基于3-乙基-2-乙酰吡嗪缩肼基甲酸甲酯的铜和锌配合物的晶体结构及荧光性质
2017-11-01毛盼东陈泽华吴伟娜
毛盼东 陈泽华*, 王 媛 秦 莉 吴伟娜 王 元*,
基于3-乙基-2-乙酰吡嗪缩肼基甲酸甲酯的铜和锌配合物的晶体结构及荧光性质
毛盼东1陈泽华*,1王 媛2秦 莉2吴伟娜1王 元*,1
(1河南理工大学化学化工学院,焦作 454000)
(2河南理工大学材料科学学院,焦作 454000)
合成并通过单晶X射线衍射、元素分析及红外光谱表征了配合物[Cu(HL)Cl2]·H2O(1)和[ZnL2](2)的结构(HL为3-乙基-2-乙酰吡嗪缩肼基甲酸甲酯)。单晶衍射结果表明,在配合物1中,Cu离子拥有四方锥配位构型,与一个中性配体HL和2个氯离子配位。配合物2中,Zn离子与来自2个阴离子配体L-的N2O电子供体配位,配位构型为扭曲的八面体。此外还研究了配合物1和2的固体荧光性质。
肼基甲酸甲酯;吡嗪;荧光;晶体结构
Transition metal complexes have become of increasing importance in synthetic chemistry,coordination chemistry,homogenous catalysis and biological chemistry[1].Among the various types of ligands,Schiff bases,including acylhydrazones[2-4],thiosemicarbazones[5-6]and semicarbazones[7-8],and their transition metal complexes have been widely investigated due to the high biological and pharmaceutical activities.However,astheir structurally analogous,carbazates(R-O-CO-NHNH2)have been paid much less attention[9].
On the other hand,Cu2+and Zn2+are crucial to the life because they are present as important cofactors of various enzymes and numerous proteins[10].Furthermore,pyrazines are an important class of nitrogen heterocyclic compounds with a variety of biological activities and are used as key structural motifs for the synthesis of various pharmaceutical agents[11-12].Our previous work has shown that the semicarbazone,namely,methyl(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)carbazatecould coordinate with Niand Cdions[9].As the continuation of our work on Schiff base metal complexes,we report here the crystal structures of Cuand Zncomplexes with methyl(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)carbazate(HL).In addition,the luminescent properties of the complexes in solid state were investigated.
1 Experimental
1.1 Materials and measurements
Solvents and starting materials for synthesis were purchased commercially and used as received.Elemental analysis was carried out on an Elemental Vario EL analyzer.The IR spectra(ν=4 000~400 cm-1)were determined by the KBr pressed disc method on a Bruker V70 FT-IR spectrophotometer.1H NMR spectra of L was acquired with Bruker AV400 NMR instrument in DMSO-d6solution with TMS as internal standard.The UV spectra were recorded on a Purkinje General TU-1800 spectrophotometer.Fluorescence spectra were determined on a Varian CARY Eclipse spectrophotometer.
1.2 Preparation of the ligand,complexes 1 and 2
As shown in Scheme 1,the ligand HL was produced by condension of 3-ethyl-2-acetyl pyrazine(1.51 g,0.01 mol)and methyl hydrazinocarboxylate(0.90 g,0.01 mol)in anhydrous methanol solution(30 mL)with continuous stirring at room temperature for 3 h.The white solid was filtered and washed three times by cold methanol.Yield:1.44 g (65%).m.p.111.9~112.5℃.Elemental analysis Calcd.for C10H14N4O2(%):C:54.04;H:6.35;N:25.21;Found(%):C:54.22;H:6.26;N:25.15.FT-IR(cm-1):ν(C=O)1 727,ν(C=N)1 605,ν(C=N)pyrazine1 560.1H NMR(400 MHz,DMSO-d6):δ10.44(1H,s,NH),8.48~8.53(2H,dd,pyrazine-H),3.73 (3H,s,CH3),3.01~3.06 (2H,q,CH2),2.26(3H,s,CH3),1.21~1.25(3H,t,CH3).
Crystals of(H2L)NO3,complexes 1 and 2 suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis were obtained by slow evaporating the methanol solution(10 mL)of the ligand HL(5 mmol)with equimolar of Ga(NO3)3·6H2O,CuCl2·2H2O and Zn(NO3)2·6H2O at room temperature,respectively.
(H2L)NO3:colorless rods.
1:green plates.Anal.Calcd.for C10H16N4O3Cl2Cu(%):C:32.05;H:4.30;N:14.95.Found(%):C:32.12;H:4.15;N:15.02.FT-IR(cm-1):ν(C=O)1 720,ν(C=N)1 566,ν(C=N)pyrazine1 508.
2:yellow plates.Anal.Calcd.for C20H26N8O4Zn(%):C:47.30;H:5.16;N:22.06.Found(%):C:47.22;H:5.12;N:22.15.FT-IR(cm-1):ν(N=C-O)1 644,ν(C=N)1 562,ν(C=N)pyrazine1 510.
1.3 X-ray crystallography
The single crystal X-ray diffraction data for(H2L)NO3,complexes 1 and 2 were performed on a Bruker SMART APEXⅡCCD diffractometer equipped with a graphite monochromatized Mo Kα radiation(λ=0.071 073 nm)by using φ-ω scan mode at 296(2)K.Semi-empirical absorption correction was applied to the intensity data using the SADABS program[13].The structures were solved by direct methods and refined by full matrix least-square on F2using the SHELXTL-97 program[14].All non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically.All the H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model.The O5 and O6 atoms of the nitrate anion in(H2L)NO3occupied two positions,with the occupancy value of OVO5(O6)/OVO5A(O6A)being 0.723/0.277.Details of the crystal parameters,data collection and refinements for(H2L)NO3,complexes1and 2 aresummarized in Table1.

Scheme 1 Synthesis route of HL

Table 1 Crystal data and structure refinement for(H 2L)NO3,complexes 1 and 2
CCDC:1544291,(H2L)NO3;1544292,1;1544293,2.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Crystal structure description
Selected bond distances and angles,hydrogen bonds information for(H2L)NO3,complexes 1 and 2 are listed in Table 2 and 3,respectively.The reaction of theligand HL with Ga(NO3)3generates crystalsof(H2L)NO3,establishing the hydrolysis of the metal salt.The asymmetric unit of(H2L)NO3contains two counter nitrate anions and two independent protonated(N2 and N6 atoms of pyrazines)organic ligands.Bond lengths of carbonyl C9-O1(0.118 2(4)nm)and C19-O3(0.117 0(4)nm)are shorter than those of some reported neutral semicarbazones[15].In the crystal,H2L molecules are linked by nitrate anions into onedimensional chains(Fig.1d)via intermolecular N-H…O hydrogen bonds.

Table 2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and angles(°)in(H 2L)NO3,complexes 1 and 2
Asshown in Fig.1b,complex 1 containsonecrystal water molecule and one discrete Cucomplex,in which the ratio of the ligand HL and metal is 1∶1 andthe ligand is neutral tridentate with carbonyl C=O bond length being 0.122 5(3)nm.The Cuion is also coordinated with two chloride anions,giving a distorted square pyramid coordination geometry(τ=0.148)[16].In the solid state,crysltal water molecules link the complexes into a one-dimensional chain along c axis (Fig.1e)through intermolecular N-H…O and O-H…Cl hydrogen bonds.

Table 3 Hydrogen bonds information for(H 2L)NO3 and complex 1

Fig.1 Diamond drawing of(H2L)NO3(a),complexes 1(b)and 2(c)with 30%thermal ellipsoids;Extended chain-like supramolecular structure in(H2L)NO3(d)and complex 1(e)
2.2 IR spectra
Theν(C=O)of the free ligand HL is at 1 727 cm-1,and it shifts to lower frequency value in complex 1,confirming the coordination of the carbonyl group[9].However,such absorption band is disappeared in complex 2,meanwhile,new(N=C-O)stretching vibration absorption is observed at 1 644 cm-1,revealing that the C=O in O=C-N moiety has enolizated and the oxygen atom coordinates to the Znion[16].Theν(C=N)bands of the imine group and pyrazine ring in the ligand HL shift to lower frequency values in both complexes,indicating that the N atoms of both units take part in the coordination[16],which is in accordance with the crystal structure study.
2.3 UV spectra
The UV spectra of HL,complexes 1 and 2 in CH3OH solution(1×10-5mol·L-1)were measured at room temperature (Fig.2).The spectra of HL features only one main band located around 285 nm(ε=6 389 L·mol-1·cm-1),which could be assigned to characteristic π-π*transition of pyrazine unit[9].Similar bands are observed at 284 nm(ε=5 143 L·mol-1·cm-1)in that of complex 2.However,there are three bonds in spectra of 1 at 257 nm(ε=9 334 L·mol-1·cm-1),291 nm(ε=10 444 L·mol-1·cm-1)and 385 nm(ε=6 864 L·mol-1·cm-1).The former two could be contributed to the characteristic π-π*transition of pyrazine and imine unit,respectively,while the final one is probably due to the ligand-to-metal charge transfer(LMCT)[16].

Fig.2 UV spectra of the ligand HL,complexes 1 and 2 in CH3OH solution at room temperature
2.4 Fluorescence spectra
Fig.3 shows the emission spectra of the ligand HL,complexes 1 and 2 in solid state.When excited at 330 nm,the ligand shows single emission band at 400 nm,while complex 2 exhibits two broad emissions at 400 and 490 nm,which is probably due to the energy transferring from the ligand to the Znion[17].The behavior of Zn2+coordinated to the ligand is regarded as that of emissive species resulting in a CHEF effect(chelation enhancement of the fluorescence emission)[18].By contrast,the center Cuion induces obvious fluorescence quenching of HL in complex 1.
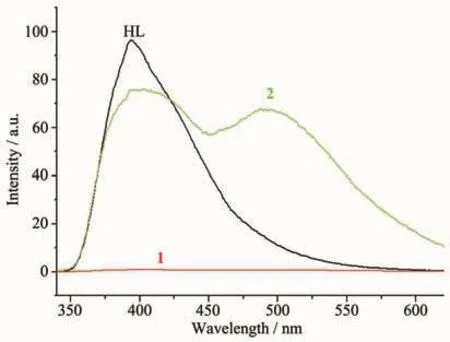
Fig.3 Fluorescence emission spectra of the ligand HL,complexes 1 and 2 in solid state at room temperature
[1]Sharma S,Chauhan M,Jamsheera A,et al.Inorg.Chim.Acta,2017,458:8-27
[2]El-Gammal O A,Bekheit M M,Tahoon M.Spectrochim.Acta A,2015,135:597-607
[3]Shaabani B,Khandar A A,Kazemi S S,et al.Polyhedron,2013,49:61-66
[4]Singh P,Singh D P,Singh V P.Polyhedron,2014,81:56-65
[5]Qi J,Deng J,Qian K,et al.Eur.J.Med.Chem.,2017,134:34-42
[6]Rogolino D,Cavazzoni A,Gatti A,et al.Eur.J.Med.Chem.,2017,128:140-153
[7]Safavi M,Foroumadi A,Nakhjiri M,et al.Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett.,2010,20:3070-3073
[8]Venkatachalam T K,Bernhardt P V,Noble C J,et al.J.Inorg.Biochem.,2016,162:295-308
[9]MAO Pan-Dong(毛盼东),HAN Xue-Feng(韩学锋),WU Wei-Na(吴伟娜),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(无机化学学报),2016,32:161-166
[10]Trusso Sfrazzetto G,Satriano C,Tomaselli G A,et al.Coord.Chem.Rev.,2016,311:125-167
[11]Li M X,Zhang L Z,Yang M,et al.Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett.,2012,22:2418-2433
[12]Li M X,Zhang L Z,Zhang D,et al.Eur.J.Med.Chem.,2011,46:4383-4390
[13]Sheldrick G M.SADABS,University of Göttingen,Germany,1996.
[14]Sheldrick G M.SHELX-97,Program for the Solution and the Refinement of Crystal Structures,University of Göttingen,Germany,1997.
[15]Soria-Martínez R,Mendoza-Meroo R,García-Granda S.J.Mol.Struct.,2016,1105:322-331
[16]WU Hao(吴浩),CHEN Ze-Hua(陈泽华),YU Ya-Ping(于亚平),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(无机化学学报),2017,33:699-704
[17]CHENG Mei-Ling(程美令),CAO Xiang-Qian(曹向前),WANG Chun-Lan(王春兰),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(无机化学学报),2006,22:1222-1226
[18]Vicente M,Bastida R,Lodeiro C,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2003,42:6768-6779
Twocomplexes,namely[Cu(HL)Cl2]·H2O(1)and[ZnL2](2)(HL=methyl(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)carbazate)have been synthesized and characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction,elemental analysis and IR spectroscopy.X-ray diffraction analysis results show that in complex 1,the Cuion with a distorted square pyramid coordination geometry is coordinated with one neutral ligand HL and two chloride anions.However,the central Znion in complex 2 is surrounded by two independent anionic ligands with N2O donor set,thus possesses a distorted octahedral coordination geometry.The luminescent properties of the complexes were also studied in detail.CCDC:1544291,(H2L)NO3;1544292,1;1544293,2.
methyl hydrazinocarboxylate;pyrazine;fluorescence;crystal structure
O614.121;O614.24+1
A
1001-4861(2017)10-1849-06
10.11862/CJIC.2017.214
MAOPan-Dong1CHEN Ze-Hua*,1WANGYuan2QIN Li2WU Wei-Na1WANG Yuan*,1
(1College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Henan Polytechnic University,Jiaozuo,Henan 454000,China)
(2School of Materials Science and Engineering,Henan Polytechnic University,Jiaozuo,Henan 454000,China)
2017-04-17。收修改稿日期:2017-07-19。
国家自然科学基金(No.21001040)、河南省科技厅基础与前沿项目(No.162300410011)、河南省教育厅自然科学基金(No.12B15001,14B150029)和河南省青年骨干教师项目(No.2014GGJS-045)资助。
*通信联系人。 E-mail:chen1861@hpu.edu.cn,wangyuan08@hpu.edu.cn;会员登记号:S06N4036M1112(王元)。
