The Effect of Clinically Used Crystalloid Solution on the Clearance Rate of Lactic Acid in Septic Shock Patients
2020-04-03XiaoYanDengLiNaXianYaPingZhuangZhiXingLinChangHuiZhongYuanZhengYang
Xiao-Yan Deng, Li-Na Xian, Ya-Ping Zhuang, Zhi-Xing Lin, Chang-Hui Zhong, Yuan-Zheng Yang
ICU, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University,Haikou 570102
Keywords:
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
Sepsis refers to a systemic inflammatory reaction caused by infection, which can easily lead to multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. It has the characteristics of high incidence, acute onset,and critical illness. With departmental statistics , there are 18 million sepsis patients worldwide each year, and 15,000 people die of the disease every day, and the number is still growing at an annual rate of 8%[1]. In recent years, although many scholars have developed various new types of antibiotics, the mortality rate of sepsis is still as high as 30%-70%. Septic shock refers to shock caused by sepsis.After the pathogen invades the body, the endotoxin and exotoxin produced by the pathogen act on the human body, causing the body to have metabolic system, microcirculatory system, coagulation system, immunity systemic disorders, which in turn triggers a systemic multiple organ dysfunction-induced shock . Patients with septic shock suffer from insufficient effective blood circulation,lack of effective perfusion of cells, tissues and organs, insufficient supply of oxygen, leading to increased anaerobic metabolism,obstacle of lactic acid clearance, and accumulation of lactic acid in the blood. Therefore, we usually test the concentration of lactic acid in the blood as a quantitative indicator of the degree of tissue perfusion and hypoxia of cells[2,3]. The higher the concentration, the more serious the disease and the worse the prognosis of the disease.[3] However, the concentration of lactic acid is often affected by factors other than sepsis and shock, such as strenuous exercise, liver dysfunction, etc. Therefore, monitoring the concentration of lactic acid in the blood alone does not completely reflect the oxygenation status of the body, the severity of the disease, and the prognosis of the patients. A large number of studies have now shown that blood lactate clearance rate is more accurate to evaluate[4,5]. The treatment of septic shock follows the principle of early detection, early assessment and early intervention. Crystalline fluid is a commonly used shock resuscitation fluid in clinical practice. Because of its small molecular weight and high safety, it can rapidly stabilize individual hemodynamics. It is used in the rescue of all kinds of shock patients [2], but there is no literature to compare the effects of different crystalloids in septic shock. The authors compared the effects of infusion of sodium lactate Ringer's solution, normal saline and compound sodium chloride injection on patients with septic shock for fluid resuscitation, with comparing the heart rate of the three groups before treatment and after 24 hours of treatment (HR ),mean arterial pressure (MAP), cardiac output, procalcitonin (PCT),C-reactive protein (CRP), also with the three groups of patients treated 24h lactate clearance rate and APACHE II score before and after, and the three groups of patients with total length of hospital stay, mortality statistics comparison is as follows.
2. Information and methods
2.1 General Information
Sixty-eight patients with septic shock who were treated in our hospital from January 2017 to January 2019 were enrolled. The patients were randomly divided into three groups: sodium lactate Ringer's solution group (LR group, 23 cases) and saline group (NS group, 22 cases) and compound sodium chloride injection group(RS group, 23 cases). In LR group: 12 males and 11 females, aged 38-62 years, average age (51.63±2.65) years old, there were 11 cases of severe pneumonia, 4 cases of celiac infection, 6 cases of intracranial infection and 2 cases of traumatic infection; NS group: 10 males and 12 females, aged 19-61 years old, average age(50.98±2.81) years old, includes 10 cases of severe pneumonia, 4 cases of celiac infection, 5 cases of intracranial infection, 3 cases of traumatic infection; RS group: 11 males, 12 females, aged 20-63 years old, average age (51.41±3.55) years old, includes12 cases of severe pneumonia, 4 cases of celiac infection, 5 cases of intracranial infection, and 2 cases of traumatic infection. There was no statistically significant difference in gender, age and course of disease among the three groups (P>0.05), suggesting comparability;Selection criteria: (1) The subjects enrolled were in accordance with the diagnostic criteria for septic shock[6] in the 2018 Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Severe Sepsis and Sepsis Shock; (2)complete medical records; (3) approved by the ethics committee of the hospital; (4) confessed to the family members of the patient the purpose, process, and significance of the study, and obtained consent and signed informed consent;
Exclusion criteria: (1) patients with congenital heart disease; (2)patients with chronic organ dysfunction such as cirrhosis, renal failure; (3) patients with autoimmune diseases; (4) those who are allergic to survey drugs;
2.2 Method
All three groups received the same basic treatment, such as vital signs monitoring, blood gas examination, antibiotic treatment, etc., in which LR group was treated with 1500ml lactated Ringer's solution for fluid resuscitation, with an infusion rate of 10ml/kg.h; NS group was resuscitated with 1500ml sodium chloride at an infusion rate of 10ml/kg.h; and in RS group, 1500ml compound sodium chloride was resuscitated with an infusion rate of 10ml/kg.h, The observation time of three groups was 24h;
2.3 Observation indicators and evaluation criteria
2.3.1 Hemodynamics
The heart rate (HR), mean arterial pressure (MAP) and cardiac output of the tthree groups of patients before treatment and 24h after treatment were recorded by ECG monitor for comparative analysis.
2.3.2 Inflammatory factor levels
5ml of radial artery blood was collected from patients in the three groups before and after 24h of treatment. After centrifugation, the serum was reserved for use. PCT, CRP and BNP levels of patients in the three groups before and after treatment were detected and compared by immunofluorescence analysis with Smartchem 600 automatic biochemical analyzer;
2.3.3 Comparison of lactic acid clearance rate
The lactate values in the arterial blood of the three groups were detected before treatment and 24h after treatment. The lactate clearance rate of the three groups was calculated at 24h. The formula is: lactate clearance rate = (pre-treatment lactate value -post-treatment lactate value) / Lactic acid value before treatment ×100%; and the APACHE II scale was used to evaluate the condition of the three groups before and after treatment. It is recommended in the guidelines for septic shock in China that lactic acid value and lactic acid clearance rate are taken as the prognostic indicators of septic shock patients, and the level of lactic acid clearance rate is positively correlated with the prognosis of patients[6]. The APACHE II scale is commonly used to clinical critical tool for assessing the physiological status of critical patients. The scale is divided into acute physiology, age and chronic health three by monitoring the patient's body temperature, heart rate, respiration, oxygenation and other indicators. The highest score is 71 points, more than 15 points is classified as severe, and the higher the score represents the more serious condition;
2.3.4 Treatment outcome
The treatment status of the three groups of patients was recorded,including the overall length of hospital stay, mortality rate and the probability of occurrence of acute renal failure, and then compared in a list;
2.4 Statistical methods
The collected data were analyzed by SPSS 23.0. The count data was expressed as the rate (%). The test was performed 2test, the measurement data was expressed as (±s ), and the comparison between the three groups was performed by one-way ANOVA (F test). ), the difference was statistically significant at P < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1 Hemodynamics
After testing, there was no significant difference in HR, MAP and cardiac output between the three groups before treatment (P>0.05).After 24 hours of treatment, the HR of all three groups decreased,accompanying MAP and cardiac output increasing, and it has Significant statistical difference (P<0.05) compared with before treatment. Meanwhile, HR of patients in the LR group were lower than the control group, and MAP and cardiac output were higher than the RS group and the NS group (P<0.05). The specific data are shown in Table 1:
3.2 Inflammatory factor levels
The values of PCT, CRP and BNP in the three groups before and after treatment were not statistically significant difference (P>0.05).The specific data are shown in Table 2:
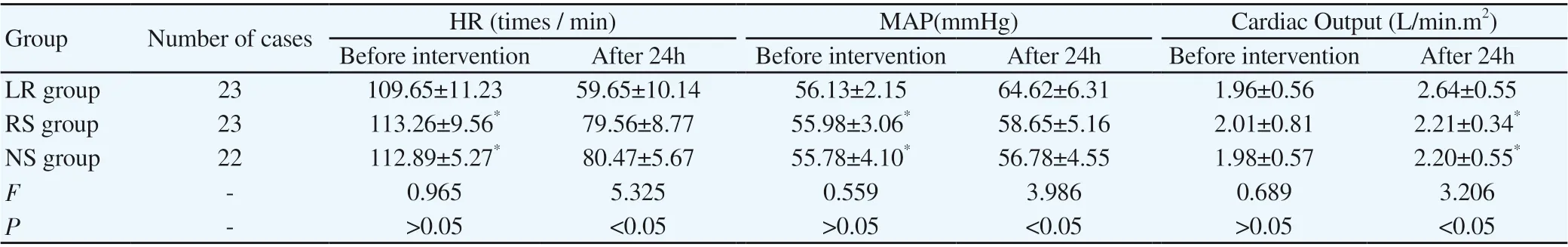
Table1 Comparison of Hemodynamic Parameters in Three Groups of Patients
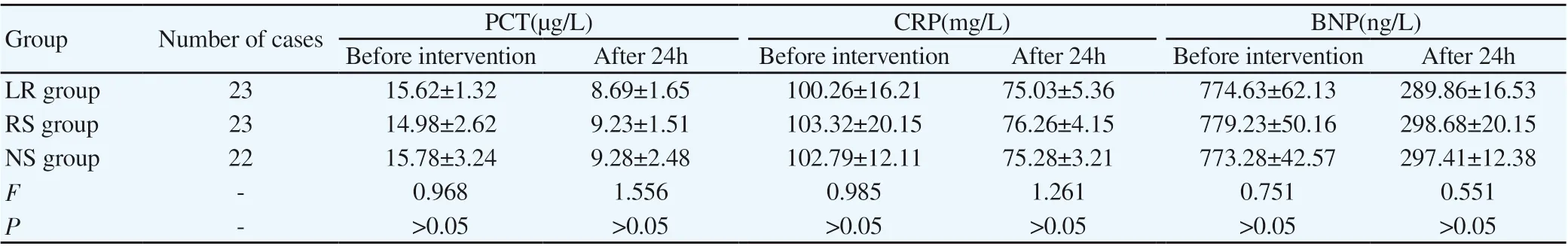
Table2 Comparison of Inflammatory Factors Levels among the Three Groups
3.3 Lactate clearance rate comparison
After calculation, it was found that there was no statistically significant difference in lactate clearance rate among the three groups after treatment for 24 hours (P>0.05). There was no significant difference in the APACHE II scores among the three groups before and after treatment (P>0.05):
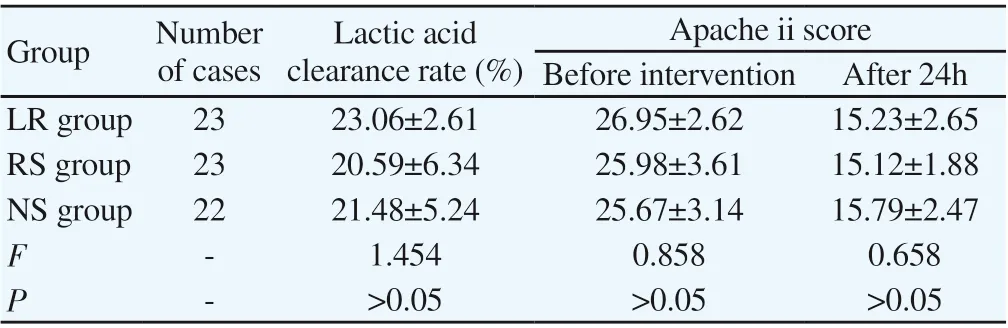
Table3 Comparison of Lactate Clearance Rates among the Three Groups
3.4 Treatment outcomes
According to statistics, the overall length of hospital stay of the experimental group was shorter, the mortality rate and the incidence of acute renal failure were lower than the control group, but the difference was not statistically significant (P<0.05). The specific data are shown in Table 4:
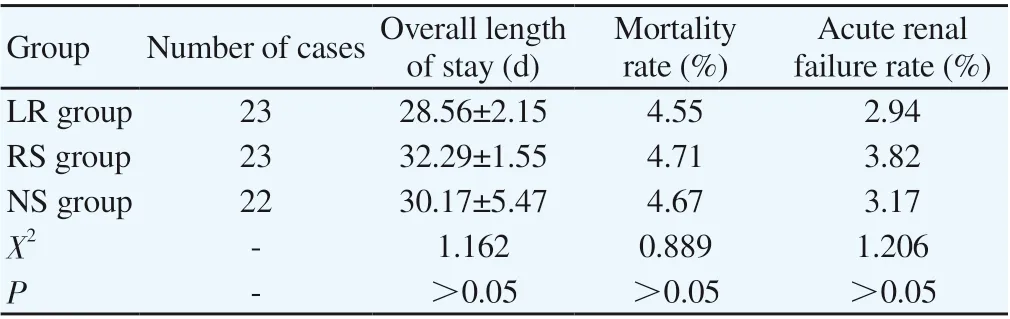
Table4 Comparison of Treatment Outcomes among the Three Groups
4. Discussion
Sepsis is one of the clinically critical types of infection. The disease occurs because the infection triggers an inflammatory reaction of the whole body, which in turn induces organ damage or failure.Sepsis is an important factor threatening human life and health. It will cause multiple organ failure and increase its mortality . Sepsis shock is caused by sepsis. The hemodynamics of patients with septic shock may change dramatically. The extensive expansion of systemic blood vessels and the increase of permeability may cause a relative decreasing in effective circulating blood volume, insufficient tissue perfusion, increasing heart rate, decreasing cardiac output,and relatively insufficient oxygen supplement to the cells. Metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide or lactic acid accumulates in the body,will exacerbate the damage to vital organs such as the brain or kidneys[8]. Fluid resuscitation can significantly improve the effective circulating blood volume of individuals, increase oxygen delivery,enhance organ perfusion, and thus prevent organ damage[9]. Early intervention of patients with septic shock is an important means to improve their prognosis. Crystalline fluid is the preferred and common type of liquid resuscitation. Currently, the clinically used crystalloids include sodium lactate Ringer's solution, normal saline and compound sodium chloride injection, however, there are few studies on how to select resuscitation crystal fluid and optimize the fluid resuscitation scheme for septic shock. The authors compared the effects of three clinical crystals on the lactate clearance rate in patients with septic shock. The results showed that the application of lactated Ringer's solution can better maintain the circulation capacity and blood pressure, which can alleviate the clinical situation of patients with septic shock. Symptoms, but no significant effect on lactic acid clearance, the use of clinically used crystalloid sodium lactate Ringer's solution, saline and compound sodium chloride injection for resuscitation did not have a statistically significant difference in the prognosis of patients with septic shock. The patients in the LR group had stable hemodynamics and improved inflammatory factors. The lactate clearance rate was higher than the other two groups using isotonic saline. Other indicators such as hospitalization time and mortality were also lower than the other two groups. , but none of them were statistically significant.The authors believe that the reduction of effective circulation in patients with septic shock is the main cause of organ dysfunction.Effective fluid resuscitation should meet the following conditions:(1) can improve and maintain blood volume; (2) no There will be accumulation and discharge from the body; (3) no metabolic waste or adverse reactions; (4) high cost-effectiveness[2]. But clinical practice indicates that no liquid at this stage can fully meet the above conditions. Isotonic saline is the most commonly used crystalloid at this stage, but the chlorine content in the liquid is high, and there is a high probability of occurrence of high chloride metabolic disorder after the application of the patient, thereby aggravating organ damage[10]. Lactated Ringer's solution is found to be significant in animal experiments. Prolong the survival time of hemorrhagic shock rats, and also reduce the inflammatory response and improve the state of tissue damage[11,12]. In the results of this study, the HR,MAP and cardiac output of the lactated Ringer's solution group were significantly improved compared with the other two groups after 24 hours of intervention, but the serum inflammatory factors CRP, BNP,PCT and other levels were not statistically different from the other two groups. difference.
All in all, compared with the three commonly used resuscitation crystalloids of sodium lactate Ringer's solution, physiological saline and compound sodium chloride injection, no one has shown significant advantages. Lactate Ringer's solution can significantly alleviate the clinical symptoms of patients with septic shock, and can better maintain the circulation capacity and blood pressure, however,it has no obvious effect on lactic acid clearance. The clinically used crystal liquid sodium lactate Ringer's solution, physiological saline and compound chlorination are used. There is no statistically significant difference in the prognosis of patients with septic shock after resuscitation with sodium injection. It is still necessary to further explore clinically and seek optimal solutions.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Meta analysis and medication analysis of TCM compound in the treatment of senile osteoporosis
- Efficacy of intravitreal injection of ranibizumab in the treatment of macular edema secondary to non-ischemic branch retinal vein occlusion
- Efficacy of PC-PRL implantation in the treatment of high myopia and its complications
- Clinical study of warm acupuncture combined with massage in treatment of periathritis of shoulder
- Expression and clinical significance of lncRNA SNHG3 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Effects of Pioglitazone on Renal Mitochondrial calcium and cytochrome C levels in Early Diabetic Nephropathy Rats
