Study on antiviral effect in vitro and long-term toxicity of fruit of Prunus cerasifera Ehrhar f.in rats
2020-04-11SHIChenxiaoNIUFengjuGUOHaoZHANGYanxueZHOUChangzheng
SHI Chenxiao,NIU Fengju,GUO Hao,ZHANG Yanxue,ZHOU Changzheng
(1.School of Pharmacy,Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Jinan 250355,China;2.Shandong Academy of Chinese Medicine,Jinan 250014,China)
[Abstract] Objective:The present study aimed to identify and obtain the antiviral active components of the fruit of Prunus cerasifera Ehrhar f.using the antiviral activity tracing method and to evaluate the long-term toxicity of the active components with oral gavage.Methods:The fruit extract was prepared by percolation with water and its antiviral effect on different kinds of viruses was evaluated in vitro by neutral red dye solution staining.Then,percolation solution was separated and purified by alcohol precipitation and macroporous resin allowing the extract with best antiviral.Lastly,through physical and chemical identification,the effective extract was qualitatively analyzed and its content was determined by UV.The long-term toxicity of the extract in rats was measured by the detection of general behavior,body weight,food intake related organ tissue sections,and delayed toxicity of experimental animals after the oral gavage.Results:The results demonstrated that the extract with best antiviral capacity was the polyphenols of Prunus cerasifera Ehrhar f.(PCEP) isolated and purified by 25% ethanol eluent and D101 macroporous resin,which had a good inhibitory effect on HSV-1 virus.Moreover,toxicity evaluation in vivo result showed no significant adverse effect in rats,revealing that PCEP was safe in use.Conclusion:PCEP could act as promising and effective antiviral therapeutics with relative safety in use.
[Key words] Prunus cerasifera Ehrhar f.;polyphenol;antiviral;long-term toxicity
PrunuscerasiferaEhrharf.has by convention been termed red leaf plum,is a medicinal and edible plant of the genus Prunus in the rose family.Its small and astringent fruits,mainly scattered naturally after ripening and rarely used for fresh food[1].Purple leaf plum,as an ornamental plant,luxuriant branches and leaves,is widely planted in parks,gardens and other places.Since the fruits of purple plum are mostly scattered directly on the ground,their application value and prospect are greatly underestimated.Purple leaf plum fruit,as a natural antioxidant,has medicinal and health care value,including protecting liver,nourishing the middle and benefiting qi,nourishing Yin,promoting body fluid,moistening intestines and laxative,etc.[2].Its main chemical constituents include flavonoids[3-4],polyphenols[5-7],and it also include some other chemical constituents[8],such as beta-carotene (4) and quercetin.It has strong antioxidant capacity[9-10]and protective effect on alcoholic liver injury (ALD) rats[11].
Despite its many benefits,its antiviral and long-term toxicity have not been studied.Traditional herbal antiviral drugs are widely used in the Asia-pacific region,especially in China.At present,the separation of chemical components of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is basically systematic separation method.After various routine means and technologies are processed,some specific substances are obtained,and then these substances are screened by activity tests.However,these obtained specific substances may not necessarily have pharmacological activity,which may waste a lot of manpower,financial and material resources.In this study,we usedinvitroantiviral activity tracking method to conduct antiviral tests on the isolated and purified substances in each isolating step,and took therapeutic index as the director to determine whether the site obtained in this step had the expected antiviral activity.This pattern of separation of active parts of TCM is obviously better than the traditional separating method.
The mechanism of antiviral action of TCM can be summarized as:to kill viruses directly or reduce their virulence;to prevent the absorption and invasion of viruses;to inhibit the transcription and replication of viral DNA or mRNA;to cause oxidation resistance;to regulate the production of cytokines,etc.Based on the antioxidative effect of the fruit and the anti-oxidative mechanism of TCM in antiviral aspect,the antiviral effect of the fruit was preliminarily studied.
At the same time,the reason for few people eat the fruit is for their astringency or some toxicity.Thus,the toxicity test of the fruit was carried out to observe the long-term toxic effect of percolation of the fruit in rats.It includes the nature of reaction,severity,dose-toxicity relationship,time-toxicity relationship,main target organs,toxicity reversibility,and delayed toxicity.The study will provide reference for its edible and clinical use.
1 Materials &Methods
1.1 Materials
1.1.1 Equipments and reagents
Carbon dioxide cell incubator was bought from FOMAS.,and carbon dioxide virus incubator was bought from Shanghai YueJin medical equipment co.,LTD..Fluorescence inverted microscope and Ckx-31 inverted microscope were bought from Olympus company.EPOCH microplate reader was bought from Labsystems.Other chemical regents were in analytical grade and purchased from Tian in Fuyu Fine Chemical Co.,Ltd (Tianjin,China).The test kit including Glucose determination kit,Triglyceride assay kit,Total cholesterol assay kit etal were provided by Desi diagnostic system co.,Ltd (Shanghai,China).
1.1.2 Cells and viruses
Hep-2 and MA104 cells were provided by the Institute of Basic Medicine of Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences.Respiratory Syncytial virus,enterovirus type 71 and herpes simplex Ⅰ viruses were provided by Influenza virus laboratory,institute of virology,Chinese center for disease control and prevention.
1.1.3 Animals
Wistar rats in SPF grade,including 40 male and 40 female,provided by Jinan PengYue experimental animal breeding co.,LTD.(Stock number:20140007).
The rats were raised in rat cages,giving water freely and a certain amount of feed.Cage tools were exchanged twice a week.Feed room was well ventilated,the temperature and humidity was 22~26 ℃ and 45%~70%,and day and night time was 12 h/12 h.The animals were fed regularly and quantitatively.
1.1.4 Test drugs
The fruits were picked in the campus of Shandong university of traditional Chinese medicine,Changqing district,Jinan city,Shandong province.
1.2 Methods
1.2.1 Extraction of fruit ofPrunuscerasiferaEhrharf.for antiviral test
(1)PreparationofpercolatefromfruitofPrunuscerasiferaEhrharf.The cores of the fruits were removed,100 g fruits were weighed and crushed.The crushed fruits were percolated with water for 48 h and then filtered.The filtrate was concentrated to 1 g/mL (equivalent to fruits’ quality),and refrigerated for later use.
(2)PrecipitationofthepercolatebydifferentconcentrationofethanolDifferent volume fraction of ethanol was used to separate and purify the percolation of the fruit.The supernatant and the precipitated part were respectively used for the anti-virus experimentinvitro,and the absorbance value was determined by EPOCH microplate reader (Table 5),and the TI value was calculated.The best parts were separated and purified by macroporous resin.
(3)Samplespurificationwithdifferenttypesofmacroporousresin①Pretreatment with macro-porous resin According to the specific components in the fruit(flavonoids,polyphenols,procyanidins,etc.),non-polar or weakly polar resins were selected.D101 (non-polar),DM301 (weak polar),X-5 (non-polar) and AB-8 (weak polar) resins were weighed 200 g respectively and screened to conduct antiviral tests.At first,they were soaked in 95% ethanol for 24 h and the ethanol liquid level 5 cm higher than the resin.Then,they were packed into the chromatographic column by wet packing and washed with 95% ethanol.Then,we needed to check the outgoing liquid at any time and mix the liquid with water at 1∶5.If the mixed solution was not white turbidity but clear and transparent,ethanol elution should be stopped.Finally,we rinsed the resin column with distilled water until the effluent didn’t have alcohol taste.Set them aside.②The loading and elution of samples on macro-porous resin column The ethanol precipitation with best antiviral effect under “1.2.1:(2)” was added into 20 mL aqueous solution and mixed to the prepared macro-porous resin column.The aqueous solution of the drug were 5 cm higher than the resin and they were standing for 1 h.After adsorption,distilled water,25%,50% and 75% ethanol were used for eluting.The volume flow was controlled to be 3 BV/h,and each eluent received 5 column volumes.The eluent was concentrated to 5 mL (equivalent to 1 g/mL),respectively,for antiviral experimentsinvitro(Table 6).The ethanol precipitation was divided into four parts,and then dissolved in distilled water (10 mL per part).Then they were respectively loaded on D101,DM301,X-5 and AB-8 resins.Next,they were eluted with distilled water,25%,50% and 75% ethanol,and the eluent was collected for anti-HSV-1 experiments[15].
1.2.2 Extraction of fruit ofPrunuscerasiferaEhrharf.for long-term toxicity test
The drug used in the long-term toxicity experiment was polyphenols isolated and purified from percolate of the fruit (PCEP).
1.2.3 Experimental design for antiviral effects
(1)CellresuscitationandcultureThe cryopreserved tubes of MA104 cells and RD cells were kept in 37~40 ℃ warm water to melt with rapid stirring.The cryopreserved tubes were centrifuged at 800 r/min for 5 min to remove cryopreserved liquid.Appropriate 10% 1640 cell culture medium was added to the cell precipitation and mixed well,then the cell suspension was transferred to culture bottle.10% 1640 culture medium was added to the culture bottle to 12 mL,and then the cells were cultured at 37 ℃ and 5% CO2.After the cells grew into a monolayer,the cells were digested with 0.25% trypsin,and then passaged 1∶2.When the cells grew into a monolayer again,the cells were used for experiment[12].
(2)VirusamplificationRSV and HSV-1 virus were inoculated in the well-growing MA104 cells,and EV-71 enterovirus was inoculated in the well-growing RD cells.2% 1640 cell culture solution was added to the cells and the cells were cultured at 37 ℃ and 5% CO2for 24~48 h.The cytopathic effect (CPE) was observed under microscope,and the experiment was stopped and the cells were collected when the CPE was 90%.The culture bottle was frozen at -20 ℃ and treated with repeated freezing and thawing from 3 times.Then the bottle was centrifuged (1 000 r/min,5 min),and the supernatant fluid was quantitatively packaged and stored at -40 ℃ environment for later use[13].
(3)DeterminationofvirusvirulenceAccording to the conventional virulence measurement,48 h was selected as the measurement time to determine the virulence required by the experiment.Reed-muench formula was used to calculate the 50% infection concentration of the virus venom (TCID50).The virus was diluted 10-fold with RPMI-1640 containing 2% FBS to obtain 12 samples with different concentrations,and the virus was successively inoculated in 96-well plates containing monolayer host cells,and the cell control group was set at the same time.Then the viruses were placed in 37 ℃ and 5% CO2virus incubator to develop and were observed day by day under an inverted microscope for 4 days.Next,they were dyed for 1 h under the condition of 37 ℃ after 50 μL 1% neutral red was added.At last,the dye solution was discarded,the excess dye solution was washed thoroughly with distilled water,then 100 μL decolorizing solution was added for decolorization at room temperature for 10 min,and measured OD value with EPOCH microplate reader at 540 nm[14]and calculating the TCID50value (Table 3).
(4)AntiviraltestThe samples were diluted with 2% 1640 cell maintenance solution.A total of 12 dilutions were performed at 2-time serial dilution.50 μL of sample was added to each well in the 96-well plate containing monolayer virus host cells and then 50μL of RSV with 100-times TCID50was added to each well.Three replicated wells were set.Virus control group,cell control group,drug toxicity group and ribavirin positive control group were set at the same time.The plates were cultivated at 37 ℃ and 5% CO2.Cell lesion was observed daily.When more than 90% lesion appeared in the viral control group,electron microscope was used to observe and find out the more effective extract sites[15].The culture medium was abandoned and 100 μL neutral red dye solution was added into each well.The plates were incubated at 37 ℃ for 1 h of reaction.Then the neutral red dye solution was poured out,and the cells were rinsed 3 to 5 times with PBS.100 μL decolorizing solution was added to each well,and was placed in the incubator for 15 min.Then,OD value was measured with an enzyme labeling instrument at 540 nm.The antiviral experiments of EV-71 and HSV-1invitrowere carried out as the same procedure.Reed-muench method was used to calculate the drug half-effective concentration (EC50) and therapeutic index (TI).
EC50=[Antilog(logp1-pd)]×initial concentration
(1)
TC50=[Antilog(logp2-pd)]×initial concentratio
(2)
TI=TC50/EC50
(3)
Thep1 is the drug dilution higher than 50% cell survival,p2 is the drug dilution higher than 50% of the cytopathic rate.The higher the therapeutic index is,the stronger the drug’s inhibition of the virus is (Table 4).
(5)PhysicochemicalidentificationPhysicochemical identification was performed on the volume eluent of the first column eluted by 25% ethanol of D101 macro-porous resin.Because the water solubility of the extracts was relatively large,only the physicochemical identification of tannins,brass,glycosides and alkaloids was conducted in the experiment,and the types of the chemicals were preliminarily determined.
(6)DeterminationoftotalpolyphenolsAccording to the modified determination method of tannin content in “CHINESE PHARMACOPOEIA”,the content of polyphenols in the first column elute by 25% ethanol of D101 macro-porous resin was measured.
1.2.4 Long term toxicity test method[16]
The samples used in the long-term toxicity experiment were polyphenols isolated and purified from percolate of the fruit (PCEP).
(1)AnimalgroupsRats were fed adaptively and were observed for 5 days before tested.General conditions of rats during adaptive feeding were observed daily.The rats were weighed on the 1st day and the last day during adaptive feeding period,and the results of weighing were recorded.Based on the body weight,male and female rats were randomly divided into 4 groups:blank control group,high dose group,medium dose group and low dose group of PCEP.Twenty rats were in each group,half male and half female.
(2)RouteandmethodofdrugadministrateIn this study,oral gavage was used for drug administion.The maximum gavage of rats is 5 mL,therefore,the high medium and low dose group was given 5,3 and 2 mL of samples respectively,which were equivalent to fruits’ mass about 5,3 and 2 g.The animals in the control group were given 5 mL distilled water by gavage.The duration of drug delivery of 4 weeks was designed.The drug was given once a day in the morning and continuously for 4 weeks.
(3)Thedeterminationmethodanddetectionfrequencyofeachindex①General symptoms and death During the experiment,general observation was made twice a day before and after drug delivery to observe the appearance,behavior and activity,gland secretion,respiration,diet,feces,etc of rats.If abnormal reactions (toxic reactions) were found,detailed observation and records were made.If death was found,autopsy was conducted in time,and anatomy and histopathological examination was performed.②Weight determination Determination times:The rats were weighed every Monday morning during the period of drug delivery,and measured before the autopsy if there were dying rats.Determination method:weighed before drug delivery during drug delivery period.Weighed on an empty stomach before dissection.③Determination of material consumption The rats were given adequate feed every week.During the whole test,each cage was measured once a day to calculate the amount of food intake of each group of rats by the following equation:
The amount of foodinate of each group rats per day=the given amount-the residural amount
(4)
④Determination of hematology indexes At the end of drug delivery (4 weeks) and the end of convalescence (2 weeks),blood was sampled from the abdominal aorta after fasting for 12 h.The hematological indexes including WBC,RBC,HGB,PLT,RC,APTT etc.were observed.There were 10 rats in each group,half males and half females.⑤Determination of serum biochemical indexes At the end of drug delivery (4 weeks) and the end of convalescence (2 weeks),blood was sampled from the abdominal aorta after fasting for 12 h.The blood was centrifuged to get serum and then serum biochemical indexes including GLU,TG,CHOL,TBIL,TP,ALB,ALT,AST,ALP,BUN,CRE,CK,Na+,K+,Cl-and so on were observed.There were 10 rats in each group,half males and half females.⑥Histopathological examination After 4-weeks drug delivery,10 rats in each group were dissected,half male and half female.The remaining rats were dissected after 2-weeks convalescence.Specific operation method:rats were anaesthetized by intraperitoneal injection with chloral hydrate (25 mg/kg-1) after 12 h fasting.The femoral artery was exsanguinated to kill the rats and a comprehensive systematic autopsy was performed.The morphological changes of the organization and visceras were observed with the by visual inspection.Then wet weight and viscera coefficient of the brain,heart,liver,kidney,lung,adrenal,thymus,spleen,testis(male) and epididymis (male),prostate (male)were measured,and the viscera were quickly fixed in 4% formaldehyde solution.If abnormal organs and tissues were found with the by visual inspection,then they would be fixed at the same time.Organs and tissues of the high-dose group and the blank control group were routinely embedded with paraffin and sectioned for microscopic examination with H-E staining.If histopathological changes occur in the high-dose group,the corresponding tissues of rats in the medium-dose and low-dose groups should also be prepared and examined by optial microscopy.⑦Discontinue medication for observation during recovery After the end of the autopsy,medication were discontinued on the remaining 10 rats in each group to observe 2 weeks to understand the reversible degree of toxic reaction and the possible delayed toxicity.The indicators of observation and detection were same as the above.⑧Statistical processing The body weight,material consumption,hematological examination indexes,serum biochemical examination indexes and organ coefficients of the rats were statistically analyzed.The experimental data were presented as “mean+/-standard deviation”,SPASS ststistics statistical software was used,one-way ANOVA method in SPSS software was used for testing,and LSD method was used for comparison.P<0.05 was considered to be significantly different.

Table 1 Detection methods of hematology indexes

Table 2 Detection methods of serum biochemical indexes
2 Results
2.1 Antiviral results in vitro of the fruit
2.1.1 Virulence of the virus
Determination of formula:
Cell survival rate=
(5)
Cytopathic=1-Cell survival rate
(6)
Cytopathic rate=
(7)
TCID50=Antilog (logC+pd×logCm)
(8)
Where TCID50is shown in Table 3.The pd is the cell ratio;C is the dilution which is higher than 50% of the lesionrate,Cm is the multiple dilution factor.

Table 3 TCID50 of each virus
2.1.2 The percolation on virus inhibition
The results of percolation on virus is as shown in Table 4.
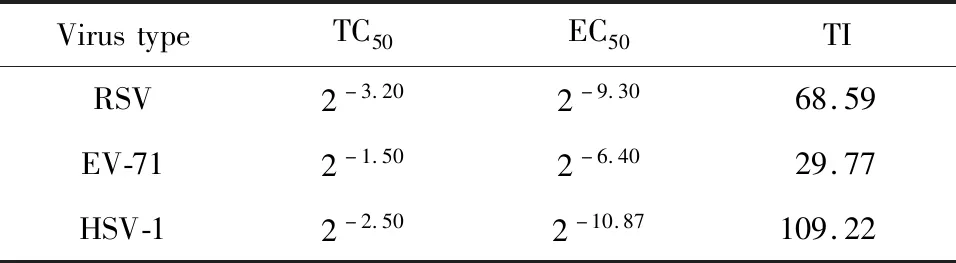
Table 4 Effect of percolation of the fruit on virus inhibition
It could be seen from Table 4 that the percolation of the fruit has the best antiviral effect on HSV-1invitro,and the TI is 109.22.
2.1.3 Inhibition effect precipitation of the percolation by different concentration of ethanol on HSV-1
The supernatant has no inhibition to HSV-1 effect,and the results of precipitation part were shown in Table 5.
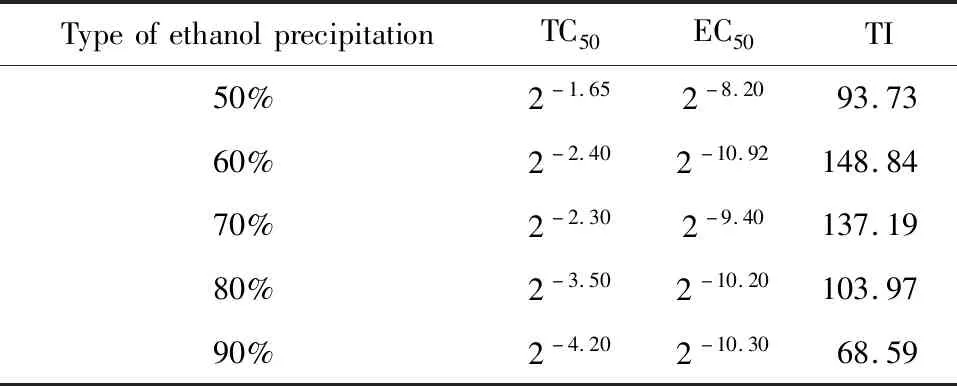
Table 5 Inhibition of HSV-1 by different concentration of ethanol precipitation of the fruit
It could be seen from Table 5 that the TI value of the 60% ethanol precipitation part of the percolation of the fruit percolation was 148.84,which showed that the 60% ethanol percolation part had the a very significant inhibition on HSV-1.
The purpose of alcohol precipitation is to take the essence and discard the dregs.When the concentration is low,impurities cannot be removed.When the concentration is high,most impurities can be removed.But some of the active ingredients will be coated,thus reducing the amount of active ingredients in the solution[17].
It can be seen from the results that 60% alcohol precipitation retains the active ingredients to the greatest extent on the basis of removing impurities[18].Then the 60% ethanol percolation was separated and purified by macro-porous resin.
2.1.4 Inhibition effect of different elution sites on HSV-1 obtained from different resins
The results were as shown in Table 6.(50%,75% ethanol elution didn’t have antiviral effect,so they were omitted)
1) Means invalid;2) The first number represents the eluent sequence and the second represents the column volume sequence
The results showed that the first column volume of 25% ethanol obtained from D101 macro-porous resin had the best antiviral effect and the TI was 200.85.
The adsorption capacity of D101 macro-porous is generally strong for organic compounds without polarity or weak polarity.It can be seen from the above results that the active components of anti-HSV-1 in the fruit should not be weakly polar chemicals[19].
2.1.5 Physical and chemical identification and content of active extracts
In the experiment,ferric chloride reaction (phenolic hydroxyl),lead acetate reaction (phenols) and vanillin concentrated sulfuric acid reaction (polyphenols) were positive;the phenomena of hydrochloride magnesium-powder reaction (to identify flavonoids),Molish test (to identify sugars) and iodine-potassium iodide reaction (to identify alkaloids) were negative.
Through physicochemical identification,it could be concluded that the chemical composition of the first column volume eluent eluted by 25% ethanol from D101 macro-porous resin column was mainly polyphenols.
As for the content assay,the modified determination method of tannin content was used to measure the polyphenol content in active extract.The linear relationship between absorbance and polyphenol content was strong in the range of 2.05~10.03 μg/mL,and the calibration curve wasY=31.653X+0.0535 (R2=0.999 2).The average recovery rate was 98.50% (RSD=0.55%),and the total average polyphenol content was 18.15 mg/g.
Polyphenols are called “the seventh nutrients”,which is found in some common plant foods.The Japanese study showed that the polyphenolic compound EGCG may block the expansion of viruses in body,which will be a group of promising active ingredients to develop antiviral drugs[20].
2.2 Long-term toxicity to rats of polyphenol from the fruit
2.2.1 General symptoms and death
During the whole test period (4-weeks drug delivery and 2-weeks convalescence,the rats in the dosing groups were generally in good condition,and abnormal symptoms weren’t observed in the appearance of signs,behavior,activity,respiration,feeding,fur,secretions,feces,etc.of the rats,and death wasn’t observed.There was no significant difference compared with the blank control group.
2.2.2 Weight determination
During the experiment,the rats in the control group and the PCEP dose groups showed good development and gradually increased quality,and there was no statistical significance between the dose groups and the blank group.After 2-weeks drug withdrawal and recovery,there was no statistically significant difference between each dose group and the blank group,as shown in Fig 1.

n=10 in each group before and after drug delivery of 1~4week,and n=5 during the observation period of convalescence.P>0.05 in the A and B.
Fig.1 Effect of PCEP on weight of male (A) and female rats (B) during the period of 4-weeks drug taking delivery and 2-weeks convalescence (g/rat)
2.2.3 Determination of material consumption
In terms of dietary intake,there was not significant difference between the dose groups and the blank group at the drug delivery stage and the convalescence stage.As shown in Fig 2.
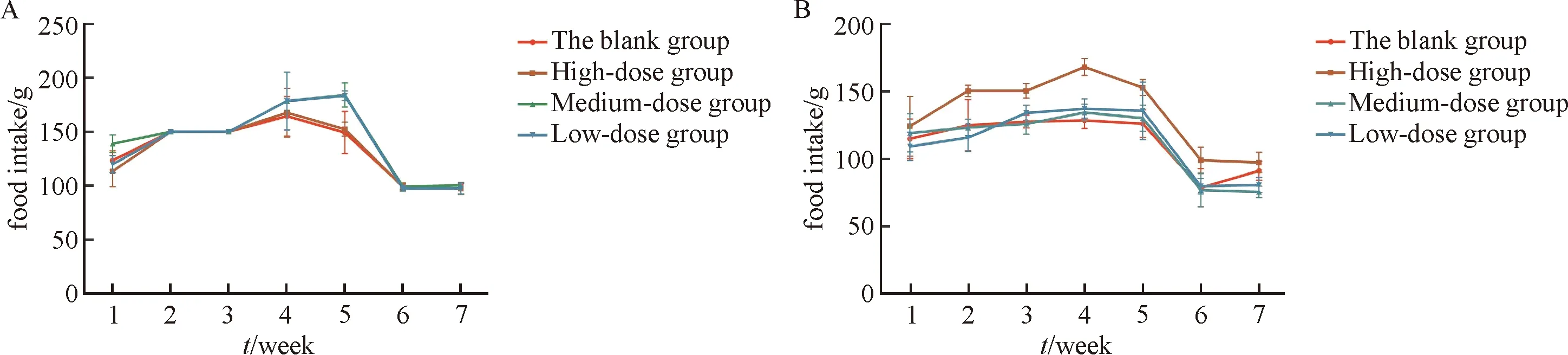
n=10 in each group before and after drug delivery of 1~4week,and n=5 during the observation period of convalescence.A:Compared with the blank control group,P=0<0.05 at the 3rd week in the low-dose group.The rest of the P>0.05.B:Compared with the blank control group,P=0.04<0.05 at the 2nd week in the low-dose group.The rest of the P>0.05.
Fig.2 Effect of PCEP on daily intake of male (A) and female (B) rats during the period of 4-weeks drug taking delivery and 2-weeks convalescence (g/day/group)
Those data suggested that food intake of rats was relatively stable.
2.2.4 Determination of hematology indexes
After 4-weeks drug delivery and 2-weeks convalescence,the hematological indexes of the rats in the low-dose,medium-dose and high-dose groups were all within the normal range with no statistical significance compared with the control group,except for individual indicators of individual dose groups,as shown in Table 7 and Table 8.

Table 7 Effect of PCEP on hematological indexes after 4-weeks drug delivery in rats
1) Half male and half female,2) Compared with the blank control group,P<0.05.

Table 8 Effect of PCEP on hematological indexes after the period of convalescence in rats
1) Half male and half female,2) Compared with the blank control group,P<0.05.
2.2.5 Determination of serum biochemical indexes
After 4-weeks drug delivery and 2-weeks convalescence,the serum biochemical indexes of the rats in the low-dose,medium-dose and high-dose groups were all within the normal range,with no statistical significance compared with the control group,except for individual indicators of individual dose groups,as shown in Table 9 and Table 10.
2.2.6 Histopathological examination
(1)AutopsyoverviewAt the end of drug delivery and convalescence observation,the rats in each group were dissected and observed by visual inspection according to the plan:the skin of the rats in each group was intact,and skin lesions such as depilation,redness and swelling were not observed.There was no secretion or trauma in natural orifice such as ear,mouth,nose and anus;There were no cyanosis,yellow and red spots in the eyes;The subcutaneous tissue was free of bleeding and masses,and the muscle was pink,shiny and elastic;There was no fluid or gas retention and no odor in chest cavity,abdomen cavity and skull cavity.The position,shape,texture and color of various organs were normal and there was no adhesion or other abnormal changes.

Table 9 Effect of PCEP on serum biochemical indexes after 4-weeks drug delivery in rats
1) Half male and half female,2) Compared with the blank control group,P<0.05.

Table 10 Effect of PCEP on serum biochemical indexes after the period of convalescence in rats
1) Half male and half female,2) Compared with the blank control group,P<0.05.
(2)VisceracoefficientAfter 4-weeks drug delivery and 2-weeks convalescence,the viscera coefficient of the rats in the low-dose,medium-dose and high-dose groups were all within the normal range,except for individual indicators of individual dose groups,with no statistical significance compared with the control group,as shown in Table 11、Table12、Table13 and Table14.
(3)EffectonpathologicalmorphologyofimportantorgansandtissuesCompared with the blank control group during the drug delivery period,liver room dilation was observed in 1 male rat in the high-dose group,lymphocyte infiltration was observed in 1 female rat in the medium-dose group,and thymus gland hyperplasia was observed in 1 male rat in the low-dose group and 1 male rat in the medium-dose group.Significant abnormalities weren’t found in other tissues.
In the convalescence period,compared with the blank control group,the small U in the center of the liver of 1 male rat in the high-dose group was widened,and lung congestion was found in 1 male rat in the medium dose group,and obvious abnormality wasn’t found in other tissues.
Table 11 Effect of PCEP on viscera coefficient after 4-weeks drug delivery in rats (male) (g/100 g)
1)Compared with the blank control group,P<0.05.

Table 12 Effect of PCEP on viscera coefficient after 4-weeks drug delivery in rats (female) (g/100 g)
1) Compared with the blank control group,P<0.05.

Table 13 Effect of PCEP on viscera coefficient after the period of convalescence in rats (male) (g/100 g)
1) Compared with the blank control group,P<0.05.

Table 14 Effect of PCEP on viscera coefficient after the period of convalescence in rats (female) (g/100 g)
1) Compared with the blank control group,P<0.05.
Due to the lack of drug dose dependence in these pathological manifestations,and the difference between each dose group and the control group was not statistically significant,it was considered that it had nothing to do with the toxic effect of the fruit,considering that it was caused by their own diseases of rats or other reasons[21].Significant abnormal change wasn’t observed in other organs.Combined with the above results of organ quality and organ coefficient,it showed that continuous drug delivery for 4 weeks didn’t have significant effect on the tissue morphology and structure of rats’ organs.
A1:Lung tissue sections of the blank group (×200);A2:Lung tissue sections of the high-dose group (×200);B1:Liver tissue sections of the blank group (×400);B2:Liver tissue sections of the medium dose group (×400);C1:Renal tissue sections of the blank group (×400);C2:Renal tissue sections of the low-dose group (×400)
Fig.3 Optical photomicrograph of some rat organs after HE staining.
3 Conclusion and discussion
In the anti-virusinvitroexperiment,the percolation of the fruit was used as antivirus liquid,which showed a good inhibitory effect on RSV,EV-71 and HSV-1.Polyphenols were selected as the antiviral active parts of the fruit,and the first column volume eluted by D101 macro-porous resin with 25% ethanol showed good efficacy TI was 200.85).The results revealed that the PCEP had a good inhibitory effect on HSV-1 virus.
At present,international anti-HSV-1 drugs mainly consists of some antibiotics[22].Several TCM has the advantages of wide spectrum antiviral,less side effects etc.,contributing TCM is widely used.In the following study,the antiviral mechanism of percolation of the fruit will be further explored.About the further research,the specific mechanism of antiviral action would be elucidated and effective monomers would be separated.
The long-term toxicity test of rats indicated that the PCEP was continuously given for 4 weeks,and no poisoning symptoms were observed in the rats.Body weight,food intake,hematology index examination,serum biochemistry,organ quality and organ coefficient were not statistically significant versus the control group,and all fell within the normal range.After anatomical and histological observation,no histopathological change was observed in the heart,liver,spleen,lung,kidney,ovary,testicle and other organs of the rats,except for slight degeneration of liver,spleen and heart that was not related to drug use factors in some rats.After 2-weeks convalescence period,rats were in the obvious health state.And there was no statistically significant difference in the effect of different doses of purple leaf plum fruit on the indexes of rats versus the control group.The experimental study showed that there was no obvious toxic reaction or delayed toxic reaction in the percolation of the fruit,and it was safe to take large doses for a long time,which provided experimental basis for clinical application.
In conclusion,PCEP has a anticipating prospect of antiviral application and a guarantee of safety and without toxicity,which is of great development and utilization value.
Acknowledgements:We would like to express our gratitude to the reviewers for their useful comments.
Disclosure statement:No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Funding:This study was supported by the Chinese medicine antiviral application foundation and key technology and industrialization of Shandong province(XTCX2014C01-04).
The authors would like to apologise for any inconvenience caused.
