蠋蝽成虫对草地贪夜蛾不同龄期幼虫的捕食能力
2019-11-27王燕张红梅尹艳琼
王燕 张红梅 尹艳琼
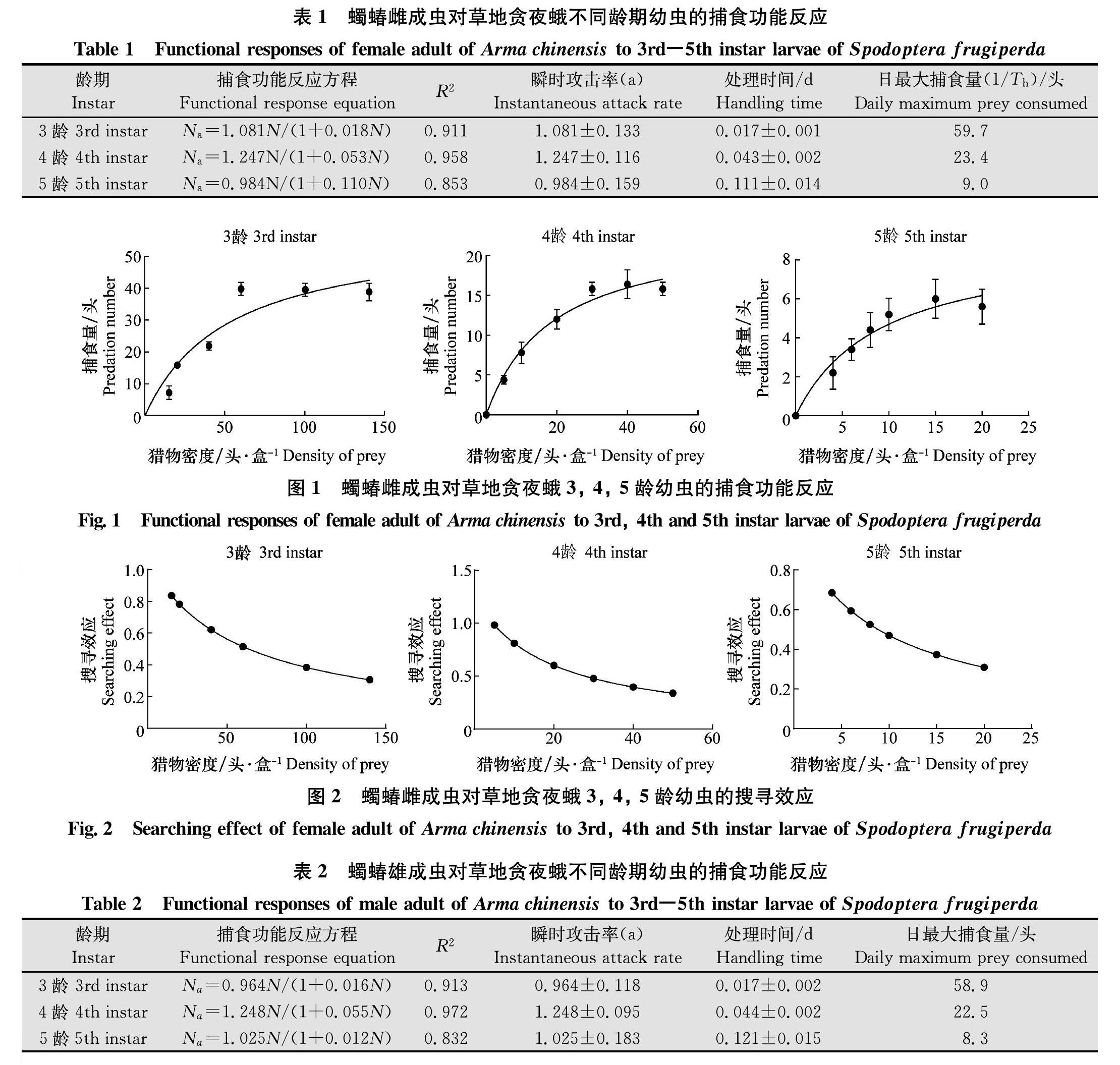

摘要 为了探究蠋蝽Arma chinensis (Fallou)对草地贪夜蛾Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E.Smith)的生防潜力,在室内条件下测定了蠋蝽成虫对草地贪夜蛾3、4、5龄幼虫的捕食能力。结果表明:雌性成虫对草地贪夜蛾3、4、5龄幼虫的日最大捕食量分别为59.7、23.4、9.0头;瞬时攻击率分别为1.081±0.133、1.247±0.116、0.984±0.159;处理时间分别为(0.017±0.001)、(0.043±0.002)、(0.111±0.014)d。雄性成虫对草地贪夜蛾3、4、5龄幼虫的日最大捕食量分别为58.9、22.5、8.3头;瞬时攻击率分别为0.964±0.118、1.248±0.095、1.025±0.183;处理时间分别为(0.017±0.002)、(0.044±0.002)、(0.121±0.015)d。蠋蝽成虫对草地贪夜蛾3、4、5龄幼虫都能捕食,对3龄幼虫捕食量最大,最喜欢捕食4~5龄幼虫,雌雄成虫都对4龄幼虫的瞬时攻击率最高。试验证实蠋蝽对草地贪夜蛾具有较好的控害效果,可用于对草地贪夜蛾的防控实践。
关键词 蠋蝽成虫; 草地贪夜蛾; 捕食; 生物防治
中图分类号: S 476 文献标识码: A DOI: 10.16688/j.zwbh.2019346
Abstract In order to investigate the biological control potential of Arma chinensis (Fallou) on Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E.Smith), the ability of adults to prey on 3rd, 4th and 5th instar larvae under indoor conditions was studied. The results showed that the maximum daily predation amount of female adults to the 3rd, 4th and 5th instar larvae of the fall armyworm was 59.7, 23.4 and 9.0 individuals, respectively. The instantaneous attack rates were 1.081±0.133, 1.247±0.116, 0.984±0.159, respectively. The handling time was 0.017±0.001, 0.043±0.002, 0.111±0.014 days, respectively. The maximum prey consumed daily of male adults to 3rd, 4th and 5th instar larvae was 58.9, 22.5 and 8.3, respectively. The instantaneous attack rates were 0.964±0.118, 1.248±0.095 and 1.025±0.183, respectively. Handling time was 0.017±0.002, 0.044±0.002 and 0.121±0.015 days, respectively. Adults of A.chinensis can prey on 3rd, 4th, and 5th instar larvae of S.frugiperda. The daily predation amount of A.chinensis adults on the 3rd instar larvae of S.frugiperda was the largest, and they prefer to prey on 4th and 5th instar larvae. The instantaneous attack rates of both male and female adults of A.chinensis against 4th instar larvae of S.frugiperda is the highest. The results indicate that A.chinensis has good control effect on S.frugiperda and can be used for the prevention and control of the moth.
Key words adults of Arma chinensis; Spodoptera frugiperda; predation; biological control
草地貪夜蛾Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E.Smith),又称秋黏虫,英文名fall armyworm,属于鳞翅目Lepidoptera夜蛾科Noctuidae,是一种原产于美洲热带和亚热带地区的杂食性害虫[1-4]。草地贪夜蛾1~6龄幼虫都可取食为害植物,其寄主植物多达76科353种[4]。低龄幼虫取食叶片后剩下叶表皮、形成半透明薄膜状“窗孔”,高龄幼虫取食后形成不规则的长形孔洞,发生严重时可导致植株死亡。
草地贪夜蛾适生区域广,迁飞能力强,繁殖倍数高,自2019年1月11日确认传入我国云南普洱市江城县后,目前在云南的16个州市124个县区都有发生为害,并已扩散蔓延到全国19个省区。对草地贪夜蛾的发生为害应采用化学防治、生物防治、农业防治、理化诱控等多项措施进行可持续综合防控。其中,生物防治具有不污染环境、持续控制效果好的特点,在综合防治体系中占有重要地位。随着草地贪夜蛾的入侵、发生和定殖,生物防治将会发挥越来越重要的作用。
蠋蝽5龄若虫对小菜蛾4龄幼虫的日捕食量可达83.33头[21],对榆紫叶甲成虫和幼虫的日捕食量可达47.33头和62.74头[16],由于草地贪夜蛾4~5龄幼虫虫体比小菜蛾和榆紫叶甲幼虫大,蠋蝽成虫对草地贪夜蛾4龄和5龄幼虫的日捕食量少于对小菜蛾4龄幼虫和榆紫叶甲幼虫的捕食量。捕食量有差异其原因与草地贪夜蛾幼虫的体积和虫体的营养成分密切相关,并且可能因为蠋蝽5龄若虫在羽化为成虫之前需要储存更多的物质和能量用于发育繁殖,而成虫的主要任务是交配,雌成虫为产卵需要补充更多营养。
在试验中观察到,蠋蝽有较强的攻击性,有许多草地贪夜蛾幼虫被蠋蝽刺死,草地贪夜蛾幼虫被刺死量大于实际取食量,而蠋蝽会继续取食部分已经刺吸致死的草地贪夜蛾幼虫。在害虫生物防治应用实践中,蠋蝽对各种猎物的致死量都较大,这对其在害虫生物防治中的应用有较大的实际价值。
由于本研究在室内进行,只是对蠋蝽的捕食功能进行初步试验,而当它们处于自然环境条件下时,气候因子(如日照、风、温度、雨水等)会影响捕食蝽对猎物的捕食效率。综上所述,在田间释放时,应综合考虑天敌的捕食攻击力、田间环境条件、猎物的密度等因素,以制定适宜的释放量和释放方式。在田间释放蠋蝽时,如果草地贪夜蛾虫口密度较大,宜选择蠋蝽5龄若虫,其迅速控害的效果比成虫好。成虫能够交配产卵,下一代蝽若虫数量会迅速增加,释放成虫也能达到较好的控制效果。
参考文献
[1] LUGINBILL P.The fall armyworm[R].USDA Technology Bulletin,1928,34:91.
[2] SPARKS A N.A review of the biology of the fall armyworm[J].The Florida Entomologist,1979,62(2):82-86.
[3] JARROD T H,GUS M L,LEONARD B R.Fall armyworm (Lepidoptera:Noctuidae) ecology in southeastern cotton[J].Journal of Integrated Pest Management,2015,6(1):1-8.
[4] MONTEZANO D G,SPECHT A,SOSAGMEZ D R,et al.Host plants of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera:Noctuidae) in the Americas[J].African Entomology,2018,26(2):286-300.
[5] SHAPIRO J,LEGASPI J C.Assessing biochemical fitness of predator Podisus maculiventris (Heteroptera:Pentatomidae) in relation to food quality effects of five species of prey [J].Annals of the Entomological Society of America,2006,99(2):321-326.
[6] MALAQUIAS J B,RAMALHO F S,OMOTO C,et al.Imidacloprid affects the functional response of predator Podisus nigrispinus (Dallas) (Heteroptera:Pentatomidae) to strains of Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E.Smith) on Bt cotton[J].Ecotoxicology,2014,23(2):192-200.
[7] ZANUNCIO J C,SILVACA D,LIMA E R,et al.Predation rate of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera:Noctuidae) larvae with and without defense by Podisus nigrispinus (Heteroptera:Pentatomidae)[J].Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology,2008,51(1):121-125.
[8] DOS SANTOS B D B,RAMALHO F S,MALAQUIAS J B,et al.How predation by Podisus nigrispinus is influenced by developmental stage and density of its prey Alabama argillacea[J].Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata,2016,158:142-151.
[9] 鄒德玉.取食无昆虫成分人工饲料蠋蝽的转录组研究及饲养成本分析[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2013.
[10] 潘明真,张海平,张长华,等.饲养密度和性比对蠋蝽存活和繁殖生物学特性的影响[J].中国生物防治学报,2018,34(1):52-58.
[11] 李娇娇,张长华,易忠经,等.三种猎物对蠋蝽生长发育和繁殖的影响[J].中国生物防治学报,2016,32(5):552-561.
[12] ZOU Deyu,COUDRON T A,LIU Chenxi,et al.Nutrigenomics in Arma chinensis:transcriptome analysis of Arma chinensis fed on artificial diet and Chinese oak silk moth Antheraea pernyi pupae [J/OL].PLoS ONE,2013,8(4):e60881.
[13] 廖平,苗少明,许若男,等.新型蠋蝽若虫液体人工饲料效果评价[J].中国生物防治学报,2019,35(1):9-14.
[14] 张海平,潘明真,易忠经,等.短期饥饿处理对蠋蝽寿命、繁殖力及捕食量的影响[J].中国生物防治学报,2017,33(2):159-164.
[15] 陈静,张建萍,张建华,等.蠋敌对双斑长跗萤叶甲成虫的捕食功能研究[J].昆虫天敌,2007,29(4):149-154.
[16] 张晓军,张健,孙守慧.蠋蝽对榆紫叶甲的捕食作用[J].中国森林病虫,2016,35(1):13-15.
[17] HOLLING C S.Some characteristics of simple types of predation and parasitism[J].The Canadian Entomologist,1959,91(7):385-398.
[18] 丁岩钦.昆虫数学生态学[M].北京:科学出版社,1994:257-258,303-304.
[19] 庄丽,李为争,杨雷,等.瓢虫对蚜虫功能反应的影响因子[M]∥雷朝亮,王满囷,赵树英.华中昆虫研究 第8卷.北京:中国农业科技出版社,2012:30-35.
[20] 唐艺婷,郭义,何国玮,等.不同龄期的益蝽对粘虫的捕食功能反应[J].中国生物防治学报,2018,34(6):825-830.
[21] 唐艺婷,李玉艳,刘晨曦,等.蠋蝽对草地贪夜蛾的捕食能力评价及捕食行为观察[J].植物保护,2019,http:∥kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1982.S.20190603.1818.001.html.
(责任编辑: 田 喆)
