Hydrocortisone, ascorbic acid and thiamine for sepsis: Is the jury out?
2020-05-12PaulEllisMarikJosephVaronSalimSurani
Paul Ellis Marik, Joseph Varon, Salim R Surani
Paul Ellis Marik, Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, VA 23507, United States
Joseph Varon, Department of Critical Care, United Memorial Medical Service, Houston, TX 77030, United States
Salim R Surani, Texas A and M University, Corpus Christi, TX 78413, United States
Abstract
Sepsis and septic shock remain a major cause of morbidity and mortality among patients admitted in the intensive care unit. Diabetes is a major risk factor for the development of sepsis. The global mortality of sepsis remains high, despite significant interventions and guidelines. It has been known for decades that patients with sepsis have reduced levels of antioxidants, most notably vitamin C.Furthermore, experimental data has demonstrated multiple beneficial effects of vitamin C in sepsis. In addition, corticosteroids and thiamine may have synergistic biological effects together with vitamin C. Preliminary data suggests that therapy with hydrocortisone, ascorbic acid and thiamine improves the outcome of patients with sepsis with the potential to save millions of lives.However, this intervention has met with much resistance and has not been widely adopted. Ultimately, we await the final jury verdict on this simple, safe and cheap intervention.
Key words: Diabetes; Vitamin C; Ascorbic acid; Sepsis; Thiamine; Septic shock; Global burden of disease
INTRODUCTION
“A new scientific truth does not triumph by convincing its opponents and making them see the light, but rather because its opponents eventually die, and a new generation grows up that is familiar with it.” Max Planck, Theoretical Physicist (1858-1947).
According to the most recent estimates from the World Health Organization over 6 million citizens of the earth die from sepsis each year. As the greatest burden of sepsis is in middle- and low-income countries where accurate epidemiological data is lacking, this is likely an underestimate of the true global burden of this devastating syndrome[1-3]. The patients with diabetes have increased risk of developing sepsis[4].The cornerstone of treatment of sepsis and septic shock is its early recognition, early appropriate antibiotics, early source control and a physiologic approach to fluid management[5]. Despite this approach the mortality of septic shock in resource reach countries approximates 30%, while that in resource poor countries the mortality is estimated to be about 60%. Sepsis is the commonest cause of death in children less than 5 years of age. Imagine for one moment that a simple, cheap and readily available intervention existed that could reduce the mortality from sepsis by 20%(conservatively). Such an intervention would save in excess of 1 million lives a year.Does such an intervention exist? We believe that the combination of hydrocortisone,ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and thiamine (HAT Rx) has the potential to prevent millions of deaths from sepsis each year and to reduce the severe life altering sequelae in the sepsis survivors[6-8]. Most importantly this intervention is cheap and without side effects (the side effects of a short course of low dose corticosteroids are minimal)[8,9]. So why has this simple, safe and cheap intervention not been more widely adopted? To answer this question, we need to question the established medical community and their power brokers. The commonest reasons cited are that the proposed benefits are not “biologically plausible” and the “jury is not out” on the benefits of this simple intervention[10,11].
A jury is a body of people convened to render an impartial verdict (in a legal case)on the basis of evidence submitted to them by a court. The jurors evaluate the totality of the evidence presented to them and base their findings on the preponderance of evidence. In many cases there is no smoking gun [or randomized controlled trial(RCT)] so they base their assessment on the entire body of the evidence. Furthermore,the jury needs to ponder the consequences of an incorrect verdict. In a trail, if they wrongly convict, this could result in the wrong penalty. Similarly, in the case of “HAT RxvsSepsis” concluding that such therapy is biologically implausible and unsafe could potentially cost millions of lives.
So, what does the evidence to date demonstrate? Firstly, it should be recognized that humans (anthropoid primates) are unique amongst the animals that roam the earth, in they have lost the ability to synthesize vitamin C[12]. Vitamin C is an essential antioxidant and co-factor for many vital biological reactions. In non-human species,Vitamin C acts as a stress hormone with increased synthesis during stress which is likely protective. Secondly, over 400 basic science experiments have been performed demonstrating the benefit of vitamin C alone and in combination with hydrocortisone in attenuating the dysregulated immune response in sepsis, in limiting organ dysfunction and reducing death of the septic animals[8]. What is remarkable is that these medications act synergisticallyviamultiple overlapping pathways.In-vitrostudies have demonstrated the synergetic effects of the combination of corticosteroids and vitamin C[13,14]. In addition, vitamin C reverses the sepsis induced oxidation (and inactivation) of the glucocorticoid receptor, while corticosteroids increase the transcription of SVCT2, the pivotal vitamin C transporter[15,16]. Thiamine may act synergistically with glucocorticoids and vitamin C to limit mitochondrial oxidative injury and restore mitochondrial function and energy production[17]. Furthermore,vitamin C and thiamine may play a critical in limiting delirium and septic encephalopathy[17,18]. The key roles of vitamin C is sepsis is provided in Table 1[8].Thirdly, the mortality benefit of vitamin C (alone) in reducing the mortality of septic shock and sepsis associated acute respiratory distress syndrome has recently been demonstrated[19,20]. Fourthly, the benefit of HAT Rx has been demonstrated in multiple observational studies[6,20]. And fifthly, we have together treated over 2000 patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. We continue to witness the remarkable ability of this treatment strategy to reduce the dysregulated immune response and improve the outcome of patients with sepsis. We have absolutely no conflicts of interest and have no reason to provide false evidence to the court of science and public opinion. It is critical to emphasize that all three components of HAT Rx are Food and Drug Administration approved drugs, which in the recommended doses are completely devoid of side effects. We are unaware of any side-effects or complications associated with HAT Rx. It should, however, be noted that there are powerful forces at play attempting to invalidate and disprove the beneficial effects of HAT Rx[10,11]. This includes designing clinical trials that are doomed to fail, by using absurd doing schedules or selectively enrolling patients likely to do poorly[21,22].
CONCLUSION
Shortly, the results of multi-center RCTs will be available[23-25]. Many will consider these trials to be the definitive evidence on which to judge the benefit of HAT Rx and to make a jury decision. However, while RCT’s are considered the gold standard, it is important to realize that most RCT’s do not replicate real world experience; mainly,due to the numerous exclusion criteria, enormous patient heterogeneity, nonstandardized co-interventions and delays in instituting therapy. In the end, the thoughtful juror (clinician) must weigh the totality of the evidence before rendering a verdict.
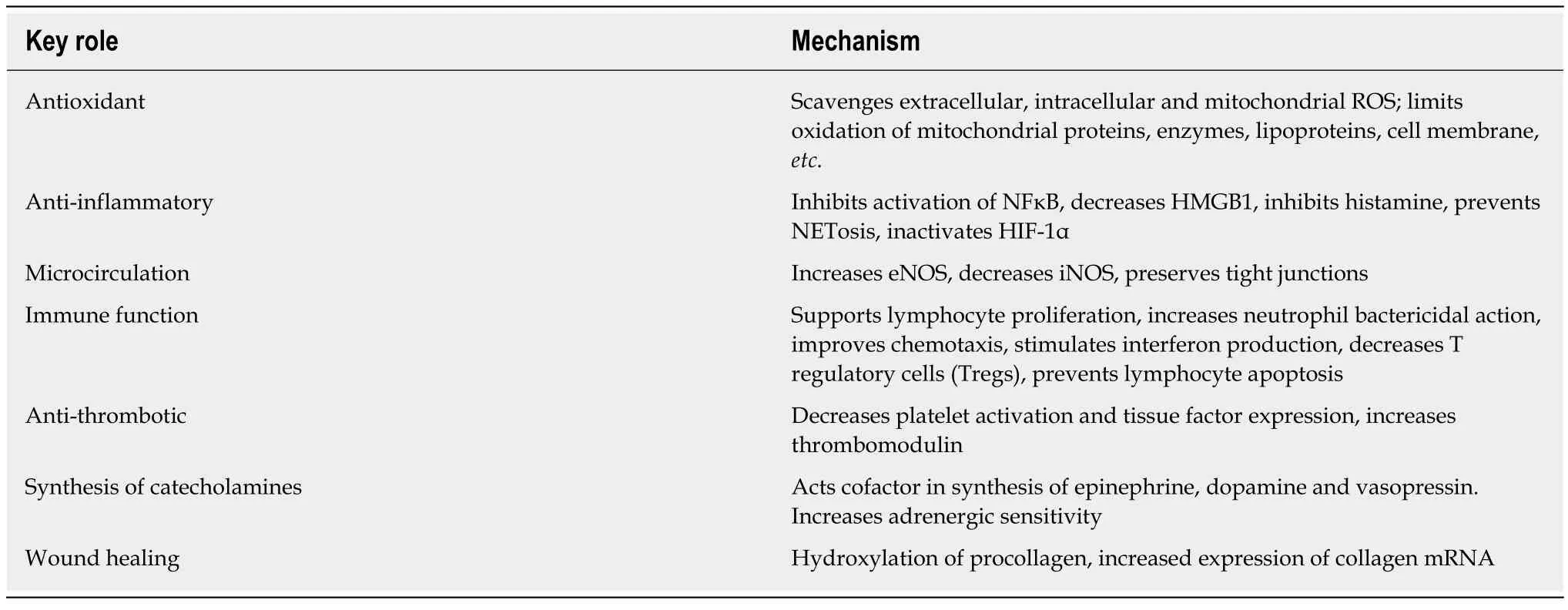
Table 1 Summary of key roles of vitamin C in sepsis
杂志排行
World Journal of Diabetes的其它文章
- Age of onset of diabetes and all-cause mortality
- Long-term effect of clopidogrel in patients with and without diabetes: A systematic review and metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials
- Novel insight into perirenal adipose tissue: A neglected adipose depot linking cardiovascular and chronic kidney disease
- Lack of Syndecan-1 produces significant alterations in whole-body composition, metabolism and glucose homeostasis in mice
- Glargine-300: An updated literature review on randomized controlled trials and real-world studies
