Nrf2通路在齐墩果酸所致肝纤维化中的作用研究
2018-07-16吴栋清秦瑞玲徐尚福徐亚沙鲁艳柳陆远富
吴栋清,秦瑞玲,徐尚福,徐亚沙,鲁艳柳,陆远富
(遵义医学院 基础药理教育部重点实验室暨特色民族药教育部国际合作联合实验室,贵州 遵义 563099)
Oleanolic acid,a pentacyclic triterpenoid,was discovered in the 1970s and has become a commonly-used hepatoprotective drug in clinics[1].It is widely found in foods,Chinese medicines and other glycosides herbs[2],for example,soybean oil contains oleanolic acid[3].The study found that it can reduce necrosis and interstitial inflammatory response,prevent the formation of fibrosis,promote the regeneration of liver cells and accelerate the recovery of necrotic tissue.However,our previous study found that large doses of oleanolic acid can lead to cholestatic liver injury,and long-term use of oleanolic acid in low doses can also lead to liver fibrosis[4-6].At the same time,it was found that intra-nucleus Nrf2 protein expression with administration of oleanolic acid was significantly increasedinvivo.Therefore,the role of Nrf2 pathway in liver fibrosis induced by oleanolic acid has aroused our interest.
Hepatic stellate cells mainly store and metabolize vitamin A,synthesize and secrete a small amount of extracellular matrix (ECM),and have certain ability to produce collagenase[7].It is currently thought that the main occurrence mechanism of liver fibrosis is the excessive increase and abnormal deposition of ECM[8].Activated hepatic stellate cells are the main cells to produce ECM[9].At present,it is thought that hepatic stellate cell activation is the final common pathway of liver fibrosis[10].HSC-T6 cell line is the most usually used hepatic stellate cell strain because of the stable and serially passaged characteristics.Therefore,HSC-T6 cells can be used as a model of hepatic fibrosis to study the effects of Nrf2 pathway on hepatic fibrosis induced by oleanolic acid.
1 Materials and methods
1.1Reagents and instrumentsOleanolic acid and sulforaphane (SFN) were purchased from Sigma Company.HSC-T6 cells were provided by the Kunming Cell Bank of Chinese Academy of Sciences.Australian fetal bovine serum was purchased from Gibico Company.DMEM high-glucose medium and pancreatin were purchased from Hyclone Company.SiRNA kit was purchased from Ribo Biotechnology Company.Total RNA extraction and reverse transcription kit was purchased from TaKaRa Company.The nuclear protein extraction kit was purchased from Thermo Company.Nrf2 antibody was purchased from Abcam Company,and α-SMA,GAPDH,PCNA antibodies were purchased from Proteintech Company.
The instruments used for the experiment include cell incubator (Thermo),microplate reader (Thermo),ultramicro tube photometer (Thermo),real-time fluorescence quantification RT-PCR (BIO-RAD),Gel Imaging System (BIO-RAD),biological microscope (Leica),and high-speed refrigerated centrifuge (Beckman).
1.2Methods
1.2.1Cell-cultureHSC-T6 cells were seeded in 6-well plate at 1×105cells/well in 2 ml and cultured in DMEM high-glucose medium with 10% fetal bovine serum and incubated in a 37 ℃ 5% carbon dioxide with saturated humidity for 12 h.Then cells at logarithmic growth phase were taken for follow-up experiments.
1.2.2Detection of the HSC-T6 cells activationThe cell culture medium was collected and cell protein samples were extracted in 0,24,48 and 72 h respectively.The level of CollagenⅠin culture medium was detected with ELISA method and the expression of α-SMA protein was detected with Western blotting method as follows.Protein was extracted from the HSC-T6 cells.The protein concentration was measured by bicinchoninic acid protein assay reagents (Beyotime Biotechnology,China).The sample (30 μg of protein) was separated on a 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and then transferred to a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane.Membrane blocking was performed in 5% bovine serum albumin Tris buffer containing 0.05% Tween 20 (TBST) at room temperature for 2 h.The blots were incubated with antibodies against α-SMA (1∶1 000,Proteintech,China) and GAPDH (1∶5 000,Proteintech,China) overnight at 4 ℃.All antibodies were diluted in TBST.After the incubation,the membranes were washed and incubated in goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP (1∶2 000,Proteintech,China) or goat anti-mouse IgG-HRP (1∶2 000,Proteintech,China) for 1 h at room temperature.Finally,the Bio-Rad CCD imaging system was used to obtain images and analyze the gray value of the protein band after ECL chemiluminescence.
1.2.3Screening of drug concentrationThe cells were grouped and treated with oleanolic acid (0,10,20,40,60,80,100 μmol/l),and SFN (0,0.5,1,2,5,7.5,10,25 μmol/l) respectively.After 24 h treatment,the survival rate of each group was measured by the MTT method.The calculation was processed as follow:(OD value of sample - OD value of blank well) / (OD value of Control - OD value of blank well) × 100%.
1.2.4The effects of OA on HSC-T6 cellsControl group,low-dose group (10 μmol/l),middle-dose group (20 μmol/l) and high-dose group (40 μmol/l) were set.The cells were treated by oleanolic acid for 24 h.The culture medium was collected and cell protein samples were extracted respectively.The content of CollagenⅠin culture medium was detected with ELISA method and the expression of α-SMA protein and intra-nuclear Nrf2 protein (1∶1 000,Abcam,USA) was detected with Western blotting method.
1.2.5siRNA on Nrf2 of HSC-T6 cellsControl group,low-dose group (10 μmol/l),middle-dose group (20 μmol/l),high-dose group (40 μmol/l),siRNA group,siRNA + low-dose group (10 μmol/l),siRNA + middle-dose group (20 μmol/l),siRNA + high-dose group (40 μmol/l) were set.For siRNA,siRNA + low-dose,siRNA + middle-dose,and siRNA + high-dose groups,the 120 μl 1 × dilution buffer mixed with 10 μl siRNA and 12 μL reagent in kit was added to the wells.The cells were continuously incubated for 12 h and then treated by oleanolic acid for 24 h.The contents of CollagenⅠand the levels of α-SMA and intra-nuclear Nrf2 protein were detected.
1.2.6SFN on Nrf2 of HSC-T6 cellsControl Group,low-dose group (10 μmol/l),middle-dose group (20 μmol/l),high-dose group (40 μmol/l),SFN group,SFN + low-dose group (10 μmol/l),SFN + middle-dose group (20 μmol/l),and SFN + high-dose group (40 μmol/l) were set.After 24 h treatment,cell culture medium was collected and cell protein samples were extracted.The content of CollagenⅠand the levels of α-SMA and intra-nuclear Nrf2 protein were detected.
1.2.7Statistical analysisData were presented as the mean±standard deviation and analyzed using a one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan's multiple range test and Dunnett's T3 (P<0.05 ) using SPSS 19.0 Software (SAS,Raleigh,NC,USA).
2 Results
2.1HSC-T6 cells had no spontaneous activationThere was no significant difference in α-SMA protein level and collagen I content at 0,24,48 and 72 h (P>0.05,Fig 1),indicating that HSC-T6 cells have no spontaneous activation within 72 h,and the experiment can be carried out within 72 h.

A:the expression of α-SMA protein was detected with Western blotting method; B:statistical result of α-SMA protein expression; C:content of collagenⅠ(Mean±SD,n=3). Fig 1 Whether HSC-T6 cells have spontaneous activation or not
2.2Screening for drug concentrationDoses of oleanolic acid were decided by MTT to be 0,10,20 and 40 μmol/l (Fig 2).Compared with control group,it was found that α-SMA protein expression and collagenⅠcontent in middle and high dose groups were higher prominently (P<0.05,Fig 3),and intra-nuclear Nrf2 protein expression was also higher.This suggested that oleanolic acid could activate HSC-T6 cell.For SFN,the dose was decided to be 5 μmol/l.

*P<0.05,in comparison with control group (Mean±SD,n=3). Fig 2 Dose Screening for Oleanolic Acid and SFN
2.3siRNA on Nrf2 of HSC-T6 cellsAfter siRNA on Nrf2,intra-nuclear Nrf2 levels was lower prominently (P<0.05),indicating thatsiRNA was transfected smoothly (Fig 5).In comparison with control group,α-SMA protein expression and CollagenⅠcontent were higher obviously (P<0.05) in siRNA group (Fig 6).This suggested that the lower level of Nrf2 protein could stimulate HSC-T6 cell activation,and that Nrf2 could play a protective role in the activation.Compared with the low-dose group,it was found that the siRNA combined with low-dose oleanolic acid could induce the α-SMA protein expression and collagenⅠ.However the α-SMA protein expression and CollagenⅠwere less than in siRNA group.This suggested that oleanolic acid may stimulate Nrf2,which in turn inhibit the protein expression of α-SMA and the secretion of CollagenⅠ.

A:detecting α-SMA protein expression by western blotting; B:statistical results of α-SMA protein expression; C:CollagenⅠcontent.*P<0.05,in comparison with control group; #P<0.05,in comparison with low group (Mean±SD,n=3). Fig 3 Impact of oleanolic acid on HSC-T6 cell activation
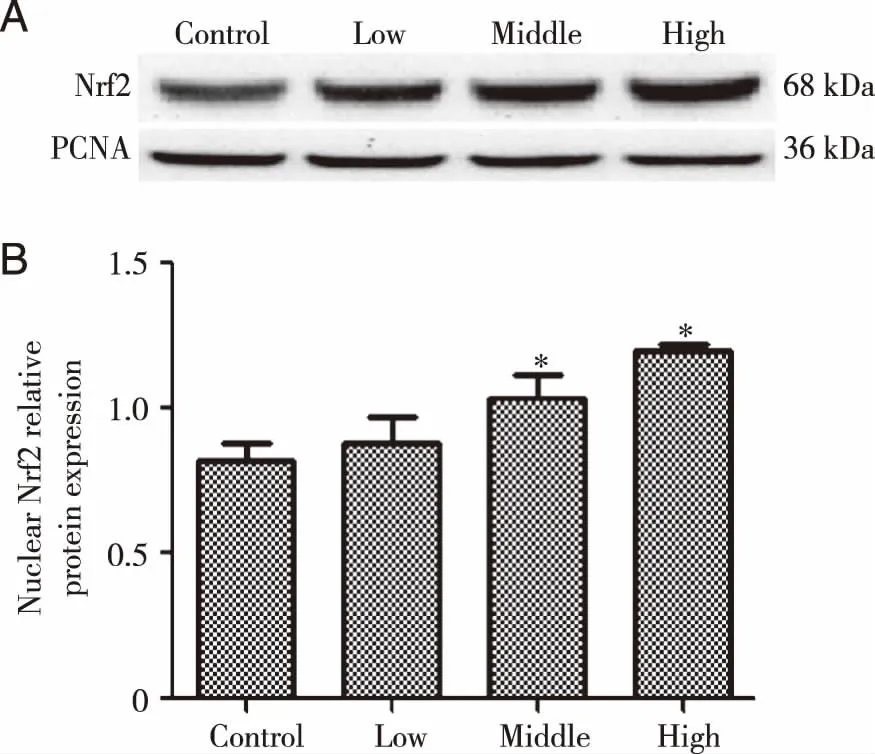
A:detecting intranuclear Nrf2 protein expression by western blotting; B:statistical results of intranuclear Nrf2 protein expression.*P<0.05,in comparison with control group (Mean±SD,n=3). Fig 4 Impact of oleanolic acid on Nrf2 of HSC-T6 cell

A:detecting intranuclear Nrf2 protein expression by western blotting; B:statistical results of intranuclear Nrf2 protein expression.*P<0.05,in comparison with control group (Mean±SD,n=3). Fig 5 Impact of siRNA on Nrf2 of HSC-T6 cell

A:detecting α-SMA protein expression by western blotting; B:statistical results of α-SMA protein expression;C:collagenⅠcontent.*P<0.05,in comparison with control group;△P<0.05,in comparison with without siRNA group;#P<0.05,in comparison with siRNA group (Mean±SD,n=3). Fig 6 Impact of siRNA and OA combination on HSC-T6 cell
2.4SFN on Nrf2 of HSC-T6 cellsAfter treatment of SFN,intra-nuclear Nrf2 protein level was higher significantly (P<0.05),which meant SFN was able to activate Nrf2 (Fig 7).In comparison with control group,α-SMA protein expression and CollagenⅠcontent were lower prominently (P<0.05) after administration of SFN (Fig 8).This meant Nrf2 was able to inhibit activation of HSC-T6.Compared with the low-dose and SFN group,it was found that the SFN combined with low-dose oleanolic acid could reduce the α-SMA protein expression and collagenⅠ.This suggested that oleanolic acid may stimulate Nrf2 which could inhibit the protein expression of α-SMA and the secretion of collagenⅠ.

A:detecting intranuclear Nrf2 protein expression by western blotting; B:statistical results of intranuclear Nrf2 protein expression.*P<0.05,in comparison with control group (Mean±SD,n=3). Fig 7 Impact of SFN on Nrf2 of HSC-T6 cell

A:detecting α-SMA protein expression by western blotting; B:statistical results of α-SMA protein expression; C:collagenⅠcontent.*P<0.05,in comparison with control group; △P<0.05,in comparison with without SFN group; #P<0.05,in comparison with SFN group (Mean±SD,n=3). Fig 8 Impact of SFN and OA combination on HSC-T6 cell
3 Discussion
It was found no prominent changes in α-SMA protein expression and collagenⅠcontent of HSC-T6 cell in 72 h.Thus,the experiment could be finished in 3 days and would not be affected.After different doses of oleanolic acid were administered,α-SMA protein expression and collagen Ⅰ content were higher prominently in middle and high dose groups.This meant a high dose of oleanolic acid was able to activate HSC-T6 cell.And intra-nuclear Nrf2 protein expression was higher prominently.Intra-nuclear Nrf2 protein expression was found to be lower prominently during detection by western blotting.This meant siRNA silences Nrf2 smoothly.In control and low dose group,α-SMA protein expression and Collagen I content were higher prominently after siRNA had been silent.However,in high dose group,α-SMA protein expression was lower prominently after siRNA had been silent.As a result,role of Nrf2 in hepatic fibrosis incurred by oleanolic acid was still unclear.Thus,the stimulation of Nrf2 protein further explored its mechanism.We used 5 μM SFN to find by western blotting that intra-nuclear Nrf2 protein expression is higher prominently.This meant SFN was an effective agonist for Nrf2.After the treatment of SFN,α-SMA protein expression and collagenⅠcontent were lower prominently,which meant Nrf2 can play a protective role.
When hepatic stellate cells were damaged,the α-SMA expression was higher prominently.With phenotype change,hepatic stellate cells were transformed into transitional cells so as to synthesize matrix protein in a way that helps tissue repair[11].When the stimulus was released,phenotype of the cell was recovered.The number of cells may become normal again due to apoptosis.However,if the stimulus continued,hepatic stellate cell would continue to proliferate.Prominent change in phenotype made hepatic stellate cell transformed into myofibroblasts.Myofibroblasts,a main cell that produces ECM,increases collagen synthesis by autocrine,inhibits production of its collagenase,and plays a major role in formation of hepatic fibrosis[12].Thus,α-SMA protein expression and collagenⅠcontent could prove whether HSC-T6 cell was activated.HSC-T6 cell could be used as a good hepatic fibrosis model to study the mechanism of Nrf2 in hepatic fibrosis incurred by oleanolic acid.
The Nrf2 pathway is an important regulator of oxidative stress.Oxidative stress refers to degraded ROS overproduction and anti-oxidative defense in cells or tissues,causing a serious imbalance between both and cell damage.ROS would incur hepatic fibrosis.In hepatic tissue,ROS stress production is increased and removal is decreased,giving rise to peroxidation damage of hepatic cells,Kupffer cells and hepatic stellate cells.ROS and extracellular matrix occurring then will further promote activation of hepatic stellate cells[13-14].In case of a stable internal environment,Nrf2 is combined with Keap1 to be inactivated.After being stimulated by ROS or electrophile and inflammatory factor,Keap1is uncoupled with Nrf2.After entering the nucleus,Nrf2 is combined with macrophage activation factor (Maf) protein so as to form hybrid dimer recognition.And it is combined with antioxidant response element (ARE) to induce downstream heme oxygenase (HO-1),quinone oxidoreductase (NQO1),glutamyl cysteine synthetase catalytic subunit (GCLC),regulatory subunit of bovine glutamatecysteine ligase (GCLM),and other gene expressions[15-16].As a result,antioxidation,anti-tumor,anti-inflammation and anti-apoptosis of cells and tissues are improved so as to play a role in protecting cells[15,17-18].As isothiocyanate,sulforaphane (sulforafan,1-isothiocyanic acid-4-methanesulfonyl butane) plays a certain role in anti-tumor,antioxidation,anti-inflammation and immunoregulation and exists widely in brassica oleracea and broccoli in crucifer[19].It is an important activator of Nrf2 and able to allow Nrf2 to enter cell nucleus and start expression of ARE downstream antioxidant enzyme[20].It was verified by our experiment that SFN could effectively antagonize hepatic fibrosis incurred by oleanolic acid.
To conclude,our study shows that Nrf2 pathway can inhibit the hepatic fibrosis incurred by oleanolic acid.
