Study of the Discount on Private Placements and Risk of Stock Market Crash in Listed Companies
2019-04-25,
,
College of Economics and Management, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430070, China
Abstract With the gradual completion of the split-share structure reform, private placement has gradually become the mainstream of refinancing. One of the points that the practical and theoretical circles are widely concerned about is that the private placement price is often higher than the market price at the time of the private placement. High discounts are often accompanied by the transmission of benefits, and the increase in insider information will lead to the risk of a stock market crash? This paper intends to use the data of A-share listed companies from 2006 to 2015 to empirically study the relationship between the discount on private placements and the risk of stock market crash. At the same time, this paper examines whether the degree of information asymmetry plays a regulatory role in the relationship between the discount on private placements and the risk of stock market crash. This paper provides a certain reference for the regulatory authorities to improve the relevant laws and regulations in the private placement, and to provide a certain reference for the protection of the interests of small and medium-sized investors.
Key words Private placement, Discount issuance, Information asymmetry, Risk of stock market crash
1 Introduction
Since the birth of China’s stock market, it has undergone high volatility, and as a new capital market, it has "soaring and plummeting" phenomenon in stock price, which is not uncommon. A new round of stock price collapse in China’s A-share market took place on June 15, 2015. The Shanghai index tumbled 35% in a matter of weeks, even several times as many as a thousand shares fell by the limit. In just two weeks in early 2016, A-shares lost more than 100 000 million yuan in market value. As a result, the risk of stock price collapse has aroused widespread concern in society, and has become a hot topic in academic research. In-depth research on the risk of stock price collapse can help regulators and investors better understand the source of the "collapse" of stock prices. At the same time, it can also maintain and promote the stability of China’s economic development and reduce the losses caused by the "collapse" to the market.
As for the earliest research on the root causes of stock price collapse risk, the most representative theory is put forward by Jin and Myers, Bleck and Liu and Hutton. They point out that the agency behavior of managers deliberately concealing the company’s significant risks and bad news in advance for private interests is the root cause of the stock price crash[1-3]. Since the implementation of theMeasuresfortheAdministrationofSecuritiesIssuanceofListedCompaniespromulgated by the Chinese Securities Regulatory Commission in 2006 (CSRC order No.30, hereinafter referred to as the "AdministrativeMeasures"), private placement (also called private offering in foreign countries) has gradually become the mainstream way of equity refinancing in China’s capital market. The "Administrative Measures" provide that investors who participate in the subscription for the targeted issuance of new shares in private placement may be given a certain discount. However, the trading price shall not be less than 90% of the average price of the company’s shares for the 20 trading days before the pricing benchmark date. A large number of related studies have confirmed that large shareholders will manipulate the price of private placement as a channel for the transmission of self-interest. Among them, the major shareholders and related parties achieve the purpose of conveying benefits to themselves by suppressing the benchmark share price of private placement and increasing the discount range[4]. In other words, the discount rate usually plays the role of transmitting insider trading and negative information to the market in the process of private placement. And does the existence and increase of this kind of insider information make the SEO enterprises face a greater risk of stock price collapse? Most of the existing literature studies show that private placement will lead to negative stock returns.
This paper intends to use the data of A-share listed companies from 2006 to 2015 to empirically study the relationship between the discount on private placements and the risk of stock price collapse. At the same time, this paper examines the difference of the relationship between the two under different degrees of information asymmetry. The results show that the higher the price discount on private placements, the higher the risk of stock price collapse. Compared with the enterprises facing low degree of information asymmetry, the discount rate of private placement of companies facing high degree of information asymmetry has a more significant impact on the risk of stock price collapse.
The possible contributions of this paper are as follows: (i) Stock price collapse is an important aspect of the change of stock price trend, and previous studies have focused on the analysis of external causes, but less attention has been paid to the internal causes of stock price collapse risk. At present, there is little research on the impact of discount rate on the risk of stock price collapse. This paper enriches the research on the influencing factors of stock price collapse. (ii) The private placement is the main way of equity refinancing, the existing literature on the discount on private placements focuses on its causes. This paper enriches the research on the economic consequences of discount on private placements.
2 Literature review
The private placement price in the private placement is often at a higher discount than the market price at the time of the private placement. Research shows that the discount rate for private placement in the United States is between 11.3% and 20.14%, while the discount rate of private placement in Taiwan is about 20%[5-7]. He Xianjieetal.[8]calculated the discount of 34.9% in the private placement of listed companies in China by taking the listed companies that had completed the private placement and issued theReportontheIssuanceofNon-publicOfferingSharesasresearch samples as of August 6, 2007. With regard to the discount on private placements, scholars at home and abroad have done a lot of theoretical and empirical researches on it, and formed several theoretical views. (i) Supervision cost compensation hypothesis: Wruck believes that discount can be regarded as a kind of compensation for investors’ future supervision cost[5]. (ii) The hypothesis of time-limited liquidity compensation: Sliber found that the discount rate of private placement can be explained as a compensation for the lack of liquidity during the ban period of subscribing for new shares[9]. (iii) Information asymmetry compensation hypothesis: Myersetal. put forward the discount rate of private placement for the first time as a compensation for the cost paid by the investor[10]. (iv) Management opportunistic compensation hypothesis: Barclay’s study found that the discount rate of private placement can be regarded as compensation for those negative investors who can not share the benefits of control[11].
With regard to the research on the discount on private placements, the existing literature pays more attention to the factors that affect the discount. The research on its economic consequences mainly focuses on the transmission of major shareholders’ interests and the transfer of wealth, as well as stock liquidity. However, there is little research on the stock price trend after the targeted issuance of shares, and no consensus has been reached. Most of the existing literature studies show that private placement will lead to negative stock returns. Spiessetal. empirically tested the overall downward trend of stock returns in the five years after SEO (equity refinancing). This is consistent with the conclusions of Myersetal.[10]. They believe that as long as the company has exceeded the expected financing behavior, it sends a message of cash flow shortage to the outside market. Therefore, the issuance of securities will have a negative impact on the market. Subsequently, He Limei and Cai Ning studied and used the samples of listed companies in China to find that because of the irrational financing and equity financing preference of listed companies, the long-term stock price return of the listed companies in the 24 months after the private placement has deteriorated[14]. However, some scholars believe that there may be selective deviation in the reference value of the above scholars in the study and there may be errors in the calculation of stock returns. Deng Luetal. also empirically confirmed the strong characteristics of the stock returns of listed companies in China within two years after the implementation of private placement by using the method of purchasing and holding excess return and calendar time combination method[15]. This is contrary to the conclusion that the long-term performance of US companies’ share prices has declined after private offerings by Hertzeletal.[12,16]. Wang Zhibin and Zhou Zijian found that the announcement of the private placement of the group company will significantly increase the stock price of the listed company by using the data of the overall listing of the group companies in the stock market of our country. In addition, some scholars remain neutral on the impact of the issuance of additional shares on the stock price[17]. They believe that the impact of the issuance of additional shares on the stock price is determined by a number of factors. Xie Yalu analyzed the relationship between equity refinancing and the risk of stock price collapse. The research shows that the implementation of public issuance will increase the risk of stock price collapse, while the implementation of private placement can reduce the risk of stock price collapse[18]. Zhang Weidong and Li Haichuan’s research started with the type of asset injection, and found that there was no significant difference in the type of asset injection with short-term cumulative excess return, but there was a significant correlation between the long-term holding of excess return and it[19]. Zhang Weidong and Li Dezhong’s research found that the lower the discount rate of the private placement price of listed companies in China, the higher the excess cumulative rate of return obtained by investors in a short period of time[20]. Xing Jingyietal. also found a similar conclusion by using the samples of private placement listed companies in China[21].
Through the review of the above literature, it can be seen that there is little literature on the relationship between private placement and stock price from the perspective of the discount rate of private placement, to study the impact of discount rate on the trend of its stock price. The discount rate of private placement usually plays the role of transmitting insider trading and information to the market in the process of private placement. In recent years, under the background of bad news hoarding theory proposed by Jin and Myers[1], scholars analyze the causes of stock price crash from the perspectives of financial reporting transparency[3], tax avoidance[22], analyst reputation[23]and earnings management[24]. Stock price collapse is an important trend of stock price change, and there is little literature on the relationship between the private placement of additional shares and the risk of stock price collapse.
3 Theoretical analysis and research hypothesis
3.1DiscountonprivateplacementandriskofsharepricecollapseAs for the earliest research on the root causes of stock price collapse risk, the most representative theories are put forward by Jin and Myers and Blecketal.. They point out that the agency behavior of managers deliberately concealing the company’s significant risks and bad news in advance for private interests is the root cause of the stock price crash[1-3]. Most of the issuing objects of listed companies in private placement in China are large shareholders or their related parties. Moreover, listed companies often have the problem of "one share domination" equity concentration, so they can control the price of private placement to a certain extent. In order to maintain their control rights not to be diluted, large shareholders will choose to encroach on the rights and interests of minority shareholders through private placement, so as to achieve the transmission of interests. It has been found that the subscription of large shareholders to private additional shares significantly increased the discount on private placements[25]. Based on the theory of information asymmetry, there are serious agency problems in listed companies in China. This is mainly manifested in the conflict of interest between the major shareholders and the minority shareholders of the company. In the private placement, the interests of large shareholders and minority shareholders are often separated. The issuance of additional shares by listed companies is essentially a dual related transaction. To a certain extent, the "buy and sell" of large shareholders’ shares infringes on the minority shareholders to a certain extent. Based on the agency theory and due to the underdevelopment of China’s capital market, private placement investors implement more related insider trading and tunneling behaviors, and conspire with managers to conceal negative news. This leads to an increase in negative news, which is not delivered to external investors in a timely manner, and makes enterprises face a greater risk of stock price collapse.
To sum up, the higher discount rate of private placement of listed companies means that to a certain extent, there are more negative news such as related insider trading, interest transmission, and tunneling behavior in the "buy and sell" of stock issuance. So that would raise the risk of a stock price crash. Based on this, the first hypothesis of this paper is put forward:
H1: The higher the discount rate of private placement of listed companies, the higher the risk of stock price collapse.
3.2Discountonprivateplacements,informationasymmetryandtheriskofstockpricecollapseIf there is a greater the degree of information asymmetry faced by the private issuing companies, the discount rate of the private placement price is also significantly increased[8]. Based on H1 hypothesis, one of the important reasons why the high discount rate of private placement has a positive impact on the risk of stock price collapse is that after large shareholders have motivation and implement more related insider trading and tunneling behavior, they collude with managers to hide more negative news. This has led to an increase in the degree of information asymmetry faced by companies. If the transparency of company information is low, it is more difficult to detect insider behavior such as tunneling of large shareholders caused by higher discount rate of private placement by deliberately driving down the stock price when carrying out private placement. Then the possibility of tunneling of large shareholders is higher, and it is easier for managers to collude with large shareholders to manipulate and conceal the negative information, which leads to the increase of negative news, and leads to a greater risk of stock price collapse. Based on this, the second hypothesis of this paper is put forward:
H2: Compared with companies with low degree of information asymmetry, the higher the discount rate of private placement of companies with high degree of information asymmetry, the higher the risk of stock price collapse.
4 Research and design
4.1SampleselectionanddatasourcesIn this paper, the A-share listed companies in Shanghai and Shenzhen stock markets from 2006 to 2015 are selected as the sample source, and the initial samples are screened as follows. (i) In order to eliminate the possible impact of multiple issuance of additional shares on the results, only the earliest one shall be retained for companies that have made multiple issuance of additional shares. (ii) Excluding the sample of financial companies. (iii) In order to ensure the reliability of the excess weekly rate of return estimation model, 30 SEO samples with low observation value of weekly return in a year are deleted. (iv) The company samples with incomplete relevant data are eliminated, and 1 159 sample observation values are finally obtained. In order to avoid the influence of extreme value, the winsorize tail reduction of 1% up and down for continuous variables is carried out in this paper. In this paper, Excel 2016 is used to preprocess the sample data, and Stata 14.0 is used for regression analysis of the sample data. The company’s financial data used in this paper come from CSMAR and Wind financial information database.
4.2Modeldesignandvariabledefinition
4.2.1Risk of share price collapse. In this paper, the methods of Jin and Myers, Kimetal., Xu Nianxingetal.[26]and Xu Nianxingetal.[27]are used for reference to calculate the risk of stock price collapse.NCSKEWandDUVOLare used as indicators to measure the risk of stock market crash. First of all, the weekly data of individual stocktare used for regression of model (1) year by year, based on the residual, the weekly return rate of individual stocks is calculated:
ri,t=α+β1,irm,t-2+β2,irm,t-1+β3,irm,t+β4,irm,t+1+β5,irm,t+2+εi,t
(1)
whereri,tis the return of stockiin weekteach year, and is the weighted average rate of return on the tradable market value of all A shares in weekt.
The market-adjusted rate of return of stockiin weektis:
Wi,t=ln (1+εi,t)
whereεi,tis the residual term obtained by regression.
Then the skewness coefficient of negative incomeandNCSKEWi,tthe ratio of up-and-down fluctuation of incomeDUVOLi,tare calculated according toWi,t, respectively. Among them, the calculation method of negative return skewness coefficient after market income adjustmentNCSKEWi,tis as follows:
(2)
wherenrepresentsthenumberofweeksastockistradedinayear,thegreaterthevalue,thehighertheriskofastockmarketcrash.
Thecalculationmethodoftheratioofup-and-downfluctuationofincomeisasfollows:
(3)
wherenuisthenumberofweeksinwhichtheweeklyholdingreturnWi,tofstockiisgreaterthantheannualaveragereturnWi,andndisthenumberofweeksinwhichtheweeklyholdingreturnWi,tofstockiislessthantheannualaveragereturnWi.Thevalueofthisvariablereflectsthedegreeofleft-skeweddistributionofstockreturns,themoreleft-skewedthestockreturns,thegreatertheriskofcrash.
4.2.2Discount rate of private placement. Index of discount on private placements. In this paper, referring to the definition of Barclay, He Xianjieetal. on discount on private placements, the discount of the private placement price relative to the closing price of the day before the announcement is used to measure the discount on the private placements, expressed in terms of. The formula is as follows:
(Pb-Pa)/Pb
wherePbis the closing price of the day before the announcement;Pais the private placement price; the announcement date is the date on which the listed company publishes theReportontheIssuanceofNon-publicOfferingShares.
4.2.3Degree of information asymmetry. Referring to the research of Hutton, this paper selects the absolute value of corporate manipulative profit as the measurement index of corporate information transparencyPIN[3].
Other control variables. According to Kimetal., this paper also adds the following control variables: the negative return skewness coefficient (NCRS), the monthly average excess turnover rate (OTurnover), the standard deviation of the company’s annual weekly return (Sigma), the annual average weekly return (Ret), the company size (Size), stock net asset-to-market ratio (BM), debt ratio (Lev), operating performance (ROE)[22,27]. In addition, this paper also adds annual virtual variables and industry dummy variables to control the fixed effects of the year and the industry, respectively.
Test model setting. (i) Test model of hypothesisH1. Using Model (4) to test hypothesisH1:
(4)
where the dependent variableCrashrepresents the risk of stock price collapse, which is measured byNCSKEWandDUVOL, respectively; the explanatory variable discount is the extent of discount for the company’s private placement;Xis the set of control variables.
This paper also adds the annual dummy variable and the industry dummy variable to control the annual and industry fixed utility, respectively. Expectedα1>0, that is, the higher the discount rate of the company’s private placement, the greater the risk of the collapse of the company’s stock price.
(ii) Test of hypothesisH2. In order to study the relationship between the degree of information asymmetry and the risk of stock price collapse, this paper uses the interaction term to test, that is, the cross termdiscount×PINis introduced into the model (4) to construct model (5):
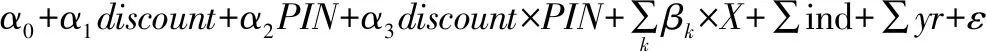
(5)
where the interaction termdiscount×PINmeasures the interaction between the discount degree of private placement and the degree of information asymmetry of the company on the risk of stock price collapse.
If hypothesisH2is assumed to be true, thenα3>0, that is, the degree of information asymmetry of the company will aggravate the impact of the discount degree of the private placement on the risk of the collapse of the company’s stock price.
5 Empirical results
5.1DescriptivestatisticalresultsTable 1 reports descriptive statistical results for each variable. As can be seen from Table 1, the average discount rate of the company is 25.45%, but the maximum value is 89.6% and the minimum value is -145.92%. The difference is wide, the standard deviation is 29.423 6, it can be seen that the discount rate of different companies is very different in the private placement. In this paper, the average and standard deviation ofNECKEW, a measure of stock price collapse risk of listed companies, are -0.051 2 and 0.832 0, respectively (the average and standard deviation ofDUVOLare -0.009 0 and 0.877 1, respectively). This shows that there is a significant difference in the negative return skewness coefficient (stock price fluctuation ratio) between the sample companies, that is, the difference in the sample stock price collapse risk is relatively large.
5.2VariablecorrelationanalysisTable 2 reports the correlation coefficients between variables. As can be seen from Table 3, the correlation coefficient between explanatory variables and control variables is very small. Except that the correlation coefficient between the skewness coefficient (NSCKEW) of the negative return of the company and the ratio (DUVOL) of the fluctuation of the return on the stock of the company is 0.990 3, the other correlation coefficients are all less than 0.5, which indicates that there is no problem of multiple collinearity between the variables. In addition, the correlation coefficient betweenNCSKEWandDUVOLis 0.990 3, indicating that both of them are reliable indicators to measure the risk of stock price collapse. There is a significant positive correlation between thediscountdegree of private placement (discount) of listed companies and the risk of stock price collapse (NSCKEWandDUVOL), which preliminarily verifies hypothesisH1. At the same time, the correlation coefficients betweenNCSKEWin lag phase 1 and currentRETandMBare 0.308 9 and 0.218 5, respectively, and are significant at the level of 1%. This suggests that higher yields in the past can trigger a fall in share prices in the future. However, the correlation analysis between variables is only a preliminary analysis test, and more reliable and accurate conclusions need further regression analysis.
Table1Descriptivestatisticalresultsofvariables

VariableObserved valueAverage valueMedianStandard deviationMaximum valueMinimum valueDiscount1 15825.445 623.835 029.423 689.600 0-145.92NECKEW1 158-0.051 20.137 20.832 01.357 0-2.023 3DUVOL1 158-0.009 00.149 50.877 11.840 0-2.724 4PIN1 1580.378 000.485 610NCRS1 1580.508 00.109 70.815 81.357 0-2.063 9OTurnover1 1581.887 41.483 721.793 5106.773 3-90.811 4Sigma1 1580.079 10.070 50.059 91.792 10.022 5Ret1 1580.010 90.009 20.016 30.285 6-0.026 5Size1 15821.992 921.805 31.012 026.134 718.826 6BM1 1582.455 81.806 52.380 530.241 30.173 7Lev1 1580.444 70.439 20.191 70.949 80.031 1ROE1 15812.025 89.779 622.994 5546.773 2-168.793 2
Table2Variablecorrelationcoefficientmatrix
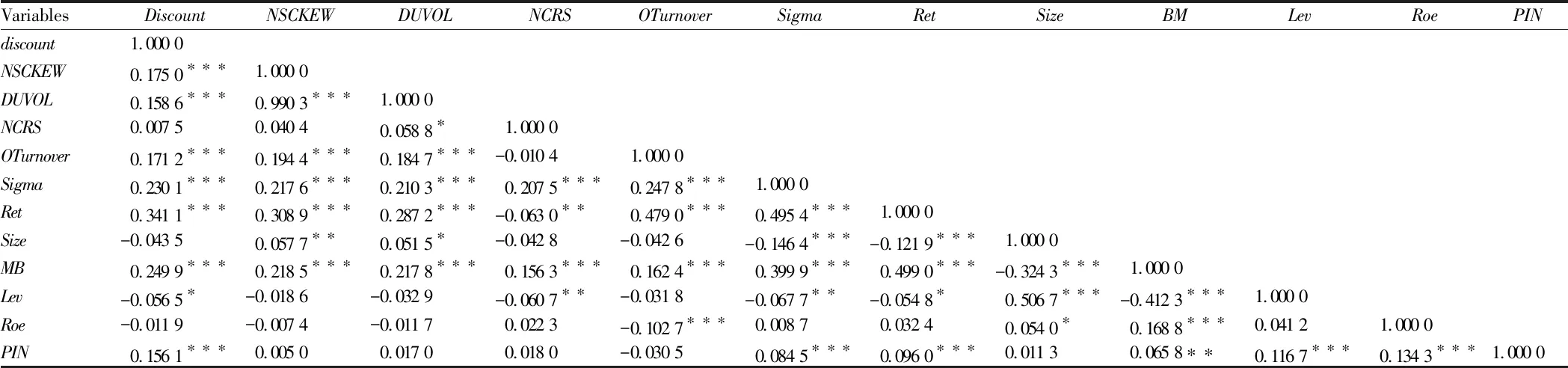

VariablesDiscountNSCKEWDUVOLNCRSOTurnoverSigmaRetSizeBMLevRoePINdiscount1.000 0NSCKEW0.175 0∗∗∗1.000 0DUVOL0.158 6∗∗∗0.990 3∗∗∗1.000 0NCRS0.007 50.040 40.058 8∗1.000 0OTurnover0.171 2∗∗∗0.194 4∗∗∗0.184 7∗∗∗-0.010 41.000 0Sigma0.230 1∗∗∗0.217 6∗∗∗0.210 3∗∗∗0.207 5∗∗∗0.247 8∗∗∗1.000 0Ret0.341 1∗∗∗0.308 9∗∗∗0.287 2∗∗∗-0.063 0∗∗0.479 0∗∗∗0.495 4∗∗∗1.000 0Size-0.043 50.057 7∗∗0.051 5∗-0.042 8-0.042 6-0.146 4∗∗∗-0.121 9∗∗∗1.000 0MB0.249 9∗∗∗0.218 5∗∗∗0.217 8∗∗∗0.156 3∗∗∗0.162 4∗∗∗0.399 9∗∗∗0.499 0∗∗∗-0.324 3∗∗∗1.000 0Lev-0.056 5∗-0.018 6-0.032 9-0.060 7∗∗-0.031 8-0.067 7∗∗-0.054 8∗0.506 7∗∗∗-0.412 3∗∗∗1.000 0Roe-0.011 9-0.007 4-0.011 70.022 3-0.102 7∗∗∗0.008 70.032 40.054 0∗0.168 8∗∗∗0.041 21.000 0PIN0.156 1∗∗∗0.005 00.017 00.018 0-0.030 50.084 5∗∗∗0.096 0∗∗∗0.011 30.065 8∗∗0.116 7∗∗∗0.134 3∗∗∗1.000 0
Note:*,**,***mean that it is significant at the levels of 10%, 5% and 1%, respectively. The same as below.
5.3Regressionresultsandanalysis
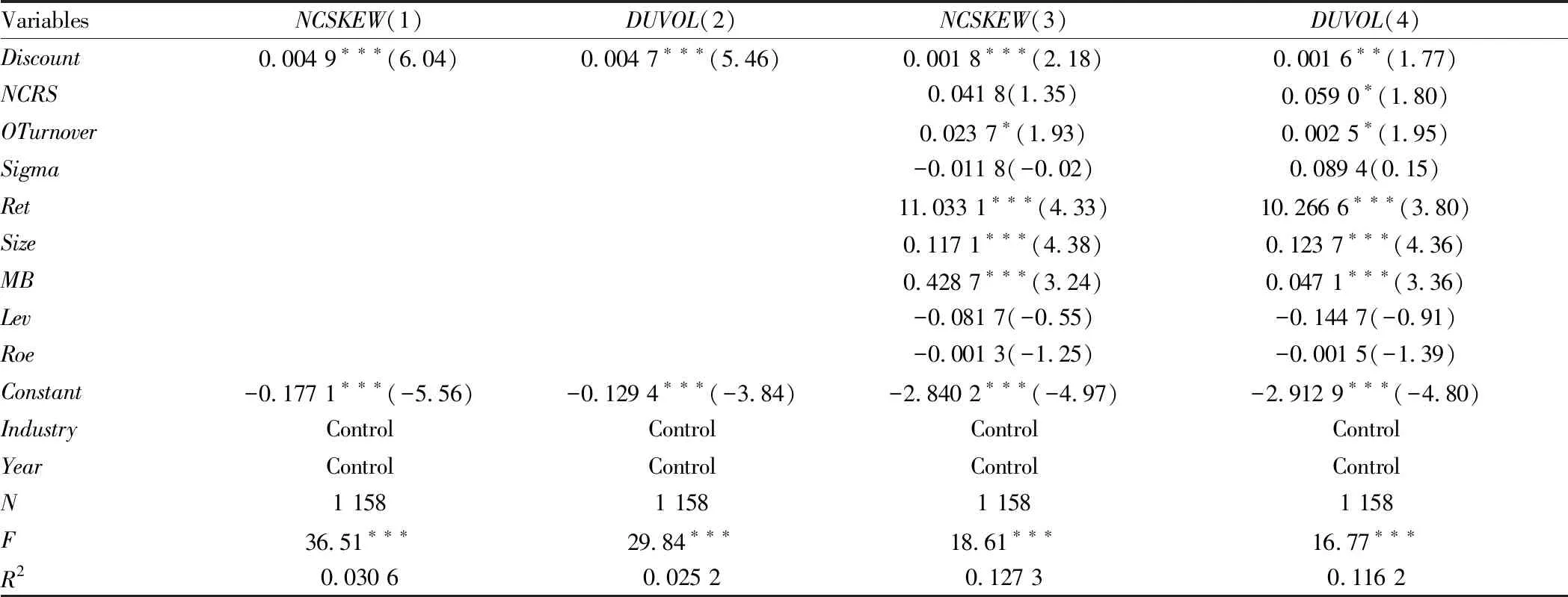
5.3.1The discount rate of private placement and the risk of stock price collapse of listed companies. Table 3 reports the linear regression results of the impact of the discount rate of the private placement company on the risk of its next stock market crash. The first column and the second column do not add control variables, only to examine the impact of the discount rate on the risk of stock price collapse. From the results, it can be seen that whetherNCSKEWorDUVOLis used as the proxy measure of the risk of stock price collapse, the coefficient of the discount rate of private placement is positive. In the third and fourth columns, we further control the relevant characteristic variables at the level of listed companies, and the discount rate of private placement is positively significant.
The regression results of Table 3 show that after controlling the relevant factors, there is still a significant positive correlation between the discount rate of private placement and the risk of future stock price collapse. Due to the underdevelopment of China’s capital market, investors in private placement mainly include major shareholders and related parties, as well as institutional investors. In the private placement activities, they will have the motivation to carry out more related insider trading and tunneling behaviors in order to obtain more personal interests, and conspire with the managers to hide the negative information. This leads to an increase in negative news, which is not delivered to external investors in a timely manner, and makes enterprises face a greater risk of stock price collapse. This is consistent with hypothesisH1.
5.3.2Effect of information asymmetry on the relationship between the institutional investors and the risk of stock price collapse. Table 4 shows the regression results for hypothesisH2. We sort the information asymmetry measurePINin which the company lags behind once a year. According to the mean value greater than the controllability accrual and the mean value smaller than the controllability accrual, it is divided into two groups: high information asymmetry group and low information asymmetry group. WhenNCSKEWandDUVOLare used as the risk measure of stock price collapse, the discount rate of private placement is only positively significant in the sub-samples of the high information asymmetry group. In the sub-samples of the low information asymmetry group, although the coefficient is positive, it is not significant. When the degree of information asymmetry is high, private placement investors can seek benefits through insider trading or access to private information. Once the number of hidden related transactions and internal negative news increases, the risk of a future collapse is higher. The results in Table 4 support the conclusions of Jin and Myers and are consistent with hypothesisH2.
Table3RegressiontestresultsforhypothesisH1
VariablesNCSKEW(1)DUVOL(2)NCSKEW(3)DUVOL(4)Discount0.004 9∗∗∗(6.04)0.004 7∗∗∗(5.46)0.001 8∗∗∗(2.18)0.001 6∗∗(1.77)NCRS0.041 8(1.35)0.059 0∗(1.80)OTurnover0.023 7∗(1.93)0.002 5∗(1.95)Sigma-0.011 8(-0.02)0.089 4(0.15)Ret11.033 1∗∗∗(4.33)10.266 6∗∗∗(3.80)Size0.117 1∗∗∗(4.38)0.123 7∗∗∗(4.36)MB0.428 7∗∗∗(3.24)0.047 1∗∗∗(3.36)Lev-0.081 7(-0.55)-0.144 7(-0.91)Roe-0.001 3(-1.25)-0.001 5(-1.39)Constant-0.177 1∗∗∗(-5.56)-0.129 4∗∗∗(-3.84)-2.840 2∗∗∗(-4.97)-2.912 9∗∗∗(-4.80)IndustryControlControlControlControlYearControlControlControlControlN1 1581 1581 1581 158F36.51∗∗∗29.84∗∗∗18.61∗∗∗16.77∗∗∗R20.030 60.025 20.127 30.116 2
Table4RegressiontestresultsforhypothesisH2

VariablesHigh information asymmetry groupNCSKEWDUVOLLow information asymmetry groupNCSKEWDUVOLDiscount0.002 8∗∗(2.17)0.002 5∗∗(1.85)0.001 3(1.22)0.001 1(0.94)NCRS0.129 3∗∗∗(2.72)0.145 7∗∗∗(2.95)-0.198 3∗∗∗(-4.65)-0.179 8∗∗∗(-3.90)OTurnover0.007 0∗∗∗(4.26)0.007 7∗∗∗(4.45)-0.001 2(-0.72)-0.001 2(-0.70)Sigma1.216 1∗∗(2.60)1.217 4∗∗(2.50)9.061 4∗∗∗(6.66)9.045 1∗∗∗(6.15)Ret16.732 1∗∗∗(4.39)16.818 4∗∗∗(4.24)1.826 1(0.53)0.539 8(0.15)Size0.074 6∗(1.81)0.075 1∗(1.76)0.168 7∗∗∗(4.83)0.181 6∗∗∗(4.80)MB0.007 5(0.43)0.009 4(0.52)0.084 7∗∗∗(4.18)0.091 8∗∗∗(4.19)Lev-0.151 0(-0.71)-0.279 2(-1.27)0.027 2(0.13)-0.018 1(-0.08)Roe-0.000 2(-0.19)-0.000 2(-0.18)-0.001 5(-0.66)-0.002 7(-1.06)Constant-1.786 0∗∗(-2.04)-1.667 2∗∗(-1.83)-4.730 0∗∗∗(-6.33)-4.942 7∗∗∗(-6.12)IndustryControlControlControlControlYearControlControlControlControlN440440718718F7.44∗∗∗7.68∗∗∗19.95∗∗∗16.55∗∗∗R20.107 60.110 70.202 30.173 8
6 Conclusions and recommendations
Based on the data of private placement of listed companies in China from 2006 to 2015, this paper empirically studies the relationship between the discount on private placements and the risk of stock price collapse, and tests the difference of the relationship between the two under different degrees of information asymmetry. The results show that the higher the price discount on private placements, the higher the risk of stock price collapse. Compared with the enterprises facing low degree of information asymmetry, the discount rate of private placement of companies facing high degree of information asymmetry has a more significant impact on the risk of stock price collapse.
Based on the empirical results of this paper, there are the following findings and recommendations. First, the empirical results of this paper show that the higher the discount rate of private placement, the greater the risk of stock price collapse faced by the company in the next phase. Therefore, while actively promoting the way of equity refinancing about private placement, we should also further improve the pricing policy stipulated in theMeasuresfortheAdministrationofSecuritiesIssuanceofListedCompanies, lest the private placement investors and the managers should collude to use the pricing date, pricing rules and so on to adjust the price in order to obtain private benefits. In addition, it is necessary to strengthen the supervision of listed companies, create a good corporate governance environment, and protect the interests of small and medium-sized investors. Secondly, this paper finds that the higher the degree of information asymmetry, the more significant the impact of the discount rate on the risk of stock price collapse faced by the company. When the company is faced with a high degree of information asymmetry, this provides an opportunity for investors who choose private placement to collude with managers to carry out more insider related transactions. Therefore, the regulatory authorities should improve the transparency of information in the market as a whole, and strengthen the management of insider trading of investors in private placement, improve the relevant laws and regulations, in order to safeguard the interests of small and medium-sized investors.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Breeding of a New Tussah Variety "Gaoyou 1"
- Identification and Control of HLB Disease in Citrus grandis
- Influence of Different Fertilization Levels on Maize Yield and Fertilizer Effect Based on the "3414" Experimental Design Scheme
- Preliminary Study on Shelf Life of Artificial Feed of Chilo suppressalis
- Content Determination of Trace Elements in Several Vegetables by Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry
- Industrial Poverty Alleviation Model in Southwestern High-altitude Mountainous Areas of China
——A Case Study of Industrial Poverty Alleviation of Xueshan Township in Luquan County of Yunnan Province through Planting Codonopsis pilosula
