基于骨干度与网络编码的链路预测模型研究
2019-09-10胡旭飞许云峰
胡旭飞 许云峰
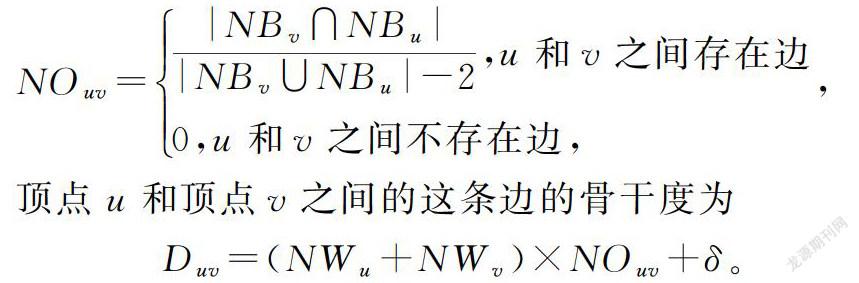

摘 要:为了研究网络表示学习在社交网络中链路预测方面的应用,提出了一种基于骨干度与网络编码的链路预测模型(BDLINE)。在网络表示学习算法LINE的基础上融入骨干度算法,通过给一阶相似度和二阶相似度中增添骨干权重,将网络编码到多维向量空间中,调试到最优参数。实验采用2个真实数据的数据集,分别在不同的算法模型上进行多次实验。实验结果表明:在链路预测方面,BDLINE均比其他网络表示学习算法的性能有所提升,AUC评测值更高,预测效果表现得更好。因此,所提出的方法可以方便地提取网络特征信息,更好地处理社交网络在链路预测中的随机性,对社交网络中预测网络节点的关联性和有效性具有一定的参考。
關键词:计算机网络;网络表示学习;链路预测;社交网络;相似性
中图分类号:TP391 文献标志码:A
Abstract:In order to study the application of network representation learning in link prediction in social networks, a link prediction model based on backbone and network coding (BDLINE) is proposed. The model integrates the backbone algorithm based on the network representation learning algorithm LINE. By adding the backbone weight to the first-order similarity and the second-order similarity, the network is encoded into the multi-dimensional vector space and debugged to the optimal parameters. The data set used in the experiment is two different real data, and multiple experiments are performed on different algorithm models. The experimental results show that in terms of link prediction, the proposed algorithm model has improved performance compared to other network representation learning algorithms; the AUC evaluation value is higher, and the prediction effect is better. It is more convenient for extracting network feature information by using the method, and can better deal with the randomness problem of social network in link prediction. The method has certain guiding significance for predicting the relevance and effectiveness of network nodes in social networks.
Keywords:computer network; network representation learning; link prediction; social network; similarity
现实世界中存在着大量而又复杂的社交网络,如何对网络数据进行有效合理的表示是现今学术研究中的一个重要挑战,网络表示学习正是为了迎接这种挑战而出现的,是解决大规模社交网络问题的基础方法[1-4],其研究领域有着非常广泛的应用场景,如可视化[5]、节点分类[6]、链路预测[7]等。网络表示学习是一个网络编码的过程,是根据网络顶点在网络中的结构作用,通过无监督学习,将网络顶点映射到多维空间。从直观的角度分析,在网络中拓扑结构[8]相似的顶点所表示出的向量关系更紧密,这里向量关系的相似性一般用向量间的余弦距离或者欧氏距离来表示[9]。
近年来,网络表示学习问题开始成为学术界的焦点,尤其是社交网络中链路预测的研究越来越受到国内外学者的广泛关注。链路预测可以识别一个不断发展的社交网络中可能存在但尚未建立的链接,从而为用户提供信息。真实世界的网络顶点数量非常多,因此,使用考虑全局结构的算法计算链路概率非常困难。早期的工作集中在顶点对之间直接的相似性度量上[10]。最近几年的网络表示学习算法主要有node2vec[11],DeepWalk[12],MMB[13],LINE[14]等,可以学习网络各顶点的潜在网络结构特征,将网络表征到多维空间中。本文提出的网络表示学习算法BDLINE是在LINE的基础上融入骨干度[15],重新调整网络参数模型,提高网络在向量空间中的相似性,最后通过链路预测实验分别进行各算法对比。结果表明所提出的算法AUC评测值更高,取得的预测效果最好。
1 基于骨干度与网络编码的链路预测
在社交网络中处理网络中的数据,需要对网络进行清晰的定义。首先定义一个信息网络
[WTBX]G=(V,E),其中V是顶点集合,E是顶点之间的边集合,边e=(u,v)∈E表示了u到v的一条边。BDLINE模型是在LINE的基础上建立的,LINE的算法定义了使用一阶和二阶相似度来解决大规模网络信息编码问题。
所有的连边计算完之后,得到AUC值。AUC值最少应大于0.5,最大值不超过1。AUC值越高,说明算法的预测结果越精确,性能越好。
2.3 实验环境与实验参数
实验环境:Linux操作系统;实验算法模型均采用Python语言实现;所提算法BDLINE和LINE使用TensorFlow机器学习框架。
实验参数设置:BDLINE设置向量size大小为128,根据实验经验,此值效果最好;负采样值为5,epoch=10;线程数为8,学习率[WTBX]lr=0.001。
2.4 实验结果
将本文提出的算法模型BDLINE分别在2个数据集上进行实验,为了呈现更好的预测效果,对训練集在真实数据集所占的比例由低到高依次选取,选取数据的过程都具有随机性。每个算法训练模型都进行11次测试,获得测试结果并取其平均值。所有的实验结果如表2和表3所示。
可以看出,当只保留15%的边用于训练时,评测AUC值都很低,所有方法的性能都很差,大多数顶点是孤立的,而且毫无意义。随着训练集所占的比例越来越大,训练的边也越来越多,AUC值也越来越高。通过纵向对比发现,BDLINE相对于其他算法来说,AUC值均有所提高,说明了该算法在链路预测任务中的有效性,验证了该算法具有精确建模顶点间关系的能力。通过引入骨干度,学习到的网络感知能力比LINE有较大的改进,即一个特定的顶点在与其他顶点交互时应该扮演不同的角色,从而有利于相关链路的预测任务。
3 结 论
1)针对现有的社交网络在链路预测方面的问题,提出了基于骨干度与网络编码的链路预测模型BDLINE,首次将骨干度引入到LINE算法中。实验证明,BDLINE比现有的众多网络表示学习算法有着更加准确的预测结果。
2)BDLINE网络表示学习算法可以学习高质量的网络结构编码,有助于准确估计顶点之间的关系,提高顶点间的相似度,对社交网络中预测网络节点的关联性和有效性有一定的借鉴意义。
3)本次实验虽然取得了不错的效果,但仍有不足之处,对于多属性的大规模复杂网络,处理的时间复杂度较高,测试结果随机性太大,不够稳定,今后会进行优化改善。在未来的研究中,会尝试用对抗性网络学习机制来处理具有复杂属性的网络,用深度学习技术进一步提高网络骨干度权重的精确值。
参考文献/References:
[1] AMED A, SERVASIDZE N, NARAYANAMURTY S, et al. Distributed large-scale natural graph factorization[C]// Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on World Wide Web. New York:ACM, 2013:37-48.
[2] LEVY O, GOLDBERG Y. Neural word embedding as implicit matrix factorization. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014(3):2177-2185.
[3] LE Q, MIKOLOV T. Distributed representations of sentences and documents[C]// Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. Beijing:[s.n.],2014:1188-1196.
[4] CANG Shiyu, AN Wei, TANG iliang, et al. eterogeneous network embedding via deep architectures[C]// Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York:ACM,2015:119-128.
[5] TANG ian, LIU ingzhou, ZANG Ming, et al. Visualization large-scale and high-dimensional data. Machine Learning,2016: 10.1145/2872427.2883041.
[6] BAGAT S, CORMODE G, MUTUKRISNAN S. Node classification in social networks. Social Network Data Analytics, 2011, 16(3):115-148.
[7] LIBEN-NOWELL D, KLEINBERG . The Link-Prediction Problem for Social Networks[M].[S.l.]: ohn Wiley & Sons, 2007.
[8] TANAY B, KANDEMIR M B. Topological structure of fuzzy soft sets. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 2011, 61(10):2952-2957.
[9] TU Cunchao, LIU an, LIU Zhiyuan, et al. CANE: Context-aware network embedding for relation modeling[C]// Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers). Vancouve: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2017: 1722-1731.
[10]L Linyuan, ZOU Tao. Link prediction in complex networks: A survey. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2011, 390(6):1150-1170.
[11]GROVER A, LESKOVEC . node2vec: Scalable feature learning for networks[C]// Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York:ACM, 2016:855-864.
[12]PEROZZI B, Al-RFOU R, SKIENA S. DeepWalk: Online learning of Social representations[C]// Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining.New York:ACM, 2014:701-710.
[13]AIROLDI E M, BLEI D M, FIENBERG S E, et al. Mixed membership stochastic blockmodels. The ournal of Machine Learning Research, 2008,9:1981-2014.
[14]TANG ian, QU Meng, WANG Mingzhe, et al. LINE: Large-scale information network embedding[C]//Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on World Wide Web. Florence:[s.n.],2015:1067-1077.
[15]XU Yunfeng, XU ua, ZANG Dongwen. A novel disjoint community detection algorithm for social networks based on backbone degree and expansion. Expert Systems with Applications, 2015, 42(21):8349-8360.
[16]TANG ie, ZANG ing, YAO Limin, et al. ArnetMiner: Extraction and mining of academic social networks[C]// Proceedings of the 14th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York:ACM, 2008:990-998.
