阿尔茨海默病患病率的Meta分析
2018-05-23张宏博钱登娟
张宏博 徐 勇 陈 彬 钱登娟 杭 蕾
(苏州大学公共卫生学院,江苏 苏州 215123)
阿尔茨海默病(AD)是老年痴呆的主要亚型,占全部痴呆类型的60%~80%〔1〕。有研究显示,在高龄老人中,女性老年痴呆患病率高于男性,而在其亚型AD中,这种性别差异更加明显〔2~12〕。在研究对象为≥60岁老年人的研究中,一些研究显示女性老年痴呆患病率与男性并没有差异,其亚型血管性痴呆(VD)男性的发病风险高于女性〔13~30〕,而女性AD患病率仍高于男性〔6,8~10,18,26,27,29,31~44〕。目前全世界关于AD患病率的调查已有较多报道,然而由于受样本量、研究设计方案、调查对象年龄、调查区域等多方面的影响,AD患病率结果不一。因此,本研究采用 Meta 分析方法综合1990年以来已经发表的有关老年人群AD患病率结果,并主要针对性别差异进行亚组分析,以期了解现阶段老年人群AD的患病率。
1 资料与方法
1.1资料检索 通过计算机检索电子数据库,以“Alzheimer′ s disease OR AD”、“prevalence” 为检索词,检索 PubMed外文数据库中有关老年人群AD的文献,检索时间为1990年1月至2016年1月,并手工检索初步筛选文献的参考文献。
1.2纳入标准 ①以一般人群为基础并且样本量大于200的横断面调查;②研究为概率抽样;③有标准的疾病诊断方法;④语种限于英文。
1.3排除标准 ①特殊样本,不能代表一般人群,如以女性为研究对象、以医院患者为研究对象;②研究设计方案不明确;③文献中的原始数据无法进行提取或者无法转化的;④重复发表、重复收录或资料雷同的研究。
1.4文献摘录 用Microsoft excel 2010建立信息摘录数据库,从文献中摘录以下内容:作者、 发表时间、研究起止时间(或研究开始时间)、研究地区、设计类型、样本量、应答率、筛检试验、诊断试验、AD粗患病率(调整患病率)。
1.5文献质量评价 由2009年世界阿尔茨海默病报告(WAR)〔45〕建议的文献质量评分来评价文献质量:①样本量<500,0.5分;500~1 499,1分;1 500~2 999,1.5分;≥3 000,2分。②两阶段的设计方法如果没有筛检阴性者,0分;两阶段的设计方法有筛检阴性者但是没有权重,1分;有合适的抽样方法和权重的一阶段或2阶段设计方法。③应答率<60%,1分;60%~79%,2分;≥80%,3分。④诊断标准涉及成套多功能认知测试、常规残疾评估、信息采访、临床采访。
1.6统计学方法 使用Stata/SE12.0软件进行Meta分析。先进行异质性检验,当I2>50%时,认为存在异质性。存在异质性时选择随机效应模型的计算方法,否则选择固定效应模型。效应量采用单样本率及其95%CI得到合并的AD患病率、不同年龄段AD及不同性别AD患病率。
2 结 果
2.1纳入文献研究基本情况 根据上述检索方式,总共检索到963篇有关AD患病率的文献,根据纳入和排除标准最终纳入分析的有44篇〔46~89〕,涉及亚洲、欧洲、非洲和美洲,合计样本量为172 444例,其中AD患者6 093例。在所纳入的文献中,其中有18篇来自亚洲,3篇来自非洲,16篇来自欧洲,6篇来自美洲,1 篇涉及美洲和非洲;13篇调查人群为农村居民,6篇为城市居民,11篇农村和城市居民均有,14篇未提及;研究对象为60岁以上老年人的文献为36篇,AD患病率为1.1%~20.5%,研究对象为70岁以上老年人文献为6篇,AD患病率为3.0%~11.0%,研究对象为85岁以上老年人的文献为2篇,患病率分别为16.0%与21.5%。纳入文献的一般情况见表1。
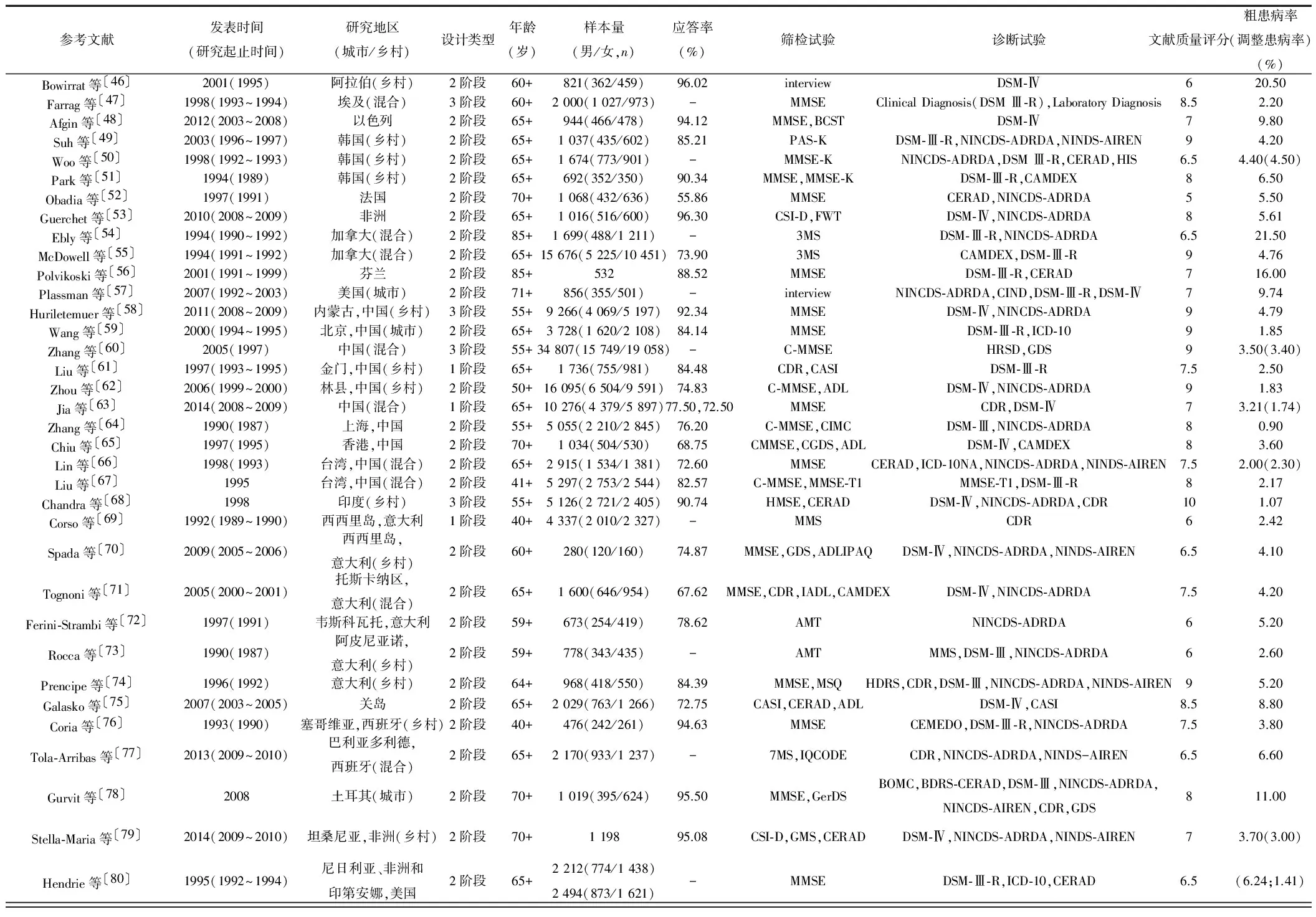
表1 纳入文献的基本情况

续表1 纳入文献的基本情况
2.2异质性检验及总体患病率分析 异质性检验结果显示各研究间存在异质性(I2=98.6%,P<0.001),故采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析,纳入的44篇文献的合并效应量结果显示,AD患病率为4.9%(95%CI:4.3%~5.5%)。
2.3不同亚组AD患病率 对年龄、性别等不同特征进行亚组分析,结果显示,男性和女性AD患病率分别为3.0%(95%CI:2.5%~3.4%)和6.1%(95%CI:5.3%~6.9%);各年龄亚组患病率见表2,各年龄亚组男性和女性AD患病率见表3。
2.4发表偏移评估 漏斗图(图1)结果显示研究可能不存在发表偏倚,Begg秩相关显示Z=2.80,P=0.005,见图2,Egger回归分析显示t=1.78,P=0.082,见图3。

表3 不同年龄亚组AD患病情况

表2 不同年龄性别亚组AD患病情况

图1 纳入文献漏斗图

图2 Begg秩相关

图3 Egger回归分析
3 讨 论
本研究得出老年人群AD患病率为4.9%(95%CI:4.3%~5.5%),高于Suh等〔89〕通过综述得到的全世界患病率(4.3%)及Ferri等〔90〕对全世界AD患病率进行综述分析得到的患病率(3.9%)。AD是老年痴呆的主要亚型,但是其患病情况和老年痴呆及VD相比有差异,尤其在患病情况的性别差异方面。国内外较多研究显示,男女老年痴呆患病率并没有差异,而AD女性患病率总是高于男性,在较低年龄人群中男性AD患病率高于女性〔2~6,8~12,18,26,27,29,31~44〕。本研究亚组分析结果显示,总体女性AD患病率高于男性,并且在每个年龄亚组中,女性患病率仍高于男性。本研究年龄亚组分析结果显示,AD患病率随着年龄的升高而明显升高,并且在极高龄年龄组中(90~95岁)患病率仍呈现升高的趋势,但是由于极高龄人群数据资料有限,AD在极高年龄人群患病率是否仍然持续升高还有待更多研究加以证实。
4 参考文献
1Carter CL,Resnick EM,Mallampalli M,etal.Sex and gender differences in Alzheimer′s disease:recommendations for future research〔J〕.J Womens Health,2012;21(10):1018-23.
2Hofman A,Rocca WA,Brayne C,etal.The prevalence of dementia in europe:a collaborative study of 1980-1990 findings〔J〕.Int J Epidemiol,1991;20(3):290-1.
3Andersen K,Launer LJ,Dewey ME,etal.Gender differences in the incidence of AD and vascular dementia:The EURODEM Studies.Euroem Incidence Research Group〔J〕.Neurology,1999;53:1992-7.
4Ruitenberg A,Ott A,Swieten JCV,etal.Incidence of dementia:does gender make a difference〔J〕.Neurobiol Aging,2001;22(4):575-80.
5Letenneur L,Gilleron V,Commenges D,etal.Are sex and educational level independent predictors of dementia and Alzheimer′s disease?Incidence data from the PAQUID project〔J〕.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat,1999;66(2):177-83.
6Brayne C,Gill C,Huppert FA,etal.Incidence of clinically diagnosed subtypes of dementia in an elderly population.Cambridge Project for Later Life〔J〕.Br J Psychiatry,1995;167:255-62.
7Clarke D,Morgan K,Lilley J,etal.Dementia and ′borderline dementia′ in Britain:8-year incidence and post-screening outcomes〔J〕.Psychol Med,1996;26:829-35.
8Fratiglioni L,Viitanen M,Von Strauss E,etal.Very old women at highest risk of dementia and Alzheimer′s disease:incidence data from the Kungsholmen project,Stockholm〔J〕.Neurology,1997;48:132-8.
9Morgan K,Lilley JM,Arie T,etal.Incidence of dementia in a representative British sample〔J〕.Br J Psychiatry,1993;163:467-70.
10Yoshitake T,Kiyohara Y,Kato I,etal.Incidence and risk factors of vascular dementia and Alzheimer′s disease in a defined elderly Japanese population:the Hisayama study〔J〕.Neurology,1995;45:1161-8.
11Jorm AF,Jolley D.The incidence of dementia:a metaanalysis〔J〕.Neurology,1998;51:728-33.
12Gussekloo J,Heeren T,Izaks G,etal.A community based study of the incidence of dementia in subjects aged 85 years and over〔J〕.Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry,1995;59:507-10.
13Hebert LE,Scherr PA,Mccann JJ,etal.Is the risk of developing Alzheimer′s disease greater for women than for men〔J〕?Am J Epidemiol,2001;153(2):132-6.
14Elby E,Parhad I,Hogan D,etal.Prevalence and types of dementia in the very old:results from the Canadian Study of Health and Aging〔J〕.Neurology,1994;44:1593-600.
15Yamada M,Sasaki H,Mimori Y,etal.Prevalence and risks of dementia in the Japanese population:RERF′s adult health study Hiroshima subjects〔J〕.Am Geriatr Soc,1999;47:189-95.
16Pfeffer RI,Afifi AA,Chance JM,etal.Prevalence of Alzheimer′s disease in a retirement community〔J〕.Am J Epidemiol,1987;125:420-36.
17Liu H,Lin K,Teng E,etal.Prevalence and subtypes of dementia in Taiwan:a community survey of 5279 individuals〔J〕.Am Geriatr Soc,1995;43:144-9.
18Rorsman B,Hagnell O,Lanke J.Prevalence and incidence of senile and multi-infarct dementia in the Lundby Study:a comparison between the time periods 1947-1957 and 1957-1972〔J〕.Neuropsychobiology,1986;15:122-9.
19Prencipe MA,Casini A,Ferretti C,etal.Prevalence of dementia in an elderly rural population:effects of age,sex and education〔J〕.Neurology,1996;60:628-33.
20Skoog I,Nilsson L,Palmertz B,etal.A population-based study of dementia in 85-year-olds〔J〕.N Engl J Med,1993;328:153-8.
21Li S,Yan F,Li G,etal.Is the dementia rate increasing in Beijing?Prevalence and incidence of dementia 10 years later in an urban elderly population〔J〕.Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica,2007;115(1):73-9.
22Li G,Shen YC,Chen CH,etal.An epidemiological survey of age-related dementia in an urban area of Beijing〔J〕.Acta Psychiatr Scand,1989;79:557-63.
23Li G,Shen YC,Chen CH,etal.A three-year follow-up study of age-related dementia in an urban area of Beijing〔J〕.Acta Psychiatr Scand,1991;83:99-104.
24Kukull WA,Higdon R,Bowen JD,etal.Dementia and Alzheimer disease incidence:a prospective cohort study〔J〕.Arch Neurol,2002;59:1737-46.
25Jorm AF,Jolley D.The incidence of dementia:a metaanalysis〔J〕.Neurology,1998;51:728-33.
26Paykel ES,Brayne C,Huppert FA,etal.Incidence of dementia in a population older than 75 years in the United Kingdom〔J〕.Arch General Psychiatry,1994;51(4):325-32.
27Bachman DL,Wolf PA,Linn RT,etal.Incidence of dementia and probable Alzheimer′s disease in a general population:the Framingham Study〔J〕.Neurology,1993;43:515-9.
28Ganguli M,Dodge HH,Chen P,etal.Ten-year incidence of dementia in a rural elderly US community population:the movies project〔J〕.Neurology,2000;54:1109-16.
29Letenneur L,Commenges D,Dartigues JF,etal.Incidence of dementia and Alzheimer′s disease in elderly community residents of southwestern France〔J〕.Int J Epidemiol,1994;23:1256-61.
30Rocca WA,Cha RH,Waring SC,etal.Incidence of dementia and Alzheimer′s disease:a reanalysis of data from Rochester,Minnesota,1975-1984〔J〕.Am J Epidemiol,1998;148:51-62.
31Launer LJ,Andersen K,Dewey ME,etal.Rates and risk factors for dementia and Alzheimer′s disease:results from EURODEM pooled analyses〔J〕.Neurology,1999;52(1):78.
32Bachman DL,Wolf PA,Linn R,etal.Prevalence of dementia and probable senile dementia of the Alzheimer type in the Framingham Study〔J〕.Neurology,1992;42:115-9.
33Canadian Study of Health and Aging Working Group.Canadian Study of Health and Aging:study methods and prevalence of dementia〔J〕.Can Med Assoc J,1994;150:899-913.
34Corso EA,Campo G,Triglio A,etal.Prevalence of moderate and severe Alzheimer′s dementia in the population of southeastern Sicily〔J〕.Ital J Neurol Sci,1992;13:215-19.
35Friedland RP,Bowirrat A,Treves T,etal.Alzheimer′s disease prevalence is high in Israeli Arabs.(Abstract)〔J〕.Neurobiol Aging,1998;19(suppl):S139.
36Folstein MF,Bassett SS,Anthony JC,etal.Dementia:case as certainment in a community survey〔J〕.Gerontology,1991;46:M132-8.
37Manubens J,Martinez-Lage J,Larcruz F,etal.Prevalence of Alzheimer′s disease and other dementing disorders in Pamplona,Spain〔J〕.Neuroepidemiology,1995;14:155-64.
38Lopez Pousa S,Llinas Regla J,Vilalta Franch J,etal.The prevalence of dementia in Girona〔J〕.Neurologia,1995;10:189-93.
39Graves AB,Larson EB,Edland SD,etal.Prevalence of dementia and its subtypes in the Japanese American population of King County,Washington State:The Kame Project〔J〕.Am J Epidemiol,1996;144:760-71.
40Kiyohara Y,Yoshitake T,Kato I,etal.Changing patterns in the prevalence of dementia in a Japanese community:The Hisayama Study〔J〕.Gerontology,1994;40(suppl 2):19-35.
41Woo JI,Lee JH,Yoo KY,etal.Prevalence estimation of dementia in a rural area of Korea〔J〕.Am Geriatr Soc,1998;46:983-7.
42Gao S,Hendrie HC,Hall KS,etal.The relationships between age,sex,and the incidence of dementia and Alzheimer′s disease:a meta-analysis〔J〕.Arch Gen Psychiatry,1998;55:809-15.
43Zhou DF,Wu CS,Qi H,etal.Prevalence of dementia in rural China:impact of age,gender and education〔J〕.Acta Neurologica Scandinavica,2006;114(4):273-80.
44Fratiglioni L,Launer LJ,Andersen K,etal.Incidence of dementia and major subtypes in Europe:a collaborative study of population-based cohorts.Neurologic Diseases in the Elderly Research Group〔J〕.Neurology,2000;54(11 Suppl 5):S10-5.
45Alzheimer′s Disease International.World Alzheimer′s report 2009〔R〕.London:Alzheimer′s Disease International,2009.
46Bowirrat A,Treves T,Friedland R,etal.Prevalence of Alzheimer′s type dementia in an elderly Arab population〔J〕.Eur J Neurol,2001;8(2):119-23.
47Farrag AKF,Farwiz HM,Khedr EH,etal.Prevalence of Alzheimer′s disease and other dementing disorders:Assiut-Upper Egypt study〔J〕.Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord,1998;9(6):323-8.
48Afgin AE,Massarwa M,Schechtman E,etal.High prevalence of mild cognitive impairent and Alzheimer′s disease in arabic villages in northern Israel:impact of gender and education〔J〕.Alzheiers Dis,2012;29(2):431-9.
49Suh GH,Kim JK,Cho MJ.Community study of dementia in the older Korean rural population〔J〕.Aust N Z J Psychiatry,2003;37(5):606-12.
50Woo JI,Lee JH,Yoo KY,etal.Prevalence estimation of dementia in a rural area of Korea〔J〕.Am Geriatr Soc,1998;46(8):983-7.
51Park J,Ko HJ,Park YN,etal.Dementia among the elderly in a rural Korean community〔J〕.Br J Psychiatry,1994;164(6):796-801.
52Obadia Y,Rotily M,Degrand-Guillaud A,etal.The PREMAP Study:prevalence and risk factors of dementia and clinically diagnosed Alzheimer′s disease in Province,France.Prevalence of Alzheimer′s Disease in Provence〔J〕.Eur J Epidemiol,1997;13(3):247-53.
53Guerchet M,M′belesso P,Mouanga AM,etal.Prevalence of dementia in elderly living in two cities of Central Africa:the EDAC survey〔J〕.Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord,2010;30(3):261-8.
54Ebly EM,Parhad IM,Hogan DB,etal.Prevalence and types of dementia in the very old:results from the Canadian Study of Health and Aging〔J〕.Neurology,1994;44(9):1593-600.
55McDowell I,Hill G,Lindsay J.Canadian study of health and aging:study methods and prevalence of dementia〔J〕.CMAJ,1994;150(6):899-913.
56Polvikoski T,Sulkava R,Myllykangas L,etal.Prevalence of Alzheimer′s disease in very elderly people:a prospective neuropathological study〔J〕.Neurology,2001;56(12):1690-6.
57Plassman BL,Langa KM,Fisher GG,etal.Prevalence of dementia in the United States:the aging,demographics,and memory study〔J〕.Neuroepidemiology,2007;29(1-2):125-32.
58Huriletemuer H,Wen S,Zhang C,etal.An epidemiological study of Alzheimer′s disease in elderly Mongolian and Hanpopulations living in rural areas of Inner Mongolia〔J〕.Aging Clin Exp Res,2011;23(5-6):470-5.
59Wang W,Wu S,Cheng X,etal.Prevalence of Alzheimer′s disease and other dementing disorders in an urban community of Beijing,China〔J〕.Neuroepidemiology,2000;19(4):194-200.
60Zhang ZX,Zahner GE,Román GC,etal.Dementia subtypes in China:prevalence in Beijing,Xian,Shanghai,and Chengdu〔J〕.Arch Neurol,2005;62(3):447-53.
61Liu HC,Fuh JL,Wang SJ,etal.Prevalence and subtypes of dementia in a rural Chinese population〔J〕.Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord,1998;12(3):127-34.
62Zhou DF,Wu CS,Qi H,etal.Prevalence of dementia in rural China:impact of age,gender and education〔J〕.Acta Neurol Scand,2006;114(4):273-80.
63Jia J,Wang F,Wei C,etal.The prevalence of dementia in urban and rural areas of China〔J〕.Alzheimers Dement,2014;10(1):1-9.
64Zhang MY,Katzman R,Salmon D,etal.The prevalence of dementia and Alzheimer′s disease in Shanghai,China:impact of age,gender,and education〔J〕.Ann Neurol,1990;27(4):428-37.
65Chiu HF,Lam LC,Chi I,etal.Prevalence of dementia in Chinese elderly in Hong Kong〔J〕.Neurology,1998;50(4):1002-9.
66Lin RT,Lai CL,Tai CT,etal.Prevalence and subtypes of dementia in southern Taiwan:impact of age,sex,education,and urbanization〔J〕.Neurol Sci,1998;160(1):67-75.
67Liu HC,Lin KN,Teng EL,etal.Prevalence and subtypes of dementia in Taiwan:a community survey of 5297 individuals〔J〕.Am Geriatr Soc,1995;43(2):144-9.
68Chandra V,Ganguli M,Pandav R,etal.Prevalence of Alzheimer′s disease and other dementias in rural India:the Indo-US study〔J〕.Neurology,1998;51(4):1000-8.
69Corso EA,Campo G,Triglio A,etal.Prevalence of moderate and severe Alzheimer dementia and multi-infarct dementia in the population of southeastern Sicily〔J〕.Ital J Neurol Sci,1992;13(3):215-9.
70Spada RS,Stella G,Calabrese S,etal.Prevalence of dementia in mountainous village of Sicily〔J〕.Neurol Sci,2009;283(1-2):62-5.
71Tognoni G,Ceravolo R,Nucciarone B,etal.From mild cognitive impairment to dementia:a prevalence study in a district of Tuscany,Italy〔J〕.Acta Neurol Scand,2005;112(2):65-71.
72Ferini-Strambi L,Marcone A,Garancini P,etal.Dementing disorders in north Italy:prevalence study in Vescovato,Cremona Province〔J〕.Eur J Epidemiol,1997;13(2):201-4.
73Rocca WA,Bonaiuto S,Lippi A,etal.Prevalence of clinically diagnosed Alzheimer′s disease and other dementing disorders:a door-to-door survey in Appignano,Macerata Province,Italy〔J〕.Neurology,1990;40(4):626-31.
74Prencipe M,Casini AR,Ferretti C,etal.Prevalence of dementia in an elderly rural population:effects of age,sex,and education〔J〕.Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry,1996;60(6):628-33.
75Galasko D,Salmon D,Gamst A,etal.Prevalence of dementia in Chamorros on Guam:relationship to age,gender,education,and APOE〔J〕.Neurology,2007;68(21):1772-81.
76Coria F,Gomez de Caso JA,Minguez L,etal.Prevalence of age-associated memory impairment and dementia in a rural community〔J〕.Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry,1993;56(9):973-6.
77Tola-Arribas MA,Yugueros MI,Garea MJ,etal.Prevalence of dementia and subtypes in Valladolid,northwestern Spain:the deminvall study〔J〕.PLoS One,2013;8(10):e77688.
78Gurvit H,Emre M,Tinaz S,etal.The prevalence of dementia in an urban Turkish population〔J〕.Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen,2008;23(1):67-76.
79Stella-Maria Paddick,Anna Longdon,Aloyce Kisoli,etal.The prevalence of dementia sub-types in rural Tanzania〔J〕.Am J Geriatr Psychiatr,2014;37(5):606-12.
80Hendrie HC,Osuntokun BO,Hall KS,etal.Prevalence of Alzheimer′s disease and dementia in two communities:Nigerian Africans and African Americans〔J〕.Am J Psychiatry,1995;152(10):1485-92.
81Fratiglioni L,Grut M,Forsell Y,etal.Prevalence of Alzheimer′s disease and other dementias in an elderly urban population:relationship with age,sex,and education〔J〕.Neurology,1991;41(12):1886-92.
82Graves AB,Larson EB,Edland SD,etal.Prevalence of dementia and its subtypes in the Japanese American population of King County,Washington state.The Kame Project〔J〕.Am J Epidemiol,1996;144(8):760-71.
83Mathuranath PS,Cherian PJ,Mathew R,etal.Dementia in Kerala,South India:prevalence and influence of age,education and gender〔J〕.Int J Geriatr Psychiatry,2010;25(3):290-7.
84Kim KW,Park JH,Kim MH,etal.A nationwide survey on the prevalence of dementia and mid cognitive impairment in South Korea〔J〕.Alzheimers Dis,2011;23(2):281-91.
85Molero AE,Pino-Ramírez G,Maestre GE.High prevalence of dementia in a Caribbean population〔J〕.Neuroepidemiology,2007;29(1-2):107-12.
86Ott A,Breteler MM,van Harskamp F,etal.Prevalence of Alzheimer′s disease and vascular dementia:association with education.The Rotterdam study〔J〕.BMJ,1995;310(6985):970-3.
87Schouboe A,Andersen MH,Thomsen MS.Prevalence,resource utilization and costs of vascular dementia compared to Alzheimer′s dementia in a population setting〔J〕.Dementia Geriatr Cogn Disord,2005;19(1):305-15.
88Dimitrov I,Tzourio C,Milanov I,etal.Prevalence of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in a Bulgarian urban population〔J〕.Am J Alzheimer′s Dis Other Dement,2012;27(2):131-5.
89Suh GH,Shah A.A review of the epidemiological transition in dementia-cross-national comparisons of the indices related to Alzheimer′s disease and vascular dementia〔J〕.Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica,2001;104(1):4-11.
90Ferri CP,Martin P,Carol B,etal.Global prevalence of dementia:a Delphi consensus study〔J〕.Lancet,2005;366(9503):2112-7.
