前置胎盘产妇合并胎盘植入危险因素及对产妇与新生儿的影响
2019-01-14曹殿玲
曹殿玲


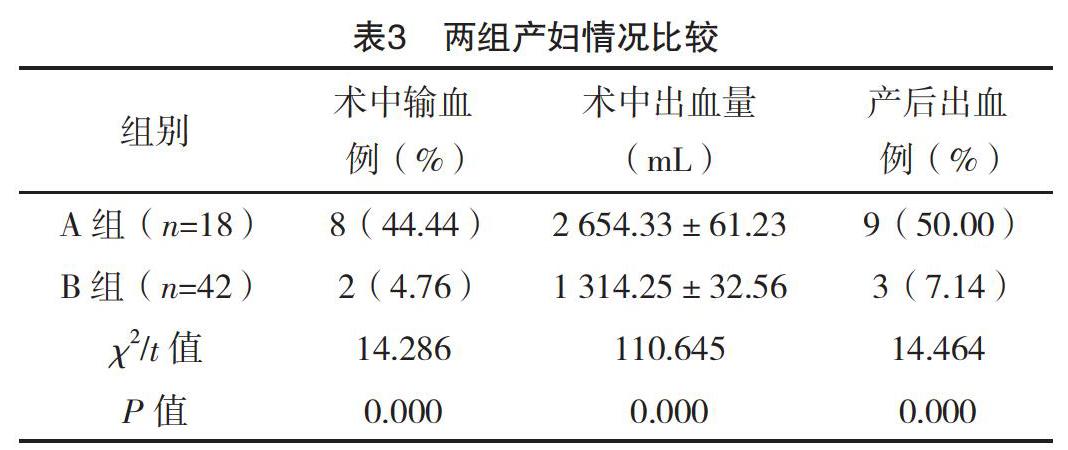
【摘要】 目的:分析前置胎盤产妇合并胎盘植入危险因素及对产妇与新生儿的影响。方法:选取本院2015年1月-2018年11月产科收治的60例前置胎盘产妇作为观察对象,对其临床资料进行回顾性分析。对所有产妇年龄、吸烟史、酗酒史、流产史、剖宫产史、前置胎盘类型等进行分析。根据是否合并胎盘植入分为A、B组,A组(n=18)发生胎盘植入,B组(n=42)未发生胎盘植入。对两组产妇情况及新生儿情况进行分析。结果:两组年龄、吸烟史、酗酒史、流产史、剖宫产史及前置胎盘类型比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),但两组孕周、孕次比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。多因素分析结果显示,年龄≥35岁、流产史、剖宫产史及中央性前置胎盘是合并胎盘植入的独立危险因素(P<0.05);A组产妇术中输血率、产后出血率及术中出血量均高于B组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);A组新生儿窒息率(44.44%)与早产率(27.78%)均高于B组的4.76%、0,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。A组新生儿1 min Apgar评分(7.02±0.42)分、出生体重(3.07±0.47)kg均低于B组的(8.32±0.88)分、(3.99±0.89)kg,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:前置胎盘严重威胁产妇及新生儿安全,合并胎盘植入与年龄、流产史、剖宫产史、中央性前置胎盘存在密切的关联,合并胎盘植入后,产妇和新生儿风险均明显增加。
【关键词】 前置胎盘 胎盘植入 危险因素
[Abstract] Objective: To analyze the risk factors of placenta previa combined with placental implantation and its influence on the pregnant women and newborns. Method: The clinical data of 60 pregnant women with placenta previa admitted to the obstetrics department of our hospital, from January 2015 to November 2018 were retrospectively analyzed. The age, smoking history, alcoholism history, abortion history, cesarean section history and type of placenta previa were analyzed. According to the combination of placental implantation or not, they were divided into group A and B. Placental implantation occurred in group A (n=18) and no placental implantation occurred in group B (n=42). The parturient and neonatal condition of two groups were analyzed. Result: There were significant differences in age, smoking history, alcohol abuse history, abortion history, cesarean section history and placenta previa type between the two groups (P<0.05). However, there were no statistically significant differences in gestational weeks and gestational times between the two groups (P>0.05). Multivariate analysis showed that age≥35 years, history of abortion, cesarean section and central placenta previa were independent risk factors for placental implantation (P<0.05). The intraoperative blood transfusion rate, postpartum hemorrhage rate and intraoperative hemorrhage volume in group A were higher than those in group B, the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05). The neonatal asphyxia rate (44.44%) and premature delivery rate (27.78%) in group A were higher than 4.76%, 0 in group B, the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05). The 1 min Apgar score (7.02±0.42) scores and birth weight (3.07±0.47) kg in group A were lower than (8.32±0.88) scores, (3.99±0.89) kg in group B, the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05). Conclusion: Placenta previa is a serious threat to maternal and neonatal safety, placenta previa combined with placenta implantation is closely related to age, abortion history, cesarean section history and central placenta previa, after placenta implantation, maternal and neonatal risks increase significantly.
[2]曾义,李杰,段光友,等.再次剖宫产产后出血危险因素分析:2442例产妇的回顾性研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2019,41(3):265-269.
[3]刘芳,罗玮.伴瘢痕子宫的前置胎盘产妇手术情况及新生儿结局观察[J].中外医学研究,2018,16(32):8-10.
[4]党志霞.胎盘植入产妇相关危险因素及结局分析[J].中外医疗,2018,37(31):43-45.
[5]蔡本硕,杜鹃.某医院前置胎盘患者术中出血相关因素的回顾性分析[J].东南大学学报(医学版),2018,37(5):908-911.
[6]吴争勇,刘丽群.彩超诊断中央性前置胎盘并胎盘植入的临床分析[J].现代诊断与治疗,2018,29(20):3253-3254.
[7]陈陶玲,李银华,张小英.产前超声检查在前置胎盘及植入孕妇分娩大出血预测中的临床应用价值[J/OL].心电图杂志(电子版),2018,7(3):27-30.
[8]杨凯乐,刘展,谢菲,等.前置胎盘并胎盘植入的高危因素及对妊娠结局的影响[J].实用预防医学,2018,25(9):1105-1107.
[9]郭吉敏,曹满瑞,刘小平,等.MRI征象回归模型在植入型凶险性前置胎盘的应用[J].临床放射学杂志,2018,37(8):1325-1328.
[10]刘冬红,李华丽,李维玲.前置胎盘伴胎盘植入术中应用宫颈COOK双球囊及卡前列素氨丁三醇防治产后出血疗效观察[J].中国计划生育学杂志,2018,26(8):731-733.
[11]覃献珍.导致中央型前置胎盘剖宫产后出血的危险因素分析[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2018,18(66):35.
[12] Karami M,Jenabi E,Fereidooni B.The association of placenta previa and assisted reproductive techniques:a meta-analysis[J].The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine,2017:1-18.
[13]薛晓玲.前置胎盘合并剖宫产史患者产后大出血危险因素研究[J].中外女性健康研究,2018(12):84,87.
[14]邱文山,黎法文,林小兰,等.90例凶险性前置胎盘的回顾性研究及危险因素分析[J].广东医科大学学报,2018,36(2):211-213.
[15]李玉梅,杨文才,陳健聪,等.一站式球囊封堵术辅助中央性前置胎盘剖宫产术的护理路径管理[J].实用医院临床杂志,2018,15(3):125-127.
[16]王恒宇,何明祥,漆洪波.凶险性前置胎盘腹主动脉球囊阻断下剖宫产术子宫切除的相关影响因素及母婴结局研究[J].医学信息,2018,31(8):49-52.
[17]张力维,李青,齐淑琴,等.前置胎盘伴胎盘植入危险因素分析及宫颈子宫下段环形缝合术对母婴结局的影响[J].中国现代医生,2018,56(6):56-59.
[18] Feng Y,Li X Y,Xiao J,et al.Risk Factors and Pregnancy Outcomes:Complete versus Incomplete Placenta Previa in Mid-pregnancy[J].Current Medical Science,2018,38(4):597-601.
[19]连旭波,韦春杏.妊娠期凶险型前置胎盘的核磁共振成像诊断价值与妊娠结局的关系[J].中国计划生育和妇产科,2018,10(1):28-31.
[20]石巍.子宫破裂及前置胎盘与瘢痕子宫再妊娠患者剖宫产产后出血的关联性分析[J].内蒙古医学杂志,2017,49(12):1436-1438.
[21]李娟,付金红,张慧娟,等.凶险性前置胎盘植入原因及母婴结局的影响回顾性研究[J].河北医药,2017,39(23):3575-3578.
[22]王志英.前置胎盘导致选择性剖宫产产妇大出血的影响因素研究[J].中外女性健康研究,2018(12):73-75.
[23]董南,胥琪琪,叶敏清,等.凶险型前置胎盘状态伴胎盘植入中期妊娠引产一例[J/OL].中华产科急救电子杂志,2018,7(1):54-57.
(收稿日期:2019-06-10) (本文编辑:田婧)
