不同产地玛咖中玛咖酰胺、玛咖烯和芥子油苷含量测定
2019-10-19李爱民赵可心党艳婷刘明曹梦思温霖李子杰高晓冬
李爱民 赵可心 党艳婷 刘明 曹梦思 温霖 李子杰 高晓冬
[摘要] 目的 調研我国不同产地玛咖中活性成分含量及主要影响因素。 方法 从云南四川两省五个地区采集40个玛咖鲜果样品,将玛咖鲜果切片,烘干、粉碎、过筛得到玛咖粉。采用高效液相色谱法测定玛咖中芥子油苷、玛咖烯胺和玛咖烯的含量,色谱条件分别为:芥子油苷的测定采用岛津C18色谱柱(3.9 mm×150 mm,5 μm),乙腈-水为流动相,梯度洗脱,流速为1.0 mL/min,检测波长为229 nm;玛咖酰胺和玛咖烯的测定采用Waters XTerra C18色谱柱(250 mm × 4.6 mm,5 μm),乙腈-水(均含0.005%三氯乙酸)为流动相,梯度洗脱,流速为0.6 mL/min,玛咖酰胺检测波长为210 nm,玛咖烯检测波长为273 nm。 结果 玛咖酰胺、玛咖烯、芥子油苷的含量分别为49.72~204.36 mg/100 g、10.22~66.73 mg/100 g、256.56~936.65 mg/100 g。相关性和显著性分析结果提示,玛咖中活性成分的含量与玛咖颜色无关(P > 0.05)。四川省和云南省其他地区玛咖中活性成分含量高于昆明市(P < 0.05)。 结论 不同产地玛咖酰胺和玛咖烯的含量与海拔呈现一定的正相关趋势,而与玛咖果颜色无关,产地也是影响玛咖活性成分的重要因素。
[关键词] 玛咖烯;玛咖酰胺;芥子油苷;海拔;产地;品种
[中图分类号] R33 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2019)10(a)-0030-05
Detection of macaamide,macaene and glucosinolate in Maca from different producing areas
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the content of active ingredients and main influencing factors in Maca from different producing areas in China. Methods Samples of 40 Maca fresh fruit were collected from five regions in Yunnan and Sichuan provinces. The fresh Maca fruits was sliced, dried, crushed and sieved to obtain maca powder. The content of glucosinolates, macaenines and macaenes in Maca was determined by high performance liquid chromatography. The determination of glucosinolates was carried out by C18 chromatographic column (3.9 mm×150 mm, 5 microns), acetonitrile-water was used as the mobile phase of the gradient elute, with the detection wavelength of 229 nm and the flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. The determination of macaene and macaamide was carried out by Waters XTerra C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm), acetonitrile-water (all containing 0.005% trichloroacetic acid) was as the mobile phase of the gradient elute, macaene with the detection wavelength of 210 nm and macaamide with the detection wavelength 273 nm and the flow rate of 0.6 mL/min. Results The content of macaene, macaamide and glucosinolate were respectively 49.72-204.36 mg/100 g, 10.22-66.73 mg/100 g and 256.56-936.65 mg/100 g. Correlation and significance analysis showed that the content of active ingredients in Maca was not related to color, but the origin. The results of correlation and significance analysis indicated that the content of active ingredients in Maca had nothing to do with the color of Maca(P > 0.05). The content of active ingredients in Maca in Sichuan Province and other areas of Yunnan Province was higher than that in Kunming(P < 0.05). Conclusion The content of macaamide and macaene in different producing areas showed a positive correlation with altitude, but has nothing to do with the color of Maca fruit. The origin is also an important factor affecting the active ingredients of Maca.
[Key words] Macaamide; Macaene; Glucosinolate; Elevation; Producing areas; Variety
玛咖(Lepidium meyenii)是十字花科(Brassicaceae)独行菜属(Lepidium)一年生或两年生草本植物,原产于秘鲁中部基宁及帕斯科附近3500 m以上的安第斯山区,为当地常用蔬菜[1-2]。玛咖中含有多种生物活性成分,如生物碱、芥子油苷及其衍生物异硫氰酸酯、玛咖烯、甾醇和多酚等,其中芥子油苷是其中含量最高的一类,在不同玛咖中含量为10.97~79.84 mg/g不等[3],其具有提高生育力、抗癌、抗氧化及抗疲劳等作用[4-7]。2002年,玛咖被正式批准在国内试种。由于云南大部分地区处于高原高寒地带,非常适合玛咖生长,玛咖产业在云南发展迅猛,在四川新疆等省份也有种植。大量研究认为玛咖的质量与其品种,产地以及产地的海拔有关[8-10],但是缺乏相关第一手的实验数据和相关研究支持。本课题组前期调研采集到我国代表性玛咖产地中5个地区40个玛咖样品并记录原产地海拔经纬度等相关信息,通过测定玛咖中活性成分的含量,将玛咖中活性成分含量与玛咖品种,产地以及产地海拔进行相关性分析。为我国玛咖品质提供了第一手数据支持,科学分析了影响玛咖活性成分的主要因素。
1 仪器与试药
1.1 仪器
高效液相色谱仪,日本岛津公司;超声波清洗仪,昆山超声仪器有限公司;pH计,上海雷磁仪器厂;GL-20G-Ⅱ型高速冷冻离心机,上海安亭科学仪器厂;DK-8D三温三控水槽,上海博迅实业有限公司;DQ-103/104型台式方形中药切片机,温岭市林大机械有限公司;DHG-9145A型电热鼓风干燥箱,上海一恒科技有限公司;BJ-500A型高速多功能粉碎机,德清拜杰电器有限公司。
1.2 试药
N-苄基亚麻酰胺标品(批号:HB-00002-20170224,纯度>98%)、N-苄基亚油酰胺标品(批号:HB-00004-20170306,纯度>98%)、N-苄基十六烷酰胺标品(批号:HB-00007-20170311,纯度>98%)、间甲氧基N-苄基亚麻酰胺标品(批号:HB-00001-20170227,纯度>98%)、间甲氧基N-苄基亚油酰胺标品(批号:HB-00003-20170302,纯度>98%),购自武汉华士特工业生物技术开发有限公司;芥子油苷标品:金莲葡糖硫苷钾盐(批号:TG039701,纯度95%),购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司;玛咖烯标品(批号:F-106006,纯度99%),购自加拿大TLC标品公司;色谱级乙腈和色谱级甲醇,购自美国迈瑞达公司;超纯水为实验室制备;三氯乙酸为国产分析纯。
2 方法与结果
2.1 玛咖样品的采集
笔者深入玛咖主产地云南四川两省开展调研工作,在香格里拉、昆明、丽江等6个地级市采集了40个玛咖鲜果样本,同时记录其产地(经纬度)和海拔的数据信息。所采集到的样品经国珍健康科技(北京)有限公司执业药师陈超鉴定为玛咖(Lepidium meyenii)是十字花科(Brassicaceae)独行菜属(Lepidium),有黄玛咖,紫玛咖和黑玛咖三个品种。
2.2 玛咖样品预处理
玛咖鲜根洗净并切2 mm薄片,37℃热风干燥至玛咖中水分含量低于5%,用粉碎机粉碎后过60目筛得到玛咖粉用于后续实验[11]。
2.3 芥子油苷含量测定
参照课题组之前发表文章中的方法完成测定[12]。
2.4玛咖烯和玛咖酰胺含量测定
2.4.1 标准曲线的绘制 用色谱级乙腈分别配制浓度为1 mg/mL N-苄基亚麻酰胺、N-苄基亚油酰胺、N-苄基十六烷酰胺、间甲氧基-N-苄基亚麻酰胺和间甲氧基-N-苄基亚油酰胺标准母液。将5种标准溶液按照表4混合稀释得到5种梯度浓度的混合标准品分析测定。
用80%的色谱级乙腈配置1 mg/mL 玛咖烯标准溶液,稀释至0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1、2、3 μg/mL,绘制标准曲线。以间甲氧基-N-苄基亚麻酰胺、N-苄基亚麻酰胺、间甲氧基-N-苄基亚油酰胺、N-苄基亚油酰胺和N-苄基十六烷酰胺浓度为横坐标,以峰面积(万)为纵坐标,分别绘制标准曲线。类似的,以玛咖烯浓度为横坐标,以峰面积(万)为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线。
2.4.2 前处理 将玛咖粉与80%乙腈按照1∶10(W/V)比例混合,100 W超声30 min,6000 r/min离心10 min后,取上清液1 mL经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后待测[10]。
2.4.3色谱条件 色谱柱WATERS C18色谱柱(5 μm,4.6 mm × 250 mm),流动相为水(A)和乙腈(B)均含0.005%三氯乙酸,洗脱梯度见表2,流速为0.6 mL/min,进样量为10 μL,玛咖酰胺检测波长为210 nm,玛咖烯检测波长为273 nm。
2.2 統计学方法
采用IBM SPSS Statistics 23软件进行数据分析。计量资料用均数±标准差(x±s)表示。采用Pearson相关系数进行分析。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2.3 结果
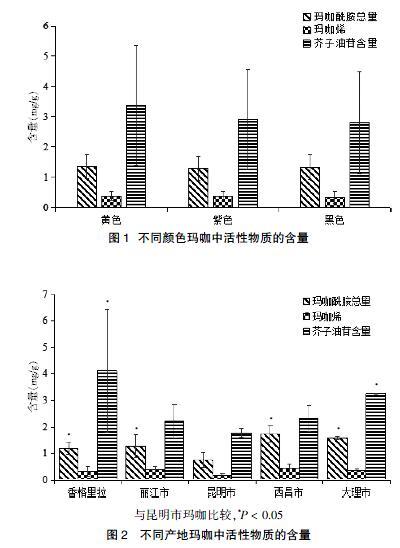
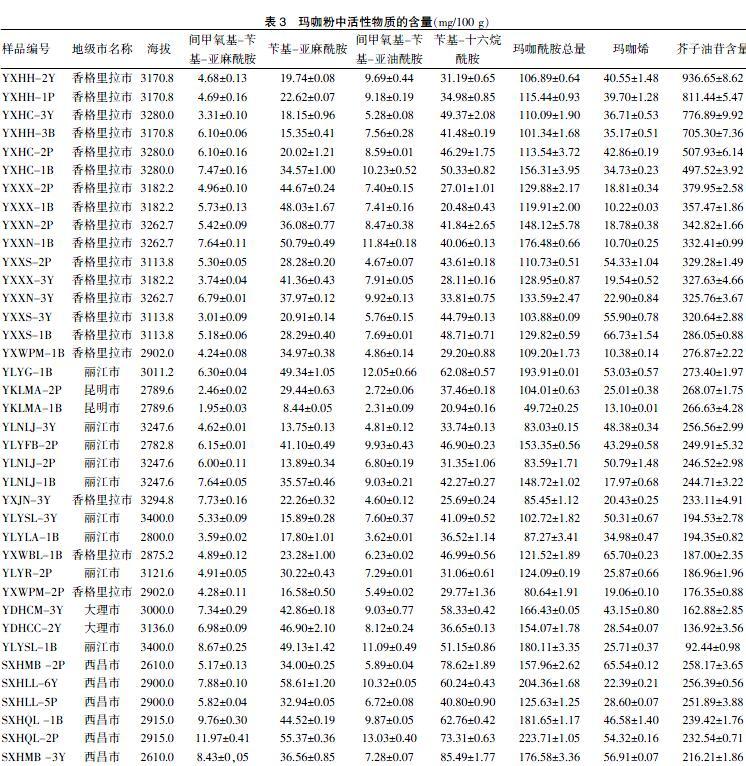
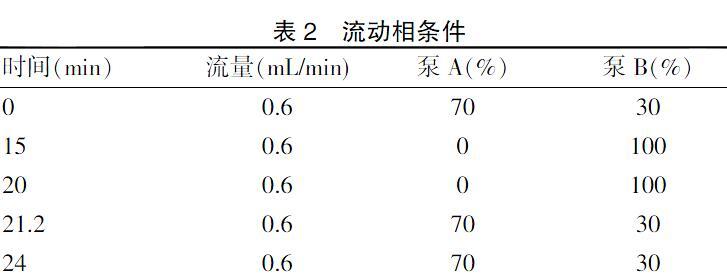
2.3.1 样品产地信息及玛咖中芥子油苷、玛咖酰胺以及玛咖烯的含量 产自云南和四川两省的40个玛咖样品中玛咖酰胺的含量为49.72~204.36 mg/100 g,玛咖烯的含量为10.22~66.73 mg/100 g,芥子油苷的含量为256.56~936.65 mg/100 g,含量相差数倍。见表3。2.3.2 玛咖品质与海拔、品种及产地的相关性分析 Pearson相关性分析结果示,玛咖酰胺、玛咖烯及芥子油苷与海拔无明显相关性(r = 0.302、0.312,P > 0.05),而玛咖烯的含量与海拔具有一定的相关性(r = 0.333,P < 0.05)。黑色、黄色、紫色玛咖中3种(类)主要活性成分含量差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。见图1。不同产地玛咖中活性成分的含量差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。整体来看,昆明市玛咖的活性成分含量最低,其他地区活性成分均高于昆明市,各地玛咖中玛咖酰胺含量均高于昆明市,香格里拉和大理市的芥子油苷含量高于昆明市,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05);各地玛咖中玛咖烯含量差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。见图2。提示玛咖的品质主要受产地和海拔的影响,而与玛咖的品种无关。
與昆明市玛咖比较,*P < 0.05
3 讨论
本课题组前期研究表明玛咖鲜果采后的加工干燥方式是影响玛咖品质的关键因素,前期工作已经建立了玛咖中玛咖烯,玛咖酰胺以及芥子油苷的含量检测方法[11-12]。玛咖中的活性成分包括生物碱、芥子油苷及其衍生物异硫氰酸酯、氨基酸、甾醇和多酚等。其中玛咖酰胺、玛咖烯以及芥子油苷是判断玛咖质量的主要指标[13-16]。有研究表明,玛咖中的活性成分玛咖酰胺、玛咖烯和芥子油苷等的含量与玛咖的产地,海拔以及品种有关[17-18]。可见不同产地的玛咖品质差距明显。为了进一步明确影响玛咖活性成分含量的其他因素,本实验检测了云南、四川两省五市40个玛咖鲜果样本中玛咖烯、玛咖酰胺以及芥子油苷的含量,发现我国不同产地的玛咖品质差别较大。将玛咖活性成分含量与海拔进行相关性分析后发现,玛咖烯的含量与海拔具有一定的相关性(P < 0.05);对不同产地和品种的玛咖中活性成分的含量进行显著性分析,发现不同颜色玛咖中活性成分的含量没有显著性差异,这一结果与黑色玛咖品质高的市场上固有观念不符[18-19],原因考虑为产地与玛咖活性成分含量有一定关系,且昆明市玛咖中活性成分含量最低。
我国的玛咖活性成分含量千差万别,质量良莠不齐[20-21]。但整体来看,玛咖的种植海拔越高,玛咖中活性成分的含量越高,呈现一定的正相关性。从种植产地来看,四川省和云南省其他地区玛咖的质量要优于昆明市。
[参考文献]
[1] Esparza E,Hadzicha A,Kofera W,et al. Bioactive maca(Lepidium meyenii.)alkamides are a result of traditional Andean postharvest drying practices [J]. Phytochemistry,2015,116:138 -148.
[2] 许敏,徐丽,宋晖,等.玛咖的研究进展[J].食品安全质量检测学报,2015,6(7):2775-2782.
[3] Zhou Y,Li P,Brantner A,et al. Chemical profiling analysis of Maca using UHPLC-ESI-Orbitrap MS coupled with UHPLC-ESI-QqQ MS and the neuroprotective study on its active ingredients [J]. Sci Rep,2017,7:44660.
[4] Cicero AF,Piacente S,Plaza A,et al. Hexanic Maca extract improves rat sexual performance more effectively than methanolic and chloroformic Maca extracts [J]. Andrologia,2002,34(3):177-179.
[5] Gasco M,Aguilar J,Gonzales GF. Effect of chronic treatment with three varieties of Lepidium meyenii(maca)on reproductive parameters and DN quantification in adult male rats [J]. Andrologia,2007,39(4):151-158.
[6] Vecera R,Orolin J,Skottova N,et al. The influence of maca(Lepidium meyenii)on antioxidant status,lipid and glucose metabolism in rat [J]. Plant Food for Hum Nutr,2007,62(2):59-63.
[7] Ikeuchi M,Koyama T,Takei S,et al. Effect benzylglucosinolate on endurance capacity in mice [J]. J Heal Sci,2009,55(2):178-182.
[8] Yudthavorasit S,Wongravee K,Leepipatpiboon N. Characteristic fingerprint based on gingerol derivative analysis for discrimination of ginger(Zingiber ocinale)according to geographical origin using HPLC-DAD combinedwith chemometrics [J]. Food Chem,2014,158:101-111.
[9] Mikulic-Petkovsek M,Schmitzer V,Slatnar A. A comparison of fruit quality parameters of wild bilberry(Vac-cinium myrtillus L.)growing at different locations [J]. J Sci Food Agric,2015,95(4):776-785.
[10] Meissner HO,Mscisz A,Mrozikiewicz M,et al. Peruvian Maca(Lepidium peruvianum.):(I)Phytochemical and Genetic Differences in Three Maca Phenotypes [J]. Int J Biomed Sci,2015,11(3):131-145.
[11] 党艳婷,苑鹏,夏凯,等.基于气味指纹图谱的玛咖品质快速鉴定方法[J].食品科学,2018,39(6):291-297.
[12] McCollom MM,Villinski JR,MC Phall KL,et al. Analysis of macamides in samples of Maca (Lepidium meyenii.) by HPLC-UV-MS/MS [J]. Phytochem Anal,2005,16(6):463-469.
[13] Yang Q,Jin W,Lv X,et al. Effects of macamides on endurance capacity and anti-fatigue property in prolonged swimming mice [J]. Pharm Biol,2016,54(5):827-34.
[14] 张红红,乔同岭,顾建仁.玛咖的生物学功能及其应用的研究进展[J].中国食物与营养,2016,22(7):71-73.
[15] 李爱民,夏凯,郝俊冉,等.不同干燥方式与粉碎粒度对玛咖活性成分和气味影响的研究[J].食品与发酵工业,2018,44(2):121-128.
[16] 金文聞.药食两用植物玛咖(Lepidium meyenii.)的功效物质研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2007.
[17] Pan Y,Zhang J,Li H,et al. Characteristic fingerprinting based on macamides for discrimination of maca (Lepidium meyenii.) by LC/MS/MS and multivariate statistical analysis [J]. J Sci Food Agr,2016,96(13):4475-4483.
[18] Pan Y,Zhang J,Li H,et al. Simultaneous analysis of macamides in Maca(Lepidium meyenii.)with different drying processby liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Food Anal Method,2016,9(6):1686-1695.
[19] 王义强,陈章靖,王启业,等.玛咖药用价值与引种培育研究进展[J].经济林研究,2014(2):167-172.
[20] 杨晶明,王竹,杨月欣.玛咖(Maca)干品营养成分分析与比较.中国食品卫生杂志,2011,19(3):201-205.
[21] Zhang JM,Xu ZM. Dye tracer infiltration technique to investigate macropore flow paths in Maka Mountain,Yunnan Province,China [J]. J Cent South Univ,2016,3(8):2101-2109.
(收稿日期:2019-01-02 本文编辑:刘永巧)
