空气载能空调房间输入(火用)算法及系统(火用)成本应用分析
2019-07-19龚光彩尹丹
龚光彩 尹丹


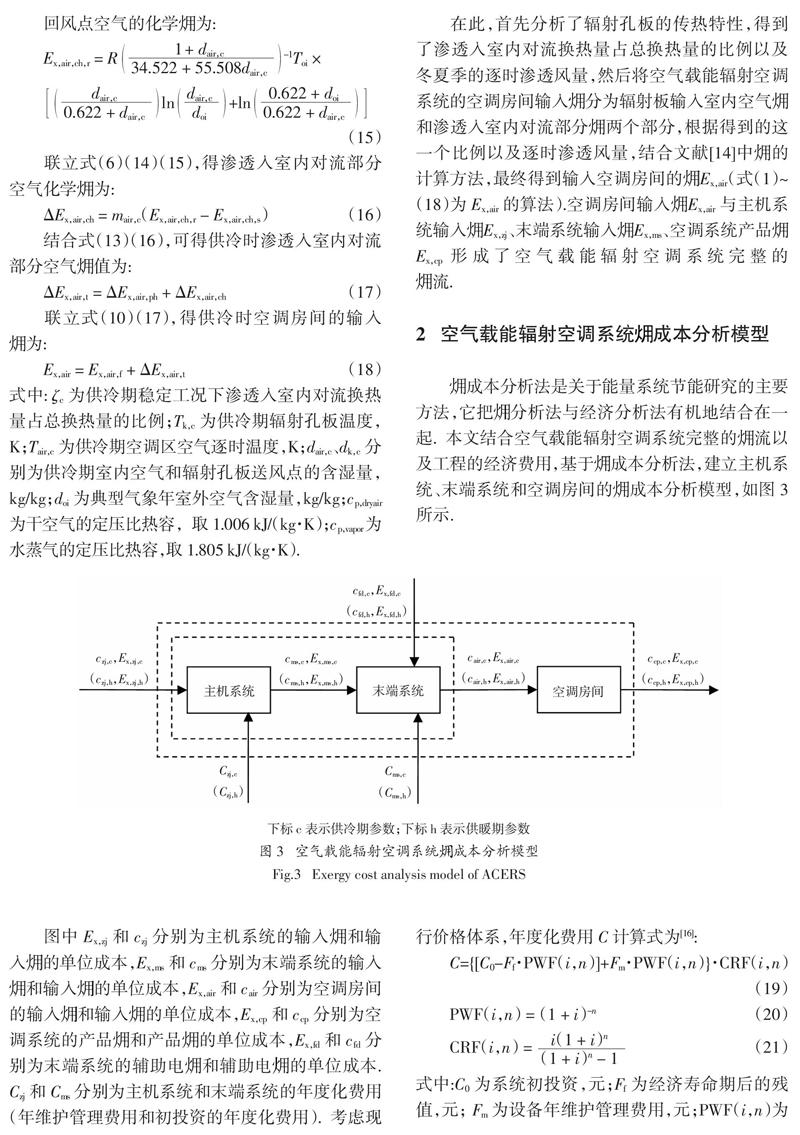
摘 要:通过分析辐射孔板的传热特性,结合金属辐射板和对流型空气处理末端的(火用)分析方法,提出了空气载能辐射空调房间的输入(火用)计算方法,并且基于(火用)成本分析法,建立了空气载能辐射空调系统的(火用)成本分析模型.在满足人体热舒适要求的前提下,以单位(火用)成本为评价指标,对空气载能辐射空调系统、毛细管辐射空调系统和分体式空调加地暖系统进行(火用)成本分析.研究发现:运用于办公建筑时,毛细管辐射空调系统的各单位(火用)成本高出空气载能辐射空调系统1~3倍;运用于住宅建筑时,分体式空调加地暖系统全年的产品(火用)单位成本为空气载能辐射空调系统的1.2倍.研究表明空气载能辐射空调系统的总体(火用)经济性更好,该研究结果对空气载能辐射空调后期在工程上的实际推广应用具有一定的指导意义.
关键词:空气载能;(火用);(火用)成本分析法;(火用)经济性
中图分类号:TU831 文献标志码:A
文章编号:1674—2974(2019)01—0133—08
Abstract: Based on the heat transfer process of orifice plate and the exergy analysis method of traditional mental radiant panel and convective air-conditioning terminal, the algorithm of room input exergy for air carrying energy radiant air-conditioning system(ACERS) was proposed. The exergy cost analysis model of ACERS was established by exergy cost analysis method. The unit exergy cost of three radiant air-conditioning systems including ACERS, capillary radiant air conditioning system and a combined system of split air conditioning with floor radiant air conditioning,was compared under the premise of thermal comfort. The results show that the unit exergy costs of capillary radiant air conditioning system are 1~3 times higher than that of ACERS in office buildings. The unit product exergy cost for the year of a combined system of split air conditioning with floor radiant air conditioning is 1.2 times higher than that of ACERS in residential building. It is found that the overall exergy economic performance of ACERS is superior to the other two radiant air-conditioning systems, which is of great significance for future engineering application of ACERS.
Key words: air carrying energy;exergy;exergy cost analysis;exergy economic
參考文献
[1] 刘艳华,刘星,王新轲,等. 暖通空调节能技术[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社,2015:V.
LIU Y H,LIU X,WANG X K,et al. Energy saving technology of the HVAC system[M]. Beijing:Mechanical Industry Press,2015:V.(In Chinese)
[2] 王晨光,马小飞,言树清,等. 辐射空调系统的发展研究现状综述[J]. 建筑热能通风空调,2014,33(5):47—50.
WANG C G,MA X F,YAN S Q,et al. Overview on development and research of radiant air conditioning system[J]. Building Energy & Environment,2014,33(5):47—50.(In Chinese)
[3] 龚光彩,杨厚伟,苏欢,等. 空气载能辐射空调末端系统辐射传热简化算法研究[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版),2013,40(12):31—38.
GONG G C,YANG H W,SU H,et al. The research on simplified algorithm of radiative heat transfer for air carry energy radiant air conditioning terminal system[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences),2013,40(12):31—38.(In Chinese)
[4] 徐春雯,龚光彩,杨厚伟,等. 空气载能辐射空调系统孔板结露特性数值研究[J]. 建筑科学,2014,30(8):79—84.
XU C W,GONG G C,YANG H W,et al. Numerical study of moisture condensation on pore panels of air-carrying energy radiation air-conditioning system[J]. Building Science,2014,30(8):79—84.(In Chinese)
[5] GONG G,LIU J,MEI X. Investigation of heat load calculation for air carrying energy radiant air-conditioning system[J]. Energy and Buildings,2017,138:193—205.
[6] 吳凡昊. 空气载能辐射末端应用试验研究[D]. 长沙:湖南大学土木工程学院,2015:15—27.
WU F H. Experimental research for application based on radiation terminal of air carrying and storing energy[D]. Changsha: College of Civil Engineering,Hunan University,2015:15—27.(In Chinese)
[7] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. GB 50736—2012 民用建筑供暖通风与空气调节设计规范[S]. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2012:7.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-rural Construction of the People's Republic of China. GB 50736—2012 Design specification for civil building heating ventilation and air conditioning[S]. Beijing:China Building Industry Press,2012:7.(In Chinese)
[8] 韩婕,龚光彩,杨厚伟,等. 高大空间空气载能辐射末端热环境与传能研究[J]. 建筑科学,2017,33(10):113—119.
HAN J,GONG G C,YANG H W,et al. Study on thermal environment and energy transfer on air-borne energy radiant terminal in large space[J]. Building Science,2017,33(10): 113—119.(In Chinese)
[9] LOZANO M A,VALERO A. Theory of the exergetic cost[J].Energy,1993,18(9):939—960.
[10] 龚光彩,曾巍,常世钧. 基于(火用)方法的空调冷热源系统优化决策[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版),2005,32(5):16—19.
GONG G C,ZENG W,CHAGN S J. Scheme-selection optimization of air-conditioning heating and cooling system based on exergy method[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences),2005,32(5):16—19.(In Chinese)
[11] 胡平放,李芬容,孙启明,等. 地源热泵系统经济性的热力学分析[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2009,37(4):97—100.
HU P F,LI F R,SUN Q M,et al. Thermodynamic analysis of the economy of GSHP systems[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition),2009,37(4):97—100.(In Chinese)
[12] ALKAN M A,KECEBAS A,YAMANKARADENIZ N. Exergoeconomic analysis of a district heating system for geothermal energy using specific exergy cost method[J]. Energy,2013,60:426—434.
[13] WANG Z,HAN W,ZHANG N,et al. Exergy cost allocation method based on energy level (ECAEL) for a CCHP system[J]. Energy,2017,134:240—247.
[14] 周燕. 建筑供暖与制冷能量系统(火用)分析及应用研究[D]. 长沙:湖南大学土木工程学院,2013:40—48.
ZHOU Y. Rsearch on the building heating and cooling system with exergy analysis[D]. Changsha:College of Civil Engineering, Hunan University,2013:40—48.(In Chinese)
[15] MIN T C,SCHUTRUM L F,PARMELEE G V,et al. Natural convection and radiation in a panel heated room[J]. Ashrae Transactions,1956,62(1):337—358.
[16] 傅秦生. 能量系统的热力学分析方法[M]. 西安:西安交通大学出版社,2005:217—218.
FU Q S. Thermodynamic analytic method of energy system[M].Xi′an:Xi'an Jiaotong University Press,2005:217—218.(In Chinese)
