类风湿关节炎患者血清25羟维生素D水平及相关因素分析
2019-04-28张玉慧宋为民孙莉马芹晓军丁香石桂秀
张玉慧 宋为民 孙莉 马芹 晓军 丁香 石桂秀


[摘要] 目的 檢测类风湿关节炎患者血清25羟维生素D水平并分析影响其水平的相关因素。 方法 收集亳州市人民医院2017年3~12月类风湿关节炎就诊患者及体检健康人群各82例,测定其血清25羟维生素D水平,并采集患者一般资料、体重指数、日晒时间、类风湿因子、抗环瓜氨酸多肽抗体、抗核抗体、血钙、疾病活动度(DAS28)、压痛关节数或肿胀关节数等临床资料,进行统计。 结果 97.6%的类风湿关节炎患者存在血清25羟维生素D不足或缺乏,类风湿关节炎患者的血清25羟维生素D含量低于健康人群(P < 0.01);病程不足2年的类风湿关节炎患者25羟维生素D水平高于病程2年以上者(P < 0.05);男性类风湿关节炎患者25羟维生素D水平明显高于女性(P < 0.05);类风湿关节炎患者25羟维生素D水平与女性(r = -0.291,P < 0.01)、平均日晒时间(r = 0.237,P < 0.05)、病程(r = -0.322,P < 0.01)、血钙水平(r = 0.300,P < 0.01)、压痛关节数(r = -0.348,P < 0.01)、肿胀关节数(r = -0.238,P < 0.05)和DAS28(r = -0.258,P < 0.05)相关。 结论 类风湿关节炎患者普遍存在25羟维生素D不足或缺乏。女性、平均每日日晒时间小于30 min、病程长、低血钙、高DAS28、高压痛关节数、高肿胀关节数可能是其预测因素。
[关键词] 类风湿关节炎;维生素D;疾病活动度;相关因素
[中图分类号] R593.22 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2019)02(b)-0142-04
[Abstract] Objective To investigate serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and its related factors. Methods Eighty-two cases of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and 82 cases of healthy controls were collected from Bozhou People′s Hospital from March to December 2017, the serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level was measured, and the general characteristics, body mass index, sun exposure time, rheumatoid factor, cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies, antinuclear antibodies, calcium, disease activity score (DAS28), tender joint count and swollen joint count were collected. Results The serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level insufficiency and deficiency was detected in 97.6% of rheumatoid arthritis patients. The serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration in rheumatoid arthritis patients were lower than that in healthy control (P < 0.01). Patients with rheumatoid arthritis with a course of less than 2 years had a higher level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D than patients with a course of more than 2 years (P < 0.05). Among patients with rheumatoid arthritis, 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in male were significantly higher than in female (P < 0.05). In rheumatoid arthritis patients, serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level was significantly associated with female (r = -0.291, P < 0.01), average sun exposure time (r = 0.237, P < 0.05), course (r = -0.322, P < 0.01), calcium level (r = 0.300, P < 0.01), tender joint count (r = -0.348, P < 0.01), swollen joint count (r = -0.238, P < 0.05) and DAS28 (r = -0.258,P < 0.05). Conclusion 25-hydroxyvitamin D insufficiency and deficiency is quite common in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Female, average daily sun exposure time less than 30 minutes, longer course, hypocalcemia, higher DAS28, more tender joint count and swollen joint count might be the predictors.
[Key words] Rheumatoid arthritis; Vitamin D; Disease activity; Related factor
类风湿关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis,RA)是最常见的炎性关节病,是以对称性、侵蚀性、多个小关节的慢性炎症为主要临床表现的自身免疫性疾病,世界范围内患病率为0.5%~1.0%[1]。其发病机制主要是巨噬细胞、淋巴细胞、成纤维细胞、软骨细胞、中性粒细胞等多种细胞参与的免疫紊乱。近年来研究发现,维生素D(VD)除了维持人体钙、磷等矿物质的平衡外,还发挥着重要的免疫调节作用[2-3]。本研究调查了RA患者血清25羟维生素D[25-hydroxyvitamin D,25(OH)D]水平及其相关影响因素。现报道如下:
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
收集亳州市人民医院2017年3~12月RA患者(RA组)和同期健康对照人群(对照组)各82例。所有RA患者均符合2009年ACR/EULAR关于RA的分类标准[4],排除严重肝肾功能不全及恶性肿瘤患者。
1.2 方法
采集患者一般信息、体重指数(body mass index,BMI)、平均每日日晒时间≥30 min(日晒)情况、病程、压痛关节数(tender joint count,TJC)和肿胀关节数(swollen joint count,SJC)、血沉和C反应蛋白、疾病活动度(disease activity score,DAS28)、25(OH)D水平、血钙水平、类风湿因子(rheumatoid factor,RF)、抗环瓜氨酸多肽(cyclic citrullinated peptide,CCP)抗体、抗核抗体(anti-nuclear antibody,ANA)、合并症(如间质性肺病和冠心病等)、既往糖皮质激素(glucocorticoid,GC)累积剂量等信息。DAS28采用计算公式:DAS28=0.56× +0.28× +0.36×ln(CRP+1)×1.10+1.15。25(OH)D≥30 ng/mL被定义为25(OH)D正常,20 ng/mL≤25(OH)D<30 ng/mL被定义为25(OH)D不足,25(OH)D<20 ng/mL被定义为25(OH)D缺乏。
1.3 统计学方法
采用SPSS 17.0统计软件对数据进行统计分析。正态分布的计量资料以均数±标准差(x±s)表示,组间比较采用t检验或方差分析;偏态分布的计量资料以中位数(四分位数间距)[M(Q)]表示,组间比较采用非参数检验;计数资料以例数表示,组间比较采用χ2检验;25(OH)D水平与其他各指标相关性分析采用Pearson(连续性变量)或Spearman(分类变量)相关性分析进行统计。以P < 0.05為差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
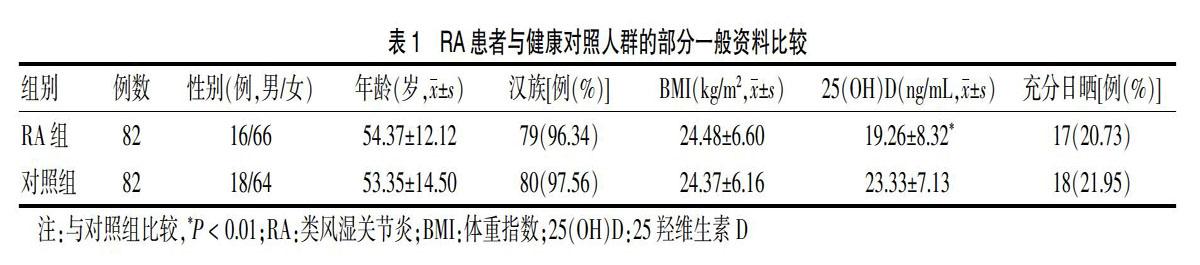
2.1 RA患者与健康对照人群的部分一般资料比较
两组性别、年龄、汉族占比、BMI、充分日晒者占比比较,差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。RA组血清25(OH)D水平低于健康对照组(P < 0.01)。见表1。RA患者中,25(OH)D水平不足者27例,缺乏者53例,不足与缺乏者总占比97.6%;健康对照人群中,25(OH)D水平不足者31例,缺乏者32例,不足与缺乏者总占比76.83%。
2.2 早期与非早期RA患者年龄及血清25(OH)D水平比较
以病程24个月为界,< 24个月的RA患者为早期组,≥24个月的RA患者为非早期组。早期组与非早期组平均病程分别为[5.2(2,10)]个月和[146.2(60, 240)]个月。早期组年龄低于非早期组(P < 0.01),早期组血清25(OH)D水平高于非早期组(P < 0.05)。见表2。
2.3 不同性别RA患者血清25(OH)D水平及日晒时间比较
本研究纳入的RA患者中,女性占80.49%。男性RA患者血清25(OH)D水平高于女性(P < 0.05);男性平均每日日晒时间>30 min者占比高于女性(P < 0.05)。见表3。
2.4 低龄与高龄RA患者的部分资料比较
将< 50岁的RA患者作为低龄组,将≥50岁的RA患者作为高龄组,低龄组病程短于高龄组(P < 0.01);两组25(OH)D水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。见表4。
2.5 不同血清25(OH)D水平RA患者的部分资料比较
按照血清25(OH)D水平将82例RA患者分为正常组、不足组及缺乏组,正常组2例(2.4%),不足组27例(32.9%),缺乏组53例(64.6%)。三组的女性、日晒时间>30 min者占比、血钙水平及压痛关节数比较,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。不足组及缺乏组血钙水平均低于正常组(P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。见表5。
2.6 血清25(OH)D水平与各指标相关性
本研究82例RA患者25(OH)D水平与女性(r = -0.291,P < 0.01)、日晒(r = 0.237,P < 0.05)、病程(r = -0.322,P < 0.01)、血钙水平(r = 0.300,P < 0.01)、TJC(r = -0.348,P < 0.01)、SJC(r = -0.238,P < 0.05)、DAS28(r = -0.258,P < 0.05)相关,与血沉(r = -0.013,P > 0.05)、C反应蛋白(r = -0.025,P > 0.05)、RF(r = -0.092,P > 0.05)、抗CCP抗体(r = -0.095,P > 0.05)、ANA(r = 0.103,P > 0.05)、合并间质性肺病(r = 0.106,P > 0.05)、合并冠心病(r = 0.022,P > 0.05)、既往GC累积剂量(r = -0.007,P > 0.05)无明显相关性,女性、平均每日日晒时间<30 min、病程长、低血钙、高TJC、高SJC、高DAS28的RA患者血清25(OH)D水平更低。
3 讨论
VD是一种类固醇类物质,通过与VD受体结合,不仅能调节钙磷代谢,还能够发挥重要的免疫调节作用。RA是一种以慢性、持续性、侵蚀性关节炎为主要临床表现的自身免疫疾病。近年来许多关于RA与VD关系的研究发现,RA患者普遍存在VD缺乏的现象[5-9],本研究结果亦印证了该现象。高达97.6%的RA患者存在25(OH)D水平不足或缺乏,但是健康人群也普遍存在VD不足或缺乏的情况。
研究发现与VD水平相关的因素很多。與男性比较,女性VD缺乏现象更加普遍[10-11]。充足并适当的紫外线照射皮肤是获取VD的重要来源,平均日晒时间[12]、季节[13]、长袖的着装习惯[14]、户外旅行[14]、肤色[15]等都是影响皮肤来源VD的因素。另外,吸烟、肥胖(BMI≥28 kg/m2)、老龄都是25(OH)D缺乏的预测指标[13,16]。日本一项对4793例RA患者的大样本研究发现,VD缺乏的相关因素包括女性、年轻、高HAQ残疾评分、低血清总蛋白、低血清总胆固醇、高血清碱性磷酸酶水平和非甾体抗炎药应用[7]。本研究分析了25(OH)D水平与性别、年龄、民族、BMI、平均日晒时间、RA病程、血钙、RF、抗CCP抗体、ANA等诸多因素的相关性,结果发现仅与性别、平均日晒时间、病程、血钙水平、DAS28、TJC、SJC相关,女性、平均每日日晒时间<30 min、高DAS28、病程长、低血钙、高TJC、高SJC可能是RA患者25(OH)D缺乏的预测因素。
尽管我们发现RA普遍存在VD缺乏现象,VD在RA中的作用并不明确,VD缺乏是否是导致RA的发病因素,还是RA导致VD缺乏,目前仍未阐明。很多研究认为VD缺乏与疾病活动度呈负相关[6,16-18],与结缔组织病相关肺间质病变的肺功能减退相关[19],VD水平与RA治疗应答呈正相关[8,17,20]。本研究发现VD与RA的疾病活动度DAS28、SJC有关,但与病程、TJC、血沉和CRP等炎症指标、类风湿因子、抗CCP抗体、抗核抗体、是否合并间质性肺病和冠心病、既往糖皮质激素累积剂量等因素无相关关系。意大利的一项临床研究表明,补充VD有利于减轻RA的炎症,改善疾病活动度,调节内皮功能,有望降低心血管风险[21],由此可见VD可能在RA的病因病机中起了重要作用,但该研究仅纳入了29例VD缺乏的RA患者,病例数少,结论尚待进一步大样本验证。
[参考文献]
[1] Firestein GS,Budd RC,Harris SE,等. 凯利风湿病学[M].栗占国,主译.北京:北京大学医学出版社,2015:1133.
[2] Palmer MT,Lee YK,Maynard CL,et al. Lineage-specific effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3)on the development of effector CD4 T cells [J]. J Biol Chem,2011,286(2):997-1004.
[3] Korf H,Wenes M,Stijlemans B,et al. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 curtails the inflammatory and T cell stimulatory capacity of macrophages through an IL-10-dependent mechanism [J]. Immunobiology,2012,217(12):1292-1300.
[4] Aletaha D,Neogi T,Silman AJ,et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria:an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative [J]. Ann Rheum Dis,2010,69(9):1580-1588.
[5] Urruticoechea-Arana A,Martín-Martínez MA,Casta eda S,et al. Vitamin D deficiency in chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases:results of the cardiovascular in rheumatology [CARMA] study [J]. Arthritis Res Ther,2015,17:211.
[6] Chen J,Liu W,Lin Q,et al. Vitamin D deficiency and low bone mineral density in native Chinese rheumatoid arthritis patients [J]. Int J Rheum Dis,2014,17(1):66-70.
[7] Furuya T,Hosoi T,Tanaka E,et al. Prevalence of and factors associated with vitamin D deficiency in 4,793 Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Clin Rheumatol,2013,32(7):1081-1087.
[8] Rossini M,Maddali BS,La Montagna G,et al. Vitamin D deficiency in rheumatoid arthritis:prevalence,determinants and associations with disease activity and disability [J]. Arthritis Res Ther,2010,12(6):R216.
[9] Kerr GS,Sabahi I,Richards JS,et al. Prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency/deficiency in rheumatoid arthritis and associations with disease severity and activity [J]. J Rheumatol,2011,38(1):53-59.
[10] Lim JS,Kim KM,Rhee Y,et al. Gender-dependent skeletal effects of vitamin D deficiency in a younger generation [J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2012,97(6):1995-2004.
[11] Carrillo-Vega MF,García-Pe a C,Gutiérrez-Robledo LM,et al. Vitamin D deficiency in older adults and its associated factors:a cross-sectional analysis of the Mexican Health and Aging Study [J]. Arch Osteoporos,2017, 12(1):8.
[12] Junaid K,Rehman A,Jolliffe DA,et al. High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among women of child-bearing age in Lahore Pakistan,associating with lack of sun exposure and illiteracy [J]. BMC Womens Health,2015, 15:83.
[13] Laird E,O'Halloran AM,Carey D,et al. The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and the determinants of 25(OH)D concentration in older Irish adults:Data from The Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing(TILDA)[J]. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci,2018,73(4):519-525.
[14] Granlund L,Ramnemark A,Andersson C,et al. Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and its association with nutrition,travelling and clothing habits in an immigrant population in Northern Sweden [J]. Eur J Clin Nutr,2016, 70(3):373-379.
[15] Dix CF,Bauer JD,Martin I,et al. Association of Sun Exposure,Skin Colour and Body Mass Index with Vitamin D Status in Individuals Who Are Morbidly Obese [J]. Nutrients,2017,9(10). pii:E1094.
[16] Cecchetti S,Tatar Z,Galan P,et al. Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in rheumatoid arthritis and association with disease activity and cardiovascular risk factors:data from the COMEDRA study [J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol,2016, 34(6):984-990.
[17] Attar SM. Vitamin D deficiency in rheumatoid arthritis. Prevalence and association with disease activity in Western Saudi Arabia [J]. Saudi Med J,2012,33(5):520-525.
[18] Raczkiewicz A,Kisiel B,Kulig M,et al. Vitamin D status and its association with quality of life,physical activity,and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients [J]. J Clin Rheumatol,2015,21(3):126-130.
[19] 程方月,黃淑婷,张锐,等.结缔组织病肺间质病变患者25羟基维生素D水平变化及临床意义[J].安徽医学,2014,35(3):288-291.
[20] Di FM,Barchetta I,Iannuccelli C,et al. Hypovitaminosis D in recent onset rheumatoid arthritis is predictive of reduced response to treatment and increased disease activity:a 12 month follow-up study [J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord,2015,16:53.
[21] Struglia M,Stamerra CA,Di GP,et al. 6D.06:VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY AND ENDOTHELIAL DYSFUNCTION IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS [J]. J Hypertens,2015,33 Suppl 1:e84.
(收稿日期:2018-03-08 本文编辑:罗乔荔)
