FSH Promoting Proliferation of Calf Sertoli Cells Through Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway with CDC25B Being Involved
2019-01-09WangHaoZhangHanMaMingjunHuangFushuoSamsonOlugbengaAdeniranZengYueZhengPengandZhangGuixue
Wang Hao, Zhang Han, Ma Ming-jun, Huang Fu-shuo, Samson Olugbenga Adeniran, Zeng Yue, Zheng Peng, and Zhang Gui-xue
College of Animal Sciences and Technology, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China
Abstract: The aim of this experiment was to investigate whether FSH could regulate the proliferation of calf Sertoli cells and the relationship with CDC25B through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. The experimental method was to culture Sertoli cells with different concentrations of FSH (40, 80, 120 and 150 ng • mL-1) and to treat the cultured cells with XAV939 (β-catenin inhibitor) and to detect the expression of CDC25B, CDC2, C-MYC and β-catenin. The results of the experiment showed that FSH could promote the proliferation of cells and its effect was good at 80 ng • mL-1 concentration. FSH could promote the expression of CDC25B, CDC2,C-MYC and β-catenin. The expression of C-MYC and β-catenin in group FSH+XAV939 was lower than that in group FSH. There was no difference in mRNA expression of CDC25B in group FSH and group FSH+XAV939. The protein expression of CDC25B in group FSH+XAV939 was lower than that in group FSH. The conclusion was that FSH could promote the proliferation of calf Sertoli cells through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. CDC25B was upregulated by FSH and CDC2 could promote the proliferation of calf Sertoli cells. The protein level of CDC25B was affected by Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Key words: FSH, calf, Sertoli cells, CDC25B, Wnt/β-catenin
Introduction
Sertoli cells exist in the spermatogenic epithelium,provide physical support and stable microenvironment for spermatogenesis, and also provide necessary cytokines for the nutrition and development of the testis (Lee and Cheng, 2004). The number of Sertoli cells determines the spermatogenesis of the adult animal's testis (Wood and Walker, 2009; Franca et al., 2000). FSH has the effect of promoting the proliferation of testis supporting (Sertoli) cells. Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway can participate in the proliferation and differentiation of normal and stem cells (Chui et al., 2011; Barker, 2008). β-catenin is the central effect factor of Wnt pathway and is involved in the functions of nucleus and cytoplasm (Logan and Nusse, 2004; Staal and Clevers, 2005). Wnt/β-catenin pathway comprises β-catenin, APC, Axin and GSK-3β (Nygren et al., 2007; Aberle et al., 1997). When Wnt is activated, the kinase complex substance dissociates and β-catenin dissociates, too. β-catenin can be transferred into the nucleus in the active form,and bind to a lymphokine or T cytokine protein, it activates downstream target genes, such as C-MYC's expression. It induces the expression of C-MYC,which can promote the proliferation of human Sertoli cells (Li et al., 2012). CDC25B family is a phosphate-esterase that regulates CDK complex. It controls the cell cycle progression by dephosphorylation of the inhibitory phosphorylation site of CDK. CDC25B plays an important role in controlling cell entry into M and G2/M detection points.
CDC25B also plays an important role in activating CDK1 (CDC2)-Cyclin B1, causing cells to enter mitosis and enable the cell to proliferate (Hoffmann et al., 1993). CDC25B may be the target gene for C-MYC (Galaktionov et al., 1996; Hernández et al.,1998; Rocco et al., 2001). It has been reported that Wnt/β-catenin plays a role in mouse Sertoli cells (Lee et al., 2003; Tanwar et al., 2010). However, there is no research about FSH promoting the proliferation of calf Sertoli cells through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Therefore, it is necessary to study the role and relationship of FSH, Wnt/β-catenin pathway and CDC25B calf Sertoli cell proliferation process in calf Sertoli cell proliferation process in order to provide the theoretical and practical bases for improving bovine spermatogenesis.
Materials and Methods
Materials
The calf testicles were obtained from the slaughterhouse in Shuangcheng City, Heilongjiang, China and were transported to the laboratory within 4 h. DMEM(Gibco); PBS (Solarbio); collagenase (SIGMA);Trypsin (1 : 250, Amresco); FSH (SIGMA); Trizol reagent (Harbin handsome Biological Technology Co.,Ltd.); Fast Start Universal SYBR Green Master (Rox)(Roche company in Germany); ReverTra Ace qPCR RT Master Mix with gDNA Remover (TOYOBO);XAV-939 (β-catenin inhibitor, Gene Operation Datasheet); CCK8 (Vazyme Biotech); CDC25B antibody (Boosen Biotechnology Co., Ltd.); β-actin antibody (Transgen Biotech).
Methods
Sertoli cell preparation
The testis tissues of calf were used as test materials,and two-step enzymatic digestion was used to separate and extract the Sertoli cells (Zheng et al., 2013; Yu et al., 2014). The supporting cells were purified by differential adherent methods and cultured in vitro.The purity of supporting cells used was more than 95%.Screening of proliferation of Sertoli cells by FSH Five FSH concentration gradients were used. Different concentrations of FSH media were prepared by the basic media: group A 40 ng • mL-1, group B 80 ng • mL-1, group C 120 ng • mL-1, group D 150 ng • mL-1and group O (blank control). Cells were inoculated in 96-well plates at a density of 1×104cells • mL-1. There werefive repetitions in each group. After 6 h, Sertoli cells were found to have adhered to the plates. Four different concentrations of FSH media were replaced,the blank group was replaced with the basic media,and this time was taken as 0 h. CCK8 was added to the plates at 6, 12 and 24 h and then incubated for 1-4 h at 37℃. The proliferation of Sertoli cells was detected by Microplate Reader, while the optimal concentration of FSH for cell proliferation was selected as the followup experiments' concentration.
Calf testis Sertoli cells and Wnt signaling pathway Sertoli cells were cultured in vitro and were divided into two groups: a group containing FSH and another containing FSH+XAV-939 (XAV-939 was a β-catenin inhibitor). Sertoli cells were then inoculated into sixwell plates at a density of 3×105cells • mL-1. After 6 h,FSH medium (80 ng • mL-1) and FSH+XAV-939(1 μmol • L-1) medium were added, respectively. This time was recorded as 0 h. At 6, 12 and 24 h, Sertoli cells were collected for the detection of β-catenin and C-MYC expression. The method of 2-ΔΔCtwas used to convert the original Ct value into the relative gene expression.
Western blotting was used to determine β-catenin expression. First collected cells, added RIPA lysate to break up cells, and then centrifuged the mixture,recovered the supernatant. Loading buffer was added to the protein supernatant, samples were boiled for 5 min at 100℃. TBST was used at room temperature to wash off unbound proteins closedfilter membrane with 50 g • L-1skimmed milk powder by upper sample,electrophoresis, separation andfilm conversion. The closedfilter membrane was carried out overnight with β-catenin (1 : 2 000) and β-actin antibody (1 : 3 000) at 4℃. Thefilter was washed in TBST, and then incubated with the second antibody (1 : 5 000) at room temperature for 2 h. An ECL kit was used to detect chemilumine-scention of the bound protein, according to the manufacturer's instruction. Afterward, Image-Pro 6 was used to analyze the gray level of the protein strip.
FSH affecting proliferation of Sertoli cells by Wnt pathway
Sertoli cells were cultured in vitro and were divided into two groups: group CON and group FSH. Sertoli cells were inoculated into six-well plates at a density of 3×105cells • mL-1. After 6 h when Sertoli cells had adhered to the plate, the medium was removed and replaced with a new medium containing 80 ng • mL-1FSH and this time was recorded as 0 h. Sertoli cells were collected at 6 h for the detection of β-catenin and C-MYC expression. The method of 2-ΔΔCtwas used to convert the original Ct value into the relative gene expression. Western blotting was used to determine β-catenin protein expression as above.
FSH promoting cell proliferation through CDC25B Sertoli cells were cultured in vitro and were divided into two groups: group CON and group FSH. The Sertoli cells were inoculated into six-well plates at a density of 3×105cells • mL-1. After 6 h, when the Sertoli cells had adhered to the plate, the medium was removed and replaced with another and this time was recorded as 0 h. After 6 h, the expression of CDC25B and CDC2 in Setoli cells was detected.
Western blotting was used to determine the expression of CDC25B. First collected cells, added RIPA lysate to break up cells, then centrifuged the mixture,and recovered the supernatant. Loading buffer was added to the protein supernatant, samples were boiled for 5 min at 100℃. TBST was used at room temperature to wash off unbound proteins closedfilter membrane with 50 g • L-1skimmed milk powder by upper sample, electrophoresis, separation andfilm conversion. The closedfilter membrane was carried out overnight with CDC25B (1 : 500), β-actin antibody(1 : 3 000) at 4℃. Thefilter was washed in TBST, and then incubated with the second antibody (1 : 5 000)at room temperature for 2 h. An ECL kit was used to detect chemiluminescention of the bound protein,according to the manufacturer's instruction. Afterward,Image-Pro 6 was used to analyze the gray level of the protein strip.
FSH, Wnt and CDC25B
Sertoli cells were cultured in vitro and were divided into two groups: a group containing FSH and another containing FSH+XAV-939. Sertoli cells were inoculated into six-well plates at a density of 3×105cells• mL-1.After 6 h, when Sertoli cells had adhered to the plate,the medium was removed and replaced with a new medium containing 80 ng • mL-1FSH and this time was recorded as 0 h. Sertoli cells were collected for the detection of the expression of CDC25B. The method of 2-ΔΔCtwas used to convert the original Ct value into the relative gene expression. Western blotting was used to determine CDC25B expression as above.
Statistical method
The data were expressed as mean (Means)±standard deviation (SD). Statistical analysis was performed by SPSS 13.0 software T-test and one-way ANOVA LSD method. p<0.05 showed a significant difference.
Design and synthesis of primers
According to cDNA sequence of C-MYC, CDC25B and CDC2 from GenBank, primer design software Primer Premier 5 and oligo 6 software were used to design primers. GAPDH gene was used as a reference gene, the primer sequences are shown in Table 1. The primers were synthesized by Jilin Comate Bioscience Company Limited.
Results
Effects of different concentrations of FSH on proliferation of cultured Sertoli cells in vitro
From Fig. 1, it could be seen that Sertoli cells treated with FSH in group B were significantly higher at 6, 12 and 24 h than those in other groups (p<0.05). At 6, 12 and 24 h, the numbers of cell proliferation in group B(80 ng • mL-1) was higher than those in group C, and there was a significant difference between groups D and O (p<0.05). There was no significant difference at 6 h among groups C, D and O (p>0.05). At 12 and 24 h, there was a significant difference among groups C, D and O (p<0.05), the numbers of cell proliferation in groups C and D was lower than those in group O.

Table 1 Gene specific primers
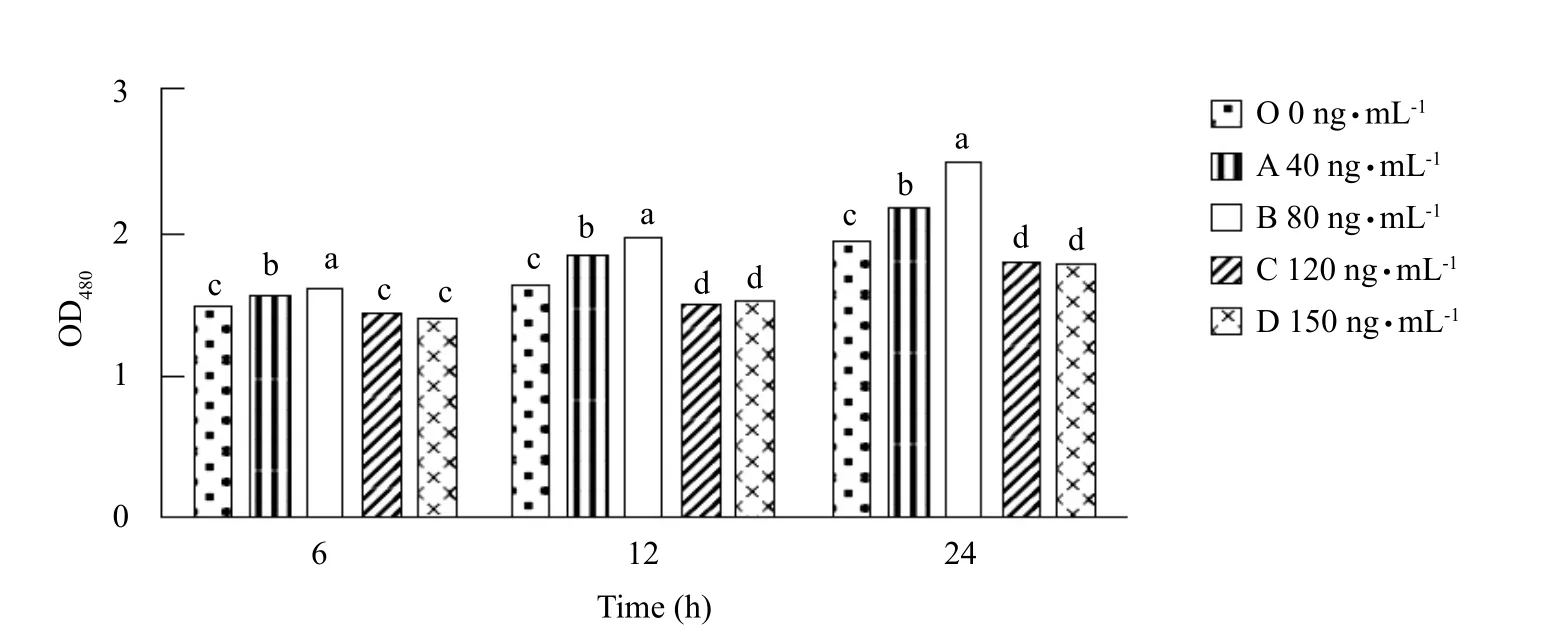
Fig. 1 Proliferation of Sertoli cells in each treatment group within 24 h
Effects of β-catenin inhibition on C-MYC expression
The results from Figs. 2 and 3 showed that the expression of β-catenin in group FSH was significantly higher than that in FSH+XAV-939 (F+X) group at 6 and 12 h (p<0.05). At 24 h, there was no significant difference in β-catenin expression between groups FSH and FSH+XAV-939 (p>0.05). C-MYC expression in FSH+XAV-939 group at 6, 12 and 24 h was lower than that in group FSH, and the difference was significant (p<0.05), as shown in Fig. 4.
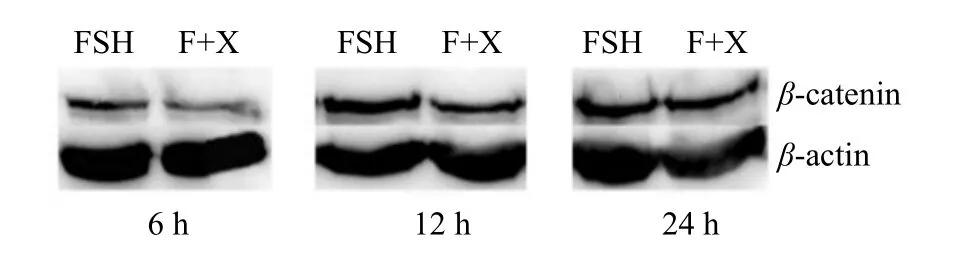
Fig. 2 Bands of β-catenin protein expression
Expression of β-catenin and C-MYC during proliferation of Sertoli cells
The results from Figs. 5 and 6 showed that β-catenin expression in groups CON and FSH was not significant (p>0.05) at 12 and 24 h. At 6 h, β-catenin expression in group FSH was significantly higher than that in group CON (p<0.05). It could be seen from Fig. 7 that C-MYC expression at 6, 12 and 24 h in group FSH was higher than that in group CON(p<0.05).

Fig. 3 Expression of β-catenin protein
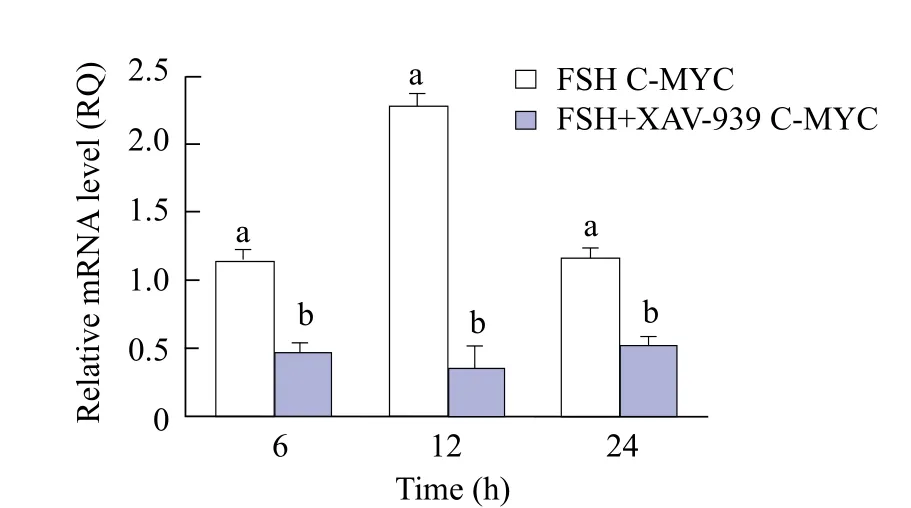
Fig. 4 C-MYC expression in each group
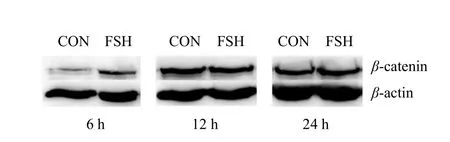
Fig. 5 Bands of β-catenin protein expression

Fig. 6 Expression of β-catenin protein
Expression of CDC25B and CDC2 expression in cell proliferation process
As shown in Fig. 8, the expression of CDC25B in group FSH was significantly higher than that in group CON (p<0.05) at 6, 12 and 24 h. From Figs. 9 and 10, the expression of CDC25B in FSH group was significantly higher than that in group CON (p<0.05).At 12 and 24 h, the expression of CDC25B in group CON was significantly lower than that in group FSH(p<0.05). The expression of CDC2 in group FSH at 6,12 and 24 h was significantly higher than that in group CON (p<0.05)( Fig. 11).

Fig. 7 C-MYC expression in each group
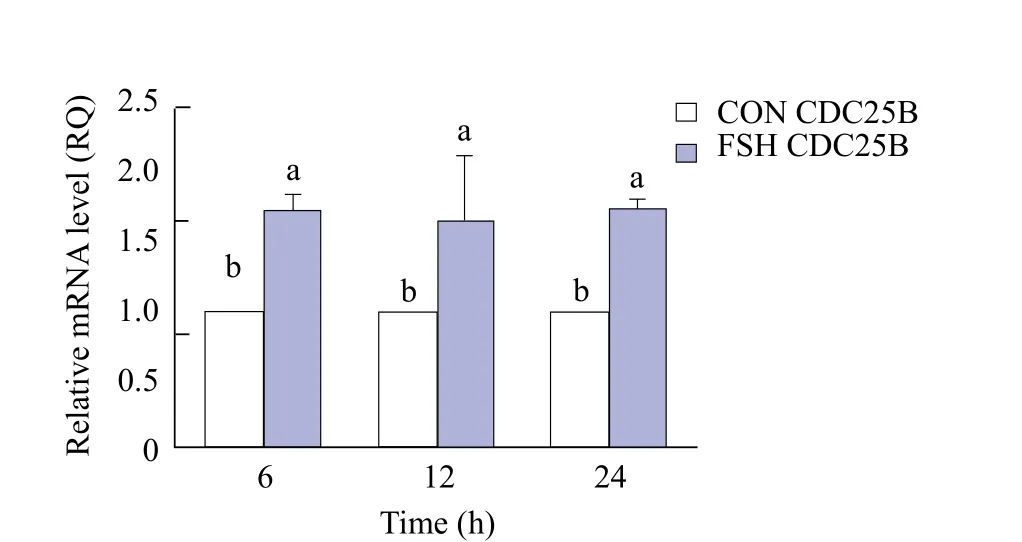
Fig. 8 CDC25B expression in each group
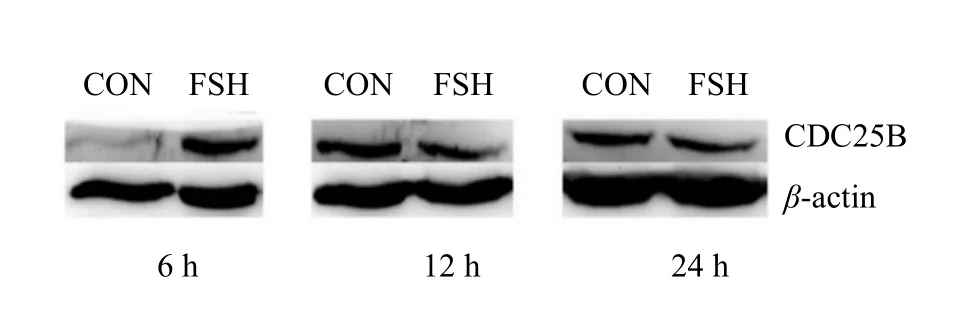
Fig. 9 Expression of CDC25B protein
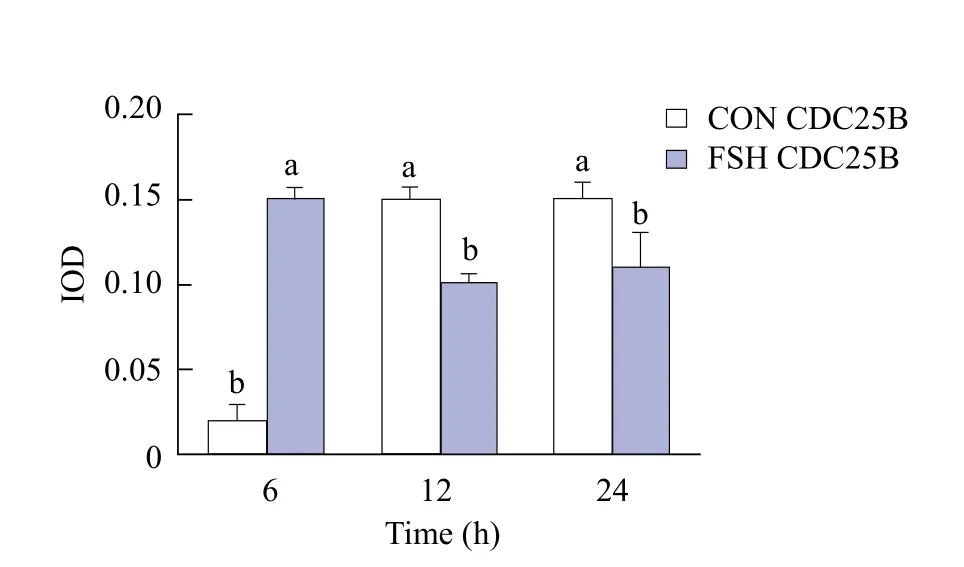
Fig. 10 CDC25B protein expression in each group

Fig. 11 CDC2 expression in each group
Effects of β-catenin inhibition on CDC25B expression
The results from Figs. 12 and 13 showed that the

Fig. 13 Effects of CDC25B protein in each group
Discussion
Effects of different concentrations of FSH on culture of Sertoli cells
FSH played an important role in the proliferation of testis Sertoli cells (Dance et al., 2017; Nascimento et al., 2016). This research showed that 40 and 80 ng • mL-1FSH could promote Sertoli cell proliferation significantly, while a high concentration of 120 and 150 ng • mL-1FSH at 12 and 24 h showed significant inhibition of Sertoli cell proliferation. So the effects of FSH on the proliferation of Sertoli cells had a concentration limit. The speed of cell proliferation would reduce, if this limit was exceeded; however,the regulation mechanism needed further studies.This study showed that the concentration of FSH at 80 ng • mL-1was more appropriate for cell culture in vitro.expression of CDC25B in cells cultured in medium containing FSH was significantly higher at 6, 12 and 24 h than that cultured in medium containing FSH+XAV-939 group (p<0.05). The expression of CDC25B in groups FSH+XAV-939 and FSH at 6, 12 and 24 h showed no significant difference (p>0.05),as shown in Fig. 14.
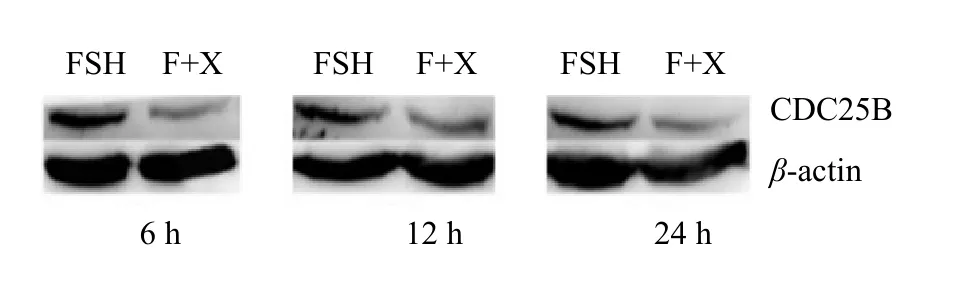
Fig. 12 Expression of CDC25B protein

Fig. 14 Expression of CDC25B in each group
Wnt pathway existing in calf testis Sertoli cells
β-catenin was the core part of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway (Hart et al., 1998). There were few reports about whether Wnt pathway existed in calf Sertoli cells. After inhibiting Wnt pathway, the expression of C-MYC decreased and the expression of β-catenin protein decreased, indicating that Wnt pathway existed in calf Sertoli cells.
The results also showed that there was no significant difference in the expression of β-catenin between Sertoli cells treated with no β-catenin inhibitor and those treated with β-catenin inhibitor at 24 h. It might be due to the in fluence of Wnt pathway on the cell proliferation and differentiation, but inhibitors could not completely inhibit gene expression at the transcriptional level, like RNA interference and gene knockout. It was probably due to the possibility that cells might enhance the level of β-catenin at the translational level in order to maintain cell proliferation and differentiation.
FSH playing a role in Sertoli cells through Wnt/β-catenin
C-MYC gene played an important role in the growth and proliferation of cells, and it was the target gene of Wnt signaling pathway (He et al., 1998). From the experimental results, it could be seen that the expression of β-catenin protein in Sertoli cells treated with FSH at 6 h is higher than the untreated Sertoli cells, which indicated that FSH could activate Wnt/βcatenin in order to promote Sertoli cell proliferation.The results also showed that there were no significant differences in the expression of β-catenin protein between untreated Sertoli cells and FSH-treated Sertoli cells at 12 and 24 h. It might be due to a reduction in cell proliferation and cell proliferation's space, which regulated the expression level of β-catenin protein to decrease, or it could be the cells' self-regulation mechanism making β-catenin no longer having high expression. There had been reported that the regulation of Wnt pathway and PI3K abnormalities might cause testicular tumors (Boyer et al., 2009). Further studies had shown that abnormal activation of β-catenin could lead to impairment in the development of primordial germ cells (Kimura et al.,2006).
FSH promoting cell proliferation by raising contents of CDC25B and CDC2
In the cell cycle, CDK1 (CDC2) /CyclinB complex was also called mitosis factor (MPF). T14 and Y15 on CDC2 were dephosphorylated under the action of CDC25B protein phosphatase, MPF activated rapidly,this phenomenon caused cell entry into mitosis(Masuda et al., 2011; Potapova et al., 2011; Xiao et al.,2011; Astuti et al., 2010).
Zhang et al. (2016) studied the ability of FSH to promote the proliferation of calves' Sertoli cells by raising the contents of CDC25B. But this study was limited to the transcriptional level, and no study had been done at the translational level. The experimental results showed that CDC25B was elevated in the transcriptional and translational expression levels. This phenomenon better showed that FSH could promote the expression of CDC2B. Results showed that the expression of CDC2 in group FSH was higher than that in group CON. This phenomenon showed that FSH activated CDC2 by raising the contents and the expression of CDC25B. So FSH could promote the proliferation of Sertoli cells.
The results also showed that the expression level of CDC25B protein in Sertoli cells treated with FSH at 12 and 24 h was lower than that in the untreated Sertoli cells. This was due to the fact that Sertoli cells were at G2/M checkpoint possibly. This phenomenon caused Sertoli cells to be arrested at G2 phase and regulated the expression of CDC25B at the translation level. However, some studies had shown that MAPK pathway prevented the cells from being blocked during G2 phase by regulating CDC25B (Astuti et al.,2009). As FSH activated MAPK pathway, it regulated CDC25B, so the expression of CDC25B protein in FSH-treated Sertoli cells was lower than that of the untreated support cells.
Relationship between CDC25B and Wnt/β-catenin pathway in Sertoli cells
Results showed there was no difference in the expression of mRNA between CDC25B treated with FSH and that treated with β-catenin inhibitor and FSH.Since C-MYC was also regulated by other pathways,it was possible to continue to regulate CDC25B at the transcriptional level to maintain cell division. It is reported that Ras-Raf-MEK pathway could regulate C-MYC. And FSH could activate Ras-Raf-MEK pathway in Sertoli cells. It was suggested that FSH could regulate the expression of C-MYC by activating Ras-Raf-MEK pathway. And CDC25B was also regulated by DNA damage repair pathway (Xu et al.,2002). This could possibly be the reason CDC25B did not change at the transcriptional level. Results also showed that the expression of CDC25B protein decreased after Wnt pathway was inhibited. This phenomenon indicated that CDC25B was regulated by C-MYC at the protein level. It also showed that Wnt pathway could regulate CDC25B cell proliferation at the protein level so that it would affect the proliferation of Sertoli cells.
Conclusions
FSH might promote the proliferation of calf Sertoli cells through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway,80 ng • mL-1FSH was a suitable concentration for culturing bovine Sertoli cells in vitro. β-catenin was inhibited, C-MYC gene expression decreased and CDC25B gene expression level unchanged, but CDC25B protein expression level decreased. This phenomenon indicated that CDC25B was affected by Wnt/β-catenin pathway at the protein level.
杂志排行
Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Laboratory Assessment of Susceptibility of Maize Varieties to Postharvest Infestation By Sitophilus zeamais (Mostchulsky) (Coleoptera:Curculionidae)
- Identification of Genes Associated with Clubroot Resistance in Chinese Cabbage
- Species Composition and Diversity Analysis of Lava Flow in Different Periods in Wudalianchi Nature Reserve, China
- Function of RanGAP1 in Mouse Oocyte Fertilization
- Porcine Parvovirus Inducing Autophagy to Benefit Its Replication
- Isolation and Characterization of E. Coli O157 : H7 from Infected Newborn Calves in Northeast China
