Efficacy of PC-PRL implantation in the treatment of high myopia and its complications
2020-04-03WanJiangDongLongChenZhongLuoSuYingYuMiaoHeJuanWuXianMingLei
Wan-Jiang Dong, Long Chen, Zhong Luo, Su-Ying Yu, Miao He, Juan Wu, Xian-Ming Lei
Department of Ophthalmology, Wanjiang Eye Hospital, Mianyang, Mianyang 621052, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
Ametropia, caused by pathological changes in the eye and refractive error is greater than 600 degrees (children > 400 degrees),is called high myopia, which often accompanied by eyeballs,decreased vision, rapid development of myopia and poor dark adaptation function [1]. It has been proved by medicine that patients with high myopia can delay the progress of myopia by wearing appropriate glasses and increasing outdoor activities. However, as the pressure of life continues to increase, slowing the progression of myopia can no longer solve the inconvenience caused by the Dis to patients' lives [2]. Refractive surgery is a kind of ophthalmic surgery that corrects myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism for the purpose of surgery and improves the optical visual quality of the whole eye.At present, this surgery is often used to treat high myopia [3]. There are a variety of procedures for refractive surgery, and implantable posterior chamber phakic refractive lens (PC-PRL) is one of them.This procedure has a good effect on low-to-moderate myopia, but there are few reports on the exact efficacy and complications of high myopia [4]. Therefore, this study selected 110 patients with high myopia as the research object, and explored the effect of PC-PRL implantation on its efficacy, naked eye vision and complications.The results are reported as follows.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 General Information
From June 2017 to February 2019, 110 patients (220 eyes) with high myopia admitted to our hospital were selected as subjects.Inclusion criteria: 1 in line with the "high myopia diagnosis and fundus lesions" in the diagnosis of high myopia [5]; 2 did not wear contact lenses 2 weeks before surgery; 3 did not wear hard contact lenses preoperative 4 weeks or more; 4 clinical complete data;5 informed consent and treatment of patients and their families.Exclusion criteria: 1PC-PRL implant contraindications; 2 abnormal intraocular pressure and scar constitution; 3 active inflammation and chronic Dis in the eye; 4 corrected diopter >-6.00D. There were 74 males and 36 females in 110 patients. The age ranged from 18 to 45 years old, with an average age of (28.47±3.97) years. The myopia degree was -9.25~-26D. The average astigmatism was -1.86±0.54 D. The anterior chamber depth is 3.02 ± 0.23 mm. This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of our hospital.
2.2 Method
2.2.1 Surgical methods
All patients underwent iridotomy 15 days before surgery to remove the iris laser site and minimize iatrogenic corneal astigmatism.Compound tropicamide eye drops (Handan Kangye Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., National Medicine Standard:20044926) were dropped once every 20 minutes 1 hour before operation, including a total of 3 times. The diameter from mydriasis to pupil is about 7mm.Then select the tunnel seamless incision, the tunnel length is about 2.0 am,the width is about 3.0~3.5 mm. Complete a side incision from the main incision. The PC-PRL of the measured degree was implanted into the anterior chamber through the main incision, and the positioning hook was adjusted to the posterior iris. The viscoelastic agent was replaced with physiological saline to avoid postoperative high intraocular pressure. Injecting carbachol into the anterior chamber (Shandong Boshilun Ruida Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.,National Medicine Standard: H10950174), the pupil was reduced to about 3 ram, and the peri-cut perforation was clearly visible. After confirming that the optical portion of the PC-PRL was centered, the excess viscoelastic material was aspirated, the depth of the anterior chamber was confirmed, and the operation was terminated after the surgical incision was closed. Patients should take appropriate amounts of antibiotics to accomplish post-operative anti-infective work.
2.3 Observation indicators
Postoperative follow-up was performed to observe the uncorrected visual acuity (UCVA), best corrected visual acuity (BCVA),intraocular pressure, corneal endothelial cell count, and intraocular lens position (anterior chamber depth, arch height) before and after treatment. The follow-up review time included the first week,1 month, 3 months, and 6 months after surgery. Jaeger table was used to check near vision and international standard eye chart was used to check and record UCVA and BCVA. Intraocular pressure measurements were performed using a Goldmann AT-900 flattening tonometer. The corneal endothelial cell counts were performed using a Topcon SP2000 corneal endothelial tester. The anterior chamber depth and arch height were measured using a SW-3200 ultrasonic biomicroscope from Tianjin Sower, and the average was measured three times. Statistical analysis was performed on the occurrence of postoperative retinal complications (high intraocular pressure,corneal edema, refractive regression, near-sightedness, etc.).
2.4 Statistical methods
Statistical analysis was performed using spss22.0 software. The gender comparison was performed by chi-square test, the visual acuity correction effect and complications were expressed as percentage, the measurement data (BCVA, UCVA, intraocular pressure, etc.) were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance, and the pairwise comparison was performed by snk-q test. P < 0.05 indicates that the difference was statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1 Analysis of visual acuity correction after 6 months of treatment
Six months after treatment, 75 patients (68.18%) had UCVA value of 0.6-0.9, 31 patients (31.81%) had UCVA of more than 1.0, and 110 patients (100.00%) had BCVA of more than 1.0.
3.2 Comparison of BCVA and UCVA before and after treatment
The BCVA and UCVA values at 1 week, 1 month, 3 months and 6 months after operation were significantly greater than those before surgery, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).There were no significant differences in BCVA and UCVA among 1 week, 1 month, 3 months and 6 months after operation (P>0.05), as shown in Table 1.
Table1 Comparison of visual acuity before and after treatment (±s)

Table1 Comparison of visual acuity before and after treatment (±s)
Note: compared with preoperative, ①P<0.05.
Items Preoperative 1 week postoperative 1 month postoperative 3 months postoperative 6 months postoperative F P BCVA 4.41±2.14 4.92±1.74① 4.93±1.97① 4.92±0.83① 4.90±0.58① 4.54 0.001 UCVA 3.54±1.21 4.85±1.12① 4.89±1.06① 4.88±1.36① 4.89±1.07① 57.61 <0.001
Table2 Comparison of intraocular pressure and corneal endothelial cell count before and after treatment (±s)
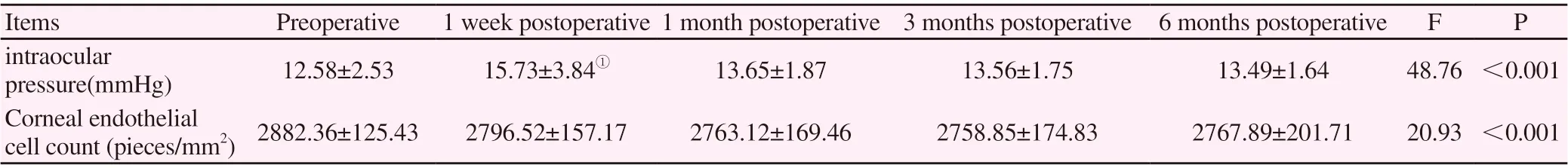
Table2 Comparison of intraocular pressure and corneal endothelial cell count before and after treatment (±s)
Note: compared with preoperative, ①P<0.05.
Items Preoperative 1 week postoperative 1 month postoperative 3 months postoperative 6 months postoperative F P intraocular pressure(mmHg) 12.58±2.53 15.73±3.84① 13.65±1.87 13.56±1.75 13.49±1.64 48.76 <0.001 Corneal endothelial cell count (pieces/mm2) 2882.36±125.43 2796.52±157.17 2763.12±169.46 2758.85±174.83 2767.89±201.71 20.93 <0.001
Table3 intraocular position examination of intraocular lens (±s)

Table3 intraocular position examination of intraocular lens (±s)
Note: compared with preoperative, ①P<0.05.
Items Preoperative 3 months postoperative 6 months postoperative F P the depth of the anterior chamber 3.15±0.27 2.58±0.21① 2.37±0.18① 719.64 <0.001 arch height 0.47±0.09 0.46±0.10 0.45±0.08 1.35 0.262
3.3 Comparison of intraocular pressure and corneal endothelial cell count before and after treatment
The intraocular pressure was significantly greater than that of the preoperative one week after surgery, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in intraocular pressure between 1 month and 6 months after operation (P>.05). There was no significant difference in corneal endothelial cell count before and after treatment (P>0.05), as shown in Table 1
3.4 intraocular lens position examination
There was no significant difference in arch height before and after treatment. There was no significant difference in the depth of the anterior chamber at 3 months and 6 months after operation (P>0.05).The depth of the anterior chamber at 3 months and 6 months after surgery was significantly less than that before surgery, with statistical significance (P <0.05), as shown in Table 3.
3.5 Occurrence of retinal complications
There were 7 cases of corneal edema, 4 cases of high pressure eyes,2 cases of refractive regression within 6 months, and 1 case of neardifficulty within 1 month. The total complication rate was 12.73%.
4. Discussion
High myopia not only makes the patient's vision diminished, but also has a limiting effect on the patient's exercise capacity, diet and daily life. In addition, with the development of myopia, the patient's retina, choroid will also undergo pathological changes, which can induce corneal edema, refractive regression, retinal detachment and many other retinal complications, seriously affecting the quality of life of patients [6-7]. Research reports that genetic factors are the cause of most high myopia patients, prevention of high myopia patients with increased vision and vision correction has become an important research topic in modern medicine [8].
At present, in addition to frame glasses, refractive surgery is the main treatment for high myopia, including clear lens extraction combined with IOL implantation, corneal refractive surgery and intraocular lens implantation. The first two are mainly used for lowto-medium myopia. For high myopia, intraocular lens implantation can ensure the integrity of the cornea, providing a choice for patients with high myopia who have a thin central corneal thickness or are not suitable for corneal refractive surgery [9]. According to the different implantation sites, the lens-like intraocular lens can be divided into three types: posterior chamber, anterior chamber support and iris fixed. The latter two types of anterior lens have a great influence on the cornea and iris, thus their application is diminishing.The posterior chamber type, PC-PRL implantation, has a good effect on vision improvement [10]. In this study, PC-PRL implantation was used to treat high myopia. After 6 months of follow-up, the patients were followed up regularly. 31.81% of patients had UCVA of more than 1.0, and the average UCVA was greater than 4.80, which was significantly higher than that before treatment. All patients had a BCVA of more than 1.0, which was significantly higher than that before treatment, suggesting that PC-PRL implantation was highly effective in treating high-myopia patients with naked eyes and corrective vision, which helped to promote vision recovery.There was no significant difference in UCVA and BCVA values between 1 week and 6 months after treatment, indicating that the postoperative visual acuity was stable. Intraocular pressure is the pressure of the contents of the eyeball on the eyeball wall. When the intraocular pressure exceeds the range that the optic nerve can bear, the characteristic optic disc depression and the defect of retinal nerve fiber layer will appear. The normal range is 10-21mmhg.Corneal transparency is closely related to the normal physiological functions of visual organs. Corneal endothelial cells play an important role in it. Clinical ophthalmologists must pay attention to the protection of corneal endothelial cells during endoscopic surgery[11]. The results of this study showed that the intraocular pressure of patients in the first week after treatment increased significantly compared with that before treatment. The reason for the analysis may be that the patient's own dysfunction of the angle of the anterior chamber or the residual viscoelastic agent in the anterior chamber blocked the angle of the anterior chamber [12]. However, there was no significant difference in intraocular pressure among 1 month,3 months and 6 months after operation. There was no significant difference in corneal endothelium count before and after treatment compared with surgery, indicating that PC-PRL implantation had no significant effect on intraocular pressure and corneal endothelial cells, which may be related to the simple operation, small incision,advanced materials and more scientific design principle of PCPRL implantation [13]. Studies have reported that avoiding anterior subcapsular cataract formation depends on the distance between the lens and the posterior surface of the intraocular lens. When the distance exceeds 0.09 mrn, cataract can be avoided [14]. This study found that the depth of anterior chamber decreased significantly 3 and 6 months after operation compared with that before operation.The reason may be that the implantation of PC-PRL resulted in the deposition of inflammatory cells or reactive protein on the front and rear surfaces of PC-PRL, which increased the proportion of PC-PRL,thus affecting its "floating" characteristics in the posterior chamber[15]. However, there was no significant change in arch height before and after treatment, which may be related to the effective reduction of inflammatory cell adhesion by the materials selected for PC-PRL implantation. In this study, the total complication rate was 12.73%,including 7 cases of mild corneal edema, 4 cases of high-pressure eyes, 2 cases of refractive regression, and 1 case of near-difficulty,but after taking carteolol hydrochloride eye drops, all returned to normal.
In summary, PC-PRL implantation is effective in the treatment of high myopia, which helps to improve the naked eye and correct vision, and the incidence of retinal complications is low, which can be applied clinically.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Meta analysis and medication analysis of TCM compound in the treatment of senile osteoporosis
- The Effect of Clinically Used Crystalloid Solution on the Clearance Rate of Lactic Acid in Septic Shock Patients
- Efficacy of intravitreal injection of ranibizumab in the treatment of macular edema secondary to non-ischemic branch retinal vein occlusion
- Clinical study of warm acupuncture combined with massage in treatment of periathritis of shoulder
- Expression and clinical significance of lncRNA SNHG3 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Effects of Pioglitazone on Renal Mitochondrial calcium and cytochrome C levels in Early Diabetic Nephropathy Rats
