基于分布式空时干扰对齐的MIMO干扰信道自由度研究
2018-03-14应腾达冯文江蒋卫恒刘国岭姚楚楠包涛涛
应腾达,冯文江,蒋卫恒,刘国岭,姚楚楠,包涛涛
基于分布式空时干扰对齐的MIMO干扰信道自由度研究
应腾达,冯文江,蒋卫恒,刘国岭,姚楚楠,包涛涛
(重庆大学通信工程学院,重庆 400044)
针对个用户MIMO干扰信道(IC),研究基于分布式空时干扰对齐(DSTIA)的信道可达自由度。利用分布式当前和过期发射端信道状态信息(CSIT)设计预编码,分别给出MISO系统可达自由度关于CSI反馈时延和反馈频率的折中域;分析发射端天线数对MISO系统可达自由度的影响,导出逼近系统自由度外界的条件。进一步研究MIMO系统接收端天线数对系统自由度的影响,给出保持系统可达自由度的CSI反馈时延范围。理论和数值分析表明,所提DSTIA方案能充分消除用户间干扰,获得更高的自由度增益,缩小可达界与外界的差距,提高系统的可达速率。
自由度;分布式空时干扰对齐;MIMO干扰信道;CSI有限反馈
1 引言
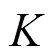
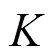
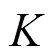
2 系统模型
2.1 K个用户MIMO IC模型
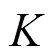
个用户MIMO IC可看成是多小区蜂窝链路间干扰的抽象。例如,个用户MISO IC是个邻近小区下行链路用户间干扰的抽象。如图1所示,个用户MIMO IC由对发射—接收节点组成。发射端配置根天线,接收端配置根天线,。每个发射端仅向相应的接收端发送单一信息。其信号模型为
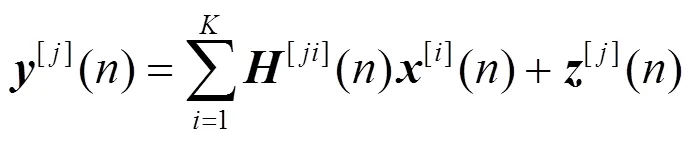
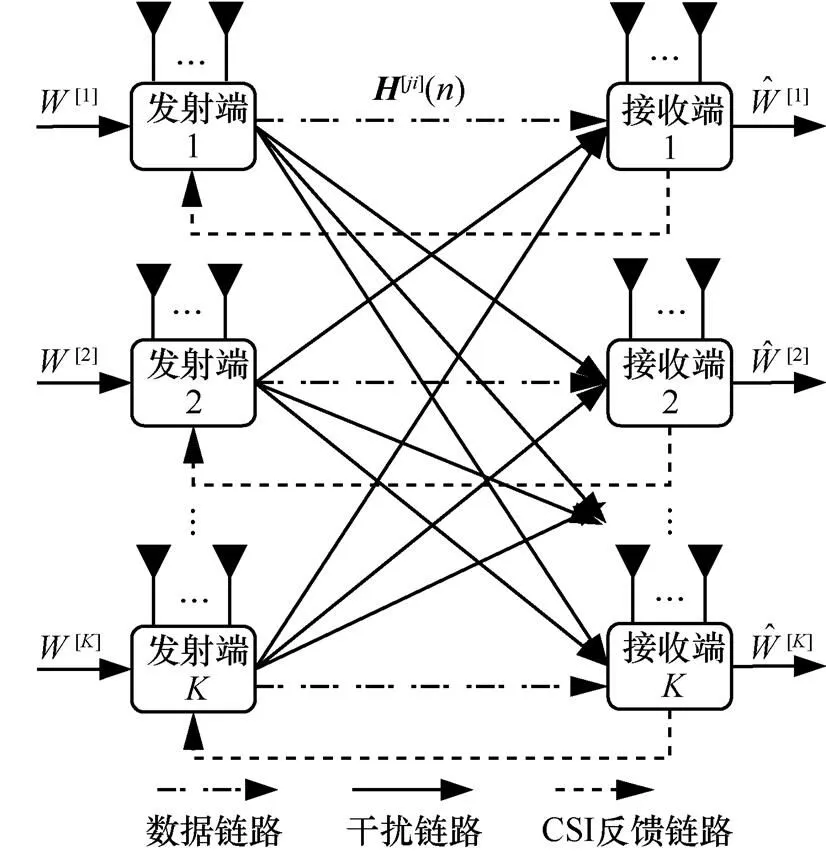
图1 K个用户MIMO IC模型
2.2 CSI反馈模型
假设接收端(用户)执行预定的周期性反馈协议将CSI反馈给发射端。周期性反馈协议可以通过控制信号实现,适用于当前主流的蜂窝移动通信标准,如3GPP LTE[22]。分别考虑2个导致CSIT时延的因素——反馈时延和反馈频率[1]。
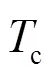
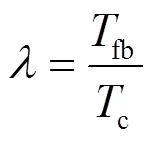
其中,为瞬时(instantaneous)CSIT;为适当延时(temperately-delayed)CSIT;为完全延时(completely-delayed)CSIT。发射端在时隙可用的本地CSI记为,这里,。因此,发射端的发送信号向量可看作是发送信息与本地延时CSIT的函数,即,为发射端的预编码函数。
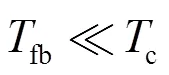
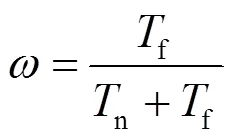
2.3 自由度
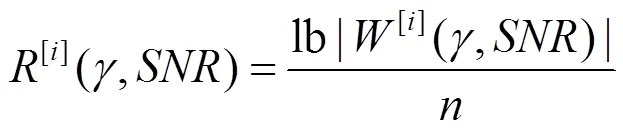
相应地,个用户MIMO IC在本地CSIT下的总自由度定义为
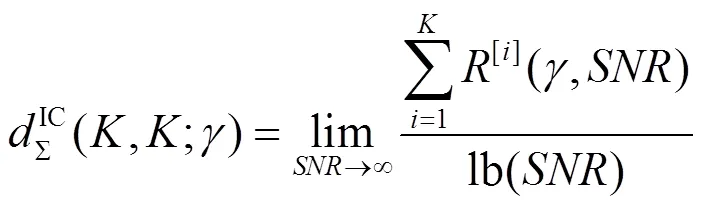
3 K个用户MISOIC的自由度折中域
3.1 分布式空时干扰对齐
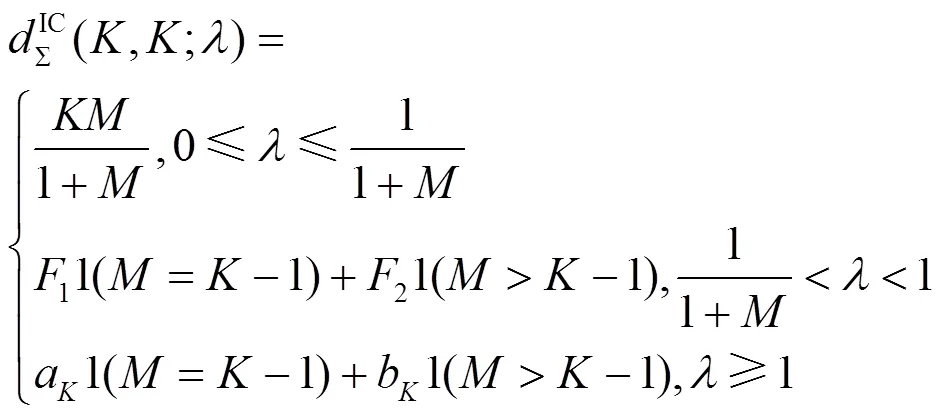
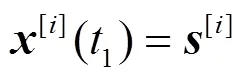
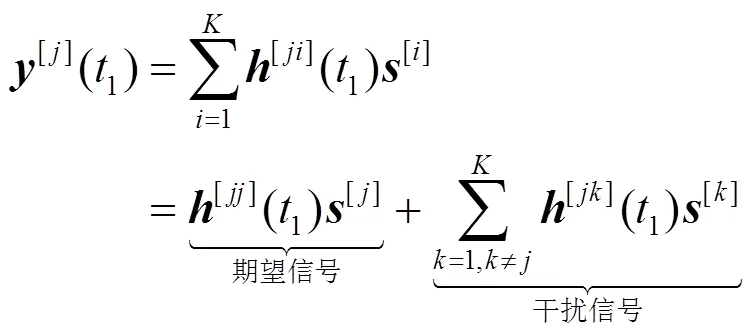
此时,各接收端观测到一个期望信号与干扰信号叠加的线性方程。
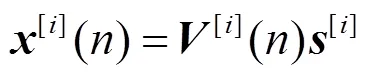
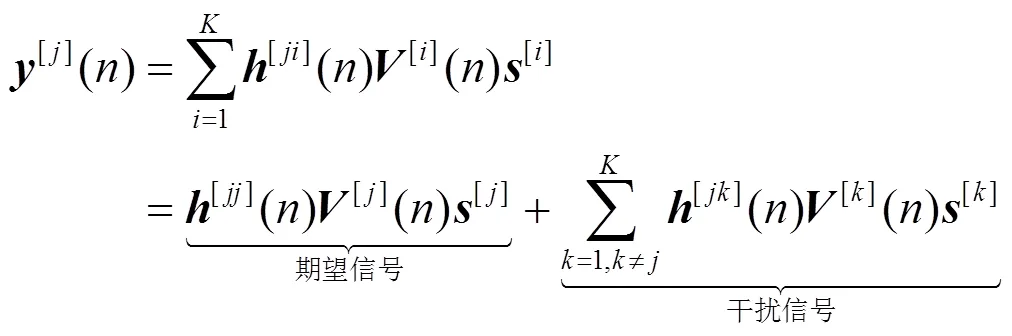
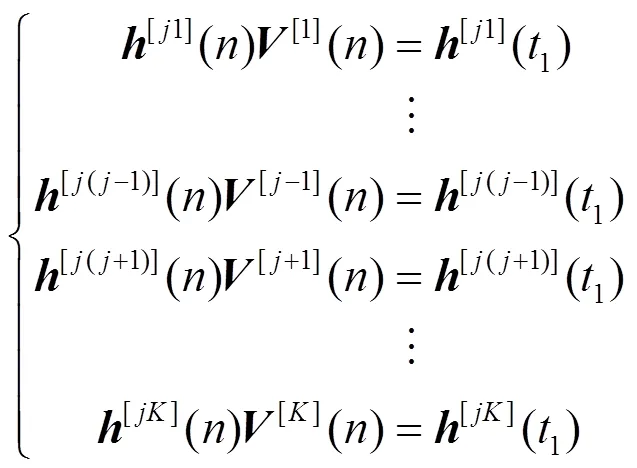
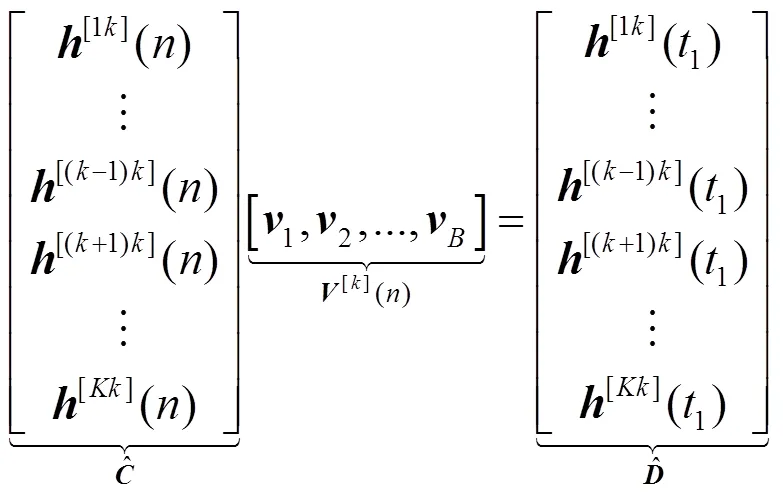
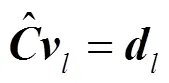
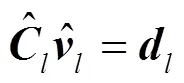
其中,表示从中选取对应中剩余个未知数的列组成的方阵,表示去除零元素后剩余未知元素按相对位置排序的矢量。由于信道系数的独立同分布特性,此时,每列求解出的未知元素以概率1不为0。
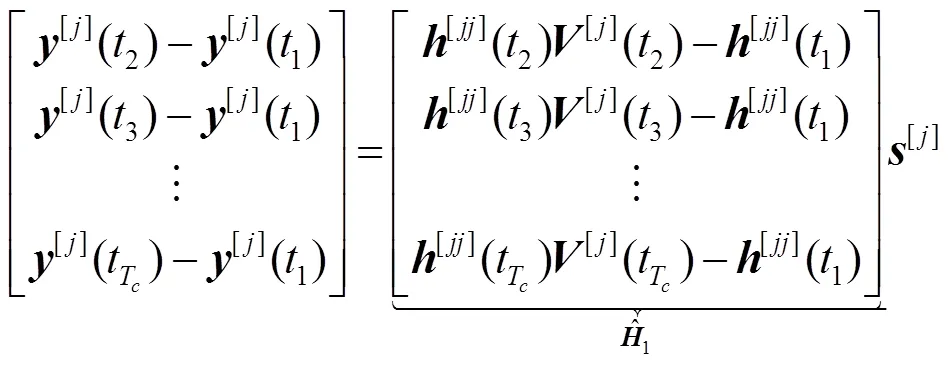
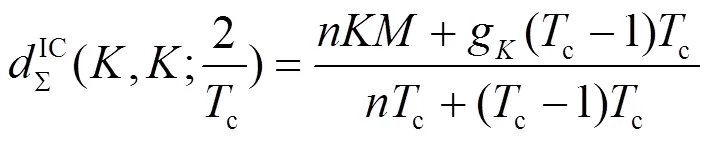
3.2 自由度折中域
3.2.1 反馈时延受限自由度折中域
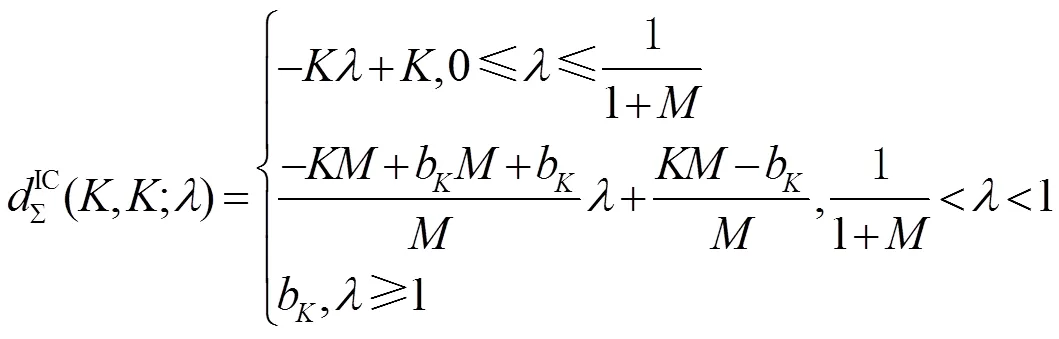
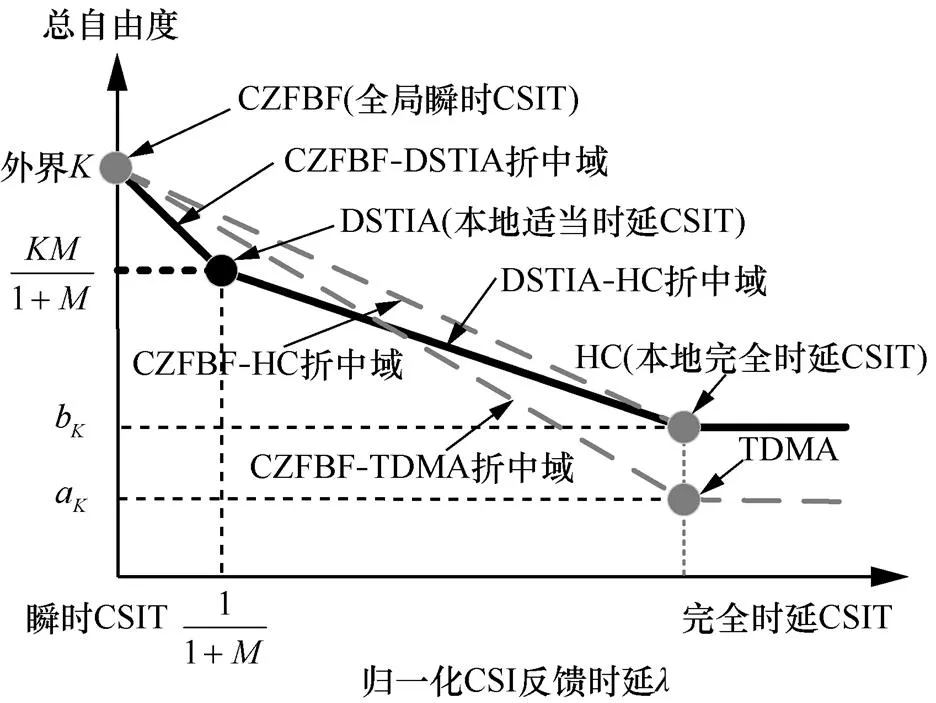
图5 K个用户MISO()IC关于反馈时延的自由度折中域
3.2.2 反馈频率受限自由度折中域
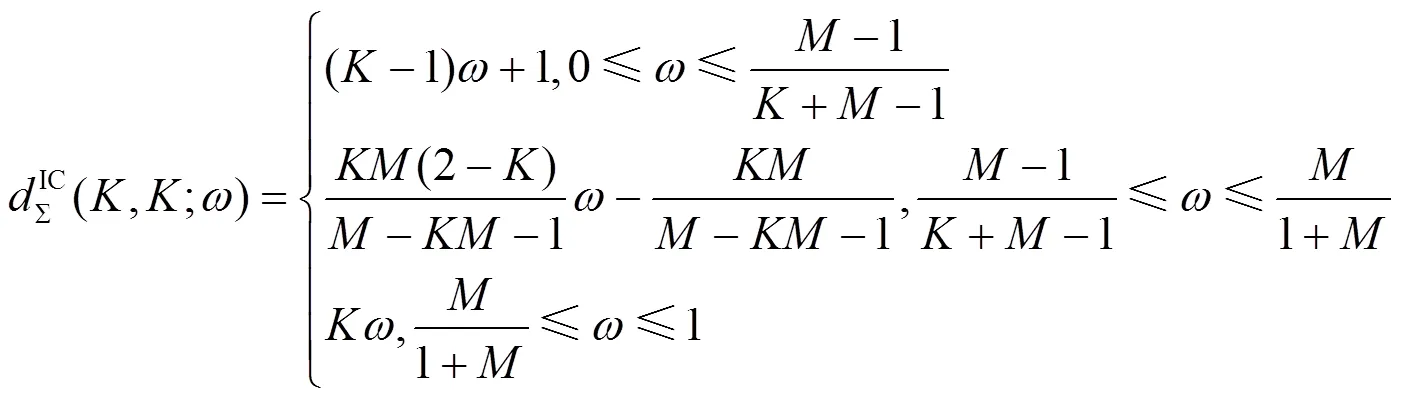
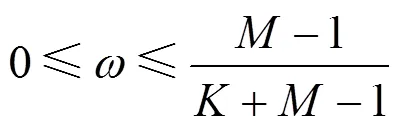
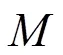
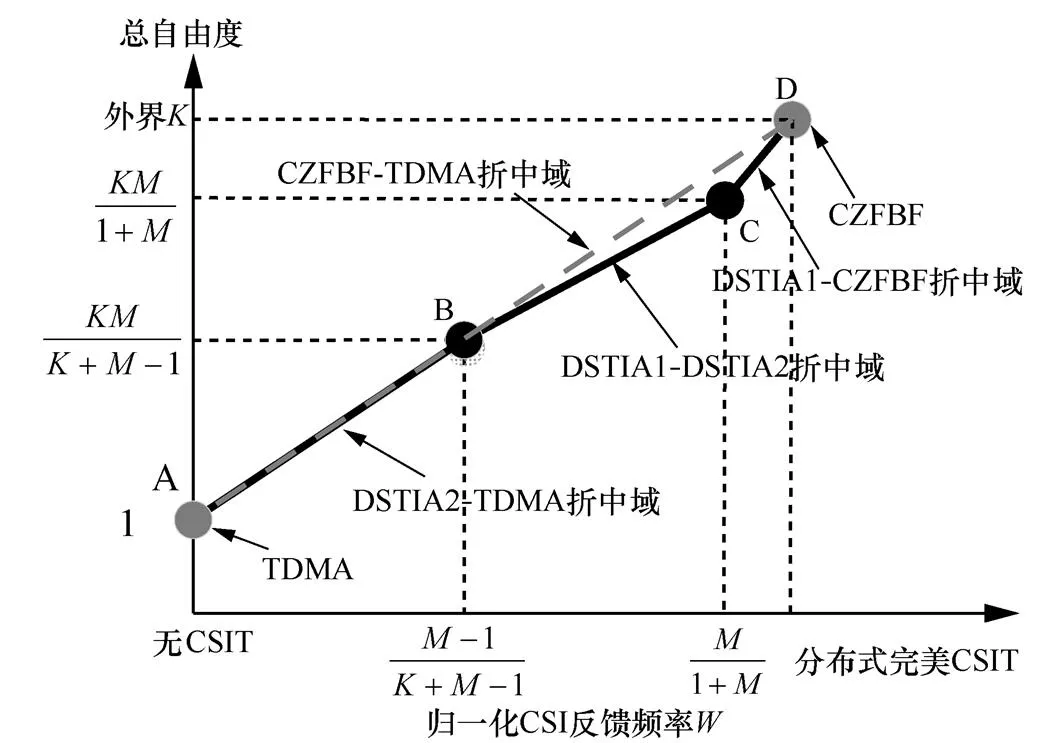
图6 个用户MISO()IC关于反馈频率的自由度折中域
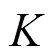
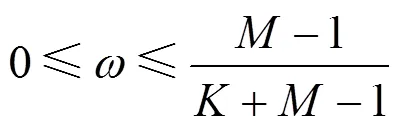
4 K个用户MIMO IC的可达自由度
4.1 可达自由度
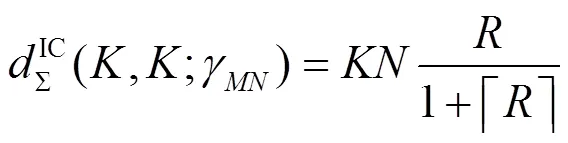
证明类似定理1,采用DSTIA方案获取定理2的可达自由度。此时,式(12)可表示为
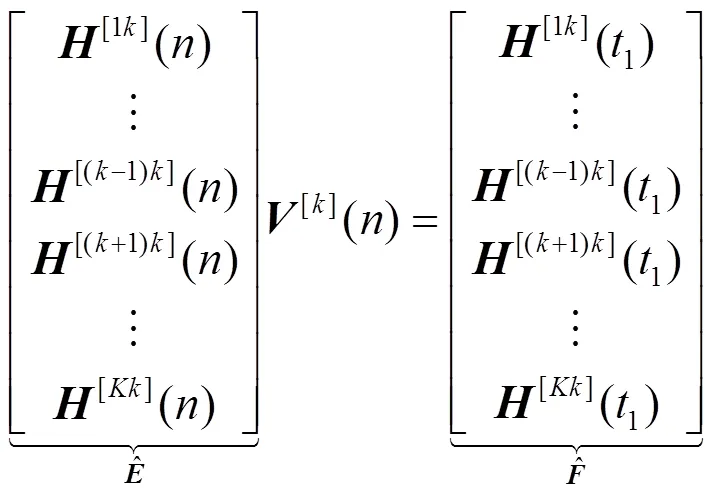
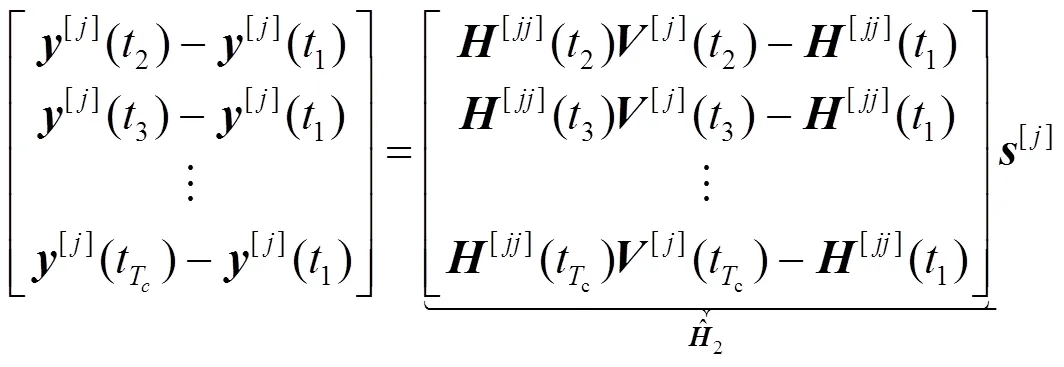
4.2 CSI有限反馈条件
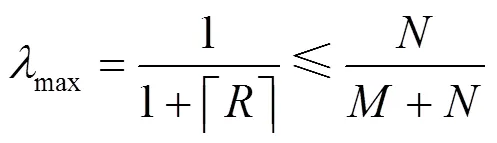
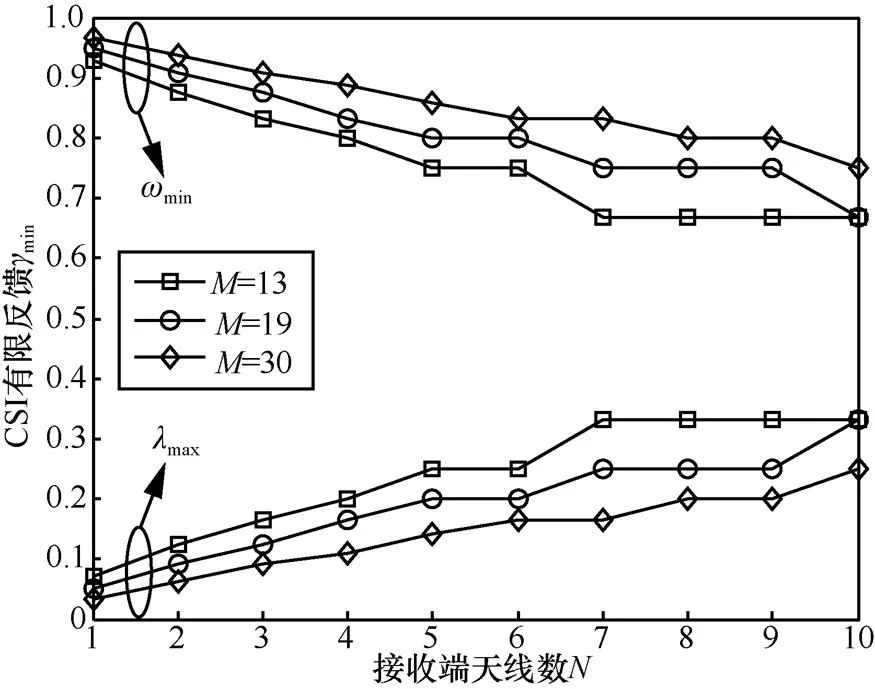
图7 最大(小)归一化CSI反馈时延(频率)随接收端天线数N的变化
5 数值分析
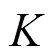
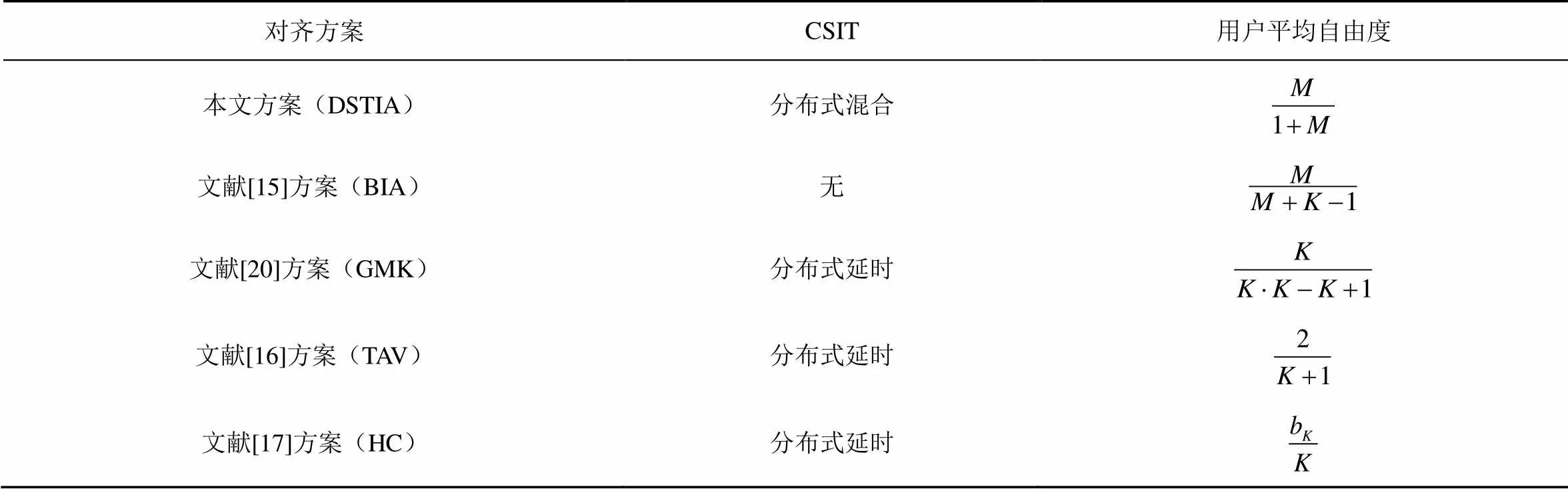
表1 K个用户M×1(M≥1) MISO IC不同方案下的总自由度

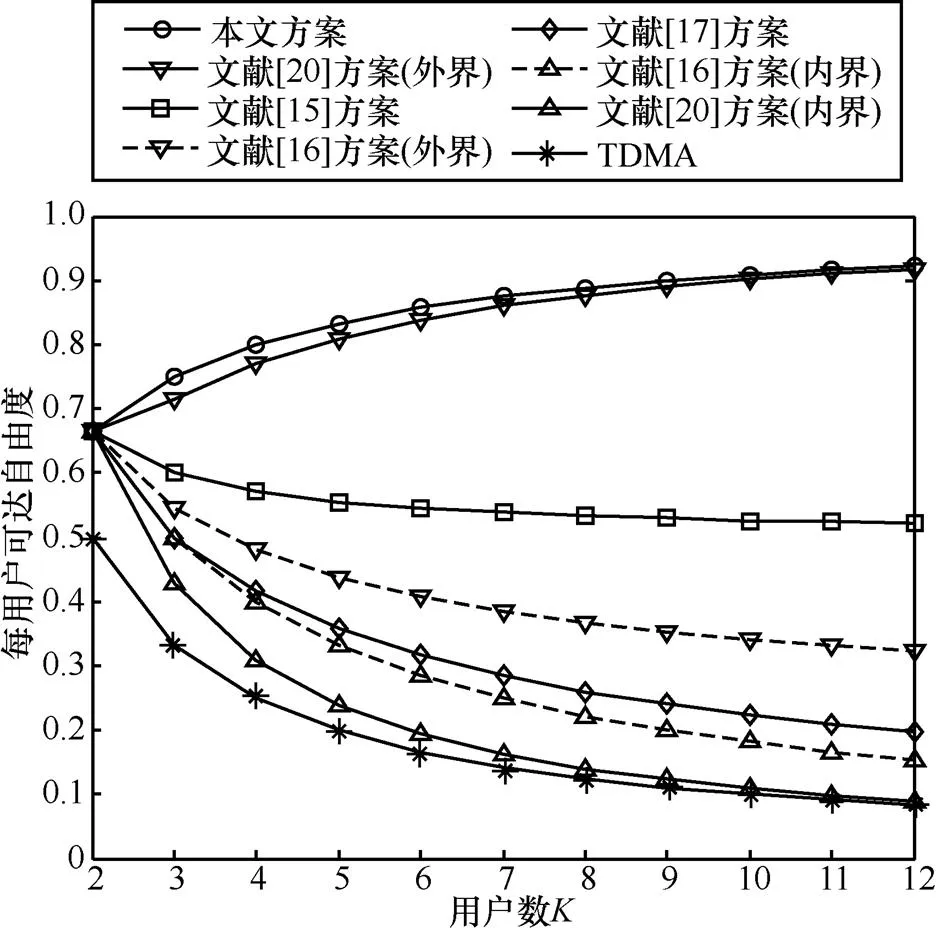
图8 用户平均可达自由度随总体用户数K的变化情况
2) 信道和速率
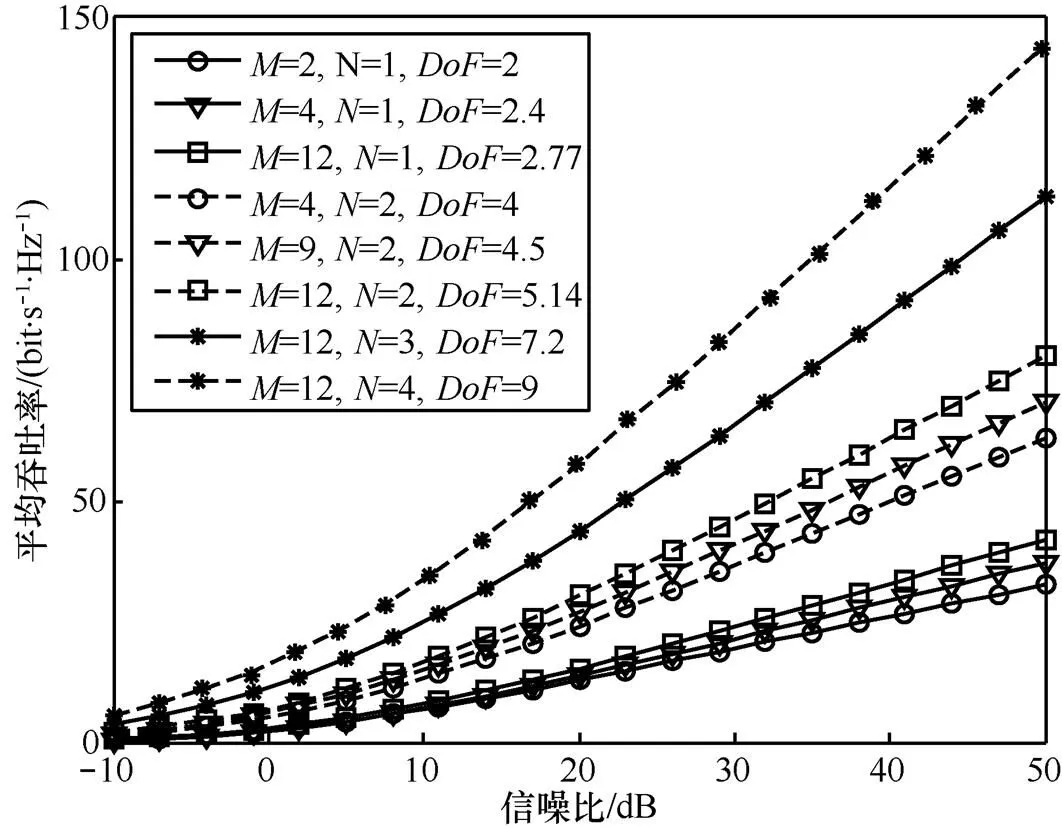
图9 3个用户MIMO IC天线数与平均吞吐率的关系
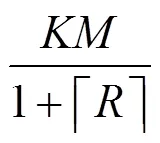
3) CSI有限反馈条件
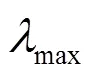
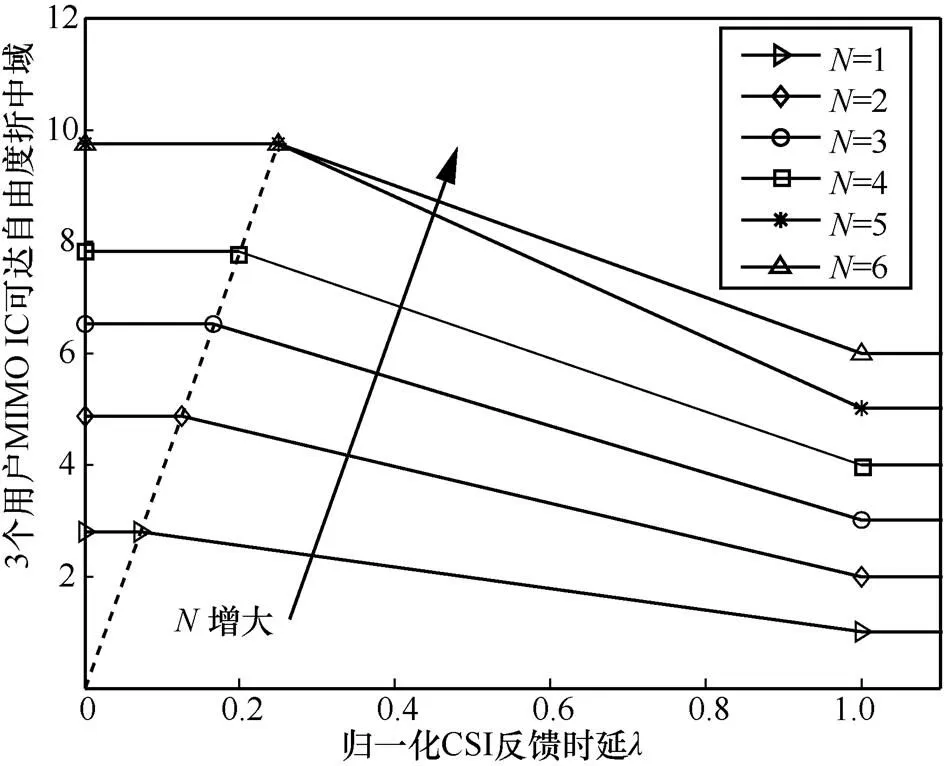
图10 3个用户MIMO IC可达自由度折中域
6 结束语
[1] LEE N, HEATH R. Space-time interference alignment and degree-of-freedom regions for the MISO broadcast channel with periodic CSI feedback[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2014, 60(1): 515-528.
[2] LEE N, TANDON R, HEATH R W. Distributed space-time interference alignment with moderately delayed CSIT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(2): 1048-1059.
[3] YING T, FENG W, SU W, et al. On the degrees of freedom of MIMO X networks with non-cooperation transmitters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(4): 2490-2504.
[4] YING T, FENG W, LIU G. Space-time interference alignment: DoF of two-user MIMO X channel with alternating CSIT[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(5): 1167-1170.
[5] 孙献, 赵晓晖. 认知无线电系统中干扰对齐的自由度分析[J]. 通信学报, 2016, 37(2): 179-189.
SUN X, ZHAO X H. Analysis on the degree of freedom of interference alignment in cognitive radio[J]. Journal on Communications, 2016, 37(2): 179-189.
[6] 朱世磊, 郑娜娥, 王盛, 等. 基于用户协作的认知MIMO干扰网络自由度上界研究[J]. 通信学报, 2015, 36(8): 153-160.
ZHU S L, ZHENG N E, WANG S, et al. Upper bound of degrees of freedom in cognitive MIMO interference network with user cooperation[J]. Journal on Communications, 2015, 36(8):153-160.
[7] CADAMBE V R, JAFAR S A. Interference alignment and degrees of freedom of the-user interference channel[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2008, 54(8): 3425-3441.
[8] JAFAR S A, FAKHEREDDIN M J. Degrees of freedom for the MIMO interference channel[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53(7): 2637-2642.
[9] GOU T, JAFAR S A. Degrees of freedom of the-user×MIMO interference channel[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2010, 56(12): 6040-6057.
[10] WANG C, SUN H, JAFAR S A. Genie chains and the degrees of freedom of the-user MIMO interference channel[C]//The 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory. 2012: 2476-2480.
[11] SOMEKH O, SIMEONE O, BAR-NESS Y, et al. Cooperative multi-cell zero-forcing beamforming in cellular downlink channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2009, 55(7): 3206-3219.
[12] HUANG C, JAFAR S A, SHAMAI S, VISHWANATH S. On degrees of freedom region of MIMO networks without channel state information at transmitters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2012, 58(2): 849-857.
[13] ZHU Y, GUO D. The degrees of freedom of isotropic MIMO interference channels without state information at the transmitters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2012, 58(1): 341-352.
[14] VAZE C S, VARANASI M K. The degree-of-freedom regions of MIMO broadcast, interference, and cognitive radio channel with no CSIT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2012, 58(8): 5354-5374.
[15] LU Y, ZHANG W. Blind interference alignment in the-user MISO interference channel[C]//IEEE GLOBECOM. 2013: 3464-3469.
[16] TORRELLAS M, AGUSTIN A, VIDAL J. On the degrees of freedom of the-user MISO interference channel with imperfect delayed CSIT[C]//The 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing. 2014: 1155-1159.
[17] HAO C, CLERCKX B. Degrees-of-freedom of the-user MISO interference channel with delayed local CSIT[C]//IEEE International Conference on Communications. 2015: 4217-4222.
[18] ABDOLI M J, GHASEMI A, KHANDANI A K. On the degrees of freedom of-user SISO interference andchannels with delayed CSIT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2013, 59(10): 6542-6561.
[19] VAZE C S, VARANASI M K. The degrees of freedom region and interference alignment for the MIMO interference channel with delayed CSIT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2012, 58(7): 4396-4417.
[20] GHASEMI A, MOTAHARI A S, KHANDANI A K. Interference alignment for the MIMO interference channel with delayed local CSIT, 2011 [J]. arXiv: arXiv 1102.5673.
[21] LEE N, HEATH R W. CSI feedback delay and degrees of freedom gain trade-off for the MISO interference channel[C]//The 46th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers. 2012: 1851-1854.
[22] GHOSH A, ZHANG J, ANDREWS J G, et al. Fundamentals of LTE[M]. Englewood Cliffs, USA: Prentice-Hall, 2010.
Degrees of freedom of MIMO interference channel with distributed space-time interference alignment
YING Tengda, FENG Wenjiang, JIANG Weiheng, LIU Guoling, YAO Chunan, BAO Taotao
College of Communication Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
In the context of-user MIMO interference channel (IC), achievable degrees of freedom (DoF) were investigated with distributed space-time interference alignment (DSTIA). By precoding with distributed current and outdated channel state information at the transmitters (CSIT), new tradeoff regions between achievable DoF and CSI feedback delay/frequency were achieved for MISO system. The impact of the number of transmit antennas on achievable DoF in the MISO system was analyzed, revealing that DoF results approach to the outer bound as the number of transmit antennas increases. Further, the impact of the number of receive antennas on achievable DoF was characterized, deriving the range of CSI feedback delay that preserves achievable DoF in the MIMO system. Theoretical and numerical analyses show that, the proposed DSTIA scheme can achieve better sum-DoFs by eliminating inter-user interference perfectly, tighten the gap between achievable DoF and outer bound, as well as improve the achievable rate of the system.
degree of freedom, distributed space-time interference alignment, MIMO interference channel, limited CSI feedback
TN919.1
A
2017-05-24;
2017-10-30
应腾达,tengdaying@cqu.edu.cn
中央高校基本科研业务费基金资助项目(No.106112016CDJXY500002);重庆市基础科学与前沿技术研究重点基金资助项目(No.cstc2017jcyjBX0047, No.cstc2015jcyjA40021)
10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2018017
应腾达(1991-),男,浙江永康人,重庆大学博士生,主要研究方向为MIMO无线通信、信息论等。

冯文江(1963-),男,四川西充人,重庆大学教授、博士生导师,主要研究方向为宽带无线接入技术、认知无线电、通信信号处理等。
蒋卫恒(1985-),男,湖北枝江人,重庆大学讲师,主要研究方向为无线通信与网络、移动云计算等。
刘国岭(1989-),男,辽宁北票人,重庆大学硕士生,主要研究方向为MIMO无线通信、全双工等。
姚楚楠(1994-),男,湖南娄底人,重庆大学硕士生,主要研究方向为MIMO无线通信、移动边缘计算等。
包涛涛(1993-),男,湖北孝感人,重庆大学硕士生,主要研究方向为MIMO无线通信、图像处理等。
: The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No.106112016CDJXY500002), The Key Project of Chongqing Basic Science and Advanced Technology Research (No.cstc2017jcyjBX0047, No.cstc2015jcyjA40021)
