Surface modification of ammonium nitrate by coating with surfactant materials to reduce hygroscopicity
2019-10-31BhElzkiYueJunZhng
Bh I.Elzki ,Yue Jun Zhng
a School of Chemical Engineering,Nanjing University of Science and Technology,Nanjing,210094,Jiangsu,China
b Department of Chemical Engineering,College of Engineering,Karary University,Omdurman,12304,Sudan
Keywords:Ammonium nitrate(AN)Coating Hygroscopicity Modification surface Surfactant
A B S T R A C T Ammonium nitrate(AN)is promising oxidizer in green propellants.In this work,the physical coating method was improved to modify the surface of ammonium nitrate particles with different surfactant materials to reduce hygroscopicity.Cetylalcohol,stearic acid,stearyl alcohol,palmic acid,lauric acid,stearsmide,tetradecylamine,dodecylamine,and tetradecanol were used as coating surfactant agents.The hygroscopicity was tested for ammonium nitrate with and without coating.Fourier transform infrared(FTIR)and scanning electron microscopy(SEM)were used to characterize the surface of coated and uncoated ammonium nitrate.The mass ratio of coating layer and decline of absorption rate of ammonium nitrate coated by cetylalcohol were 1.00%,and 28.40%,respectively.The results indicate that coating with cetylalcohol surfactant have advantages over the other surfactants in term of low mass ratio of coating layer,and high decline of moisture absorption rate.Thus,cetylalcohol would be a promising coating surfactant material for ammonium nitrate.The idea and approach presented in this study have potential to made hydrophobic layer on the surface of particles to reduce hygroscopicity of AN,and also help the researcher to improving anti-hygroscopicity of ammonium salts.
1. Introduction
Ammonium nitrate(AN)is produced by the reaction of anhydrous ammonia gas(NH3),and aqueous nitric acid(HNO3)[1—3].AN is present as a major component in the most industrial explosive,such as amatol,AN fuel oil(ANFO),and it is also used in fertilizers[4—8].AN has a considerable interest in potential eco-friend oxidizing agent in solid propellants[9,10].The risk of commonly used oxidizer ammonium perchlorate(AP)in solid propellants was realized with the hydrogen chloride(HCL)with water form hydrochloric acid,which produces obvious signal easily traced and highly toxic smoke leading to significant damage in the environment,therefore AN will become possible replacement after treatment its drawback such as hygroscopicity,phase transitions,and low performance[11—15].However,its use of large rocket motors and as solid propellant is restricted due to the hygroscopicity[16,17],because of the molecules polarity of AN,it can easily absorb moisture from the surrounding.There are different kinds of coating methods such as physical,chemical,and encapsulation coating methods,which are belonged to one of the main ways to reduce the hygroscopicity of AN particles[18].The surfactant materials has been used to reduce the hygroscopicity of AN in the different study such as mineral jelly,calcium stearate,kaoline,octadecane amine,resin wax and silane coupling agent KH792[19—21].Although the study of anti-hygroscopic of AN using different coating agent and coating method,obtained under certain conditions of moisture absorption rate,a large decline-coated sample have been reported in the previous literatures.However,many challenges are still remaining.For instance,the index evaluation of AN hygroscopic effect did not precisely mention the mass ratio of the coating layer.Moreover,the hygroscopicity test conditions of AN coated remain unclear.As example,the time of moisture absorption is quite short,while both the particles size of AN and the size of weighting bottle are unknown,as well as the process of surface modification of AN have not been thoroughly mentioned,particularly the coating time and temperature [22—24]. In this paper, the physical coating method with the ten different surfactant materials directed at reducing hygroscopicity was used in the surface modification of AN.Moreover,the phenomenon of water droplets on surface of AN particles were explained.The surface morphologies of AN particles were monitored by electronic scanning microscope,and the surface of coated AN particles are assayed by FTIR spectra.Furthermore,this paper presents the effect of surfactant amount on the moisture absorption rate and mass ratio coating layer.
2. Experimental procedures
2.1. Materials
Ammonium nitrate supplied by Kecheng fine chemical CO.Ltd(≥99.0%Shanghai,China),chloroform(≥99.0%,Shanghai Ling Feng Chemical Reagent Co.LTD,China)and cyclohexane(≥99.5%Industrial development zone,Chengdu,China).Surfactant materials used cetylalcohol,stearic acid,octadecylamine,stearyl alcohol,palmic acid, lauric acid, stearsmide, tetradecylamine, dodecylamine,and tetradecanol(≥99.0%Chengdu Kelong Chemical Reagent,China).
2.2. Procedure of coating processing
Physical coating method was improved to modify the surface of AN particles[17,23].6g of AN coated by 2 g of surfactant materials in the mixture of solvents consist of 15 ml chloroform and 15 ml cyclohexane.Choosing the solvents for coating has been based on the solubility of surfactant materials,and AN insoluble in solvents.The reaction was started with stirring at constant temperature 60°C.After 2 h the heating was stopped,and then the temperature was gradually decreased within 8 h—30°C,at this stage the water of bath heating was changed,and when the temperature reached to 25°C.AN coated was filtered by vacuum filter,and dried at a certain temperature with considering the melting and boiling point of each surfactant materials.Finally,the hygroscopicity test was carried out under conditions 5 g AN 60×30 mm weighing bottle at temperature of 35°C,humidity(67.5%),and time of absorption rate tested 24 h.
2.3. Evaluation and characterization of results
Ammonium nitrate samples coated with surfactant materials and the anti-hygroscopicity performance of coating will be assessed by evaluated and characterized the results.The evaluation indexes are mainly increasing the decline of the moisture absorption and the mass ratio of coating layer,and the main characterization methods are scanning electron microscopy observation,and infrared characterization.
2.3.1. Measurement of moisture absorption rate
The moisture absorption rate of ammonium nitrate is the rate of changing on the moisture absorption rate of samples before and after test the hygroscopicity of coating ammonium nitrate[21].According to GJB770B-2005“hygroscopicity dryer balance method”[22],in this study,5 g of AN sample will put in 60×30 mm weighing bottle without a cap will be placed into a desiccator containing saturated solution of strontium chloride(relative humidity 67.5%)the temperature at 35°C for 24 h.The sample will be scaled up from 5 g to 20 g AN and the test conditions will be used to measure the moisture absorption rate:the relative humidity is 92%by using the saturated solution of potassium nitrate in the bottom glass desiccator inside oven constant temperature at 35°C,the amount of modified AN is 20 g put inside the 60×30 mm weighing bottle without cover and time of absorption rate tested 24 h.The following equation will be calculated the moisture absorption rate(HR):

Where:HR-moisture absorption rate,%
M0-The weight of sample before absorbed moisture,g
M-The weight of the sample after absorbed moisture,g
Meanwhile,according to the above methods,the ammonium nitrate samples will be measured moisture absorption rate and uncoated blank sample,the decline of the moisture absorption rate calculated by the following equation:

Where:A-decline of hygroscopicity,%
HR1-absorption rate of blank AN sample,%
HR-absorption rate of coated AN sample,%
2.3.2. Determination method of the mass ratio of coating layer
The determination method of the mass ratio of the coating layer will be improved to achieve more accuracy than previous literature[21]as following steps:
Firstly: a filter paper of 18 cm diameter was wetted with deionized water.
Secondly:the filter paper placed into an oven for 1 h at the temperature 100°C,then the filter paper was weighed(WB).
Thirdly:the sample of the coated AN after absorption humidity was dissolved in deionized water,and filtered through a tapered funnel,and the filter paper was washed several times with deionized water,and placed in an oven at 100°C for 1 h.
Finally,the filter paper was weighed again(WA).
The mass ratio of the coating layer was calculated by the following equation:

Where:W-mass ratio of coating layer to ANparticles,%,M0-Blank AN particles,g,M1-The weight of coating layer(WA-WB),g.
2.3.3. Fourier transform infrared(FTIR)characterization
The surface of modified AN with cetylalcohol,stearic acid,stearyl alcohol,and AN without coating samples were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy(FTIR).IR spectra will be recorded in the range 400-4500 cm-1on FTIR spectrophotometry(Thermo Scientific Nicolet,I S10,Thermo Fisher USA)using KBr pellets.
2.3.4. Scanning electron microscopy(SEM)observation
The surface of coated AN samples were observed with scanning electron microscopy(JEOL JSM 6380LV,Japan),based on the SEM pictures of AN/cetylalcohol,AN/stearic acid,AN/Stearyl alcohol and AN without coated were observed the surfaces morphology to examine the particles in details.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Performance of coated AN,and hygroscopicity test
Table 1 showed the moisture absorption rate,mass ratio ofcoating layer and decline of AN coated with ten different kinds of surfactant materials. The data from hygroscopicity test clearly indicate that cetylalcohol was best one of surfactant materials used as coating of AN with decreased of moisture absorption rate from 11.55%(AN control)to 8.27%with lower mass ratio of coating layer of 1.00%,and high decline of absorption rate of 28.40%.Stearic acid and octadecylamine were found to be the second and third superior results,respectively,while stearyl alcohol,palmitic acid,lauric acid,tetradecanol,tetradecylamine,dodecylamine,and stearamide followed the order in sequence.Moreover,increasing the mass ratio of coating layer may greatly reduce the performance.This result clearly indicates that,the decline of moisture absorption rate of AN coated by cetylalcohol and mass ratio of coating layer were quite significant compared to those reported in Previous studies[19,25].These results fit to be a basis for surface modification of ammonium nitrate particles to improvement the anti-hygroscopicity.

Table 1 The performance of anti-hygroscopicity of AN/surfactants.
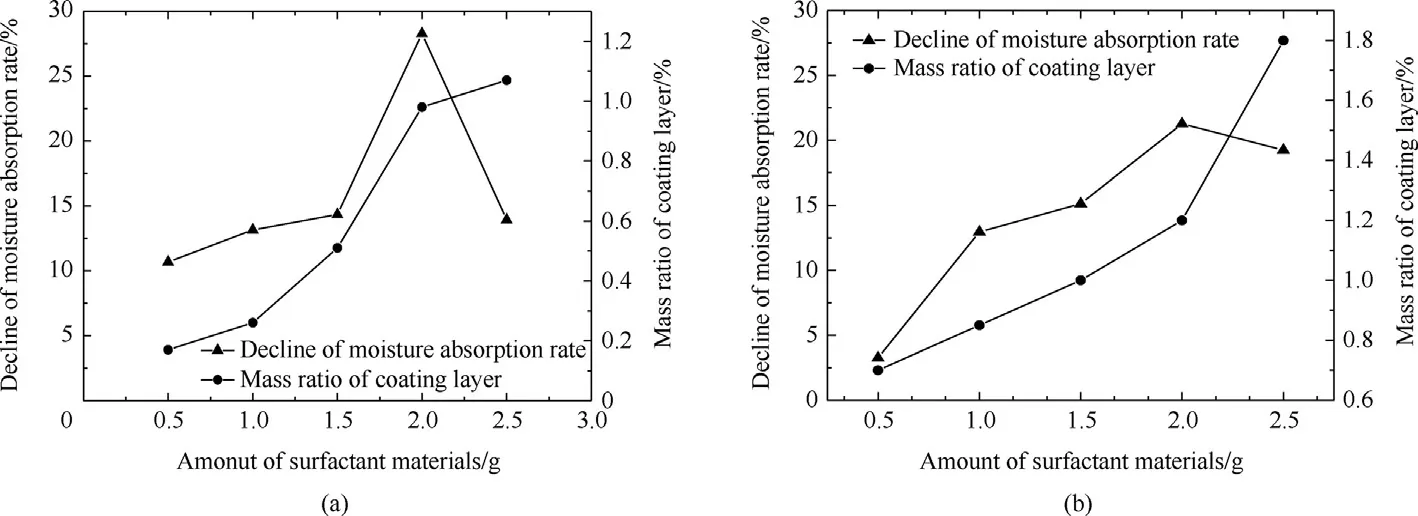
Fig.1.The effect of amount of surfactants materials in the decline of moisture absorption rate and mass ratio of coating layer,(a)Cetylalcohol;(b)Stearic acid.
3.2. Effect amount of surfactant materials
Effect amount of surfactant materials:The influence of the amount of surfactant materials on the decline of moisture absorption rate and mass ratio of coating layer were studied using different amounts of cetylalcohol and stearic acid(0.5,1.0 1.5,2.0.and 2.5 g)to coat AN particles.The regression of decline of moisture absorption rate was increased to high value at 2.0 g,and then decreased at 2.5 g.This phenomenon is because the polar head of surfactant not absorb in the surface of AN particles,but stuck with other polar head together and cause hydrophilic surface leads to increased hygroscopicity.Thus,the decline of absorption rate was decreased,and the mass ratio of coating layer directly proportional with the amount of surfactant materials as obviously shown in Fig.1(a and b).
3.3. The phenomenon of water droplets on surface of AN particles
Table 2 shows the moisture absorption rate,mass ratio of coating layer and decline of ammonium nitrate coated with cetylalcohol and stearic acid using different amount of surfactant and strong hygroscopicity test conditions.The results showed that the cetylalcohol significantly outperforms stearic acid with higher decline and lower mass ratio coating layer and also no water droplet on surface as depicted in Fig.2.Nevertheless,after absorbed water droplets the stearic acid was the best.There are two reasons to form water droplets on surface of AN after coated by surfactant.The first one is because the cracked of coating layer due to the hard filtration process.The second one is that the evaporation solvent was agglomerated two particles together during drying process as shown in Table 3,and Fig.3.These results provide clear understand of coating AN by surfactant materials,and the particles did not deliquesce compared with literature[26].
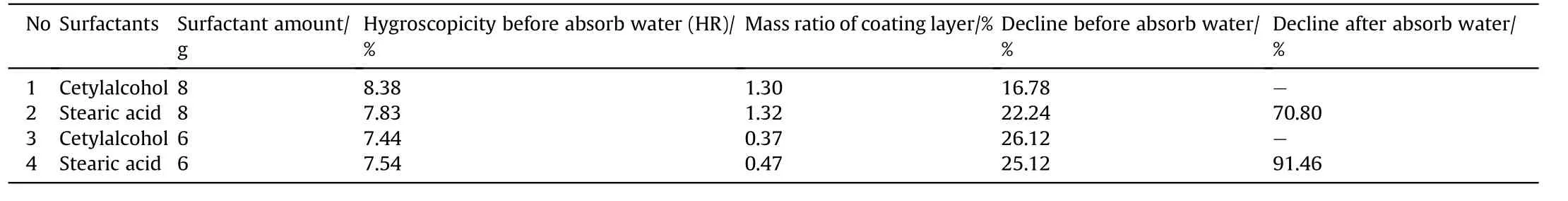
Table 2 The performance of anti-hygroscopicity of AN/Cetylalcohol and Stearic acid.

Fig.2.The phenomenon of water droplets on surface after hygroscopicity test sample No.(4)in Table 2.
3.4. FTIR spectra characterization
Surface modified of AN particle with cetylalcohol,stearic acid and stearyl alcohol were monitored by using FTIR measurement as depicted in Fig.4.It is observed that upon the surface modification of AN and surfactant materials,two peaks appear in the region 3000-2800 cm-1,which are attributed to CH3stretching vibrations(a,b,c).Whereas,these peaks were not observed in the FTIR recorded for blank AN.It was important to note that a medium intense peak is observed at 1703 cm-1for modified AN particles by stearic acid.This peak originated mainly due to carbonyl group C=O stretching of the stearic acid(d).FTIR spectrum results showed that cetylalcohol and stearic acid existed on the surface of AN particles.
3.5. SEM observations
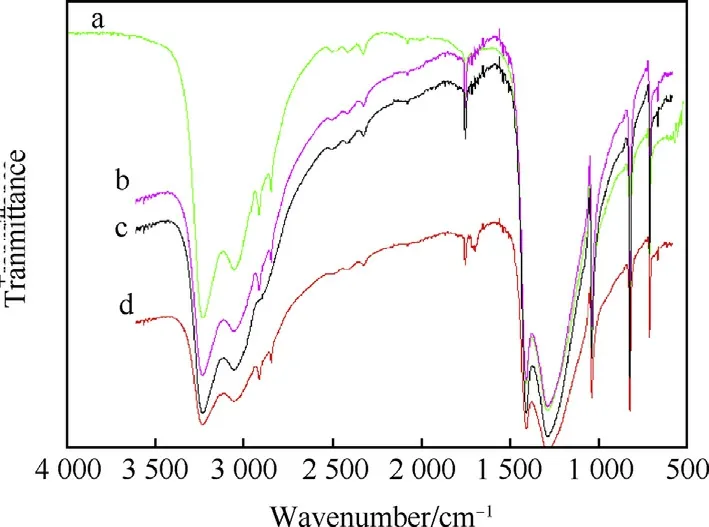
Fig.4.FTIR spectra of the AN/cetylalcohol(a),AN/stearyl alcohol(b),uncoated AN(c),AN/stearic acid(d).
To observe the surface morphology of coating ammonium nitrate particles.Different scale bar of 100 μm,50 μm,and 10 μm Electron micrographs are demonstrated in Fig.5.These figures present the surface morphology of AN/cetylalcohol (a) which showed a clear difference in the shape particles and the surface smooth as compared to AN/stearic acid(b),which have fractured on surface of particles,and stearyl alcohol(c),which have cracked,and it can be seen this hollow clear on the surface,and also appear on the particles surface of AN without coating(d),and also show the clear difference between the coated AN and AN without coating.In contrast in the AN coated with cetylalcohol no hollow particles were found.In addition,adhesion between particles cannot be seen in all samples this explains no caking and agglomeration happened after coating AN particles.
4. Conclusions
In this study physical coating method was improved to modify surface of AN particles with ten different kinds of surfactant materials.Our conclusions are listed below:
(i)The cetylalcohol has been found to be the best surfactant materials for coating AN among all tested materials with significant mass ratio of coating layer 1.0%and decline of moisture absorption 28.40%.
(ii)Strong hygroscopicity test conditions were used in this work as relative humidity 92%,time of hygroscopicity test 24 h.
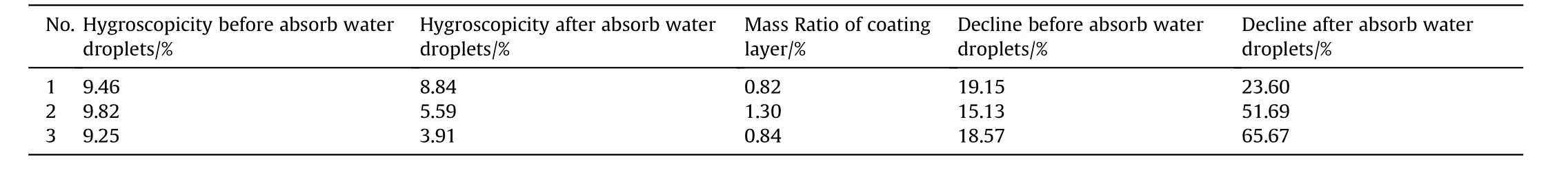
Table 3 The performance of anti-hygroscopicity of AN particles coated by 1.5 g Stearic acid.
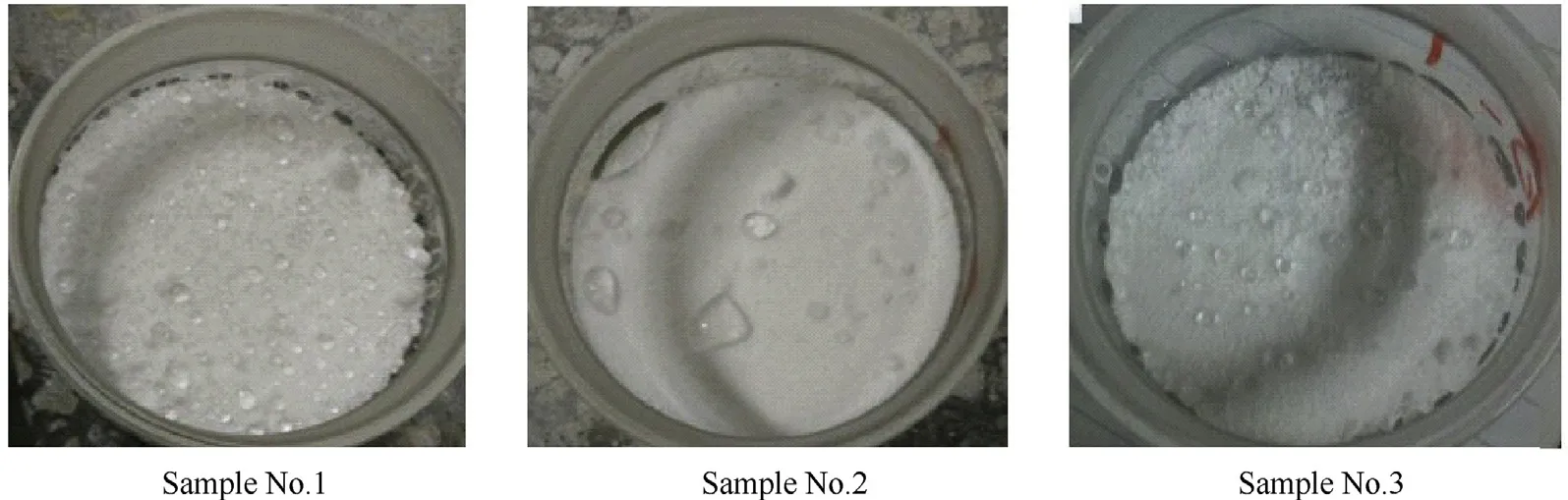

Fig.3.The phenomenon of water droplets on surface after hygroscopicity test samples in Table 3.
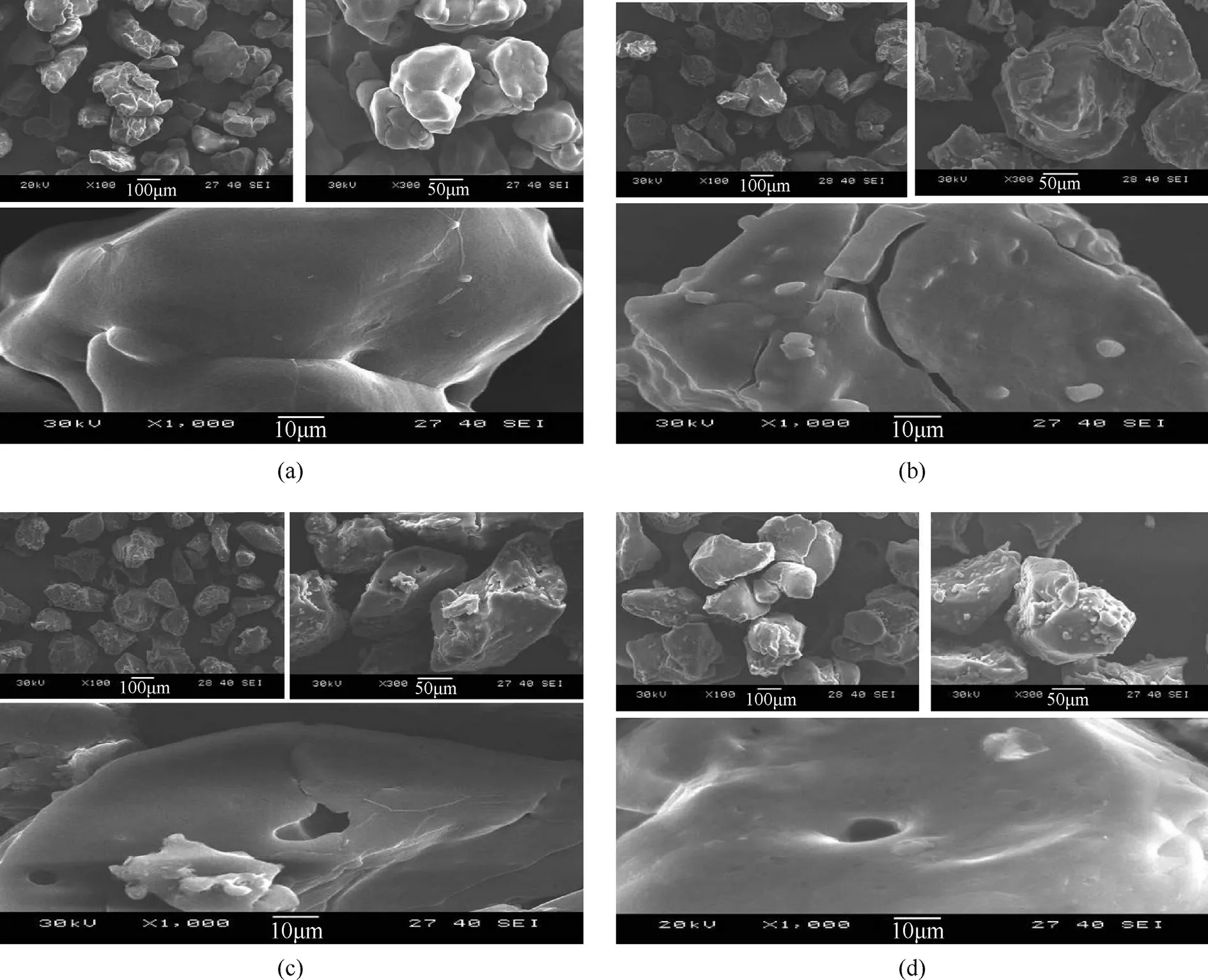
Fig.5.Scanning electron microscope of surface modification of AN coated by cetylalcohol(a),stearic acid(b),stearyl alcohol(c),and uncoated AN(d),the scale bar represents 10,50 and 100 μm.Electron micrographs.
(iii)In the AN/stearic acid,AN/stearyl alcohol and AN without coating samples were hollow and crack.In contrast the AN/cetylalcohol particles were solid and smooth surface.
(iv)AN/stearic acid after hygroscopicity test observed water droplets on surface.In contrast,no water droplets on the surface of AN/cetylalcohol.
(v)The cetylalcohol showed a promising coating surfactant material for ammonium nitrate,and it should be subjected for further investigations as anti-hygroscopicity.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
杂志排行
Defence Technology的其它文章
- Defence Technology
- Electrodynamic response study on railgun launcher based on electromechanical coupling model
- Effect of tongue clearance on hydraulic performance of double support vortex pump
- Electroless nickel fabrication on surface modified magnesium substrates
- The catalytic activity of transition metal oxide nanoparticles on thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate
- Nuclear radiation shielding effectiveness and corrosion behavior of some steel alloys for nuclear reactor systems
