without considering the cross coupling issues.In this paper,we will extend this result to design observer based composite finite-time guidance law.
Finite-Time Stability (FTS) indicates that the states of the controlled system converge to the equilibrium point within finite time,13which is a preferred property of guidance system due to the limited duration of terminal interception process.Without active disturbance rejection technique, high gain based feedback control is required to compress the guidance error to a sufficient small vicinity,such as finite-time ISS guidance law.5SMC method is a widely used finite-time robust control method, which depends on the high-frequency switching discontinuous control term to handle the matched disturbance. Numerous guidance solutions have been proposed,such as finite-time robust guidance law,1,14angle constrained guidance law15,16and adaptive guidance solutions,17,18Disturbance Observer Based Control (DOBC) is another broadly applied approach to solve the guidance problems. For example, guidance laws based on high-order Robust Exact Disturbance Observer (REDO),3,19non-homogeneous high-order REDO,20Extended State Observer (ESO)4,21-23and so on.However, the convergence rate of the abovementioned observers mainly depends on the magnitude of the gains, and the transient process of the observers may adversely affect system performance.
Recently, the research on Fixed-Time Stability13(FxTS)provides another approach to design the disturbance observers. The fixed-time convergent observers ensure that the observation errors converge to the origin within fixed-time independent of the initial conditions, which implies that the estimation of the expected system state can be fast obtained.A switched framework is proposed to ensure the FxTS of the robust exact observer,24which has been redesigned to be a disturbance observer for Brunovsky systems25and fault tolerant control.26However,the high-order power observer is too conservative to promote the convergence rate of the robust exact observer. Generalized super twisting differentiator27was proposed to enhance the performance of traditional super twisting differentiator. Continuous fixed-time convergence observers are also presented.28-30The observers in Ref.30were designed based on the time scale paradigm, by which the nonlinearity of the double power correction terms was greatly enhanced.Fixed-time ESO and solutions for improving the performance of the observers were proposed in the Refs.30,31and the references therein.
This paper will employ robust exact observers and fixedtime ESO to construct the generalized composite 3D guidance law for intercepting high-speed maneuverable target. The main contributions of this work are summarized as follows:firstly, a relative LOS velocity based generalized 3D guidance design framework is proposed,and the classical TPN guidance law, finite-time ISS guidance law and sliding mode guidance law are analyzed via this framework. Secondly, new fixedtime convergent disturbance observers are proposed, whose stability is verified based on Lyapunov method. Thirdly,finite-time robust 3D composite guidance laws based on fixed-time convergence disturbance observers are presented,where the target maneuver can be fast estimated and compensated. Moreover, the solutions to deal with the peaking effect of the fixed-time convergent observers are proposed and tested.
2. Problem statement and preliminaries
2.1. Problem statement
The interceptor missile and the target are regarded as point masses, and the velocities of the missile VMand the target VTare assumed to be constants. Then, the 3D interception geometry can be described as in Fig.1.Oxyz is the inertial reference frame whose origin is moved to the missile gravity center;r is the relative range from missile to target;θLand ψLare the elevation and azimuth angles of the LOS respectively; θMand ψMare the flight-path angle and heading angle of the interceptor missile respectively; the same definition is for θTand ψTof the target; all of the angles are Euler angles with respect to the inertial reference frame; er, eθ, eψare the unit vectors along the corresponding rectangular LOS coordinate axes.
By virtue of the principles of kinematics and dynamics,

The relative motion between the interceptor missile and the target in the LOS coordinate can be derived as

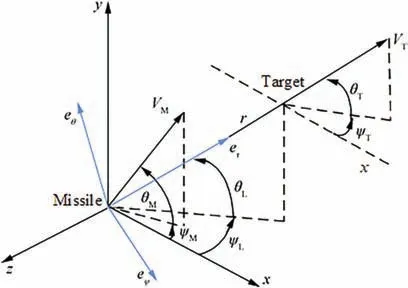
Fig. 1 Three-dimensional interception geometry.







Table 1 Initial simulation parameters for diving interception (Case I).

Table 2 Initial simulation parameters for lifting interception (Case II).
Without active disturbance rejection technique, the interception accuracy of the TPN guidance law is the worst one for both cases (see miss distance in Table 3, and subgraphs(a)and(b)in Fig.2 and Fig.3).The guidance laws with active disturbance rejection technique perform small miss distances(see Table 3). The finite-time ISS guidance law depends on the high-gain error feedback term to handle the target maneuver. This method can fast eliminate the initial guidance deviation (see subgraphs Fig. 2(a), Fig. 2(b) Fig. 3(a), and Fig. 3(b)). However,the acceleration of the interceptor is easy to be saturate in the initial phase of the interception (see subgraphs Fig. 2(c) Fig. 2(d), Fig. 3(c) and Fig. 3(d)). At the end of the interception, there exist slight divergences of the interceptor accelerations based on FTISSGL, which is generated by the decreasing relative distance and the hysteresis of feedback control method. The SMGL depends on the discontinuous control term to deal with the target’s maneuver. Saturate function is employed to eliminate the chattering problem by the price of scarified robustness and exactness.Seen from subgraphs Fig. 2(a), Fig. 2(b) Fig. 3(a), and Fig. 3(b), the normal relative velocities of LOS are not stabilized at the origin.There still exists a potential problem for FTISSGL and SMGL in practical application, which is that the measurement noise may arouse oscillation due to the high gain or nonlinearity of the saturation function. Disturbance observer based finitetime guidance laws reject the target’s maneuver by estimation and compensation.The target’s maneuver can be fast compensated based on the proposed fixed-time convergence disturbance observers, and then the relative normal velocities smoothly converge to zero (see subgraphs Fig. 2(a), Fig. 2(b)Fig. 3(a), and Fig. 3(b)). In contrast, the transient process of the traditional REDO dramatically influences the guidance performance. Compared with the FTISSGL and SMGL, disturbance observer based guidance law needs to design and calculate the observer system, which requires more resource for application.However,the missions of disturbance cancellation and initial guidance error elimination can be separately designed, which provides a feasible approach to guarantee the performance of the guidance system.
The results of the disturbance estimation in Fig. 2(e) and Fig. 2(f) show that the proposed SREDO admits fast convergence rate with respect to REDO. For a continuous varying disturbance, the SREDO needs almost 0.7 second for convergence, while the REDO needs almost 1.8 second for convergence. For the switching disturbance, the SREDO needs almost 0.7 second for eliminating the initial error and almost 0.73 second to dispel the error generated by the disturbance switching. The REDO does not track the disturbance in the initial phase. After the first switch of disturbance, the REDO needs almost 2.4 s for convergence.Fig.3(e)and Fig.3(f)show that second-order disturbance observer can perform monotonous estimation for the target accelerations. For a continuous varying disturbance, 0.3 s is required for the GSTDO and the DPO to eliminate the initial error.For a switching disturbance,GSTDO needs almost 0.24 s for eliminating the initial error and 0.26 s for convergence again. DPO needs almost 0.43 s for eliminating the initial error and almost 0.44 s for convergence again. With the application of Proposition 1, the state z2could monotonously fast converge to the target’s acceleration without overshoot. However, although GSTDO admits theoretical exactness and robustness, Fig. 3(e) and Fig. 3(f)show that chattering phenomenon is present, which lead to lower stable accuracy of the GSTDO than the DPO.
Compare the third-order SREDO and the GSTDO or DPDO. The third-order disturbance observers supply more accurate disturbance estimations. For a continuous target maneuver,the stable observation error of SREDO and REDO belong to the interval -1,1( ), whereas the error interval of GSTDO and DPDO are bigger.Moreover,for the SMC based disturbance observer, the estimation accuracy of third-order disturbance observer is better than the second-order GSTDO.In fact, the choice of Lipschitz constant is crucial to the SMC based disturbance observer, which depends on the trade-off among robustness, exactness, dynamical properties, application steps and so on.

Fig. 2 Simulation results for Case I.

Fig. 3 Simulation results for Case II.

Table 3 Data of interception performance.
5. Conclusions
(1) When first-order 3D guidance law is designed, the coupling effect in the relative motion equations between the interceptor missile and the target can be ignored so that most 2D first-order guidance law can be directly extended to the 3D case.
(2) A new high-power observer is applied to enhance the performance of the original switched robust exact observer, and the corresponding disturbance admits fast convergence rate and still obtains the theoretical exactness and robustness.
(3) The fixed-time disturbance observer based generalized 3D finite-time guidance laws are proposed and verified via numerical simulation. The third-order disturbance observer based guidance law obtains high interception accuracy, while second-order disturbance observer based guidance law obtains the best transient properties.
(4) Proposition 1 is a useful observer application rule,based on which the performance of the disturbance observer is enhanced so that the effect of the observer transient process on the guidance system is greatly weakened.
杂志排行
CHINESE JOURNAL OF AERONAUTICS的其它文章
- Reliability and reliability sensitivity analysis of structure by combining adaptive linked importance sampling and Kriging reliability method
- Aeroelastic dynamic response of elastic aircraft with consideration of two-dimensional discrete gust excitation
- Thermal damage analysis of aircraft composite laminate suffered from lightning swept stroke and arc propagation
- An aerospace bracket designed by thermo-elastic topology optimization and manufactured by additive manufacturing
- Applications of structural efficiency assessment method on structural-mechanical characteristics integrated design in aero-engines
- An energy-based coupling degradation propagation model and its application to aviation actuationsystem
