Ore prospecting model and targets for the Dashuigou tellurium deposit,Sichuan Province,China
2018-08-30QuanjiangZhangYingpingLiuMingyouHeJunBaiWeiXuCongZhao
Quanjiang Zhang•Yingping Liu•Mingyou He•Jun Bai•Wei Xu•Cong Zhao
Abstract The Dashuigou tellurium(Te)deposit in Shimian city,Sichuan Province is the only known independent Te ore deposit in China.Samples were collected by 1/50,000 stream sediment survey and analyzed by inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry,X-ray fluorescence spectrometry,emission spectrometry,and atomic absorption spectroscopy.An ore prospecting model for the Dashuigou Te deposit was then established.In the Dashuigou area,bismuth(Bi),Te,and gold(Au)concentrations in stream sediment samples displayed weak-positive anomalies,while silver(Ag)displayed a weaknegative anomaly.Bi,Te,Ag,and Au anomalies are regarded as indicators of Te deposits;the greater the ratio of Te+Bi/Au+Ag,the larger the possibility of an independent tellurobismuthite deposit.The ratio calculated from our samples is 7.288.Five locations were identified for prospecting for Te minerals by this model,including the northern part of the Dashuigou Te deposit,Majiagou,Tizigou,southeastern Miaoping,and northern Baishuihe.These five regions are within the Dashuigou dome anticline,the exposed strata of which are controlled by tracing the tensile shear fracture;the metallogenic geological conditions and geochemical characteristics are the same as those of the known Dashuigou Te deposit.Already,Te–Bi veins have been found in some of these areas.
Keywords 1/50,000 steam sediment survey·Ore prospecting model and targets·Dashuigou Te deposit·Sichuan Province
1 Introduction
Tellurium(Te)is an extremely scarce element in the crust,with a clarke value of 1–10 ng/g.Li(1985)estimated the abundance of Te in the continental crust at 16 ng/g.The content of Te is also at the ng/g level in soil and sediments(Belzile and Chen 2015).Despite its rarity,Te remains a research focus due to its economic value.Qin et al.(2017)studies of the distribution and chemical species of Te in contaminated soil are of geochemical and environmental significance for better understanding the solubility,mobility,and bioavailability of Te in the surface environment.Mal et al.(2017)demonstrated the application of an up flow anaerobic granular sludge bed reactor for continuous tellurite removal from tellurite-containing wastewater coupled to elemental Te recovery.You et al.(2014)have explored the effect of the paleoredox environment change on Te concentration and the enrichment mechanism of Te in cobalt(Co)-rich crusts.Other researchers have focused on Te deposits such as the Dashuigou;the Te-bearing gold(Au)deposit in Shandong Province(China)(Hu et al.2016);the Te–Au deposits in Kalgoorlie(western Australia)(Shackleton et al.2003),Paramashan(northeastern Greece)(Voudouris et al.2005),and Ecuador(Vikentyev et al.2005);and the Te–Pb deposit in Geordie Lake(Ontario)(Mulja and Mitchell 1991).
Since the discovery of the Dashuigou Te deposit in Sichuan Province many geologists have examined its geology,geochemistry,and isotopic characteristics(e.g.Luo et al.1994,Luo and Cao 1996;Mao et al.1995a,b;Yin et al.1996;Wei and Zhang 1999).Lead(Pb)and sulfur(S)isotopes provide an effective method for tracing the source of materials(Zartman and Doe 1981,Zartman and Haines 1988;Gwiazda et al.1996;Townley and Godwin 2001;Chang and Zhu 2002;Baker et al.2004;Shen et al.2012;Cloquet et al.2015;Ickert et al.2015;White et al.2016;Cook and Hoefs 1997;Field et al.2005;Robert and Seal 2006;Defouilloy et al.2016;Tanner et al.2016;Giulian et al.2016).Wang et al.(1995,2011b)studied the Pb isotopes of the Dashuigou Te deposit and found that207Pb/204Pb–206Pb/204Pb projection points fell between the orogenic belt and the upper crustal evolution curves,while208Pb/204Pb–206Pb/204Pb projection points fell between the mantle and the lower crustal evolution curves,indicating that the Pb in these samples derived from both the crust and the mantle.In Wang et al.’s(1995)study of the Dashuigou Te deposit,the δ34S values of pyrite,pyrrhotite,and tetradymite were 1.13‰ to 1.16‰,-0.38‰ to 2.36‰,and-0.50‰ to 3.17‰,respectively;Wang concluded the S was mainly derived from the deep Earth,likely in relation to magmatic activity or metamorphism.Although scientists have carried out extensive research on the Dashuigou,the existence of other Te deposits similar to the Dashuigou is undetermined.
Geochemical prospecting is widely used in mineral exploration,resource prediction,and other applications(e.g.Qian et al.2011;Zhou et al.2013;Horiuchi et al.2014;Mokhtari et al.2014;Spiridonov et al.2014;Zhang et al.2017).Chabaux et al.(2017)deciphered the diversity of the water flow and the associated water–rock interactions in elementary mountainous catchments by combining geochemical tracing and geochemical modeling approaches on surface and deep borehole waters.Gad and Saad(2017)applied a geochemical model to simulate net geochemical mass-balance reactions between initial and final waters along a hydrologic flow path.Other researchers have compiled models of typical ore deposits to guide prospecting(e.g.Bai and Liu 1996;Li and Zeng 2007;Sun 2008;Xu et al.2008;Shi et al.2011;Ren et al.2014;Wen and Teng 2014).Wang et al.(2009)established a prospecting model for Pb-zinc(Zn)ore based on geological background of the metallogenic belt,basic characteristics of Pb–Zn deposits,and the conditions controlling Pb–Zn ore.Wu et al.(2011)established the metallogenic model of molybdenum(Mo)deposits on the basis of deposit geology,geochemistry,and isotope geochronology data.Gong et al.(2013)constructed a prospecting model for typical Jiama copper(Cu)-polymetallic deposits,based on regional geologic features,geologic and geochemical characteristics of the deposit,geochemical anomalies,and important orecontrolling conditions.Lang et al.(2017)established a comprehensive information prospecting model with the aim of searching for Cu–Au ore deposits and expanding the quantity of resources.To date there are no ore prospecting models to guide prospecting for Te deposits.
In this paper,we analyzed the geology,structure,and geochemical characteristics of the area of the Dashuigou tellurobismuthite deposit,and summarized S and Pb isotopic compositions and prospecting indicators in order to establish an ore prospecting model that can be used to guide prospecting of deposits similar to the Dashuigou Te deposit in other regions.
2 Geologic setting
2.1 Regional geology
Dashuigou is located in the platform-trough junction zone of the Yangtze Platform,at the eastern edge of the Songpan–Ganzi geosyncline,and in the central sector of the Longmen Mountain–Daxue Mountain–Jinping Mountain nappe structure(Chen et al.1994).
The strata exposed are Sinian,Ordovician,Silurian,Devonian,Permian,and Triassic(Fig.1).Magmatic activity is relatively developed in the Jinningian,Hercynian,and Indosinian–Yanshanian.Diabase is widely distributed in the eastern region.Due to the influence of the Indochina–Yanshan movement,NNE-,NS-,and NNW-trending faults and folds are widespread,and there are many nappe structures.The strata have been subjected to varying degrees of metamorphism.
2.2 Geology of the Dashuigou Te deposit
The core strata of the Dashuigou dome anticline are the Ordovician Dahebian Formation(Fm)and the overlying Silurian Tonghua Group(St)(Fig.2).Stis divided into seven formations,from top to bottom:
Seventh Fm(St7)variegated mudstone and dolomite structure with lagoon facies.The upper part is composed of gray or grayish-green chlorite-albite schist and muscovite dolomite schist interbedded with dolomite;the lower part is composed of gray sericite-chlorite-quartz phyllite.
Sixth Fm(St6)carbonate structure with open-platform facies.It is composed of gray or dark gray thin-thick block fine crystalline limestone with two-mica schist and albitedolomite schist.

Fig.1 Regional geology of the Dashuigou Te deposit

Fig.2 Geological sketch of the Dashuigou region
Fifth Fm(St5)gray sandy shale structure with shelf slope facies,variegated volcaniclastic rocks and carbonate Fm of marine facies.The upper part is composed of gray sericite phyllite intercalated with fine-grained phyllitic greywacke,while the lower part is composed of grayishgreen two mica(green mud)albite schist with gray-white thin-massive marble and metabasalts.
Forth Fm(St4)limestone structure with open-platform facies.It is composed of light-gray to gray-white thick massive dedolomitized marble.
Third Fm(St3)upper member is composite terrigenous clastic sand-shale structure with shelf facies,which is composed of grayish-green,gray-white two-mica calcite schist,sericite-chlorite schist,and muscovite schist with siderite spots.The lower member is a complex unit of shales,sands,and volcaniclastic rocks with shelf facies,manifesting as gray thin-to-thick bedded phyllitic quartz greywacke and grayish-green sericite quartz phyllite.
Second Fm(St2)limestone structure with platform facies.It is composed of gray-white massive coarsegrained marble interbedded with dark-gray carbonaceous muscovite-calcite schist in the lower part;and of dark gray,thin marble intercalated with grayish-green muscovite-albite schist at the bottom.
First Fm(St1)volcanic rock structure with marine facies.It is composed of dark-gray,grayish-green actinolite schist;biotite-actinolite-epidoteschist;epidote-chlorite schist;actinolite-biotite-epidote quartz schist interbedded with same-colorstilpnomelane plagioclase granulite;muscovite-quartz schist;muscovite-dolomite schist;and small amounts of grayish-green chlorite-garnet-muscovite schist and arfvedsonite calcite schist.
Dahebian Fm(Od)limestone structure with platform facies.Not exposed.It is composed of white or gray-white,thick-massive,coarse-pegmatite marble.
Igneous rock is widely distributed in the Dashuigou dome anticline.Silurian mafic volcanics exist in St1and St3,while hornblende and actinolite schists intruded by diabase veins have been documented in the Tizigou region.Concealed intermediate-felsic igneous rock of the Xiyoufang and Dashuigou ring structures provided the oreforming hydrothermal fluids for the Dashuigou Te deposit during the Yanshan Orogeny.The mining area experienced the main orogenic deformation and the post-orogenic adjustment stage;the following tectonic features have been observed:slip-shear deformation,shrinkage deformation,upwelling extension,and thrust and nappe tectonics(Wang et al.2011a).
The Dashuigou Te deposit is in the plunging end of the Dashuigou dome anticline.It is hosted in metamorphic basic volcanic rocks of St1,which is the core of this dome(known as hornblende schist)(Cao et al.1995),controlled by tracing shear tensile fracture.Most of the Te ore veins or vein branches extend from north to northeast;a few extend from north to northwest.
2.3 Mineralogy and wall rock alteration
Ore minerals in the Dashuigou Te deposit are pyrite,pyrrhotite,tetradymite, joseite,chalcopyrite and sphalerite,tellurobismuthite,tsumoite,empressite,and native gold,with lesser amounts of calcite,albite,and calaverite(Table 1).
Tellurobismuthite ore accounts for 70%–80%of the Te(S)compounds and pyrrhotite ore accounts for 90%of all S compounds(Wen et al.1993).Gangue minerals are mainly dolomite and ankerite with some calcite,quartz,and muscovite.Ores show massive,disseminated,veinlet,plaque-like,and brecciform structures,and exhibit a wide range of petrographic textures:xenomorphic granular,metasomatic relict,erosion,cataclastic,emulsion,poikilitic,and exsolution.
Wall rock alteration is widespread in the mining area as dolomitization,ankerite alteration,silicification,sericitization, tourmalinization,and chloritization.This alteration is distributed in a band that stretches from the vein to the surrounding rock.
2.4 Elemental content in rocks
The Dashuigou Te deposit contains two major ore types:pyrrhotite-pyrite and tetradymite.The former is valuable mainly for S and Cu.The elemental content of the pyrrhotite-pyrite ore includes: Cu,0.12%–1.32%; Te,5.4–445 μg/g;Au,0.08–0.24 μg/g;Ag,0.15–4 μg/g;and S,30%–45%.These ores are relatively rich in zinc(Zn)but poor in Pb,with Zn/(Zn+Pb)of 0.75–0.95 and little Te.
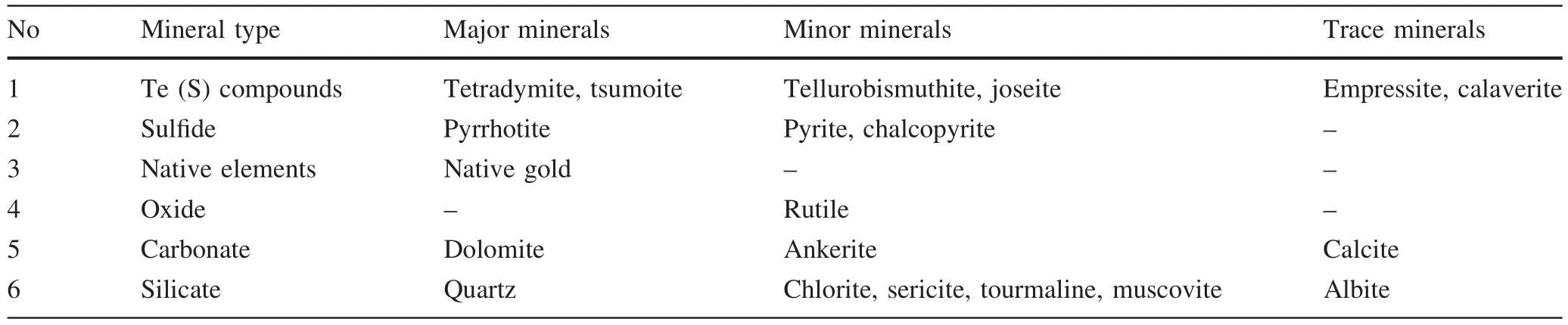
Table 1 Mineral composition of the Dashuigou Te deposit
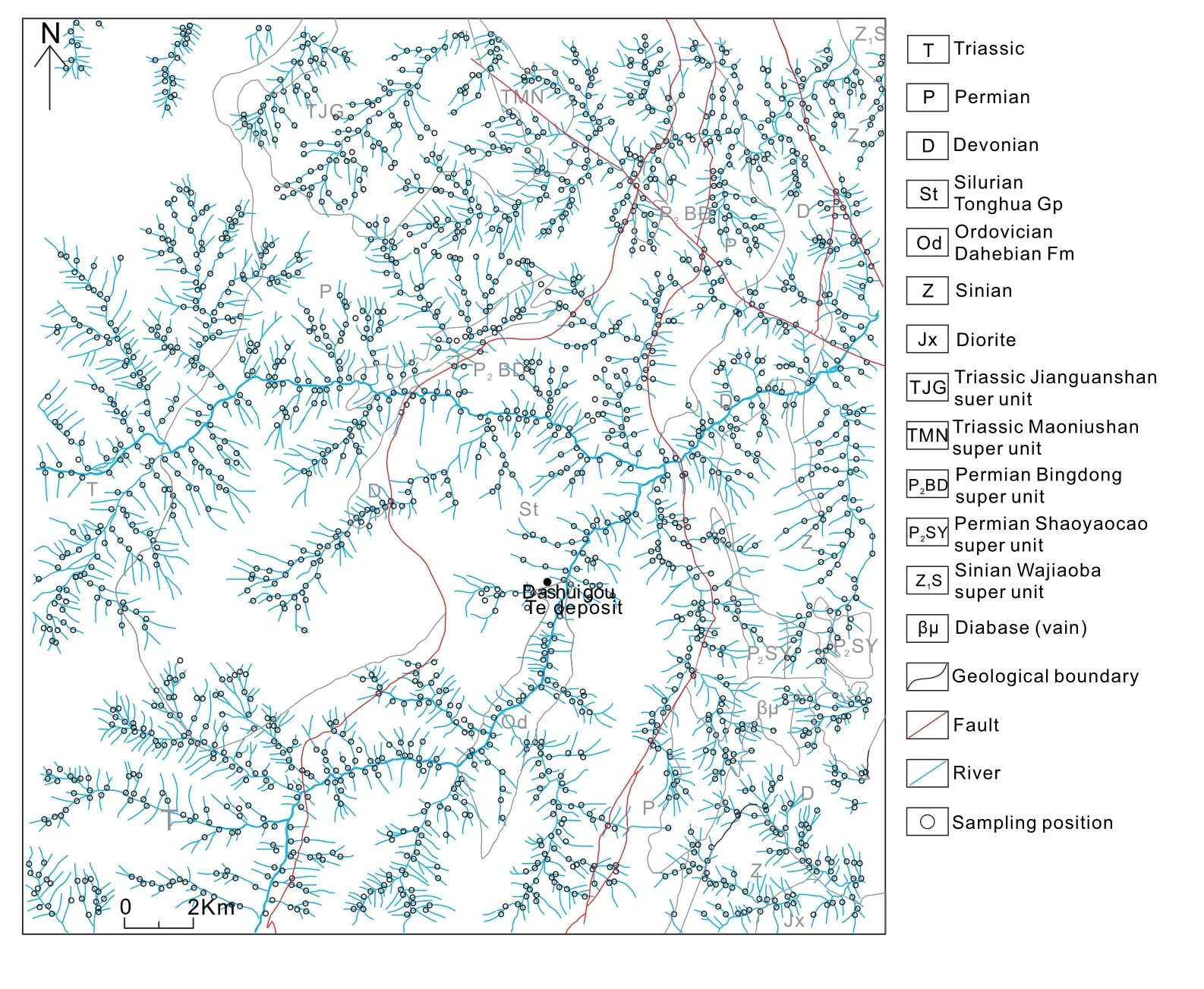
Fig.3 Stream sediment sample locations
The tetradymite ore in the Dashuigou deposit carries Te primarily as the mineral tetradymite(Bi2Te2S),with minor tsumoite(BiTe)and tellurobismuthinite(Bi2Te3).The Te content of bulk ore is generally 0.2%–10%but can reach 25%;Bi is typically 3%–10%but ranges up to 32%.Au content is 2.1–82 μg/g,Ag content is 148–266 μg/g,Pb content is<300 μg/g(Mao et al.1995c).
2.5 Geochemical characteristics of stream sediment
Stream sediment consists of eroded rocks(ores)within a given watershed.They show good inheritance of geochemical features and geological processes(metallization)from rocks on the Earth’s surface(Chi and Yan 2007).Stream sediment survey is a very effective method for geochemical prospecting.It can delineate and trace primary anomalies and ultimately locate the source of the anomaly(ore body or mineralization).Anomalies of stream sediments superimposed on super gene geochemical anomalies can indicate ore deposits in the region.This technique has been widely used all over the world(Nude and Arhin 2009;Landry et al.2014;Omang et al.2014;Sharma,Putirka,and Stone 2016).Stream sediment surveys at scales of 1/200,000 and 1/50,000 have good prospecting application and are widely used(e.g.Wang et al.2010;Miao et al.2014).
A geochemical atlas of 76 elements in southwestern China(Xie and Cheng 2008)shows that distribution of Te is similar to that of the rare earth elements and Sb,As,Cd,Pb,and Zn.Distribution anomalies of Te is concentrated in western Guangxi Province and eastern Yunnan Province.In the Dashuigou region,Ag,Au,Pb,Cd,and tin(Sn)show strong anomalies,while As,Mo,and Te show weak anomalies.
Zhang et al.(2013)compared the average elemental content in the Dashuigou area with elemental background content in 1/200,000 stream sediments across China and with elemental background content in the Shimian region.In that report,the contents of Fe2O3,Ni,Pb,and Zn in stream sediments in the Dashuigou area were determined to be similar to those in stream sediments across China.In addition,cobalt(Co)is weakly enriched;Ag,As,and Cd are enriched;and Cr,Sb,and Au are strongly enriched.The enrichment coefficient of Au is highest—up to 8.2.Mo,Bi,and Sn contents are lower than background values,and tungsten(W)is poorly enriched.The contents of Fe2O3,Bi,Cd,and Cu in Dashuigou area stream sediments are similar to those in the Shimian region,while Co and Ni are weakly enriched,Ag is enriched,and Au,As,chromium(Cr),and Sb are strongly enriched.The enrichment coefficient of Sb is highest(up to 7.75).Mo,Pb,Sn,and Zn contents are lower than background values,and W is poorly enriched.
3 Samples and analytical methods
3.1 Samples
We used a 1/50,000 stream sediment survey in the Shimian area,with a sampling point density of 4–8/km2;according to conditions of the study area,we selected sampling points to maximize the control of the sink water and obtain a representative sample.
First,we marked all streams longer than 300 m on the 1/50,000 topographic map;we then designated sampling points at the end of first-order streams and the middle of second-order streams.For first-order streams longer than 1000 m,sampling points were added in their middle segments.Finally,the map was divided into 1 km2squares,then subdivided into four small sampling units per square,which were numbered from left to right and top to bottom.
During field sampling,we used GPS and topographic maps to confirm the sampling sites.Samples were collected from river bottoms and sandy shores.Each sample was a mix of stream sediment from several points near the designed sites(within 30 m),weighing about 1 kg,mainly composed of sand with particle size from 0.3 to 2 mm.For rivers without sand,the sampling medium was soil from 20 to 50 cm under the surface.All sample bags were marked and recorded.During the sampling,silt,organic matter,and other pollutants near the mining area,village,and traffic arteries were avoided.
We collected 1991 samples of 1/50,000 stream sediments in the Shimian area,including 54 samples from the Dashuigou Te deposit area(Fig.3),and tested the contents of Au,silver(Ag),tin(Sn),Mo,bismuth(Bi),Fe2O3,Co,and nickel(Ni)in these samples.
3.2 Analytical methods
After processing stream sediment samples,we tested them for Ag,Au,Bi,Co,Mo,Ni,Sn,Te,and iron(Fe).Analytics were conducted preferentially by inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry(ICP-MS),with X-ray fluorescence spectrometry(XRF),emission spectrometry(ES),and atomic absorption spectroscopy(AAS)as supplementary methods(Table 2).
National primary standard samples,replicate samples,and monitoring samples were used to verify the analytical results.Analytical results of Au were measured against geochemical sample percent of report(PR),relative error(RE),and the repeatability relative deviation(RRD).Thoseof other elements were measured by PR,accuracy(A),relative standard deviation(RSD),and the RRD(Table 3);the PR and RRD of analytical methods was kept to greater than 90%.Calculation results show that the analytical methods of stream sediment samples are correct and the analytical results reliable.

Table 2 Analytical methods and detection limits of stream sediment samples

Table 3 Analytical results of stream sediment samples
4 Results
We calculated geochemical parameters of these elements in stream sediments from Shimian(Table 4)and Dashuigou(Table 5).Except for Co,Sn,and Fe2O3,the relative standard deviations of the elements were>1,reflecting that these three elements’anomalies are less strong than those of other elements in the Shimian region 1/50,000 stream sediments.The maximum contents of Ag,Au,and Bi are 33,400 ng/g,3420 ng/g,and 40.6 μg/g,respectively;the relative standard deviations were higher than other elements,indicating that dispersion distribution is strong in this area.While the maximum Te content was determined to be 0.868 μg/g,the relative standard deviation wasrelatively high,indicating that Te has strong anomalies in some parts of the Shimian region.The maximum content of all elements was smaller in the Dashuigou region than in the Shimian region.

Table 4 Geochemical parameters of elements in the Shimian area

Table 5 Geochemical parameters of elements in the Dashuigou area
The element content in the Shimian area was repeatedly eliminated by average± 3×standard deviation until it obeyed normal distribution,then we obtained the average content of stream sediments in the Shimian area(S)and used it as the background value to highlight the weaknegative anomalies of Te and Bi.The threshold of anomaly of these two elements was calculated by average+1.25×standard deviation;the threshold of anomaly of remaining elements was calculated by average+2×standard deviation.Finally,the average contents of Dashuigou were compared with P and S to obtain the relative enrichment coefficients K1and K2,respectively(Table 6).
The Co contents in the Dashuigou Te deposit area were determined to be similar to southwest China background values,while Te,Ni,Ag,and Fe2O3were weakly enriched,and Au and Bi were lower than the back ground values for the five southwest China provinces,and Sn and Mo were poor.Compared to background values for the Shimian region stream sediment,Sn and Mo were similar,Bi and Te were most enriched,and Ag was weakly enriched;the contents of Au,Co,Ni,and Fe2O3were lower in the Dashuigou Te deposit area than in the Shimian region.Compared with the Zhang et al.’s(2013)study,ours is more suitable for the real characteristics of Dashuigou and Shimian.
The 1/200,000 stream sediments in the Dashuigou Te deposit arefine sand(grain size-60 mesh).In this sample,Au content was 0.94 ng/g and Ag 80 ng/g;Bi,Mo,Ni,Sn,and W were 0.75,0.70,42.14,1.97,and 1.25 μg/g,respectively;and iron oxide(Fe2O3)comprised 6.88%.Sediment samples(grain size-10 to+60mesh)were tested from 1/50,000 stream sediment in the Dashuigou Te deposit,with the following results:Au,1.55 ng/g;Ag,51 ng/g;Bi,Te,Mo,Ni,and Sn—0.304,0.079,0.436,38.1,and 2.16 μg/g,respectively;and Fe2O3,5.81%.These results are similar to those of 1/200,000 stream sediments;with the exception of Au and Sn,element contents of 1/50,000 stream sediments were lower.The enrichment of stream sediment elements is different from granularity;the elements associated with sulfides are more likely to be enriched in fine particles,have strengthened abnormality,and better guide prospecting.

Table 6 Elemental enrichment in the Dashuigou area

Fig.4 Geochemical maps of Te,Bi,Au,and Ag in Dashuigou region
We generated geochemical maps of Te,Bi,Ag,and Au(Fig.4)in the Shimian region based on the 1/50,000 stream sediments.The figures show a shared Te+Bi anomaly trending NE–SW through the region,but also separate strong anomalies of Te without Bi and of Bi without Te,separate from the trend.The low Bi content is distributed on both sides of the area with high Bi content.The stream sediment contents of Au,Bi,Ag,and Te were not high in the Dashuigou area(Dashuigou Te deposit and its downstream and upstream river system of about 4 km2),where Te,Bi,and Au concentrations of 1/50,000 stream sediment showed weak-positive anomalies,Ag showed weak-negative anomaly,and the other basic metallogenic elements showed no anomalies.The formed anomaly of stream sediment can effectively indicate the location of a deposit;therefore,anomalies in Bi,Te,Ag,and Au can be regarded as indicator elements of a tellurobismuthite deposit.
5 Discussions
5.1 Anomaly analysis

Fig.5 Comprehensive anomalies of the Dashuigou region
Based on the1/50,000 stream sediment composite anomalies,eight integrated anomalies were delineated in the Dashuigou region(Fig.5).Anomalies 1,2,3,4,and 6 are in the Dashuigou dome,while anomalies 5,7,and 8 are located east of the dome.The Dashuigou Te deposit is within integrated anomaly No.1,with a general Te content of0.069–0.087 μg/g (maximum=0.124 μg/g),and a general Bi content of 0.244–0.357 μg/g (maximum=0.599 μg/g).The Te,Bi,and Au contents showed weak-positive anomalies,while Ag showed a weak-negative anomaly.Integrated anomaly No.2—a combined anomaly of Ag,Au,Mo,Sn,and Te—appeared in southern Guizhichang.The maximum contents of Ag,Au,and Te were 930 ng/g,9.29 ng/g and 0.232 μg/g,respectively.Integrated anomaly No.3 is in northern Qilongdong with a combined anomaly of Ag(125 ng/g),Au(4.78 ng/g),Bi(29.3 μg/g),Mo,and Te(0.482 μg/g)(maximum contents in parentheses).
Integrated anomaly No.4 is in Tizigou with a combined anomaly of Ag(4900 ng/g),Au(18.8 ng/g),Bi(18.8 μg/g),Sn,Te(0.786 μg/g),and W.Located in eastern Baishuihe,comprehensive anomaly No.5 is a combined anomaly of Au,Co,Fe,Mo,and Ni.Integrated anomaly No.6 in southeastern Miaopin is a combined anomaly of Ag(33,400 ng/g),Au(122 ng/g),Bi(0.94 μg/g),Mo,Sn,Te(0.859 μg/g),and W.Anomalies No.7 and 8 are in southern Qilongdong.Anomaly 7 includes Ag,Au,Bi,Te,and W;anomaly 8 Ag,Au,Co,Ni,and Te.
5.2 Ore prospecting model
We developed an ore prospecting model for tellurobismuthite deposits based on geology,mineralogy,geochemical characteristics(elemental contents of rock,soil,and stream sediment;dispersion and enrichment of elements in stream sediment),S and Pb isotopic characteristics,and prospecting indicators.The model is described in Table 7.
5.3 Ore prospecting targets
Although researchers have established geochemical prospecting models for Au,Mo,and Cu deposits and others,most have not discussed the rationality and practicability of their model;only a few researchers have made a superficial introduction(e.g.Wang et al.2005;Gong et al.2013;Wen and Teng 2014;Wen et al.2013;Li et al.2016).The geological features of five areas are only consistent with the model in some complex anomaly areas wheremetallogenic geologic conditions and geochemical characteristics are the same as those of the Dashuigou Te deposit.We infer that these five areas are favorable for Te mineralization in the Shimian area,including the northern part of the Dashuigou Te deposit,Majiagou,Tizigou,southeastern Miaoping,and northern Baishuihe(Fig.6).

Table 7 Ore prospecting model for the Dashuigou Te deposit
These five areas are in the Dashuigou dome anticline.The exposed strata are Od,St1,St2,and St3,controlled by the tracing tensile shear fracture.The metallogenic characteristics of this area are similar to those of the Dashuigou Te deposit.Geochemically anomalous elements comprise Ag,Au,Bi,and Te in those areas.
The 1/50,000 stream sediment samples showed low positive anomalies of Te and Bi,and low-negative anomalies of Au and Ag in the northern part of the Dashuigou Te deposit,the ratio of Te+Bi/Ag+Au was ~ 10.625 (>7.288),indicating that Te and Bi anomalies are more significant and indicate greater possibility of tellurobismuthite mineralization.This plot has geochemical anomalies including low-positive anomalies of Te,Bi,and Au and a low-negative Ag anomaly.The ratio Te+Bi/Ag+Au of~5.992 may indicate tellurobismuthite mineralization.
In the Tizigou area,contents of Te,Bi,Ag and Au were 0.786 μg/g,1.58 μg/g,4900 ng/g,and 18.8 ng/g,respectively.Anomalous elements included Ag,Au,Bi,and Te.The ratio of Te+Bi/Ag+Au— ~ 0.468—was much lower than the parallel value in the Dashuigou Te deposit.Because of the high content of Ag and Au and low ratio,this plot is favorable for prospecting Ag or associated Te.Contents of Bi,Te,Au,and Ag were 29.3 μg/g,0.483 μg/g,4.78 ng/g,and 125 ng/g,respectively,in the northern part of Baishuihe,where anomalies comprised Ag,Au,Bi,and Te,The Te+Bi/Ag+Au ratio of~165.6(>7.288)indicates high Te and Bi anomalies and thus greater possibility of tellurobismuthite mineralization.
The content of Te,Bi,Ag,Au,and Pb in 1:50,000 steam sediment samples were 0.859 μg/g,0.94 μg/g,33,400 ng/g,122 ng/g,and 6135 μg/g,respectively,in Southeastern Miaoping;the ratio of Te+Bi/Ag+Au was 0.053,revealing weak tellurobismuthite mineralization.Cu–Pb–Zn mines are located in the marble in this area.Therefore,this area can be an important target for prospecting polymetallic deposits associated with Te ores.
We verified the northern part of the Dashuigou Te deposit.In this area, five pyrite veins containing bismuth telluride have been found in the southwest.The ore body is mainly veinlike;ore-hosting stratum is rich Te green schist of the Tonghua Group;ore components are mainly pyrite,pyrrhotite,tetradymite;and ores show massive,disseminated,and veinlet structures,and exhibit a wide range of petrographic textures:xenomorphic granular,metasomatic relict,erosion,and cataclastic.The content of Te in ore samples was 7.26–183 μg/g.Wall rock alteration is widespread in this area as dolomitization,ankerite alteration,silicification,sericitization,and chloritization.Due to the difficulty of the terrain and the lack of time,the other four areas were not verified,but the data(Ruan 2013)show some rocks contain high Te content(up to 100 μg/g),underscoring the validity and rationality of our geochemical prospecting model.It is an inadequacy of this article that we do not have further study on S and Pb isotopes in these five favorable areas.

Fig.6 Te ore prospecting targets in Dashuigou region
Our model can be well applied in the Dashuigou area and the discovery of the tellurobismuthite deposit.However,can the model be expanded to other areas?Outside of Dashuigou,areas are favorable for tellurobismuthite mineralization in accordance with the geologic,structural,and geochemical characteristics and S-Pb isotopic composition of the model and have great possibility of tellurobismuthite deposits;at present,there is no known area with similar geology and structure to the model.The geologic and structural conditions of integrated anomaly No.7 are different from the model:it is located in the middle of two faults on the periphery of the Dashuigou and the exposed stratum is St3.The geochemical characteristics are consistent with the model and show weak anomalies of Te,Bi,Au,and Ag;the ratio of Te+Bi/Au+Ag is about 5.616;and there is pyrite mineralization.We infer that it is also a favorable area for mineralization of tellurobismuthite.Although there are no geologic and structural conditions that are the same as the model outside Dashuigou,the area(for example integrated anomaly No.7)is consistent with the model’s geochemical characteristics and S–Pb isotopic composition can be regarded as an indicator of tellurobismuthite mineralization.
6 Conclusion
This paper describes the elemental content of the rock-soilstream sediment and the dispersion and accumulation characteristics of major elements in stream sediment in the Dashuigou region.An ore prospecting model was established based on geologic,mineralogic,and geochemical characteristics;S and Pb isotopic characteristics;and prospecting indicators.
Five locations were identified by this model for prospecting Te:the area north of the Dashuigou Te deposit,Majiagou,Tizigou,southeastern Miaoping,and northern Baishuihe.At present,some Te-Bi veins have been found in some of these areas,indicating that the model is feasible.
AcknowledgementsThis study was supported by the Institute of Geochemistry,Chinese Academy of Sciences(03JY029-027-1)and Sichuan Geological Survey(12120113051400).The authors would like to thank the State Key Laboratory of Ore Deposit Geochemistry,Chinese Academy of Sciences for its open program funding and the Sichuan Provincial Institute of Geological Geochemical Exploration for providing necessary data.Wei Xu and Jun Bai are thanked for insightful and constructive comments on this paper.We are also grateful to Mingyou He and Yingping Liu for proofreading and commenting on the manuscript.
Compliance with ethical standards
Conflict of interestOn behalf of all authors,the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
杂志排行
Acta Geochimica的其它文章
- The vanadium isotopic composition of L ordinary chondrites
- Variations of tr ace elements under hydrological conditions in the Min River,Eastern Tibetan Plateau
- Effects of carbon anhydrase on utilization of bicarbonate in microalgae:a case study in Lake Hongfeng
- Enrichment characteristics and risk assessment of Hg in bird feathers from Caohai wetland in Guizhou Province,China
- Carbazoles and benzocarbazoles confirm migration of leaked petroleum through caprocks and overlaying formations of Valhall Well 2/8-8 in the North Sea
- Basic formation mechanisms of Lake Doroninskoye soda water,East Siberia,Russia
