湖南省植被覆盖遥感反演信息量化统计
2017-11-28符静秦建新
符静+秦建新


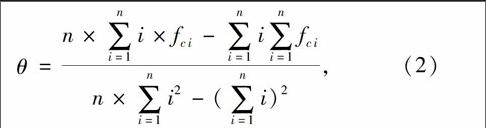
摘 要 本文基于2001—2013年MODIS NDVI多时序遥感影像,利用像元二分模型估算植被覆盖度,以湖南省14個地州市为对象进行统计,并探讨植被覆盖度变化产生的人为原因.结果表明:(1)整体上,近13年湖南省各市州植被覆盖度水平均较高,波动幅度较小;(2)湖南省西部各市州植被覆盖度水平略高于东部各市;(3)湖南省植被覆盖度变化大致以112°E为界,以西呈增加趋势,以东则表现为衰减趋势;(4)湖南省植被覆盖度变化显著增加的面积明显小于显著减少的面积;(5)植被覆盖度的短期变化受人类活动影响较大.
关键词 湖南省;MODIS NDVI;植被覆盖度;遥感;统计
中图分类号 Q948 文献标识码 A 文章编号 1000-2537(2017)05-0001-07
Quantitative Statistics on Vegetation Coverage of Hunan Province Derived from Long-term Remote Sensing Image Series
FU Jing, QIN Jian-xin*
(College of Resources and Environmental Science, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410081, China)
Abstract Based on the multi-temporal MODIS NDVI data for the period from 2001 to 2013, in this work, we estimated the vegetation coverage in Hunan province. Taking 14 administrative districts of the studied area as examples, we systematically conduct statistic studies on vegetation coverage. Our results show that: (1) overall, the vegetation coverage was relatively high when changes were not significant over the span of 13 years (2001—2013); (2) the vegetation coverage of western Prefecture-level cities and West Hunan Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture was slightly higher than that of eastern regions; (3) the change tendency of the vegetation coverage was approximately divided by 112° E , with regions located in the west of the line showed an increase whereas others demonstrated a reduction; (4) the area with significant increase of vegetation coverage was much smaller than that with significant reduction; and (5) it is noteworthy that human activities are the major driving force behind the spatial-temporal pattern variations for the vegetation coverage in the studied area during a relative short time period.
Key words Hunan province; MODIS NDVI; vegetation coverage; remote sensing; statistics
由于经济快速发展、人口不断增长和城镇化进程加快等,人类活动对自然环境的负面影响有目共睹,导致人地矛盾激化,主要表现为环境污染与生态破坏.20世纪70年代以来,生态环境问题一直是国内外关注的热点.植被是陆地地表自然生态系统的核心组成要素,具有保持水土、涵养水源、调节气候、美化环境等生态功能[1].区域地表植被状况可用植被覆盖度来衡量[2],其作为生态环境综合指示器,是生态系统质量及其服务功能评估以及生态环境评价的重要指标[3].
Rouse等1973年提出归一化植被指数[4] (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index, NDVI),该指数与植被覆盖度高度相关[5-7],广泛应用于遥感估算植被覆盖度[3, 8-11].近年来,通过植被覆盖状况监测生态环境变化的研究已成热点.Wang等利用2000—2010年MODIS NDVI时序数据,研究了中国南方丘陵山地带植被覆盖时空变化及其驱动因素[12].Zhang等基于MODIS数据,以中亚温带沙漠区为研究对象,得出该区域植被覆盖度与生物量的时空特征,并分析了二者与气候要素的关系[13].Liu等以中国山西大型露天矿山为研究对象,利用1990—2015年Landsat遥感影像计算出植被覆盖率,分析了矿山复垦后植被覆盖变化及其稳定性[14].为改善区域生态环境,需了解地理环境的整体性,同时也要研究更小尺度环境变化状况.
本文以湖南省为研究对象,首先获取了近13年的MODIS NDVI数据,利用最大值合成法得到月最大NDVI,基于像元二分法估算植被覆盖度,然后对该区域14个行政区年最大植被覆盖度均值进行统计分析,最后探讨了植被覆盖度变化的人为因素.以期长期监测该区域生态环境变化,为植被恢复及生态工程建设等决策提供参考.endprint
