两个包含联苯类三羧酸配体的钴(Ⅱ)和镍(Ⅱ)配位聚合物的合成、晶体结构及磁性质
2019-07-10冯安生邹训重
赵 娜 黎 彧 冯安生 邹训重
(广东轻工职业技术学院,广东省特种建筑材料及其绿色制备工程技术研究中心/佛山市特种功能性建筑材料及其绿色制备技术工程中心,广州 510300)
0 Introduction
Coordination polymers have attracted tremendous attention owing to their intriguing architectures and topologies,as well as potential applications in catalysis,magnetism,luminescence,molecular sensing,and gas absorption[1-8].However,it is difficult to predict the structure of a coordination polymer,because there are many factors,such as the coordination geometry of the metal centers,type and connectivity of organic ligands,stoichiometry,reaction conditions,template effect,presence of auxiliary ligands,and pH values influencing the structures of target coordination polymers during self-assembly[9-14].Undoubtedly,organic ligands play a crucial role in the construction of coordination polymers.
As we known,the multi-carboxylate biphenyltype ligands have been certified to be of great significance as constructors due to their abundant coordination modes,which could satisfy different geometric requirements of metal centers[13-20].Besides the main organic building blocks,many other components of a reaction system such as co-ligands or template agents can also play an important role in the generation of coordination polymers[21-22].It is well known that co-ligands coordinate to metal centers as ancillary moieties,while the template agents do not coordinate to metal centers and often do not enter into the final structure,but have a structure-guiding behavior during the self-assembly synthesis.4,4′-Bipyridine(4,4′-bipy)represents one of the most common examples of such a co-ligand or template agent[14,23-24].
Therefore,based on theabovereasons,wedesigned and synthesized two Co(Ⅱ) and Ni(Ⅱ) coordination polymers based on two biphenyl-type tricarboxylate ligands:biphenyl-2,4,4′-tricarboxylic acid(H3btc)and 5-(3,4-dicarboxylphenyl)picolinic acid(H3dppa).In this article,we report the syntheses,crystal structures,and magnetic properties of two Co(Ⅱ) and Ni(Ⅱ) coordination polymers constructed from biphenyl-type tricarboxylate ligands.
1 Experimental
1.1 Reagents and physical measurements
All chemicals and solvents were of AR grade and used without further purification.Carbon,hydrogen and nitrogen were determined using an Elementar Vario EL elemental analyzer.IR spectra were recorded using KBr pellets and a Bruker EQUINOX 55 spectrometer.Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA)data were collected on a LINSEISSTA PT1600 thermal analyzer with a heating rate of 10℃·min-1.Magnetic susceptibility data were collected in the 2~300 K temperature range on a Quantum Design SQUID Magnetometer MPMSXL-7 with a field of 0.1 T.A correction was made for the diamagnetic contribution prior to data analysis.
1.2 Synthesis of[Co(μ2-H 2btc)2(4,4′-bipy)2]n(1)
A mixture of CoCl26H2O (0.036 g,0.15 mmol),H3btc(0.086 g,0.30 mmol),4,4′-bipy(0.047 g,0.3 mmol),NaOH(0.012 g,0.30 mmol),and H2O(10 mL)was stirred at room temperature for 15 min,and then sealed in a 25 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel vessel,and heated at 160 ℃ for 3 days,followed by cooling to room temperature at a rate of 10℃·h-1.Pink blockshaped crystals of 1 were isolated manually,and washed with distilled water.Yield:55%(based on H3btc).Anal.Calcd.for C50H34CoN4O12(%):C 63.77,H 3.64,N 5.95;Found(%):C 63.44,H 3.61,N 5.98.IR(KBr,cm-1):1 677s,1 604s,1 571s,1 414m,1 375w,1319w,1287s,1237w,1209w,1174w,1119w,1097w,1 069w,1 008w,914w,840w,812m,763m,706w,685w,622w.
1.3 Synthesis of{[Ni3( μ4-dppa)2(H 2O)6]·2H 2O}n (2)
A mixture of NiCl2·6H2O(71.0 mg,0.30 mmol),H3dppa(57.4 mg,0.20 mmol),4,4′-bipy(0.047 g,0.3 mmol),NaOH(24.0 mg,0.60 mmol),and H2O(10 mL)was stirred at room temperature for 15 min,then sealed in a 25 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel vessel,and heated at 160 ℃ for 3 days,followed by cooling to room temperature at a rate of 10 ℃·h-1.Green block-shaped crystals of 2 were isolated manually,washed with distilled water,and dried.Yield:60%(based on H3dppa).Anal.Calcd.for C28H28Ni3N2O20(%):C 37.84,H 3.18,N 3.15;Found(%):C 38.06,H 3.19,N 3.17.IR(KBr,cm-1):3 440m,3 067w,1 627m,1 597s,1495w,1 474w,1 444m,1368m,1 311w,1 240w,1158 w,1 117w,1 087w,1 041w,1 016w,852w,817w,776m,735w,709w,654w.
The compounds are insoluble in water and common organic solvents,such as methanol,ethanol,acetone and DMF.
1.4 Structure determinations
Two single crystals with dimensions of 0.27 mm×0.22 mm×0.21 mm(1)and 0.25 mm×0.23 mm×0.21 mm(2)were collected at 293(2)K on a Bruker SMART APEXⅡ CCD diffractometer with Mo Kαradiation(λ=0.071 073 nm).The structureswere solved by direct methods and refined by full matrix least-square on F2using the SHELXTL-2014 program[25].All non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically.All the hydrogen atoms except those of the water molecules in 2 were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model.The hydrogen atoms of the water molecules in 2 were located from the difference Fourier maps.A summary of the crystallography data and structure refinements for 1 and 2 is given in Table 1.The selected bond lengths and angles for compounds 1 and 2 are listed in Table 2.Hydrogen bond parameters of compounds 1 and 2 are given in Tables 3 and 4.
CCDC:1889686,1;1889687,2.

Table 1 Crystal data for compounds 1 and 2
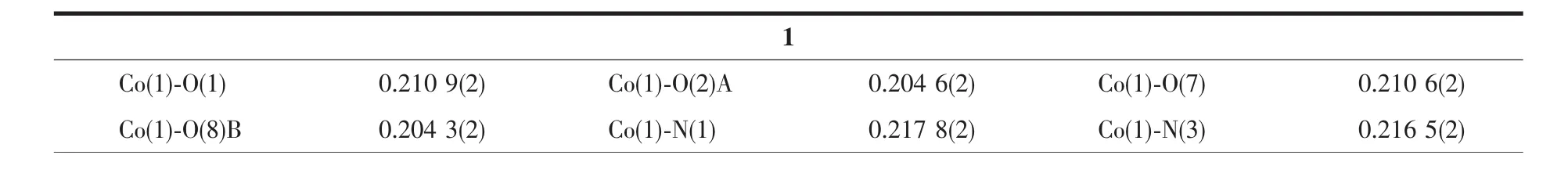
Table 2 Selected bond distances(nm)and bond angles(°)for compounds 1 and 2

Continued Table 2
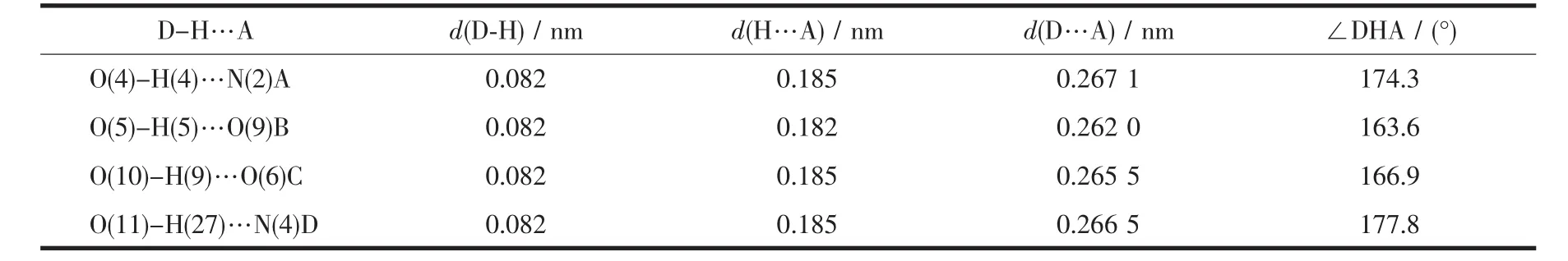
Table 3 Hydrogen bond parameters of compound 1

Table 4 Hydrogen bond parameters of compound 2
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Description of the structure
2.1.1 [Co(μ2-H2btc)2(4,4′-bipy)2]n(1)
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis reveals that compound 1 crystallizes in the triclinic space group P1.The asymmetric unit of 1 contains one crystallographically unique Co(Ⅱ) ion,two μ2-H2btcblocks,and two 4,4′-bipy ligands.As shown in Fig.1,Co1 ion is six-coordinated by four O from four individualμ2-H2btc-blocks and two N atoms from two different 4,4′-bipy ligands,constructing a distorted octahedral geometry.The Co-O bond lengths range from 0.204 3(2)to 0.210 9(2)nm,whereas the Co-N bonds vary from 0.216 5(2)to 0.217 8(2)nm;these bonding parameters are comparable to those found in other reported Co(Ⅱ) compounds[13-15].In 1,the H2btcligand adopts the coordination mode Ⅰ (Scheme 1),in which a deprotonated carboxylate group shows aμ2-η1∶η1bidentate mode.The dihedral angles of two benzene rings in the H2btc-ligands are 42.34°and 42.39°,respectively.The 4,4′-bpy ligands adopt a terminal coordination mode,their pyridyl rings are not coplanar showing the dihedral angles of 36.44°and 52.78°.The carboxylate groups of H2btc-blocks bridge alternately adjacent Co(Ⅱ)ions in a syn-anti coordination mode to form the infinite right-handed or lefthanded helical Co-O-C-O-Co chains (Fig.2)with the Co…Co separation of 0.491 3(2)nm.Two types of these helical chains are interconnected to each other through the Co(Ⅱ)centers to produce double-helix chains.These chains are further extended into a 3D supramolecular framework via the O-H…O and O-H…Nhydrogen-bondinginteractions(Fig.3 and Table3).

Fig.1 Drawing of the asymmetric unit of compound 1 with 30%probability thermal ellipsoids

Fig.2 One dimesional double-helix chain in compound 1
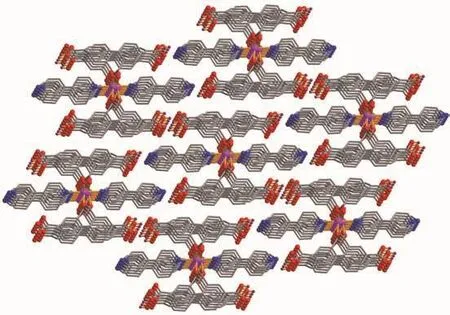
Fig.3 Perspective of 3D supramolecular framework along the b and c axes in 1
2.1.2 {[Ni3( μ4-dppa)2(H2O)6]·2H2O}n(2)
The asymmetric unit of 2 possesses two crystallographically independent Ni(Ⅱ) ions (Ni1 having full occupancy,Ni2 having half occupancy),one dppa3-block,three H2O ligands,and one lattice water molecule.As shown in Fig.4,the Ni1 atom is six-coordinated and adopts a distorted octahedral{NiNO5}geometry formed by three carboxylate O and one N atom from two distinctμ4-dppa3-blocks and two O atoms from two water ligands.The six-coordinated Ni2 center is located on a 2-fold rotation axis and is surrounded by four O atoms from four different dppa3-blocks and two O atoms from two coordinated H2O molecules,thus adopting a distorted octahedral{NiO6}geometry.The Ni-O distances range from 0.203 8(5)to 0.214 8(4)nm,whereas the Ni-N distance is 0.212 0(5)nm,and these bonding parameters agree with those observed in other Ni(Ⅱ) compounds[13-14,16].In 2,the dppa3-block acts as a μ4-spacer(modeⅡ,Scheme 1),in which the carboxylate groups exhibit the monodentate and the bidentate modes.In dppa3-,the dihedral angle between the pyridyl and phenyl rings is 31.46°.Although 4,4′-bipy was added during the synthesis of 2,a coordination of 4,4′-bipy to Ni(Ⅱ)is not observed in compound 2.Interestingly,4,4′-bipy acts as a template.The neighboring Ni(Ⅱ)ions are bridged by means of carboxylate groups from the dppa3-moieties,giving rise to a 1Dchain(Fig.5).These 1D chains are multiply held together by the remaining COO-groups and N atoms of theμ4-dppa3-moieties to generate a 2D network(Fig.6).

Fig.4 Drawing of the asymmetric unit of compound 2 with 30%probability thermal ellipsoids

Fig.5 One dimensional chain unit in compound 2

Fig.6 Perspective of a 2D network in 2 along the b and c axes
2.2 TGA analysis
To determine the thermal stability of polymers 1 and 2,their thermal behaviors were investigated under nitrogen atmosphere by thermogravimetric analysis(TGA).As shown in Fig.7,TGA curve of compound 1 showed that the sample remained stable until 322℃,followed by a decomposition on further heating.Compound 2 lost its two lattice water molecules and six H2O ligands in a range of 99~154 ℃ (Calcd.16.2%,Obsd.16.0%),followed by the decomposition at 281℃.

Fig.7 TGA curves of compounds 1 and 2
2.3 Magnetic properties
Variable-temperature magnetic susceptibility measurements were performed on powder samples of 1 in the 2~300 K temperature range(Fig.8).As shown in Fig.8,the χMT value at room temperature was 3.83 cm3·mol-1·K,which was higher than the value(1.87 cm3·mol-1·K)for one magnetically isolated high-spin Co(Ⅱ) ion (S=3/2,g=2.0).This is a common phenomenon for Co(Ⅱ)ions due to their strong spin-orbital coupling interactions[13-15].Upon cooling,the value decreased gradually and reached a minimum of 3.23 cm3·mol-1·K at 17.4 K.Below 17.4 K,however,the χMT value increased rapidly to a maximum of 6.62 cm3·mol-1·K at 2.0 K.In the 30~300 K temperature range,the magnetic susceptibility obeyed the Curie-Weiss law,χM=C/(T-θ),with θ=1.37 K,C=3.78 cm3·mol-1·K.The positive θvalue indicates the presence of dominant ferromagnetic interactions between the adjacent Co(Ⅱ)centers.According to the chain structure of 1(Fig.2),there is one magnetic exchange pathway within the chain through two syn-anti carboxylate bridges,which could be responsible for the observed ferromagnetic exchange.

Fig.8 Temperature dependence ofχM T(○)and 1/χM(□)vs T for compound 1
3 Conclusions
In summary,we have successfully synthesized and characterized two new cobalt(1)and nickel(2)coordination polymers by using two biphenyl-type tricarboxylic acids as bridging ligands under hydrothermal conditions.The polymers 1 and 2 feature 1D double-helix chain and 2D network,respectively.Magnetic studies for compound 1 demonstrate a ferromagnetic coupling between the adjacent Co(Ⅱ)centers.The results show that such biphenyl-type tricarboxylic acids can be used as versatile multifunctional building blocks toward the generation of new coordination polymers.Moreover,4,4′-bipyridine can tune the structures of the coordination polymersby itscoordination or template effect.
