微生物介导植物次生代谢产物累积及在药用植物作用机制中的研究进展
2019-09-10郜玉钢莫琪琪赵岩臧埔
郜玉钢 莫琪琪 赵岩 臧埔
摘要:植物次生代謝产物是植物长期与生态环境适应的结果,具有多种药理、生理和生态学功能,已广泛应用于医药、保健品、化妆品、食品和农药等行业。文章重点介绍了病原菌、诱导子和内生菌介导植物次生代谢产物累积的概况,指出利用病原菌介导植物次生代谢累积作用不持久和不安全,诱导子介导虽安全但更不持久,内生菌介导远比生物侵害因子更安全、更可控和更持久,且经济可靠效率高,应用前景更理想;同时总结了内生菌介导植物次生代谢产物累积的主要途径,归纳了内生菌与宿主植物次生代谢的互作机制,并指出内生菌在药用植物药效成分累积中的作用机制。今后应借助高通量测序、SSH、HPLC、TLC、IR、MS和NMR等手段确定内生菌介导药用植物次生代谢产物累积的途径、种类及其差异基因,再结合药用植物次生代谢单体和差异基因表达量相关分析、Unigene注释、差异基因结构分析筛选候选基因并验证其功能,综合Unigene蛋白互作网络等分析和关键酶基因作用信号通路,确定内生菌介导药用植物次生代谢累积的分子机制。
关键词: 微生物;植物;药用植物;次生代谢产物;互作机制
中图分类号: S182 文献标志码: A 文章编号:2095-1191(2019)10-2234-07
Microbial mediated accumulation of plant secondary metabolites and its action mechanism in medicinal
plants: A review
GAO Yu-gang1,2, MO Qi-qi1,2, ZHAO Yan1,2, ZANG Pu1,2*
(1College of Traditional Chinese Medicinal Materials, Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun 130118, China; 2Ginseng Engineering Technology Research Center of Jilin Province, Changchun 130118, China)
Abstract:Plant secondary metabolites are the result of long-term adaptation of plants to the ecological environment, they have a variety of pharmacological, physiological and ecological functions and are widely used in medicine, health care products, cosmetics, food and pesticide industries. The accumulation of plant secondary metabolites mediated by microorganisms was reviewed in this article, focusing on the pathogens, elicitors, endophytes to mediate plant secondary metabolism:pathogens were not persistent and unsafe. Elicitors were safe but less persistent. Endophytes were far safer, more controllable and lasting, and economically reliable and more efficient than biological aggressor. The main pathways of secondary metabolism mediated by endophytes, and the interaction mechanism between endophytes and host plants were summarized. The function mechanism of endophytes in effective component accumulation of medicinal plants was pointed out. High-throughput sequencing, SSH, HPLC, TLC, IR, MS and NMR were used to determine the pathways and species and differential genes of endophytes mediated medicinal plants secondary metabolism accumulation. In combination with the secondary metabolites of medicinal plants and differential gene expression analysis, Unigene annotation and differential gene structure analysis, candidate genes were screened and their functions were verified. The molecular mechanism of endophytes mediated the accumulation of secondary metabolism in medicinal plants were determined combining with the Unigene protein interaction network and key enzyme gene signaling pathways.
Key words: microbe; plant; medicinal plants; secondary metabolic products; interaction mechanism
0 引言
植物次生代谢产物是一类特殊的小分子有机化合物,其种类繁多,但并非是植物生长发育过程中所必需的物质。植物次生代谢产物在增强植物抗病性、抵御害虫侵害及其对环境的适应中起着重要作用,是植物长期与生态环境相適应的结果(牛丽丽等,2016;顾小辉等,2017),而植物次生代谢产物作为天然的活性成分,也具有一定的药理作用和生物活性,在抗菌、抗炎、抗肿瘤、防治心血管疾病及抗心肌缺血等方面发挥重要作用(华晓雨等,2017;张建红等,2018),已广泛应用于医药、保健品、化妆品、食品和农药等行业,但次生代谢产物通常含量低,因而限制了其研究与应用。作为药用植物道地性的物质基础,次生代谢产物的含量及种类通常被用于评价植物道地药材质量的优劣(Liu et al.,2018;Wang et al.,2018)。生物(病原菌、害虫、有益菌等)与非生物(干旱、盐碱、重金属、温度等)因素可显著影响植物次生代谢物的含量,寻找次生代谢合成途径、关键酶基因及其机理已成为研究热点。本研究就微生物介导植物次生代谢产物累积及在药用植物中的作用机制进行综述,不仅有助于阐明次生代谢产物累积的分子机制,还对药用植物道地性成因及其质量调控研究具有参考价值。
1 病原菌介导植物次生代谢
植物次生代谢产物与植物的防御反应和被胁迫程度有密切关系。Brader等(2001)研究发现,胡萝卜软腐欧文氏菌(Erwinia carotovora)促进拟南芥3-吲哚基甲基芥子油苷增加;Huffaker等(2011)研究发现,禾谷镰刀菌(Fusarium graminearum)接种玉米可合成萜类化合物;Stotz等(2011)研究发现,拟南芥受到核盘菌(Sclerotinia sclerotiorum)侵染后可合成亚麻荠素,增加芥子油苷含量;龙月红等(2012)研究发现,尖孢镰孢菌(Fusarium oxysporum)、葡萄座腔菌(Botryosphaeria dothidea)和角担菌(Ceratoba-sidium spp.)在宿主刺五加体内可提高刺五加苷E含量1.86~5.23倍;Onrubia等(2013)研究发现,单胞菌(Pseudomonas syringae)产生的植物毒素Coronatine使紫杉烷含量增加。植物次生代谢产物合成需要消耗很高能量,对植物本身也有一定的毒害作用,因此,植物次生代谢受到本身的严格调控,一般处于关闭或半关闭状态,只有受到外界侵害时植物防御反应才会被激活而启动次生代谢产物合成(杨欣等,2013;Xia et al.,2016)。药用植物被病原菌感染后会出现病症,甚至死亡,严重影响药用植物的生产性能和品质。可见,利用病原菌介导植物次生代谢产物的累积作用具有不持久性和不安全性。
2 诱导子介导植物次生代谢
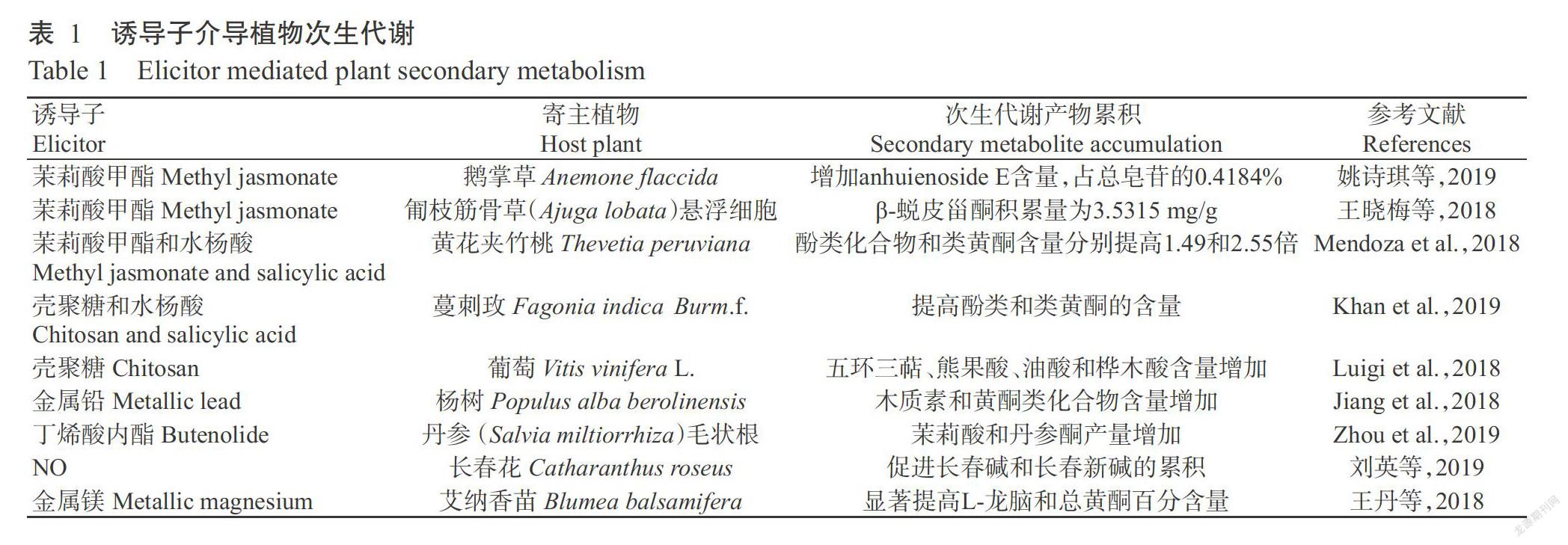
诱导子是一种特殊的触发因子,分为生物诱导子和非生物诱导子,具有效率高、成本低和可操控性强等特点,其被广泛应用于提高植物次生代谢产物含量。生物诱导子如细菌和真菌的菌丝体、菌丝体降解产物、发酵液及分泌物等;非生物诱导子包括金属离子、茉莉酸甲酯、水杨酸、茉莉酸和乙烯等。由表1可知,诱导子能促使植物产生防御反应,从而诱导植物次生代谢产物的合成,其中,茉莉酸及茉莉酸衍生物是植物次生代谢物合成和积累最有效的诱导子。可见,直接应用诱导子能有效模拟外来病原菌胁迫因子诱导次生代谢产物合成。但诱导子容易被植物本身降解而快速失活,这种介导植物次生代谢产物累积作用更不持久。
3 内生菌介导植物次生代谢
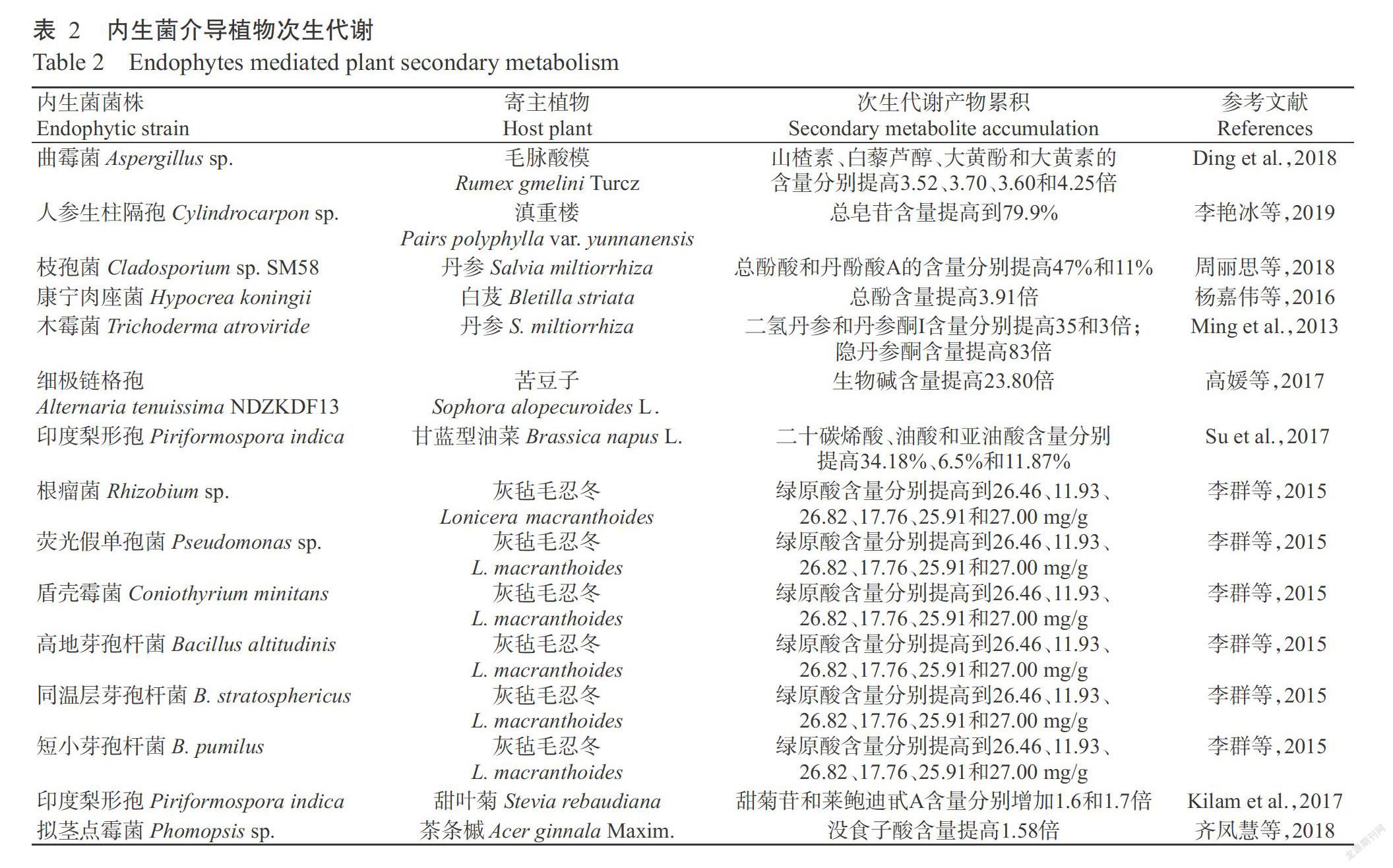
内生菌广泛存在于植物体内,其长期与宿主植物协同进化,不仅促进植物生长,还能持续性促进药用植物活性成分累积,提高药用植物的品质和产量,且不会引发宿主植物出现明显感染症状(Cui et al.,2013;Chen et al.,2019)。目前研究发现,多粘类芽孢杆菌喷施和灌根处理的1~4年生人参中,9种单体皂苷加和值与同年人参比较,分别提高36.83%、44.52%、67.96%和79.44%;多粘类芽孢杆菌与死态人参共培养显著提高了12种人参皂苷单体加和值含量,特别是稀有人参皂苷CK和Protopanaxadiol含量分别提高1.38和7.78倍(Gao et al.,2015;Ji et al.,2015)。由表2可知,利用内生菌模拟病原菌侵害因子来诱导植物次生代谢合成的防御反应,远比生物侵害因子更安全、更可控和更持久,且经济可靠效率高,应用前景更理想。
4 内生菌介导植物次生代谢产物累积的主要途径
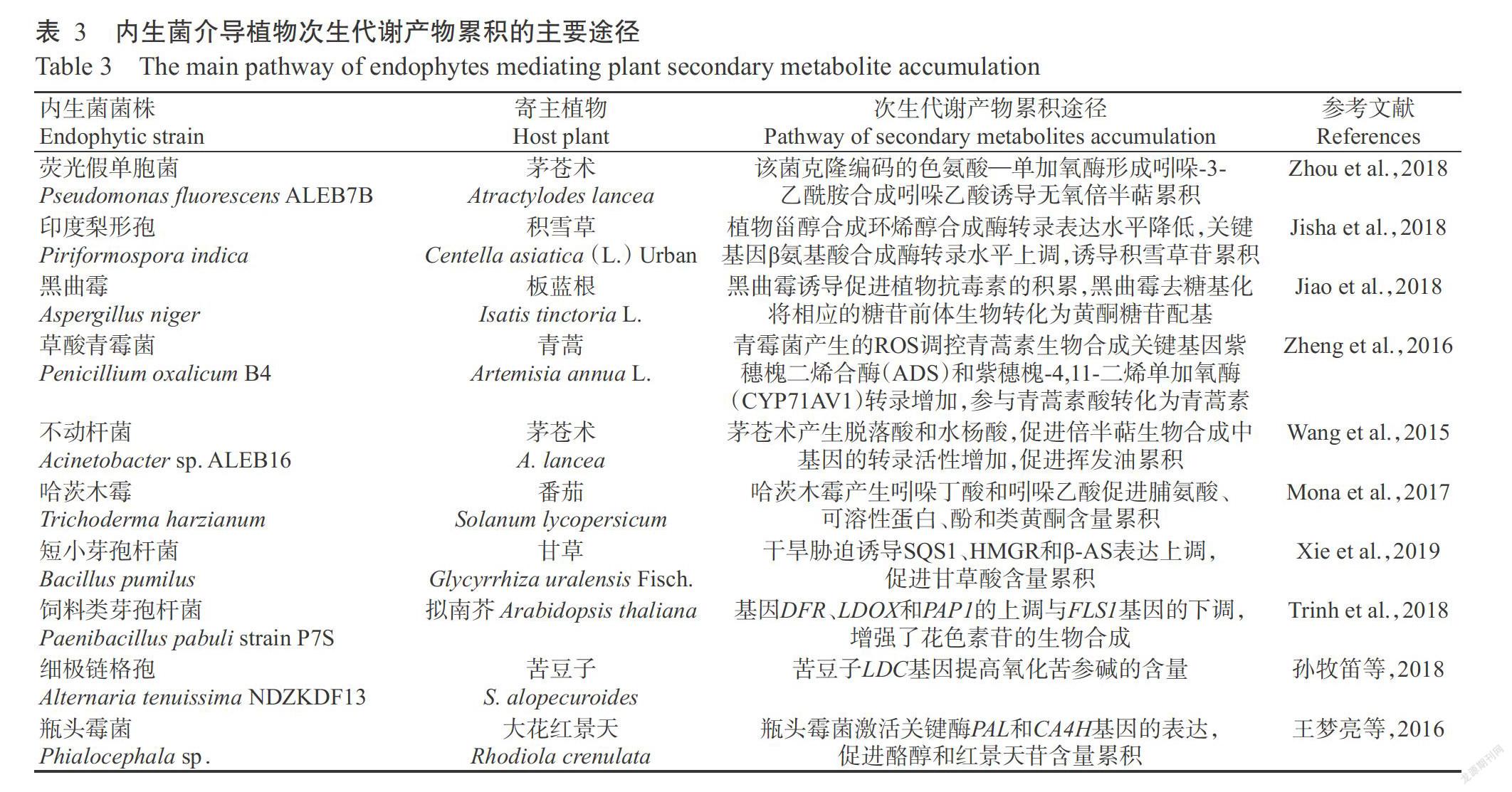
内生菌介导植物次生代谢产物累积的主要途径可能包括:①内生菌直接产生各种化合物,成为宿主活性成分,或作为宿主的次生代谢产物前体再通过宿主合成酶催化合成活性成分,或被植物吸收调控,进而影响宿主次生代谢累积(Hassan and Mathesius,2012);②内生菌通过诱导子效应或横向基因转移等改变宿主基因表达和代谢途径,导致相关基因活性的变化,进而介导某些次生代谢物的累积(Gluck-Thaler and Slot,2015);③内生菌可通过生物转化作用对宿主化合物产生影响(Tian et al.,2014)。由内生菌促进植物次生代谢产物累积的主要途径(表3)可知,内生菌介导植物次生代谢产物累积,在不同植物中可能存在各自不同的互作作用,内生菌与宿主互作介导次生代谢产物累积的分子机制还有待进一步研究。
5 展望
5. 1 内生菌与宿主植物互作机制研究现状
内生菌与宿主植物互作机制存在马赛克理论、获得性免疫系统、外源性化学兴奋效应及平衡对抗等假说(Venugopalan and Srivastava,2015;Khan et al.,2017)。其中,公认的平衡对抗假说认为,内生菌与宿主互作不同于病原菌,是其毒力因子与宿主防御反应间的平衡对抗,二者只有通过协同进化达到平衡才能长期共存,但实际上平衡维持机制远比平衡对抗更复杂和精密(Raman and Suryanarayanan,2017)。研究发现,喜树碱能抑制内生菌拓朴异构酶的活性,但同时内生菌能通过特有的氨基酸残基结合在拓扑异构酶与喜树碱结合的活性结构域,防止拓扑异构酶失活,进而免受自身或宿主产生的喜树碱的抵抗,而不产生喜树碱的内生菌通过直接编码拓朴异构酶的方式来抵抗宿主喜树碱活性(Kusari et al.,2012);内生菌单培养时,许多活性内生菌的活力不稳定,甚至逐步消失,该菌能产生喜树碱的前体,但缺少来自宿主植物提供的活性成分合成酶,而无法合成活性成分。说明平衡对抗不仅存在二者之间横向基因的简单转移(Kusari et al.,2011),还存在宿主植物同时与多种微生物间相互作用、同一宿主植物各内生菌间相互作用,加之体外试验很难模拟其真实互作关系,这些难题在研究中均需排除或加以解决。
植物次生代谢产物的生物途径只有在生物和非生物因子胁迫下才被激活。基因是酶的基础,因此植物受到胁迫时,激发植物体内的细胞信号转导通路先将信号传递给受胁迫的转录因子,提高mRNA的转录水平,进而诱导次生代谢物关键酶的表达。如促进人参皂苷合成的关键酶基因3-羟基-3-甲基戊二酰辅酶A还原酶基因(HMGR)、法尼基焦磷酸合酶基因(FPS)、达玛烷二醇合酶基因(DS)、角鲨烯合成酶基因(SS)和角鲨烯环氧酶基因(SE)等,但内生菌介导人参单体皂苷的累积具体对应哪个关键酶基因尚不明确,需更深入探究。可见,阐明内生菌与宿主植物互作介导药用植物活性成分单体累积的理论及信号通路等分子机制,更需要直接证据加以证明。
5. 2 确定内生菌介导药用植物次生代谢累积的分子机制建议
宿主植物同时与多种微生物间相互作用,同一宿主植物各微生物间也存在相互作用,导致体外试验很难模拟其真实互作关系,而利用内生菌与宿主植物发根互作试验材料,研究微生物介导植物次生代谢产物累积,既能模拟内生菌与植物间的真实互作关系,又能排除其他微生物的干扰。
首先,借助高通量测序与SSH联用筛选内生菌介导药用植物转录组的差异mRNA,且利用HPLC、TLC、IR、MS和NMR分析和鉴定药用植物次生代谢产物单体,确定内生菌介导药用植物次生代谢产物累积的途径和种类及其差异基因;其次,综合药用植物次生代谢单体和差异基因相关分析、Unigene注释、差异基因结构分析及相关次生代谢途径信息,筛选内生菌介导药用植物次生代谢产物累积的候选基因,再依次用qRT-PCR、原核表达、真核过表达和沉默表达验证该候选基因功能,确定内生菌介导药用植物次生代谢产物累积的关键酶基因;最后,综合Unigene蛋白互作网络等分析和关键酶基因作用信号通路及相关次生代谢途径信息,确定内生菌介导药用植物次生代谢累积的分子机制。
参考文献:
高媛,孙牧笛,徐全智,吕茜,张庆宸,顾沛雯. 2017. 苦豆子内生真菌对宿主培养物生长及喹诺里西啶类生物碱合成的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究,35(3): 212-218. [Gao Y,Sun M D,Xu Q Z,Lü X,Zhang Q C,Gu P W. 2017. Effect of Sophora alopecuroides L.endophytic fungi on the growth of the host plant culture and synthesis of qui-nolizidine alkaloids[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas,35(3): 212-218.]
顾小辉,魏建和,王国全,高志晖. 2017. 虫害诱导植物合成防御性次生代谢产物的研究进展[J]. 生命科学研究,21(5):458-465. [Gu X H,Wei J H,Wang G Q,Gao Z H. 2017. Progresses on the defensive secondary metabolites induced by herbivorous insects in plants[J]. Life Science Research,21(5):458-465.]
华晓雨,陶爽,孙盛楠,郭娜,阎秀峰,蔺吉祥. 2017. 植物次生代谢产物——酚类化合物的研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报,33(12): 22-29. [Hua X Y,Tao S,Sun S N,Guo N,Yan X F,Lin J X. 2017. Research progress on phenolic compounds of plant secondary metabolites[J]. Biotechno-logy Bulletin,33(12): 22-29.]
李群,汪超,唐明,程世君,马丹炜,王亚男,卢红. 2015. 灰毡毛忍冬‘渝蕾1号’内生菌对其悬浮细胞生物量及绿原酸含量的影响[J]. 植物生理学报,51(11): 1997-2005. [Li Q,Wang C,Tang M,Cheng S J,Ma D W,Wang Y N,Lu H. 2015.Effects of endophytes of Lonicera macranthoides cultivar ‘Yulei1’ on the bio-mass accumulation and chlorogenic acid production[J]. Plant Physiology Journal,51(11): 1997-2005.]
李艷冰,林亮,廖秋红,杨生超,刘涛. 2019. 促进滇重楼皂苷类活性成分积累的内生真菌筛选[J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学),34(1): 132-137. [Li Y B,Lin L,Liao Q H,Yang S C,Liu T. 2019. Screening of endophytic fungi for promote the accumulation of active components of saponins from Pairs polyphylla var. yunnanensis[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University(Natural Science),34(1): 132-137.]
刘英,杨超,于莉莉,付金颖,付玉杰,李德文. 2019. 遮光胁迫下外源NO对长春花幼苗生长及生物碱积累的影响[J]. 中国药学杂志,54(1):16-21. [Liu Y,Yang C,Yu L L,Fu J Y,Fu Y J,Li D W. 2019. Effects of exogenous nitric oxide on growth and alkaloid accumulation of Catha-ranthus roseus seedlings under light-shading treatment[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal,54(1):16-21.]
龙月红,何闪,熊亚南,劳凤云,陈龙,邢朝斌. 2012. 三株提高刺五加苷E含量内生真菌的鉴定及其作用方式分析[J]. 现代生物医学进展,12(13): 2429-2432. [Long Y H,He S,Xiong Y N,Lao F Y,Chen L,Xing Z B. 2012. Identification of three endophytic fungus that increase eleutheroside E and analysis on its function mechanism[J]. Pro-gress in Modern Biomedicine,12(13): 2429-2432.]
牛丽丽,袁肖寒,顾成波,刘紫薇,马慧,宁文娟. 2016. 内生真菌产植物次生代谢产物研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学,44(11):12-16. [Niu L L,Yuan X H,Gu C B,Liu Z W,Ma H,Ning W J. 2016. Research progress on secondary metabolites produced from endophytic fungi[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,44(11):12-16.]
齐凤慧,陈思齐,景天忠,张宇昕,詹亚光. 2018. 真菌诱导子对茶条槭细胞没食子酸积累的影响[J]. 植物研究,38(6): 948-955. [Qi F H,Chen S Q,Jing T Z,Zhang Y X,Zhan Y G. 2018. Effect of fungal elicitor on gallic acid accumulation in the cells of Acer ginnala Maxim.[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research,38(6): 948-955.]
孙牧笛,张庆宸,胡丽杰,李文学,闫思远,吕苗苗,顾沛雯. 2018. 苦豆子内生真菌诱导子促进宿主生物碱合成关键酶基因表达的荧光定量PCR检测[J]. 中草药,49(19): 4621-4627. [Sun M D,Zhang Q C,Hu L J,Li W X,Yan S Y,Lü M M,Gu P W. 2018. Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection of key enzyme genes expression of alkaloid biosynthesis promoted by endophytic fungal elicitor in Sophora alopecuroides[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,49(19): 4621-4627.]
王丹,蓝惠萍,张影波,于福来,陈晓鹭,黄梅,王凯,庞玉新. 2018. 镁对两年生艾纳香生物量、抗氧化酶活性及有效成分积累的影响[J]. 热带农业科学,38(7): 50-56. [Wang D,Lan H P,Zhang Y B, Yu F L,Chen X L, Huang M, Wang K,Pang Y X. 2018. The effect of magnesium on biomass,antioxidant enzyme activities,and active component accumulation of two years old Blumea balsamifera[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture,38(7): 50-56.]
王梦亮,焦晋,邢婕,田俊生,崔晋龙,王俊宏. 2016. 内生真菌ZPRa-R-1对红景天中关键信号分子及主要次生代谢物的影响[J]. 植物研究,36(3): 416-420. [Wang M L,Jiao J,Xing J,Tian J S,Cui J L,Wang J H. 2016. Effects of endophytic fungi ZPRa-R-1 on the key singnal molecules and the main secondary metabolites in Rhodiola crenulata.[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research,36(3): 416-420.]
王晓梅,迟德富,宇佳. 2018. 茉莉酸甲酯对匍枝筋骨草细胞生长和β-蜕皮甾酮积累的影响[J]. 草业学报,27(9): 95-109. [Wang X M,Chi D F,Yu J. 2018. The effect of jasmonic acid methylester on cell growth and β-ecdysterone accumulation in Ajuga lobata[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica,27(9): 95-109.]
杨嘉伟,王康才,梁君怡,王娟,夏天爽,梁永富. 2016. 外源MeJA,SA及2种內生菌处理对白芨幼苗生理及总酚含量影响[J]. 中国中药杂志,41(15): 2794-2801. [Yang J W,Wang K C,Liang J Y,Wang J,Xia T S,Liang Y F. 2016. Effects of exogenous MeJA,SA and two kinds of endophytic fungi on physiology and total phenols content of seedlings of Bletilla striata[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,41(15): 2794-2801.]
楊欣,徐艳红,魏建和,刘娟,张岩. 2013. 几种重要植物次生代谢防御反应物质的生物合成途径及分子调控机制研究进展[J]. 生物技术通讯,24(2): 285-289. [Yang X,Xu Y H,Wei J H,Liu J,Zhang Y. 2013. Advances on the biosynthesis pathways and molecular regulation mechanism of several important defensive substances in plant secondary metabolism[J]. Letters in Biotechnology,24(2): 285-289.]
姚诗琪,曹洒,侯帅红,黄芳,莫国艳,韩林涛. 2019. 茉莉酸甲酯对鹅掌草中三萜皂苷anhuienoside E含量积累的影响[J]. 湖北中医药大学学报,21(1): 38-41. [Yao S Q,Cao S,Hou S H,Huang F,Mo G Y,Han L T. 2019. Effects of methyl jasmonate on the accumulation of triterpenoid saponin anhuienoside E in Anemone flaccida[J]. Journal of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine,21(1): 38-41.]
张建红,刘琬菁,罗红梅. 2018. 药用植物萜类化合物活性研究进展[J]. 世界科学技术—中医药现代化,20(3): 419-430. [Zhang J H,Liu W J,Luo H M. 2018. Advances in activities of terpenoids in medicinal plants[J]. World Science and Technology-Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine,20(3): 419-430.]
周丽思,唐坤,郭顺星. 2018. 内生真菌枝孢属Cladosporium sp.对丹参生长和丹酚酸含量的影响[J]. 菌物学报,37(1): 95-101. [Zhou L S,Tang K,Guo S X. 2018. Active endophytic fungus Cladosporium sp. promoting growth and increasing salvianolic acid content of Salvia miltiorrhiza[J]. Mycosystema,37(1): 95-101.]
Brader G,Tas ,Palva E T. 2001. Jasmonate-dependent induction of indole glucosinolates in Arabidopsis by culture filtrates of the nonspecific pathogen Erwinia carotovora[J]. Plant Physiology,126(2): 849-860.
Chen L,Shi H,Heng J Y,Wang D X, Bian K. 2019. Antimicrobial,plant growth-promoting and genomic properties of the peanut endophyte Bacillus velezensis LDO2[J]. Microbiological Research,218: 41-48.
Cui J L,Wang C L,Guo S X,Xiao P G,Wang M L. 2013. Stimulation of dragon’s blood accumulation in Dracaena cambodiana via fungal inoculation[J]. Fitoterapia,87: 31-36.
Ding C H,Wang Q B,Guo S L,Wang Z Y. 2018. The improvement of bioactive secondary metabolites accumulation in Rumex gmelini Turcz through co-culture with endophytic fungi[J]. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology,49(2): 362-369.
Gao Y G,Liu Q,Zang P,Li X,Ji Q,He Z M,Zhao Y,Yang H,Zhao X L,Zhan,L X. 2015. An endophytic bacterium isolated from Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer enhances growth,reduces morbidity,and stimulates ginsenoside biosynthesis[J]. Phytochemistry Letters,11:132-138.
Gluck-Thaler E,Slot J C. 2015. Dimensions of horizontal gene transfer in eukaryotic microbial pathogens[J]. PLoS Pathogens,11(10): e1005156.
Hassan S,Mathesius U. 2012. The role of flavonoids in root-rhizosphere signaling:Opportunities and challenges for improving plant-microbe interaction[J]. Journal of Expe-rimental Botany,63(9): 3429-3444.
Huffaker A,Kaplan F,Vaughan M M,Dafoe N J, Ni X, Rocca J R,Alborn H T,Teal P E,Schmelz E A. 2011. Novel acidic sesquiterpenoids constitute a dominant class of pathogen-induced phytoalexins in Maize[J]. Plant Physio-logy,156(4): 2082-2097.
Ji Q,Gao Y G,Zhao Y,He Z M,Zang P,Zhu H Y,Yang H,Li X,Zhang L X. 2015. Determination of ginsenosides by Bacillus polymyxa conversion and evaluation on pharmacological activities of the conversion products[J]. Process Biochemistry,50(6): 1016-1022.
Jiang D,Wang Y Y,Dong X W,Yan S C. 2018. Inducible defense responses in Populus alba berolinensis to Pb stress[J]. South African Journal of Botany,119: 295-300.
Jiao J,Gai Q Y,Wang W,Zang Y P,Niu L L,Fu Y J,Wang X. 2018. Remarkable enhancement of flavonoid production in a co-cultivation system of Isatis tinctoria L. hairy root cultures and immobilized Aspergillus niger[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,112: 252-261.
Jisha S,Gouri P R,Anith K N,Sabu K K. 2018. Piriformospora indica cell wall extract as the best elicitor for asiaticoside production in Centella asiatica (L.) Urban,evidenced by morphological,physiological and molecular analyses[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,125: 106-115.
Khan A L,Waqas M,Asaf S,Kamran M,Shahzad R,Bilal S,Khan M A,Kang S M,Kim Y H,Yun B W,Rawahi A A,Harrasi A A,Lee I J. 2017. Plant growth-promoting endophyte Sphingomonas sp. LK11 alleviates salinity stress in Solanum pimpinellifolium[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany,133: 58-69.
Khan T,Khan T,Hano C,Abbasi B H. 2019. Effects of chitosan and salicylic acid on the production of pharmacologically attractive secondary metabolites in callus cultures of Fagonia indica[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,129: 525-535.
Kilam D,Saifi M,Abdin M Z,Agnihotri A,Varma A. 2017. Endophytic root fungus Piriformospora indica affects trans-cription of steviol biosynthesis genes and enhances production of steviol glycosides in Stevia rebaudiana[J]. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology,97: 40-48.
Kusari S,Hertweck C,Spiteller M. 2012. Chemical ecology of endophytic fungi:Origins of secondary metabolites[J]. Chemistry & Biology,19(7): 792-798.
Kusari S,Zühlke S,Spiteller M. 2011. Effect of artificial reconstitution of the interaction between the plant Camptotheca acuminata and the fungal endophyte Fusarium solani on camptothecin biosynthesis[J]. Journal of Natural Products,74(4): 764-775.
Liu S L,Xu Y H,Gao Y G, Zhao Y,Zhang A H,Zang L S,Wu C S,Zhang L X. 2018. Panaxadiol saponins treatment caused the subtle variations in the global transcriptional state of Asiatic corn borer,Ostrinia furnacalis[J]. Journal of Ginseng Research,331(11): 1-11.
Luigi L,Greta B,Youssef R,Giuseppe C,Luigi B,Marco T. 2018. Chitosan treatment elicited defence mechanisms,pentacyclic triterpenoids and stilbene accumulation in grape(Vitis vinifera L.) bunches[J]. Phytochemistry,156: 1-8.
Mendoza D,Cuaspud O,Arias J P,Ruiz O, Arias M. 2018. Effect of salicylic acid and methyl jasmonate in the production of phenolic compounds in plant cell suspension cultures of Thevetia peruviana[J]. Biotechnology Reports,19: e00273.
Ming Q L, Su C Y, Zheng C J, Jia M, Zhang Q, Zhang H, Rahman K, Han T, Qin L. 2013. Elicitors from the endophytic fungus Trichoderma atroviride promote Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root growth and tanshinone biosynthesis[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany,64(18): 5687-5694.
Mona S A,Hashem A,Abd_Allah E F,Abdulaziz A A,Dina W K S,Stephan W,Dilfuza E. 2017. Increased resistance of drought by Trichoderma harzianum fungal treatment correlates with increased secondary metabolites and proline content[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture,16(8): 1751-1757.
Onrubia M,Moyano E,Bonfill M,Cusidó R M, Goossens A, Palazón J. 2013. Coronatine,a more powerful elicitor for inducing taxane biosynthesis in Taxus media cell cultures than methyl jasmonate[J]. Journal of Plant Physio-logy,170(2): 211-219.
Raman A,Suryanarayanan T S. 2017. Fungus-plant interaction influences plant-feeding insects[J]. Fungal Ecology,29: 123-132.
Stotz H U,Sawada Y,Shimada Y,Hirai M Y,Sasaki E,Krischke M,Brown P D,Saito K, Kamiya Y. 2011. Role of camalexin,indole glucosinolates,and side chain modification of glucosinolate-derived isothiocyanates in defense of Arabidopsis against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum[J]. The Plant Journal,67(1): 81-93.
Su Z Z,Wang T,Shrivastava N,Chen Y Y,Liu X,Sun C,Yin Y,Gao Q K,Lou B G. 2017. Piriformospora indica promotes growth,seed yield and quality of Brassica napus L.[J]. Microbiological Research,199: 29-39.
Tian Y,Amand S,Buisson D,Kunz C,Hachette F,Dupont J,Nay B Prado S. 2014. The fungal leaf endophyte Paraconiothyrium variabile specifically metabolizes the host-plant metabolome for its own benefit[J]. Phytochemistry,108: 95-101.
Trinh C S,Jeong C Y,Lee W J,Truong H A,Chung N Y,Han J Y,Hong S W,Lee H J. 2018. Paenibacillus pabuli strain P7S promotes plant growth and induces anthocya-nin accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Plant Physio-logy and Biochemistry,129: 264-272.
Venugopalan A,Srivastava S. 2015. Endophytes as in vitro production platforms of high value plant secondary metabolites[J]. Biotechnology Advances,33(6): 873-887.
Wang W D,Liu X F,Liu J P,Cai E, Zhao Y, Li H, Zhang L, Li P, Gao Y. 2018. Sesquiterpenoids from the root of Panax ginseng attenuates,Lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior through the brain-derived neurotrophic factor/tropomyosin-related kinase B and sirtuin type 1/nuclear factor-κB signaling pathways[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,66(1): 265-271.
Wang X M,Yang B,Ren C G,Wang H W,Wang J Y,Dai C C. 2015. Involvement of abscisic acid and salicylic acid in signal cascade regulating bacterial endophyte-induced volatile oil biosynthesis in plantlets of Atractylodes lancea[J]. Physiologia Plantarum,153(1): 30-42.
Xia P G,Guo H B,Zhao H G,Jiao J,Deyholos Michael K,Yan X J,Liu Y,Liang Z S. 2016. Optimal fertilizer application for Panax notoginseng and effect of soil water on root rot disease and saponin contents[J]. Journal of Ginseng Research,40(1): 38-46.
Xie Z C, Chu Y K, Zhang W J,Lang D Y, Zhang X H. 2019. Bacillus pumilus alleviates drought stress and increases metabolite accumulation in Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch.[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany,158: 99-106.
Zheng L P,Tian H,Yuan Y F,Wang J W. 2016. The influence of endophytic Penicillium oxalicum B4 on growth and artemisinin biosynthesis of in vitro propagated plantlets of Artemisia annua L.[J]. Plant Growth Regulation,80(1): 93-102.
Zhou J,Ran Z F,Liu Q,Xua Z X,Xiong Y H,Fanga L,Guo L P. 2019. Jasmonic acid serves as a signal role in smoke-isolated butenolide-induced tanshinones biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root[J]. South African Journal of Botany,121: 355-359.
Zhou J Y,Sun K,Chen F,Yuan J, Li X, Dai C C. 2018. Endophytic Pseudomonas induces metabolic flux changes that enhance medicinal sesquiterpenoid accumulation in Atractylodes lancea[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,130: 473-481.
(責任编辑 麻小燕)
