Effects of Lanthanum and Cerium on Chlorophyll Content,Yield and Components of Soybean in Northeast China
2020-04-28RenHongyuTaoPeiZhuangZhongLiXinLiXuecongandZhangXingwen
Ren Hong-yu,Tao Pei,Zhuang Zhong,Li Xin,Li Xue-cong,and Zhang Xing-wen
1 College of Resources and Environmental Sciences,Northeast Agricultural University,Harbin 150030,China
2 College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Harbin Institute of Technology,Harbin 150001,China
Abstract: In this paper,three soybean varieties with different qualities were used as experimental materials for potted plants. In the seedling stage and the flowering stage,different concentrations of lanthanum and cerium (120,150 and 180 mg · L-1 LaCl3; 30,60 and 90 mg · L-1 CeCl3; 30,40 and 60 mg · L-1 LaCl3+30,40 and 60 mg · L-1 CeCl3) were sprayed to study the effects of lanthanum and cerium on soybeans (leaf photosynthetic pigment content,yield and the constituent factors). The results showed that chlorophyll contents of different qualities soybean leaves reached the maximum under 120 mg · L-1 LaCl3 treatment. The yield of high protein soybean was the highest under 60 mg · L-1 CeCl3 treatment,the yield of high fat soybean was the highest under 30 mg · L-1 CeCl3 treatment,and the yield of dual-purpose soybean was the largest under 30 mg · L-1 CeCl3 treatment. Therefore,the lanthanum and cerium solutions had the effect of "low promotion and high inhibition" on chlorophyll content of soybeans,and the cerium solution could increase the yields of different quality soybeans.
Key words: rare earth,lanthanum,cerium,soybean,chlorophyll,yield
Introduction
China,the country of origin of soybeans,has been the undefined largest importer of soybeans in the world since 1996 (Yanet al.,2018),while the planting area of soybean in China is still decreasing year by year. Therefore,increasing soybean planting area and increasing soybean yield are important ways to revitalize China's soybean industry and ensure China's food security. The northeast region is an important commodity grain production base in China and a major soybean producing area with a series of environmental conditions conducive to crop growth(Daiet al.,2018). As the world's rare earth center,China's rare earth content accounts for about 23% of the world's total reserves,and more than 90% of the world's total output. Rare earths have physiological activity. Appropriate amount of rare earth elements can increase plant chlorophyll content,photosynthetic rate and photosynthesis,so as to enhance plant accumulation of dry matter and promote plant nutrient quality (Huanget al.,2008; Liuet al.,2007; Gaoet al.,2012; Luet al.,2010). Chlorophyll is a key catalyst in the photosynthesis process,and its content indirectly reflects the growth of the crops.Appropriate amount of the rare earth elements can increase the contents of soybean chlorophyll a,chlorophyll b and carotenoids,and promote the photosynthesis of soybean plants (Lianget al.,2011; Liet al.,2007). However,the excessive concentration of rare earth solution inhibits the photosynthetic rate of soybean (Renet al.,2013). Studies have shown that the rare earths have a "low promotion and high inhibition"effect on plant growth,and higher concentrations of Ce3+(60-150 mg · L-1) have an inhibitory effect on chlorophyll content (Qiet al.,2004; Zhao,2017). The role of the rare earths in promoting crop yield increase has been confirmed (Wanget al.,2013; Luoet al.,2009; Renet al.,2014; Deng,2006). A large number of studies have shown that regardless of the field or potted plants,the use of the rare earth elements,foliar application or stem application to crops can increase the average yield of rice and soybean by 8% to 10%,and increase the yield of wheat and corn by 8% to 15% (Lianget al.,2005; Niet al.,2006; Luoet al.,2009; Wanget al.,2013; Zhaoet al.,2004; Ouet al.,2014). However,relevant reports on the regulation of lanthanum and cerium on different quality soybeans(leaf photosynthetic pigment content,yield and the constituent factors) have not been retrieved. In this experiment,soybean Dongnong 42,Dongnong 52 and soybean Dongnong 47 were used in pot experiment under the northeast climate of China. Different concentrations of lanthanum and cerium were sprayed on the leaves of the seedling stage and the early flowering stage. The effects of different concentrations of lanthanum and cerium on soybeans with different qualities were studied. The results of the study provided technical supports for scientific and rational using of rare earths and for soybean planting with good quality and high yield.
Materials and Methods
Experimental materials
The soybean varieties tested were Dongnong 42,Dongnong 47 and Dongnong 52,all of which were provided by the Soybean Research Institute of Northeast Agricultural University. The pot culture method (with a height of 30 cm,an upper diameter of 35 cm and a lower diameter of 25 cm) was adopted,with 17.5 kg soil in each pot,and eight seeds with full and uniform seeds were planted. When the seedling grew to 5-8 cm,four seedlings were set. The soil used for the test was taken from black soil of Horticulture Experiment Station of Northeast Agricultural University. The chemical properties of the soil that was used for testing were provided organic matter 31.3 g · kg-1,pH (H2O) 7.62,available nitrogen 147 mg · kg-1,available phosphorus 74 mg · kg-1,available potassium 202 mg · kg-1,the total nitrogen 3.58 g · kg-1and the total phosphorus 1.2 g · kg-1.Fertilization in each pot was 0.44 g of urea,1.22 g of diamine and 1.25 g of potassium sulfate. The soybeans were sown on 17 May,2016,and they were harvested on 29 September,2016.
Experimental treatment
In soybean seedling stage (17 June,2016) and the early flowering (1 July,2016),the spray treatment concentrations of 120,150 and 180 mg · L-1LaCl3solution (labeled as La12,La15 and La18) and the concentrations of 30,60 and 90 mg · L-1CeCl3solution(labeled as Ce3,Ce6 and Ce9 ),and 30,40 and 60 mg · L-1LaCl3+ 30,40 and 60 mg · L-1CeCl3mixture(labeled as LC3,LC4 and LC6) were respectively evenly sprayed with soybean leaves,until the spay became drops. The seedling stage was about 50 mL per plant and the flowering stage was about 100 mL per plant. The same amount of distilled water was sprayed in the control (CK),and each treatment was repeated for three times. Among them,the spraying concentrations of different rare earth solutions were selected according to the previous test (Zhao,2017).
Determination of indexes and methods
Photosynthetic pigment content: chlorophyll and carotenoids were determined by ethanol spectrophotometry (Renet al.,2013),0.20 g of fresh soybean leaves (inverted three-leaf and inverted four-leaf period) from the main veins was weighed to be cut into a mortar,and a small amount of calcium carbonate powder and quartz sand and 3-5 mL of 95% ethanol were added and grounded to a homogenate,after that about 10 mL of 95% ethanol was added,diluted and grounded,and filtered into a 25 mL volumetric flask with filter paper. After that,the filter paper was washed with 95% ethanol until there was no green color left.Finally,after being scaled to the fixed volum and shaken evenly,the chlorophyll extract was obtained.Absorbance was measured at a spectrophotometer with wavelengths of 470,649 and 665 nm,and calculated according to the photosynthetic pigment mass fraction formula (Liet al.,2000).
Yield and constituent factors: after soybean ripening,nine plants were selected for each treatment,including the number of pods per plant,the number of grains per plant,weight per plant (g) and 100-grain weight (g).
Data processing
Microsoft Excel 2010 was used to collect,calculate and draw the experimental data,and SPSS19.0 software system was used to analyze the significance of differences in various indicators.
Results
Effects of lanthanum and cerium on chlorophyll content in soybean leaves
Fig. 1 showed that the contents of chlorophyll a,chlorophyll b and carotenoids in high protein soybean Dongnong 42 increased first,then decreased with the increase of La concentration,and were higher than those of the CK. When the concentration of LaCl3solution was 120 mg · L-1,the three contents reached the maximum,increasing by 47.66%,75.06% and 61.64% (p<0.05),respectively compared with those of the CK. When the concentration of LaCl3was higher than 120 mg · L-1,the content of each index showed a downward trend. After treatment with 180 mg · L-1solution,the contents of all the three were the lowest,which were 12.45%,26.34% and 30.03%,respectively lower than the maximum. The results showed that the concentration of LaCl3solution at 120 mg · L-1promoted the content of photosynthetic pigments in soybean leaves most significantly,and with the increase of concentration,it inhibited the synthesis of photosynthetic pigments,resulting in the phenomenon of "low promotion and high inhibition" of rare earths on plants (Zhouet al.,2009).
Fig. 2 showed that the contents of chlorophyll a,chlorophyll b and carotenoids in soybean Dongnong 42 increased slowly with the increase of Ce concentration. When CeCl3solution was 90 mg · L-1,the contents of all the three reached the maximum,which were 42.39% (p>0.05),102.96% (p<0.05)and 74.95% (p>0.05),respectively. The content of photosynthetic pigment in soybean reached the highest at Ce9,but chlorophyll a and carotenoid did not reach significant difference with the CK. Therefore,when the concentration of CeCl3was 30-90 mg · L-1,it could promote the synthesis of photosynthetic pigments of soybean Dongnong 42 and the promoting effect was most obvious when the concentration was 90 mg · L-1.

Fig. 1 Effects of rare earth La on chlorophyll content of high protein soybean Dongnong 42

Fig. 2 Effects of rare earth Ce on chlorophyll content of high protein soybean Dongnong 42
Fig. 3 showed that with the increase of the concentration of LaCl3and CeCl3,the contents of chlorophyll a,chlorophyll b and carotenoids tended to increase and then gradually decrease. When the concentration of LaCl3and CeCl3was 30 mg · L-1,the contents of chlorophyll a,chlorophyll b and carotenoid reached the maximum. The increase rates were 59.79%(p>0.05),95.80% (p<0.05) and 58.59% (p<0.05),respectively. It showed that the low concentration of LaCl3and CeCl3mixture could significantly increase the contents of chlorophyll a,chlorophyll b and carotenoids. When the concentration of LaCl3and CeCl3was 60 mg · L-1,the increase was 14.54% (p>0.05),1.98%(p>0.05) and 38.80% (p>0.05),respectively. It could be seen that the photosynthesis of the high protein soybean Dongnong 42 leaves also had a phenomenon of"promotion at low concentation and inhibition at high concentation" on the mixture of LaCl3and CeCl3.

Fig. 3 Effects of rare earth La and Ce on chlorophyll content of high protein soybean Dongnong 42
Fig. 4 showed that the contents of chlorophyll a,chlorophyll b and carotenoids in fatty soybean Dongnong 47 increased first and then decreased with the increase of La concentration,and were higher than those of the CK. When the concentration of LaCl3solution was 120 mg · L-1,the three contents reached the maximum,increasing by 15.98% (p>0.05),70.30%(p<0.05) and 25.41% (p>0.05),respectively compared with those of the CK. As the concentration increased,the content of each index showed a downward trend.After treatment with 180 mg · L-1solution,the contents of all the three were the lowest,but still higher than those of the CK. It could be seen that when the concentration of LaCl3was 120-180 mg · L-1,the synthesis of photosynthetic pigments of soybean Dongnong 47 also had a low promotion and high inhibition effect.Although the concentration was higher than that of the CK at 180 mg · L-1,if the concentration increased,photosynthesis was severely inhibited,which was harmful to the growth and development of soybean.

Fig. 4 Effects of rare earth La on chlorophyll content of high fatty soybean Dongnong 47
Fig. 5 showed that the contents of chlorophyll a,chlorophyll b and carotenoids in soybean Dongnong 47 increased first,and then decreased with the increase of Ce concentration. When the concentration of CeCl3was 60 mg · L-1,the contents of chlorophyll a,chlorophyll b and carotenoids reached the maximum,increasing by 24.71% (p<0.05),55.58% (p<0.05) and 12.51% (p>0.05),respectively compared with those of the CK. When the concentration of CeCl3solution was 90 mg · L-1,the three contents reached the maximum,increasing by 3.71% (p>0.05),3.92% (p>0.05) and 0.91% (p>0.05),respectively compared with those of the CK. When the concentration was greater than 60 mg · L-1,CeCl3solution inhibited its photosynthetic pigment content. Therefore,CeCl3solution had a positive effect on the photosynthetic pigment within a suitable range,if it was not reached or excessive,it would have had the opposite effect and adversely affected the plants. The proper concentration of the cerium solution could promote the activity of the plant PSII protein complex and speed up the photosynthetic electron transfer,and increase the content of the chlorophyll a,thereby promoting the whole light energy conversion and photochemical reaction process.

Fig. 5 Effects of rare earth Ce on chlorophyll content of high fatty soybean Dongnong 47
Fig. 6 showed that the contents of chlorophyll a,chlorophyll b and carotenoids tended to decrease slowly as the concentration of LaCl3and CeCl3increased. At a concentration of 60 mg · L-1,the content reached a minimum. The reductions were 16.47%,12.51% and 27.68%,respectively. When the concentration of LaCl3and CeCl3mixed solution was 30 mg · L-1,the decrease was 5.10%,1.67% and 13.60% compared with that of the CK. There was no significant difference between the two groups (p>0.05). It could be seen that as the concentration increased,the content of soybean photosynthetic pigments decreased,probably because the concentration of LaCl3and CeCl3mixture reduced the photosynthetic capacity of soybeans,so that a large amount of light energy could not be converted into electrical energy. Entering the acyclic electron transport chain,a large amount of singlet oxygen was generated by excess energy,consuming photosynthetic pigments.
Fig. 7 showed that the contents of chlorophyll a,chlorophyll b and carotenoids in dual-purpose soybean Dongnong 52 increased first and then decreased with the increase of La concentration. When the concentration of LaCl3solution was 120 mg · L-1,the contents of Chla,Chlb and carotenoids in soybean leaves reached the maximum,increasing by 6.42%,1.48% and 3.60%,respectively compared with those of the CK,but the difference was not significant (p>0.05). When the concentration of LaCl3was 180 mg · L-1,the index reached the minimum value.

Fig. 6 Effects of rare earth La and Ce on chlorophyll content of high fatty soybean Dongnong 47

Fig. 7 Effects of rare earth La on chlorophyll content of dual-purpose soybean Dongnong 52
Compared with the CK,the decrease was 6.99%(p>0.05),10.96% (p>0.05) and 25.01% (p<0.05). It could be explained that lanthanum solutions had a dual effect on plants,and excessive lanthanum solution concentration could inhibit the normal growth of the plants. Fig. 8 showed that the contents of chlorophyll a,chlorophyll b and carotenoids increased first and then decreased with the increase of CeCl3concentration.The photosynthetic pigment content reached a maximum when CeCl3concentration was 30 mg · L-1.
The increase rates were 7.57%,37.26% and 17.80%,respectively compared with those of the CK (p>0.05).When the concentration of CeCl3was 90 mg · L-1,the content was significantly lower than that of the CK,with a decrease of 27.36% (p<0.05),21.47%(p<0.05) and 18.30% (p>0.05). It could be seen that the concentration of dual-purpose soybean photosynthetic pigment reached the highest concentration at 30 mg · L-1,but did not reach a significant difference with the CK. It could be explained that CeCl3could promote the synthesis of photosynthetic pigments of soybean Dongnong 52 at a concentration of 30 mg · L-1. When it was greater than this concentration (Ce9),the photosynthesis of soybean leaves could be significantly inhibited,which affected the normal growth of plants.

Fig. 8 Effects of rare earth Ce on chlorophyll content of dual-purpose soybean Dongnong 52
Fig. 9 showed that the contents of chlorophyll a,chlorophyll b and carotenoids decreased first,and then increased slowly with the increase of the concentration of LaCl3and CeCl3mixture. At the concentration of 60 mg · L-1,the contents of chlorophyll a,chlorophyll b and carotenoids reached the maximum and were higher than those of the CK,which increased by 12.08%(p>0.05),2.43% (p>0.05) and 1.37% (p>0.05); when the concentration of CeCl3was 30 mg · L-1,the content of photosynthetic pigments reached the minimum,which was 5.01%,16.47% and 20.73% (p>0.05)compared with that of the CK. It could be concluded that the treatment of a suitable concentration of LaCl3and CeCl3mixture could increase the content of soybean photosynthetic pigment and enhance its photosynthesis ability.

Fig. 9 Effects of rare earth La and Ce on chlorophyll content of dual-purpose soybean Dongnong 52
Effects of lanthanum and cerium on yields and component factors of different quality soybeans in northeast China
Table 1 showed that different concentrations of lanthanum and cerium solutions were sprayed on the leaves at the seedling stage and the early flowering stage. With the increase of La concentration,the number of pods,grains per plant and grain weight per plant first increased and then decreased. Under La15 treatment,the number of pods,the number of seeds per plant and the weight per plant reached the maximum,which were 0.72% (p>0.05),15.65% (p>0.05) and 23.23% (p>0.05),respectively. The 100-grain weight increased gradually with the increase of the concentration of strontium solution. The maximum 100-grain weight of the seed under high concentration of La18 treatment was 20.90 g,which was 5.02% higher than that of the CK (p>0.05). The yield increased first and then decreased with the increase of La concentration.The maximum yield was 60.04 g · pot-1under La15 treatment,but there was no significant difference with CK (p>0.05).
With the increase of Ce concentration,the number of pods,grains per plant and grain weight per plant first increased and then decreased,which were higher than those of the CK. The pod number per plant,grain number per plant and grain weight per plant under Ce6 treatment were 37.20 g · plant-1(p<0.05),87.60 g · plant-1(p>0.05) and 17.00 g · plant-1(p>0.05). The 100-grain weight was the highest under Ce6 treatment,which was 2.11% higher than that of the CK (p>0.05).The yield increased with the increase of the concentration of the sputum solution,and then decreased,which was higher than that of the CK,and reached a maximum of 68.00 g under Ce6 treatment. There was no significant difference with CK (p>0.05).
With the increase of the concentration of La-Ce mixed solution,the number of pods,grains per plant and grain weight per plant first increased and then decreased. Under LC4 treatment,the number of pods per plant,the number of grains per plant and the weight of grains per plant were 32.50,85.75 and 16.65 g,respectively. The number of pods increased significantly (CK) compared with that of CK(p<0.05),but there was no significant difference in grain number and grain weight per plant (CK) (p>0.05).The 100-grain weight first increased and then decreased with the increase of the concentration of La-Ce mixed solution,reaching a maximum of 22.67 g under LC4 treatment,which was 13.9% higher than that of the CK (p<0.05). The maximum yield was 66.58 g · pot-1,which was significantly higher than that of the CK (p<0.05).

Table 1 Effect of rare earth lanthanum and cerium on yields and components of Dongnong 42
Table 2 showed that spraying La solution of different concentrations on the leaves of the seedling and the early flowering stages,pod number,grain number per plant and grain weight per plant after maturation of soybeans reached the maximum under the treatment of La18,but there was no significant difference with CK(p>0.05). The 100-grain weight was the highest under La15,which was significantly increased by 10.96%compared with that of the CK (p<0.05). The yield of La18 reached the maximum of 42.88 g · pot-1,which was not significantly different from that of the CK(p>0.05).
The 100-grain weight of soybean decreased with the increase of Ce concentration,and the 100-grain weight of soybean was the largest under low Ce3 concentration,which was 10.26% higher than that of the CK (p<0.05). The yield of Ce solution treatment was higher than that of the CK,and the highest yield was 43.29 g · pot-1under low concentration Ce3 treatment,which was not significantly different from that of the CK (p>0.05). The number of pods,seed number per plant and grain weight per plant were all higher than those of the CK,but the difference was not significant(p>0.05).
The number of pods per plant increased first,and then decreased with the increase of La-Ce mixed solution concentration,but there was no significant difference compared with that of the CK (p>0.05).The grain number per plant and grain weight per plant decreased with the increase of concentration of La-Ce mixed solution,and the difference was not significant(p>0.05) under high concentration LC6 treatment.The 100-grain weight reached the maximum of 20.90 g under LC4 treatment,and the yield decreased with the increase of La-Ce mixed solution,and reached the maximum of 33.87 g · pot-1under LC3 treatment,with no significant difference compared with those of the CK (p>0.05).
Table 3 showed that different concentrations of rare earth lanthanum and cerium solution were sprayed on the leaves at the seedling and the early flowering stages. With the increase of La concentration,the number of pods,grains per plant and grain weight per plant decreased gradually,and reached the maximum under low concentration La12 treatment. The number of pods,grains per plant and grain weight per plant increased by 7.64% (p>0.05),7.58% (p>0.05) and 1.73% (p>0.05),respectively compared with those of the CK. The 100-grain weight was significantly higher than that of the CK (p<0.05),and the treatment with high concentration of La18 was the largest,and the 100-grain weight was 21.10 g. The yield decreased with the increase of La concentration,and increased by 1.8% compared with that of the CK under La12 treatment (p>0.05),but the difference was not significant.
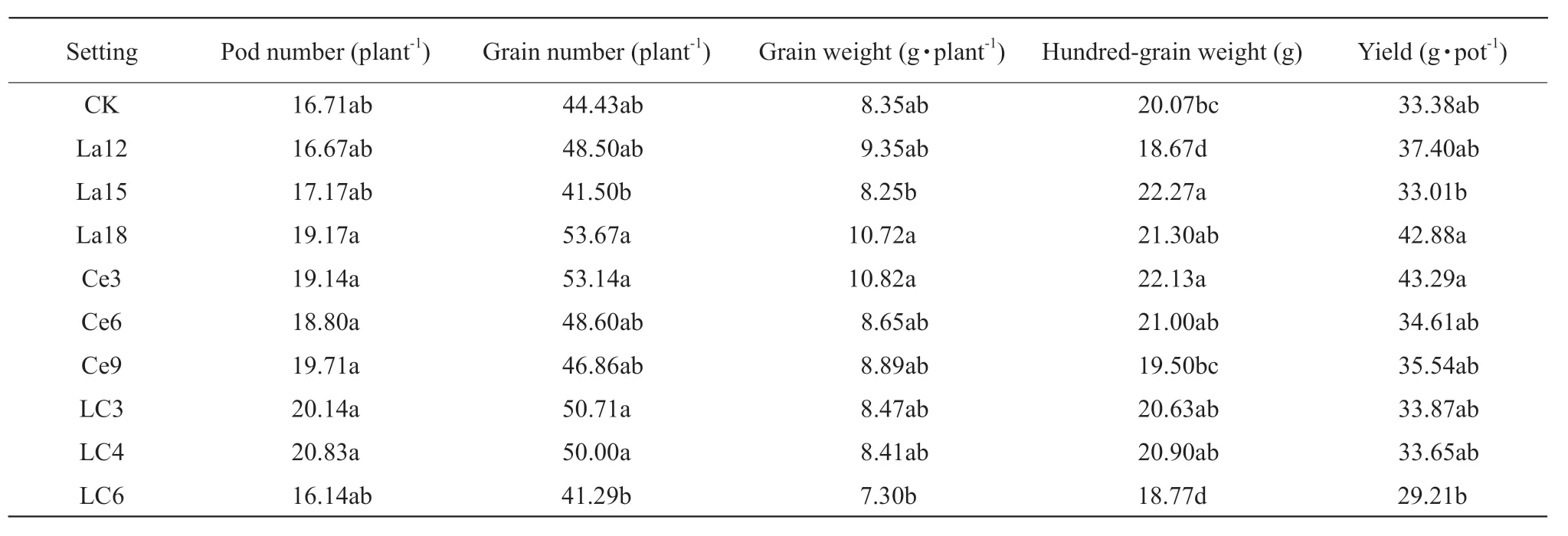
Table 2 Effects of rare earth lanthanum and cerium on yields and components of Dongnong 47
The number of pods per plant was lower than that of the CK under different Ce solutions,and the difference was not significant (p>0.05). The number of grains per plant was the highest under high concentration of Ce9,which was 3.53% higher than that of the CK (p>0.05). The grain weight of single plant reached the maximum under low concentration of Ce3,which was 3.86% (p>0.05) higher than that of the CK. The 100-grain weight of all the treatments was significantly higher than that of the CK,but there was no significant difference among treatments. Under Ce9 treatment,the maximum 100-grain weight was 21.87 g. The maximum yield was 62.26 g · pot-1under low concentration of Ce3,and the difference was not significant (p>0.05).
The maximum number of pods per plant under LC4 treatment was 32.67 plant-1under the mixed solution of La-Ce. The index of other treatments was lower than that of the CK,but the difference was not significant. Seed number per plant and grain weight per plant were the largest under LC3 treatment,and other treatments were smaller than those of the CK,but there was no significant difference compared with those of CK (p>0.05). The 100-grain weight increased first and then decreased with the increase of La-Ce mixed solution concentration,and increased significantly under LC4 treatment compared with that of the CK,reaching a maximum of 21.43 g. The yield decreased with the increase of La-Ce mixed solution concentration. The maximum yield was 60.55 g · pot-1under LC3 treatment,which was not significantly different from that of the CK (p>0.05).

Table 3 Effects of rare earth lanthanum and cerium on yields and components of Dongnong 52
Discussion
Effects of lanthanum and cerium on content of photosynthetic pigment in different quality northeast soybeans
The experiment showed that the effects of lanthanum and cerium on the photosynthetic pigment content of different quality soybeans were different,and the direct or indirect interaction among chlorophyll a,chlorophyll b and carotenoids affected the photosynthetic pigment contents of soybean leaves. The analysis of the results of this experiment found that the suitable concentration of lanthanum and cerium had a promoting effect on the photosynthetic pigment contents,but the concentration of rare earth and the effect of different varieties on soybeans had interspecies differences. The contents of photosynthetic pigments in all the quality soybeans reached the peak under La12 treatment. The low concentration of La solution promoted the chlorophyll contents of soybean leaves,and the high concentration of La decreased the chlorophyll contents of soybean leaves,indicating that the concentration effect of lanthanum had universality and applicability to the effect of chlorophyll in soybean leaves,which was consistent with the results of previous trials. And predecessors had the same results in other crops,such as rape (Zenget al.,2001). The experiment also showed that high concentration of La inhibited the synthesis of chlorophyll,probably because excessive La caused damage to important organs of photosynthesis,so that excessed light energy could not be converted into organic matter,and other reactions occurred in the cells; different quality soybeans had different effects on different concentrations of Ce solution,and the contents of photosynthetic pigments of Dongnong 42,Dongnong 47 and Dongnong 52 reached extreme values at Ce9,Ce6 and Ce3,respectively. Studies have shown that the promot-ing effect of Ce on crop photosynthetic might be the promotion of photosynthetic protein synthesis in chloroplasts (Weiet al.,2005),which increased the content of photosynthetic pigments,and might also improve the composition of membrane systems and improve the efficiency of magnesium ion synthesis of chlorophyll (Ji and Li,2000). In this research,the effect of Ce on soybean had interspecies differences,and different quality soybeans had specificity for the concentration of cerium. In general,applied different concentrations of Ce at the seedling and early flowering stages of Dongnong 42,Dongnong 47 and Dongnong 52 foliar,suitable concentration of Ce could significantly increase leaf areas,photosynthesis efficiency and soybean yields. The principle might be that La and Ce had a synergistic effect on the chlorophyll structure produced in the chloroplast,and promoted the formation of photosynthetic pigments under the effect of a lower concentration of superposition.This experiment showed that the mixed solution of La and Ce had a positive effect on chlorophyll. In the appropriate concentration range,the synthesis rate of chlorophyll could be increased,and the most important light-harvesting organ protein complex in photosystem II in crop leaves was promoted. It could also accelerate the rate of photosynthetic electrons in its transport chain,thereby driving all the conversion reactions between optical energy and chemical energy to provide a basis for high yields and high qualities of crops.
Effects of lanthanum and cerium on yields and component factors of different quality soybeans
This experiment showed that the effects of lanthanum and cerium on the yields and components of different quality soybeans were different,and the direct or indirect interaction between the yields and components affected the final yield of soybean,which was consistent with the results of Zhanget al(2006). The analysis of the results of this experiment found that the appropriate concentration of lanthanum and cerium had a promoting effect on the yields and components,but there were interspecies differences in the effects of different concentrations of rare earths and soybean varieties. Pan (2014) believed that rare earths could not only significantly increase the number of soybean branches,but also significantly increase the number of seeds per plant,100-grain weight and yields. At the same time,it could also significantly increase the proportion of multiple pods in soybean plants,so that four pods increased significantly and pellets were significantly reduced,meaning that an increase in multi-powder pods could significantly increase soybean yields. In terms of single-grain number and 100-grain weight,this experiment verified the dose effect of lanthanum and cerium "low promotion and high inhibition". Liuet al. (2016) have shown that the number of pods per plant and the number of seeds per pod had a certain effect on soybean yields,which would make the pods of soybeans fell off more easily,resulting in fewer pods and production reduce.Lanthanum and cerium could effectively increase the leaf area index,the light energy intercepted by the leaves and the utilization of light energy,promote plant photosynthesis,improve the ability of plants to accumulate and transport photosynthetic products,promote plant seed germination and root growth,and regulate metabolic enzyme activities in the crop,thereby promoting plant growth and development,to regulate its metabolic level,and ultimately to increase production. Lanthanum and cerium could combine with chlorophyll to form rare earth chlorophyll,enhance the activity of carboxylase in photosynthesis,promote the assimilation of carbon dioxide,and at the same time effectively enhance the resistance of plants and increase the yields. Ce6 and La12 had the greatest influences on pod number and seed number per plant in Dongnong 42 and Dongnong 52,indicating that these two treatments could effectively reduce the phenomenon of flower pod shedding,promote the formation of soybean pods and increase the rate of pod formation,allowing more nutrients to be distributed to the reproductive organs,ultimately increasing soybean yields. The highest yield and quality of soybeans could not be achieved at the same time. In modern agricultural production,it was necessary to balance and coordinate the relationship between soybean yield and quality in order to achieve the best production results. The water and fertilizer status had a great influence on the 100-grain weight of soybeans. In the bulging stage of reproductive growth,sufficiently water could help the synthesis of the full grain,which could help the growth of 100-grain weight. The yields and 100-grain weight of Dongnong 42 reached the maximum under Ce6 and LC4 treatments,respectively.The yields and 100-grain weight of Dongnong 47 reached the maximum under Ce3 and La15 treatments,respectively. The yields and 100-grain weight of Dongnong 52 were maximum under Ce3 and Ce9 treatments.
Conclusions
Lanthanum and cerium had the effects of "low promotion and high inhibition" on chlorophyll content of high protein soybean,high fatty soybean and dualpurpose soybean. The effects of lanthanum solution on the chlorophyll contents of different quality soybeans were universal and applicable. The effects of cerium solution on different quality soybeans were different.
Cerium solution could increase the soybean yields of different quality types. High protein soybeans had the highest yield under 60 mg · L-1CeCl3treatment,and high fat soybeans and dual-purpose soybeans had the highest yield under 30 mg · L-1CeCl3treatment.
杂志排行
Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Spatiotemporal Change of Agrometeorological Flood Disasters in Heilongjiang Province
- Technical Parameter Optimization for Straw Fibre Mulching Film Raw Material from Corn Stalk
- Prokaryotic Expression of IBV N Protein and Development of Indirect IBV N Protein-mediated ELISA
- Effect of Zinc Acetate on Broiler Nutrient Metabolism and Skeleton Characteristic
- Effects of Facultative Anaerobic Cellulolytic Bacteria and Nitrogen-fixing Bacteria Isolated from Cow Rumen Fluid on Rumen Fermentation and Dry Matter Degradation in Vitro
- Effects of Different Feeding Methods on Behaviors,Immunities and Growth Performances of Suckling Calves
