Chemical constituents of the genus Pithecellobium:a systematic review
2018-04-02HanZhangZhiyangYanXiaoxiaoHuang
Han Zhang, Zhiyang Yan, Xiaoxiao Huang*
Department of Natural Products Chemistry, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang 110016, PR China
1 Introduction
Pithecellobium Mart, a perennial aiphyllium herb, is mainly distributed in tropical and subtropical regions, especially in tropical America.It was also found in Vietnam and India [1].There are four species distributed in China [2],including pithecellobium clypearia (Jack) Benth,Pithecellobium dulce (Roxb.) Benth, pithecellobium lucidum Benth, pithecellobium utile Chun & F. C.How. The leaves, stems, fruits and seeds of plants in Pithecellobium Mart have been used as Chinese folk medicine for the treatment of rheumatalgia, wounds,acute tonsillitis, acute gastroenteritis and bacterial dysentery [3].
Previous studies on the chemical components of the genus revealed the presence of flavonoids,triterpenoids, steroids, phenolic acids, lignans.Among the compounds, the presence of flavonoids may be the reason for its prominent biological activities especially antiviral potentials [4].Therefore, the further study on the chemical compositions of the genus will contribute to the development of new drugs and make full use of natural medicinal resources. This paper summarized the latest research progress of chemical compositions of this genus.
2 Research progress of chemical constituents
2.1 Flavonoids
As the typical constituents in Pithecellobium Mart, flavonoids are effective antioxidants and may protect against several chronic diseases [5], which are the most typical constituents in Pithecellobium Mart. Forty-one compounds have been isolated from the Pithecellobium Mart at present. Among them,most of the flavonoids are classified into six types on the basis of their chemical structural characteristics and skeletons. They are flavanols, flavanones,flavones, isoflavones, flavonols and anthocyanins.
2.1.1 Flavans
Twenty flavans have been isolated and identified from the Pithecellobium Mart at present,which mainly exist in the P. clypearia and P. dulce.They are (-)-epigallocatechin (1) [6], (-)-5,7,3',4',5'-pentahydroxyflavan (2) [6], (+)-catechin (3) [7,8],robinetinidol (4) [9], 3',4',7-trihydroxy-3,4-flavandiol (5) [9,10], 3',4',5',7-tetrahydroxyflavan-3-flavandiol (6) [9], (2R,3R)-7,8,3',4'-tetrahydroxydihydroflavonol (7) [11], (2R,3S)-5,7,3'-tri-omethyl-(-)-epicatechin (8) [11], (-)-epigallocatechin-7-gallate (9) [6], (-)-5,3',4',5'-tetrahydroxyflavan-7-gallate (10) [6-7, 12], (-)-(2R,3R)-epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (11) [7], 7,3'-di-O-galloyltricetiflavan(12) [13,14], 7,4'-di-O-galloyltricetiflavan(13) [12-14], gallocatechin gallate (14) [8],epifisetinidol-4β-catechin (15), dimeric epicatechuns(16), bis-epifisetinidol-4β-catechin (17), fisetinidol-4β-catechin-epifisetinidol (18), trimeric epicatechuns(19), fisetinidol-4β-epicatechin-epifisetinidol(20) [15]. There are flavonoids with one or two galloyl groups in Pithecellobium Mart, such as compounds 9-14. In addition, several bisflavone were also found in this genus and mainly present in the methanol extract of P. dulce. Previous research showed that these bisflavones exhibited antibacterial activity [15]. Their structures are listed in Fig. 1.

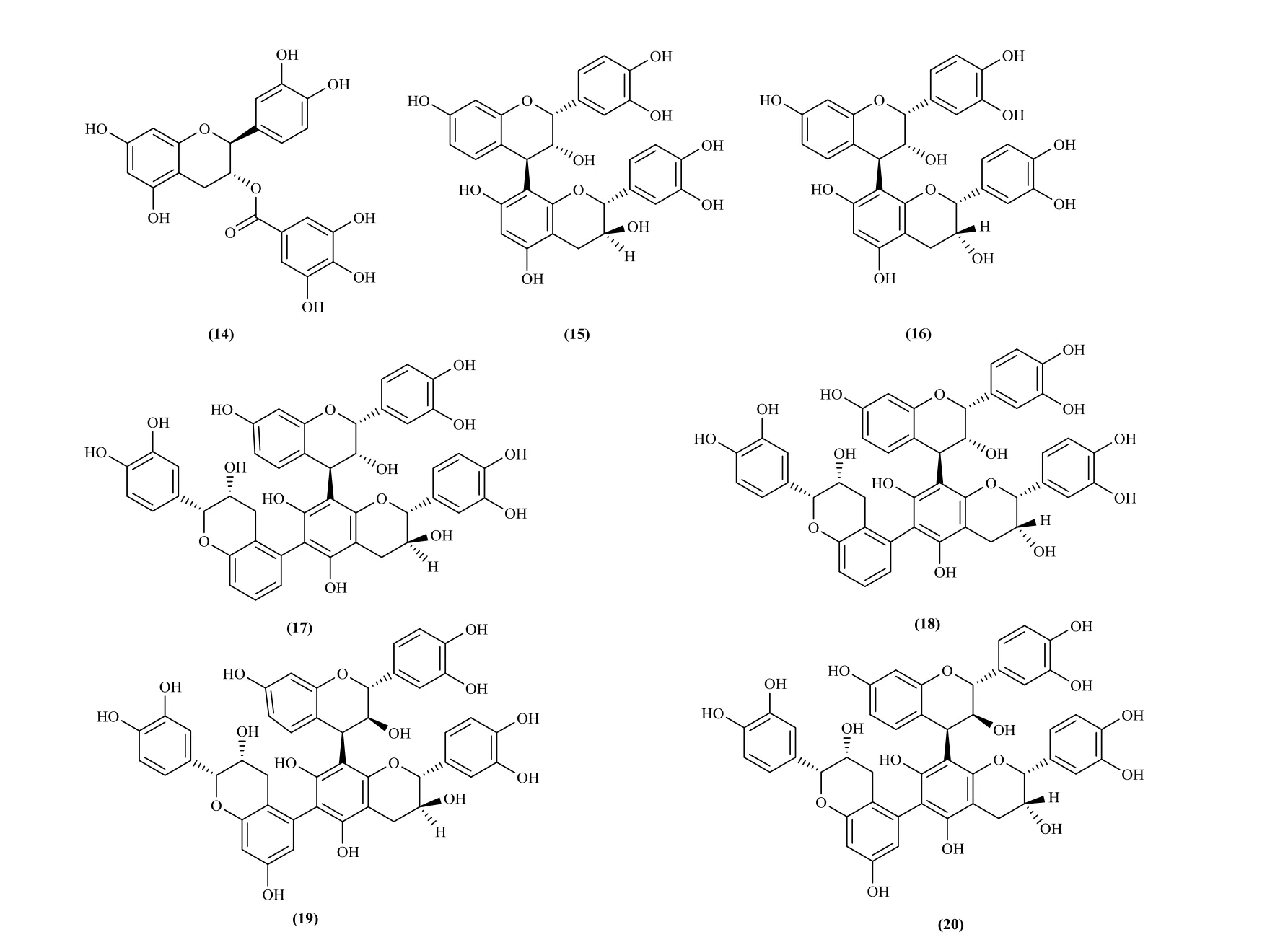
Fig. 1 Flavans in Pithecellobium Mart
2.1.2 Flavones and flavonoid glycosides
It is reported that there are a number of flavones and flavonoid glycosides in Pithecellobium Mart,which mainly exist in P. clypearia and P. dulce.They are 5-hydroxy-3,7,3',4'-tetramethoxyflavone(21) [16], 5,4'-dihydroxy-3,7,3'-trimethoxyflavone(22) [16], luteolin (23) [11,16], kaempferol(24) [8,17], quercetin (25) [11], quercitin-3-O-α-L-rhamnpyranoside (26) [6,18], myricitin-3-O-α-L-rhamnpyranoside (27) [6,18], luteoloside (28) [18],kaempferol-3-Ο-α-L-rhamnosid (29) [19],3'-prenylapigenine-7-O-rutinoside (30) [20], homoflavoyadorinin-B (31), rhamnazin-4'-Ο-α-D-[apiosyl(1→2)glucoside] (32), flavoyadorinin B(33), rhamnazin-3,4'-di-O-glucoside (34) [21] (Fig.2).
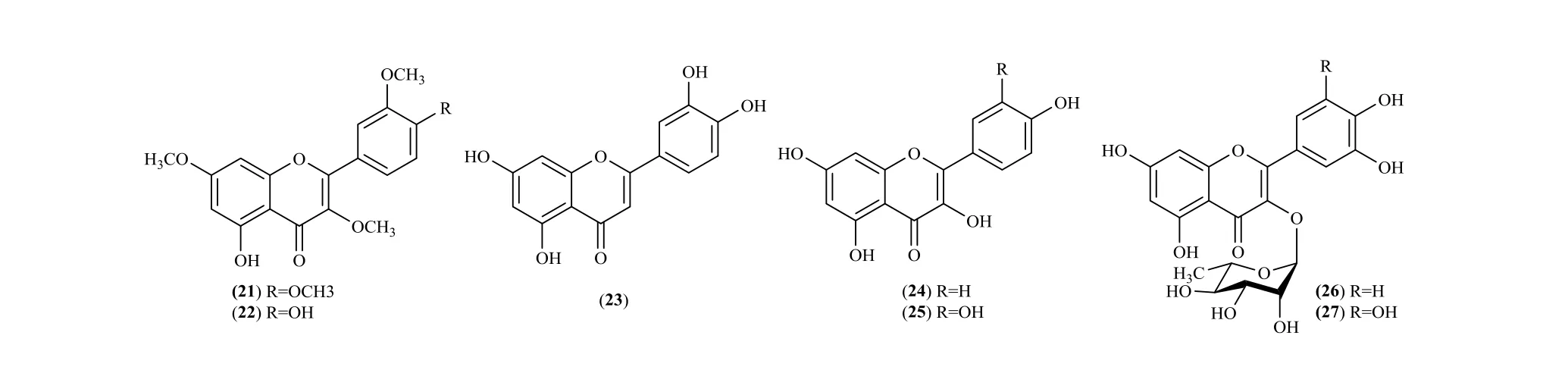

Fig. 2 Flavones and flavonoid glycosides in Pithecellobium Mart
2.1.3 Chalcones, isoflavones and flavonoid derivatives
Two chalcones, two flavonoid derivatives and one isoflavone were isolated and identified from the Pithecellobium Mart, including clypesides A (35), clypesides B (36), genistein-4'-Ο-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (37) [21], pithecellobiumol A(38), pithecellobiumol B (39) [22] (Fig. 3).
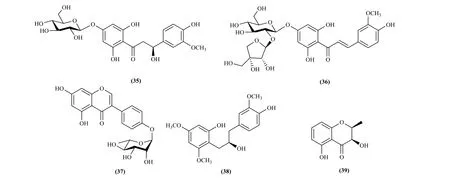
Fig. 3 Chalcones, isoflavones and flavonoid derivatives in Pithecellobium Mart
2.2 Triterpenoids and steroids
Triterpenoids and steroids are another main chemical constituents of the genus. All triterpenoids in the genus are almost pentacyclic triterpenoid, with ursane and oleanane as the majority [2].
2.2.1 Pentacyclic triterpenoids
Eighteen oleananes and five ursanes were isolated and identified from the Pithecellobium Mart at present. They are listed in Table 1. The parent structure (I) and substituent groups of compounds are shown in Fig. 4. Chemical structures of ursanes are shown in Fig. 5.
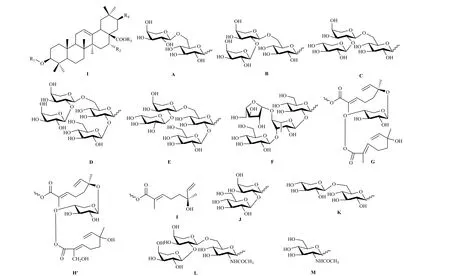
Fig. 4 Parent structure (I) and substituent groups of triterpenoids from plants of Pithecellobium Mart
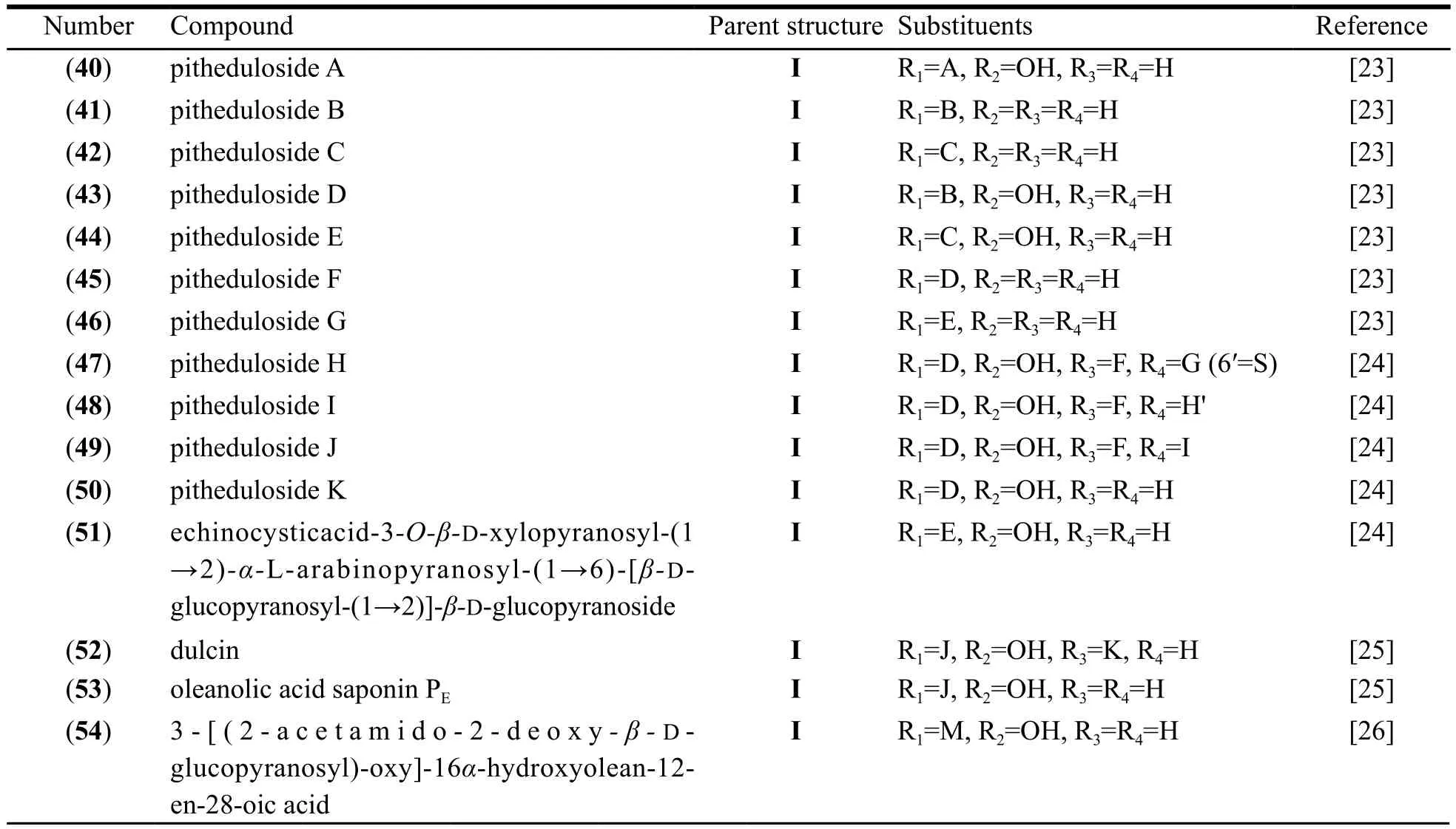
Table 1 Pentacyclic triterpenoids from the Pithecellobium Mart

Continued Table 1
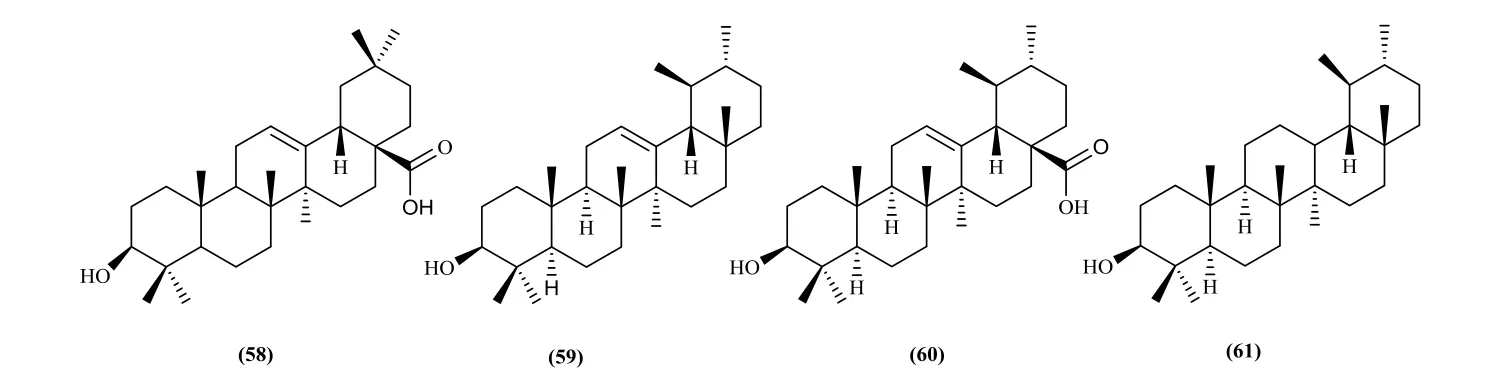
Fig. 5 Chemical structures of compounds 58-61
2.2.2 Tetracyclic triterpenes
Seven tetracyclic triterpenes were isolated and identified from the P. clypearia, including â-Sitosterol (62), campesterol (63), stigmasterol(64) [16], á-spinasterol (65) [16,29], α-D-glucoside of α-spinasterol (66), 3-O-6'-O-palmitoyl-α-D-glucosyl-spinasta-7,22(23)-diene (67), 3-O-6'-O-stearoyl-α-D-glucosylspinasta-7,22(23)-diene(68) [30] (Fig. 6).
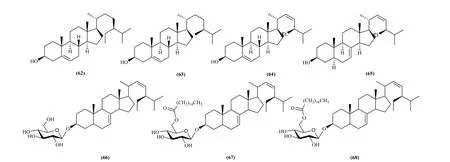
Fig. 6 Tetracyclic triterpenes in Pithecellobium Mart
2.3 Phenolic acids
Phenolic compounds are also important constituents. Polyphenolic compounds could affect on cells due to their antioxidant activities as well as their modulation of different pathways including signaling cascades, antiapoptotic processes and the formation of the amyloid β peptide [5].
Thirteen phenolic acids were isolated and identified from the Pithecellobium Mart, which mainly exist in the P. clypearia, including gallic acid(69) [6,11,18], ethyl gallate (70) [6,18,31], methyl gallate (71) [31], protocatechuic acid methy ester(72) [11], methyl 2-Ο-α-D-glucopyranosylbenzoate(73) [31], canthoside A (74) [31], clypearoside A(75) [32] (Fig. 7).
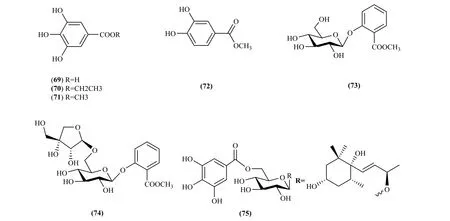
Fig. 7 Phenolic acids in Pithecellobium Mart
2.4 Lignans and phenylpropanoids
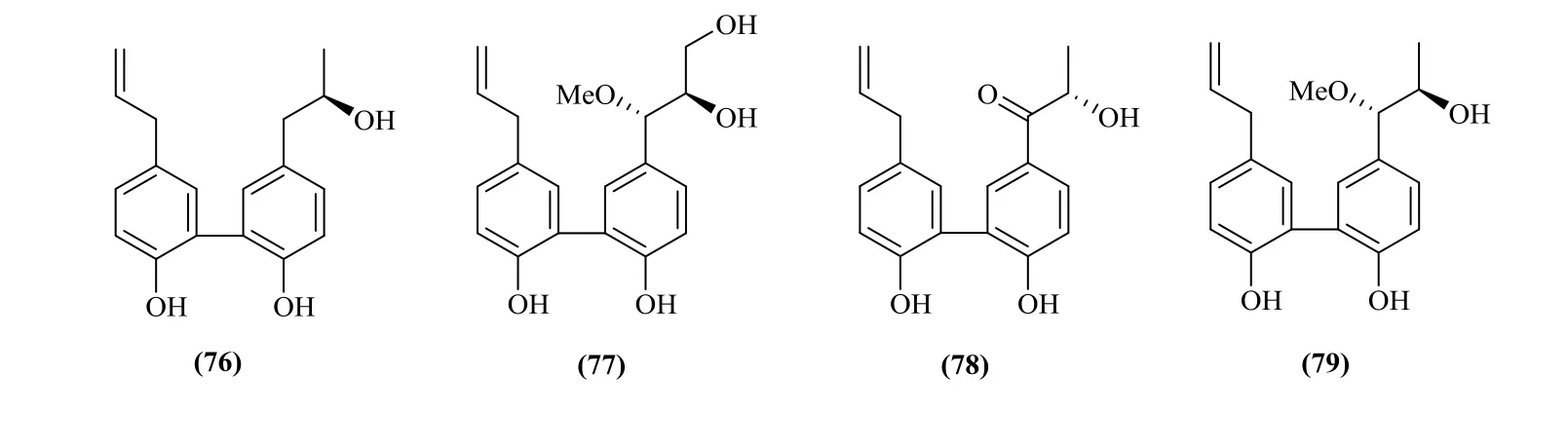
Lignans and phenylpropanoids have been found in this genus. They are divided into four different classes dependeding on different molecular structures. They are biphenyl derivatives, arylnaphthalenes, tetrahydrofurans,furofurans, which mainly exist in the P. clypearia.They are clypearianin A-G (76-82), (7'R,8'R)-7'-methoxyl strebluslignanol (83), magnolol(84), magnaldehyde (85), randaiol (86) [33],polystachyol (87), (+)-lyoniresinol-3-α-Ο-β-D-glucopyranoside (88), (-)-lyoniresinol-3-α-Ο-β-D-glucopyranoside (89), alangilignoside C (90),(+)-pinoresinol (91), lawsoniaside B (92), 3-(4β-D-glucopyranosyloxy-3-methoxy)-phenyl-2E-propenol(93), polygalatenoside E (94) [34], 3-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1,2-propanediol(95),3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,2-propanediol (96),4-Ο-β-D-glucopyranosyl-p-coumaric acid (97) [7],chlorogenic acid ethyl ester (98) [7], 4-Ο-α-D-glucopyranosyl-trans-p-coumaric acid (99) [7] (Fig.8).
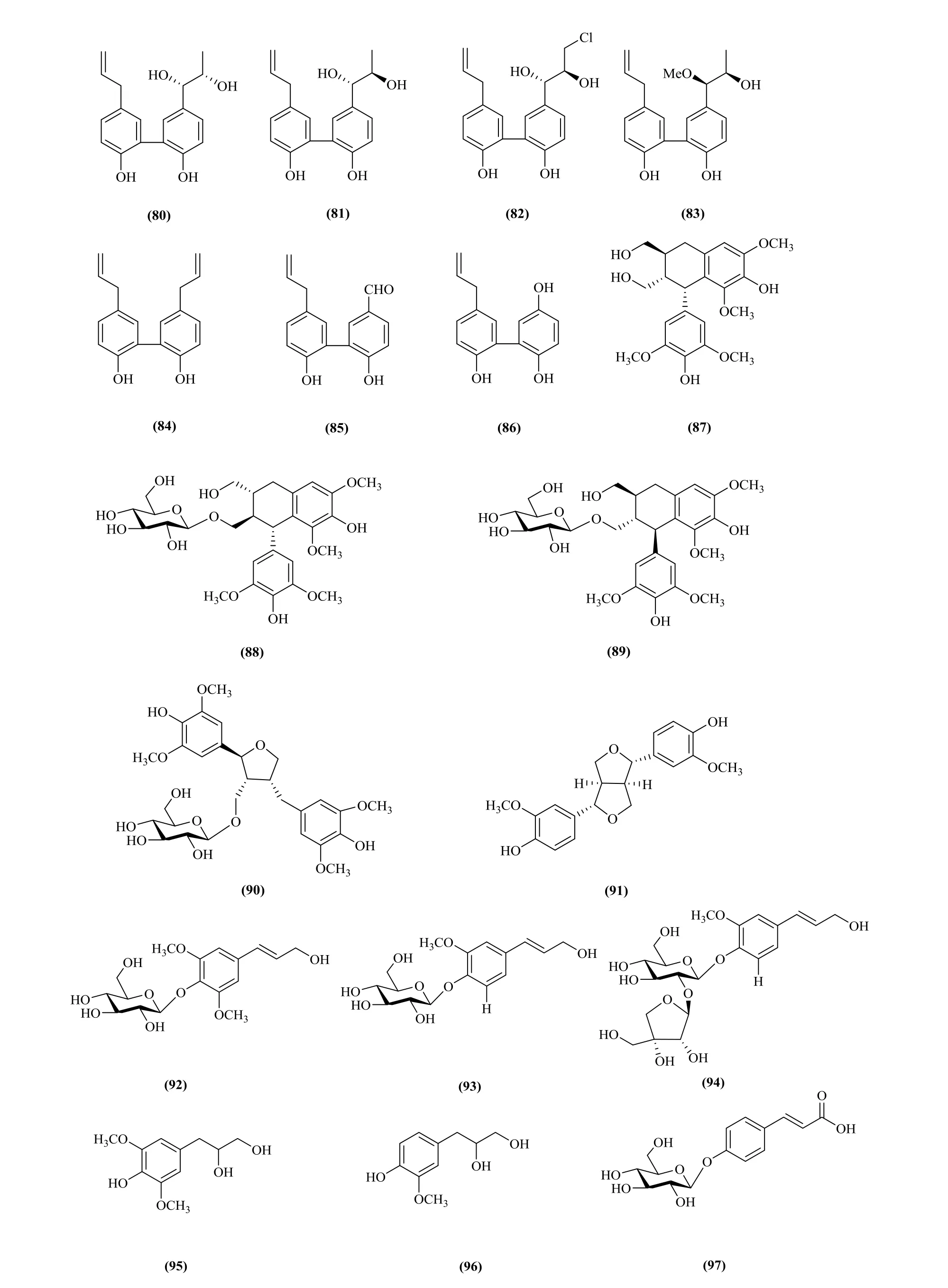
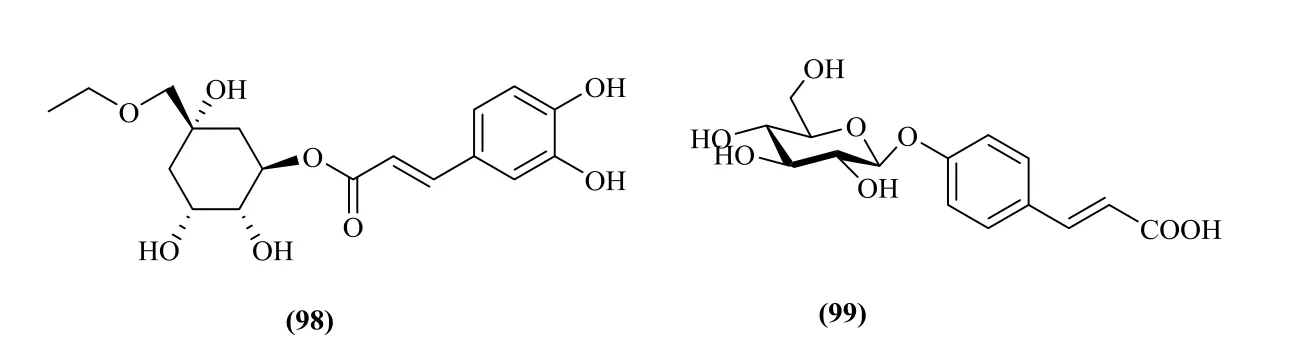
Fig. 8 Lignans and phenylpropanoids in Pithecellobium Mart
3 Conclusion
Phytochemical researches demonstrated that the chemical compositions of Pithecellobium Mart included flavonoids, triterpenoids, steroids, phenolic acids, lignans and phenylpropanoids. The researchs showed that flavonoids, triterpenes and steroids were mainly chemical constituents of the genus and possessed potent biological activities, such as antiarrhythmic activiry, anti-oxidant, antibacterial,antiviral and so on. Therefore, further study of the chemical compositions and pharmacological activities of Pithecellobium Mart is of great significance. This paper provided crucial material for the further development and utilization of Pithecellobium Mart.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(81502954).
[1] Ma SG, Hu YC, Yu SS, et al. Cytotoxic Triterpenoid Saponins Acylated with Monoterpenic Acid from Pithecellobium lucidum. Journal of Natural Products,2008, 71: 41-46.
[2] Liu LY, Kang J, Chen RY. Research progress in chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of plants in Pithecellobium Mart. Zhongcaoyao, 2013, 18:2623-2629.
[3] Li B, Yao XS, Xu JK, et al. Effects of Pithecellobium clypearia Benth extract and its main components on inflammation and allergy. Fitoterapia, 2009, 80:349-353.
[4] Kujumgiev A, Tsvetkova I, Serkedjieva Y, et al.Antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral activity of propolis of different geographic origin. Ethnopharmacology,1999, 64: 235-240.
[5] Sangkitikomol, Warin Edited. Antioxidants in Thai Herb,Vegetable and Fruit Inhibit Hemolysis and Heinz Body Formation in Human Erythrocytes. Environmental Induction and Dietary Antioxidants, 2012: 289-306.
[6] Guo XY, Wang NL, Li B, et al. Chemical constituents from Pithecellobium clypearia and their effects on T lymphocytes proliferation. Journal of Chinese Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2007, 16: 208-213.
[7] Chen YH. Isolation and Identification of Chemical Components from Pithecellobium clypearia Bemth.Tianjin Pharmacy, 2015, 27: 5-8.
[8] Saxena, VK, Singhal Madhuri. Bioactive flavonoidal constituents from Pithecellobium dulce (leaves). Journal of the Institution of Chemists, 1998, 70: 168-171.
[9] Sahu NP, Mahato SB. Anti-inflammatory triterpene saponins of Pithecellobium dulce: Characterization of an echinocystic acid bisdesmoside. Phytochemistry, 1994,37: 1425-1427.
[10] Rajadurai S. Chemistry of Pithecellobium dulce tannins.I. Isolation of (+)-3',4',7-trihydroxy-3,4-flavandiol.Leather Science(Madras), 1963, 10: 340-343.
[11] Li LG, Liu QB, Huang XX. Isolation and Identification of Chemical Components of Pithecellobium clypearia Benth and Determination of Their Antioxidant Activity.Journal of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, 2015,32: 343-346.
[12] Li YL, Leung KT, Yao FH, et a1. Antiviral flavans from the leaves of Pithecellobium clypearia. Journal of Natural Products, 2006, 69: 833-835.
[13] Su MX, Tang ZY, Huang WH, et al. Studies on the Chemical Comstituents of Pithecellobium clypearia.Zhongyaocai, 2009, 32: 705-707.
[14] Lee MW, Morimoto SN. Tannins and related compounds.III.Flavan-3-O-L-gallates and proanthocyanidins from Pithecellobium lobatum. Phytochemistry, 1992, 31:2117-2120.
[15] Steynberg P, Steynberg Jan P, Brandt EV, et a1.Oligomeric flavanoids.Stmcture and the first profisetinidins with epifisetinidol constituent units.Organic and Bio-Organic Chemistry, 1997, 13:1943-1950.
[16] Xie CY, Lin LW. Study on the Chemical Constituents of Pithecellobium clypearia. Zhongyaocai, 2011, 34:1060-1062.
[17] Mena-Rejon GJ, Sansores-Peraza P, Brito-Loeza WF, et al. Chemical constituents of Pithecellobium albicans.Fitoterapia, 2008, 79: 395-397.
[18] Li YL, Li KM, Su MX, et al. Studies on antiviral constituents in stems and leaves of Pithecellibium clypearia. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2006, 31: 397-399.
[19] Nigam SK, Mitra CR. Pithecellabium dulce V. Chemistry of the seed saponin and constituents of the leaves. Planta Medica, 1970, 18: 44-54.
[20] Saxena V K, Singhal M. Novel prenylated flavonoid from stem of Pithecellobium dulce. Fitoterapia, 1999,70: 98-100.
[21] Nguyen, Phuong Thao, Luyen, et al. Identification,characterization, kinetics, and molecular docking of flavonoid constituents from Archidendron clypearia(Jack.) Nielsen leaves and twigs. Bioorganic &Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2016, 24: 3125-3132.
[22] Wang YX, Ren Q, Yan ZY, et al. Flavonoids and their derivatives with β-amyloid aggregationinhibitory activity from the leaves and twigs of Pithecellobium clypearia Benth. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2017, 27: 4823-4827.
[23] Nigam S K, Misra G, Uddin R, et al. Pithedulosides A-G, oleanane glycosides from Pithecellobium dulce.Phytochemistry, 1997, 44: 1329-1334.
[24] Yoshikawa K, Suzaki Y, Tanaka M, et al. Three acylated saponins and a related compound from Pithecellobium dulce. Journal of Natural Products, 1997, 60: 1269-1274.
[25] Ma SG, Lv HN, Ding GZ, et al. Chemical constituents from the roots of Pithecellobium lucidum and their cytotoxic activity. China Joural of Chinese Materia Medica, 2011, 36: 1769-1771.
[26] Saxena VK, Singal M. Geinstein 4'-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside from Pithecellobium dulce.Fitoterapia, 1998, 69: 305-306.
[27] Sahu NP, Koike K, Jia ZH, et al. A minor acylated triterpenoid saponin from the seeds of Pithecellobium dulce. Journal of Chemical Research, 1999, 32: 558-559.
[28] Khan IA, Clark AM, McChesney JD. Antifungal activity of a new triterpenoid glycoside from Pithecellobium racemosum(M.). Pharmaceutical Research, 1997, 1:358-361.
[29] Nigam SK, Mitra CR. Pithecellobium dulce IV.Constituents of flowers, heartwood, and root bark.Planta Medica, 1968, 16: 335-337.
[30] Ferreira-Gomes DDC, Vilela-Alegrio L. Acyl steryl glycosides from Pithecellobium cauliflorum.Phytochemistry, 1998, 49: 1365-1367.
[31] Xian J, Luo XF, Yu T, et al. Isolation and Identification of Chemical Constituents from leaf of Pithecellobium clypearia Benth. Journal of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, 2014, 31: 262-264.
[32]Li LZ, Peng Y, Hu C, et al. Antioxidant activity of chemical constituents isolated from Pithecellobium clypearia. Records of Natural Products, 2015, 9:284-291.
[33] Lou LL, Li LG, Liu QB, et al. 3,3'-Neolignans from Pithecellobium clypearia Benth and their antiinflammatory activity. Fitoterapia, 2016, 112: 16-21.
[34] Thao NP, Luyen BT, Vinh le B, et al. Rat intestinal sucrase inhibited by minor constituents from the leaves and twigs of Archidendron clypearia (Jack.) Nielsen.Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2016, 26:4272-4276.
杂志排行
Asian Journal of Traditional Medicines的其它文章
- Absolute configuration of curdione and its three isomers by NMR, ECD and DFT calculations: an insight into the scope of unsaturated ketone helicity rule based on an ECD study
- Exploring the active ingredients, potential targets and pathways of quassinoids in Simaroubaceae plants by network pharmacology approachs
- Main chemical constituents and pharmacological properties of Harrisonia perforata (Blanco) Merr.
- Chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of the fruits of Camptotheca acuminata: a review of its phytochemistry
- Studies on the Chemical Components and Biological Activities of Stellera chamaejasme L.
