双氢青蒿素对低氧下人肺动脉内皮细胞增殖和分泌功能影响
2020-04-05余华王良兴刘静静董一枝夏晓茹管华琴
余华 王良兴 刘静静 董一枝 夏晓茹 管华琴
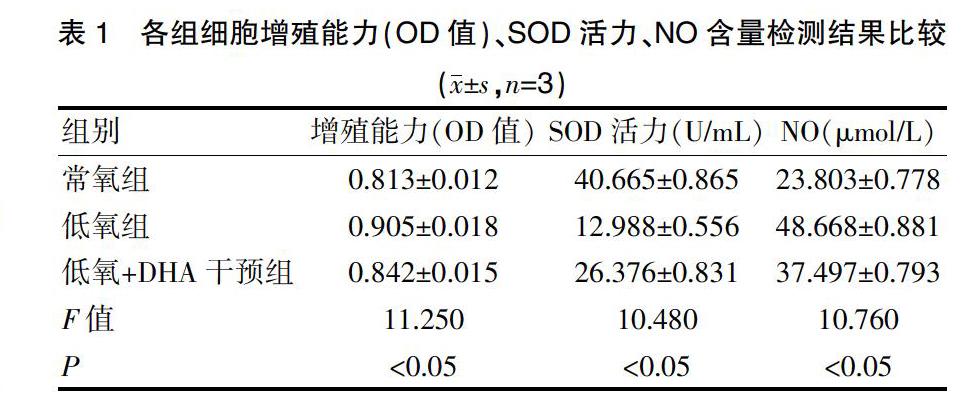
[摘要] 目的 探討双氢青蒿素(Dihydroartemisinin,DHA)对低氧条件下人肺动脉内皮细胞的数量和功能影响,寻找治疗低氧性肺动脉高压的新方法。 方法 将人肺动脉内皮细胞株进行复苏、传代、鉴定,然后细胞实验分为常氧组、低氧组、低氧+DHA干预组,造模48 h后,分别检测人肺动脉内皮细胞的增殖能力(CCK-8法)、ELISA法检测细胞上清液中超氧物歧化酶(SOD)活性和一氧化氮(NO)含量。 结果 常氧组、低氧组、低氧+DHA干预组的CCK-8法检测OD值分别为(0.813±0.012)、(0.905±0.018)、(0.842±0.015),各组间比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);各组SOD活力检测分别为(40.665±0.865)U/mL、(12.988±0.556)U/mL、(26.376±0.831)U/mL, 各组间比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);各组 NO含量分别为(23.803±0.778)μmol/L、(48.668±0.881)μmol/L、(37.497±0.793)μmol/L,各组间比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 DHA可以抑制低氧诱导下人肺动脉内皮细胞的增殖能力,改善低氧诱导下SOD活性和抑制低氧诱导下分泌NO的能力;提示DHA对低氧诱导的人肺动脉内皮细胞具有保护作用,推测其对低氧性肺动脉高压的形成可能具有拮抗作用。
[关键词] 双氢青蒿素;低氧;肺动脉内皮细胞;肺动脉高压
[中图分类号] R563.9 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2020)04-0015-04
Effects of dihydroartemisinin on proliferation and secretion of human pulmonary artery endothelial cells under hypoxia
YU Hua1 WANG Liangxing2 LIU Jingjing2 DONG Yizhi2 XIA Xiaoru3 GUAN Huaqin2
1.Department of Cadre Health, the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Hangzhou 325000,China;2.Department of Respiratory Medicine, the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Hangzhou 325000,China;3.Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Hangzhou 325000,China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the effects of dihydroartemisinin (DHA) on the number and function of human pulmonary artery endothelial cells under hypoxic conditions, and to find a new treatment for hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Methods Human pulmonary artery endothelial cells were resuscitated, passaged and identified. Then the cells were divided into normoxia group, hypoxia group and hypoxia+DHA group. Human pulmonary artery endothelial cells were resuscitated, passaged and identified. Then the cells were divided into normoxia group, hypoxia group and hypoxia+DHA group. After 48 hours of modeling, the proliferation of human pulmonary artery endothelial cells was detected (CCK8 method). The superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and nitric oxide (NO) content in the cell supernatant were determined by ELISA method. Results The OD values of CCK-8 method in normoxia group, hypoxia group and hypoxia+DHA group were (0.813±0.012), (0.905±0.018), and (0.842±0.015), respectively. The differences between the groups were statistically significant (P<0.05). The SOD activity of each group was (40.665±0.865)U/mL, (12.988±0.556)U/mL, and (26.376±0.831)U/mL, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The NO content of each group were (23.803±0.778)μmol/L, (48.668±0.881)μmol/L, and (37.497±0.793)μmol/L, and the differences were statistically significant among groups. Conclusion DHA can inhibit the proliferation of human pulmonary artery endothelial cells induced by hypoxia, improve the activity of SOD and inhibit the secretion of NO; suggesting that DHA has protective effect on hypoxia-induced human pulmonary artery endothelial cells, and it may have an antagonistic effect on the formation of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension.
