不同剂量阿托伐他汀联合美托洛尔治疗急性充血性心力衰竭合并肾功能不全的临床效果
2019-04-28李静吕国芬刘俊法
李静 吕国芬 刘俊法
[摘要] 目的 研究不同劑量阿托伐他汀联合美托洛尔治疗急性充血性心力衰竭(CHF)合并肾功能不全患者的临床效果。 方法 纳入2017年4月~2018年4月河北省邯郸市第二医院120例急性CHF合并肾功能不全患者作为研究对象,随机抽签法分为观察组和对照组,每组60例。观察组行美托洛尔+大剂量阿托伐他汀(40 mg/d)干预,对照组行美托洛尔+小剂量阿托伐他汀(20 mg/d)干预。4周后,比较两组患者治疗效果,记录两组治疗前后心、肾功能及炎性因子表达水平,记录治疗期间不良反应发生情况。 结果 两组总有效率比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),观察组疗效优于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。治疗后,观察组左室射血分数(LVEF)和6 min步行试验(6MWT)距离显著高于本组治疗前及对照组治疗后,左室舒张末期内径(LVEDD)显著低于本组治疗前和对照组治疗后,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。治疗后,观察组肾小球滤过率(GFR)显著高于本组治疗前及对照组冶疗后,尿素氮(BUN)和血肌酐(Scr)显著低于本组治疗前及对照组治疗后,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。治疗后,观察组超敏C反应蛋白(hs-CRP)、白介素-6(IL-6)及肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)水平显著低于本组治疗前及对照组治疗后,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。两组不良反应发生率比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。 结论 大剂量阿托伐他汀联合美托洛尔治疗急性CHF合并肾功能不全患者效果优于小剂量阿托伐他汀,且安全性较高。
[关键词] 阿托伐他汀;剂量;美托洛尔;急性充血性心力衰竭;肾功能不全
[中图分类号] R541.6 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2019)02(b)-0051-05
[Abstract] Objective To study the effect of different doses of Atorvastatin combined with Metoprolol in the treatment of acute congestive heart failure (CHF) complicated with renal insufficiency. Methods A total of 120 patients with acute CHF combined with renal insufficiency from April 2017 to April 2018 admitted to the Second Hospital of Handan City were selected as the research subjects and they were divided into observation group and control group by method of random sampling, with 60 cases in each group. The observation group was given Metoprolol and high-dose Atorvastatin (40 mg/d), and the control group was given Metoprolol and low-dose Atorvastatin (20 mg/d). After four weeks, the treatment effect of the two groups was compared, the cardiac function, renal function and levels of inflammatory factors were recorded before and after treatment in the two groups, and the incidence of adverse reactions during the treatment was recorded. Results There was no significant difference in the total effective rate between the two groups (P > 0.05). The effect of the observation group was significantly better than that of the control group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). After treatment, the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and the distance of 6 min walking test (6MWT) in the observation group were significantly higher than those before treatment and than those of the control group after treatment. After treatment, the left ventricular end diastolic diameter (LVEDD) of the observation group was significantly lower than that before treatment and that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). After treatment, the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of the observation group was significantly higher than that before treatment and that of the control group. After treatment, the blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and the serum creatinine (Scr) of the observation group were significantly lower those before treatment and those of the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). After treatment, the levels of hs-CRP, IL-6 and TNF-α in the observation group were significantly lower than those before treatment and those of the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in the incidence of adverse reactions between the two groups (P > 0.05). Conclusion High dose Atorvastatin combined with Metoprolol is superior to small dose in the treatment of acute CHF patients complicated with renal insufficiency, and the safety is high.
[Key words] Atorvastatin; Dose; Metoprolol; Acute congestive heart failure; Renal insufficiency
充血性心力衰竭(congestive heart failure,CHF)是各种原因引起的以心功能障碍和运动耐力降低为主要表现的临床症候群,预后较差,尤其是急性CHF患者,院内死亡率可达3%[1]。临床对CHF的具体病因尚未阐明,可能涉及神经-体液因素、心肌重塑及心肌细胞凋亡[2]。但多项资料证实急性CHF多与肾功能不全相伴发生[3-4],随着CHF的进展,心脏充盈压和心输出量失衡,导致肾脏灌注和血流量持续减少,肾小球滤过率(glomerular filtration rate,GFR)降低,最终造成肾功能不全。目前,对于急性CHF伴肾功能不全患者尚缺乏具有循证医学证据的有效药物。美托洛尔是指南推荐用于CHF的一线抗心衰药物,但单药效果有限,常配伍其他药物联合治疗[5]。阿托伐他汀属3-羟基-3甲基戊二酰辅酶A还原酶抑制剂,既往报道显示阿托伐他汀对心功能和肾功能均具有保护作用[6-7],但临床对阿托伐他汀的具体用药剂量尚未有统一规范。本研究纳入120例急性CHF伴肾功能不全患者作为研究对象,探讨不同剂量阿托伐他汀的治疗效果。现报道如下:
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
纳入2017年4月~2018年4月河北省邯郸市第二医院(以下简称“我院”)120例急性CHF伴肾功能不全患者作为研究对象。纳入标准:①符合中华医学会心血管病学分会推荐CHF标准[8];②30 mL/(min·1.72 m2)≤GFR≤90 mL/(min·1.72 m2);③患者签署知情同意书。排除标准:①严重肾功能不全需透析治疗者;②合并有造血系统或恶性肿瘤患者;③对试验药物过敏者。随机抽签将患者分为两组,每组各60例,观察组男35例,女25例;年龄40~74岁,平均(58.27±13.34)岁;体重指数(BMI)为(20.33±2.54)kg/m2;美国纽约心功能分级(NYHA):Ⅱ级21例,Ⅲ级28例,Ⅳ级11例;GFR(58.35±15.44)mL/(min·1.72 m2)。对照组男41例,女19例;年龄41~73岁,平均(60.09±14.46)岁;BMI(21.02±2.91)kg/m2;NYHA分级:Ⅱ级20例,Ⅲ级25例,Ⅳ级15例;GFR(61.11±14.82)mL/(min·1.72 m2)。两组患者性别、年龄、BMI、NYHA分级及GFR水平比较,差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05),具有可比性。本研究通过我院医学伦理委员会批准。
1.2 治疗方法
两组患者入院后均给予CHF基础治疗,嘱患者半卧位休息,限钠盐(<2 g/d)、NYHA分级Ⅳ级者应控制液体摄入量(摄入量=出量+500 mL,总量<2000 mL/d),水肿、瘀血症状消退后,应使出入量平衡。对于有呼吸困難或有低氧血症者予1~2 L/min吸氧,并予呋塞米、多巴胺等利尿和扩血管药物,均从小剂量开始。对照组:静脉注射5 mg美托洛尔(江苏苏中药业集团股份有限公司,批号:20101109,规格:5 mL),间隔5 min后再次静脉注射5 mg美托洛尔。1次/d,连续治疗3~5 d,待患者症状改善后改为口服美托洛尔(阿斯利康制药有限公司,批号:20100905,规格:25 mg×20 s),起始剂量6.25 mg/次,1次/d,逐渐加量至25 mg/d,并维持该剂量。同时口服阿托伐他汀(辉瑞制药有限公司,批号:20121008,规格:20 mg×7 s),20 mg/d,1次/d。观察组的美托洛尔用法与对照组相同,另外口服阿托伐他汀40 mg/d,1次/d。两组患者均连续治疗4周。
1.3 观察指标
在治疗结束后评定疗效[9]。显效:临床症状体征完全缓解,NYHA心功能改善2级及以上,血肌酐(Scr)降低≥20%;有效:临床症状体征改善,心功能改善1级,10%≤Scr降低<20%;无效:未达到上述标准。总有效率=(显效+有效)/总例数×100%。
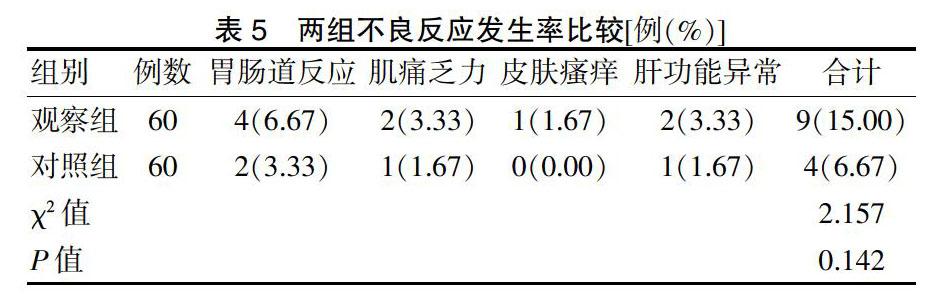
分别在治疗前后评估两组患者心、肾功能,采用BLS-X6型彩色多普勒超声诊断仪,记录左室射血分数(left ventricular ejection fraction,LVEF)和左室舒张末期内径(left ventricular end diastolic diameter,LVEDD),进行6 min步行试验(6 minutes walking test,6MWT),记录步行距离。于清晨空腹取肘静脉血,常规检测尿素氮(BUN)和Scr,根据慢性肾脏病学流行病学合作研究公式计算GFR[10]。同时采用双抗体夹心酶联免疫吸附法检测肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)、白介素-6(IL-6)及超敏C反应蛋白(hypersensitive C reactive protein,hs-CRP)水平。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 19.0统计学软件分析数据,计量资料采用均数±标准差(x±s)表示,组间比较采用t检验,计数资料采用百分率表示,组间比较采用χ2检验。等级资料采用秩和检验。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 两组疗效比较
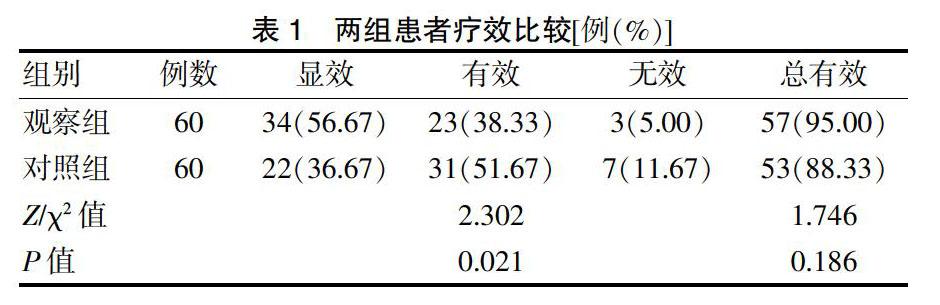
两组总有效率比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),观察组疗效显著优于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表1。
2.2 两组心功能指标比较
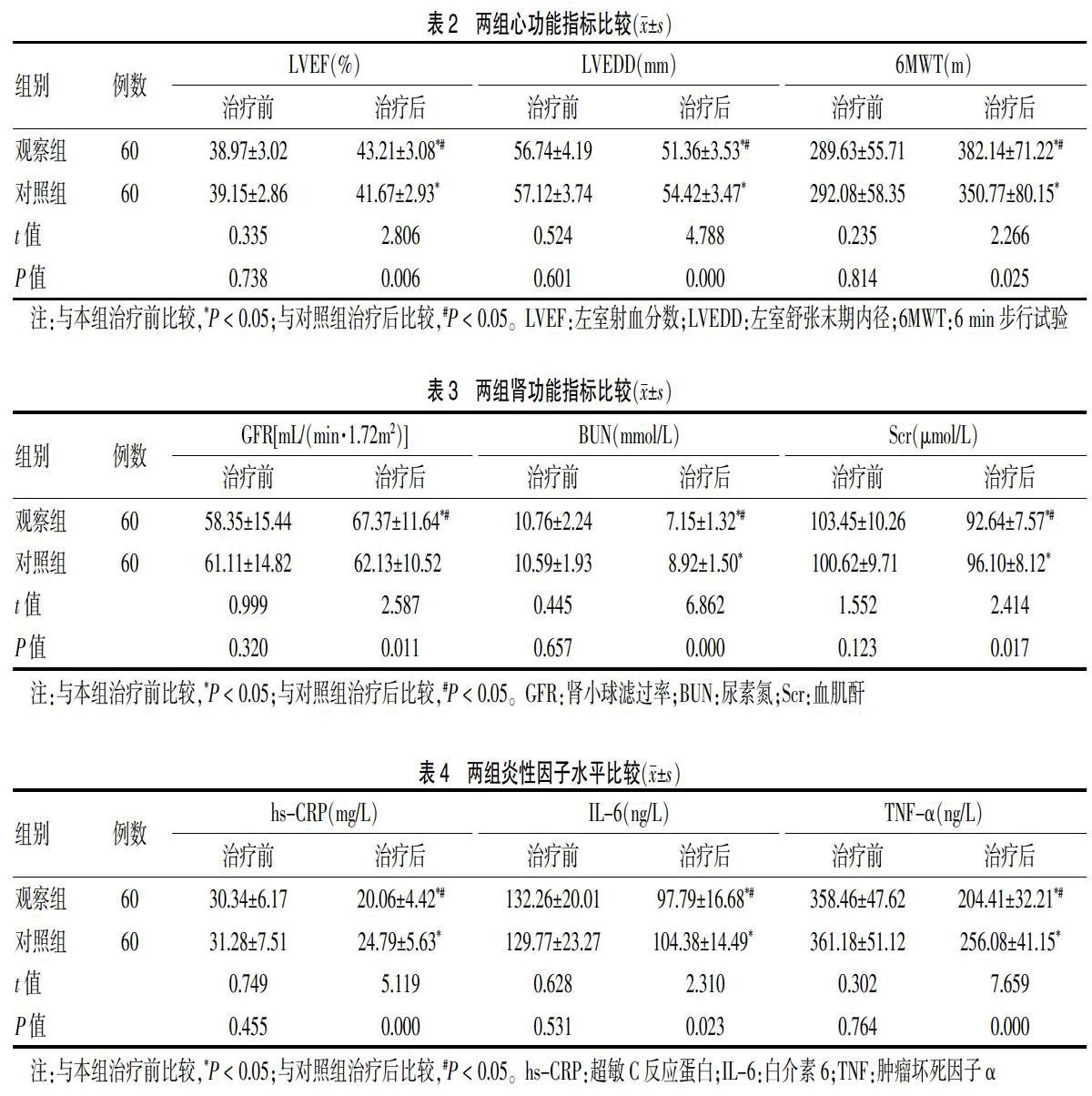
治疗后,两组LVEF和6MWT显著高于本组治疗前,且观察组高于对照组(P < 0.05);治疗后,两组LVEDD显著低于本组治疗前,且观察组低于对照组(P < 0.05)。见表2。
