铰链组局部损伤的非充气弹性车轮负荷接地及固有特性
2017-11-01臧利国赵又群孙海燕尹荣栋
臧利国,赵又群,孙海燕,尹荣栋,林 棻
铰链组局部损伤的非充气弹性车轮负荷接地及固有特性
臧利国1,2,赵又群2※,孙海燕1,尹荣栋1,林 棻2
(1. 南京工程学院汽车与轨道交通学院,南京 211167;2. 南京航空航天大学能源与动力学院,南京 210016)
为研究重要承载部件损伤对非充气弹性车轮性能的影响,对单组铰链组断裂前后的车轮进行了性能对比试验。采用拆除单组铰链组的方法模拟断裂损伤失效,基于台架试验对损伤前后车轮的负荷特性、接地压力分布特性及模态试验等进行了对比。结果表明:铰链组断裂损伤对车轮负荷特性的影响表现为径向刚度的下降,且与损伤所在车轮的位置有关。当损伤分别位于水平和竖直位置时,铰链组断裂损伤车轮的平均径向刚度较无损伤车轮的数值分别下降25%和35%;在相同垂向载荷作用下,铰链组断裂损伤对车轮接地压力分布的影响表现为接地印迹长度和接地面积的增大,垂向载荷为7 262 N时,损伤车轮的接地印迹长度较无损伤车轮的数值增大15%,接地印迹宽度没有变化,接地面积增大;整体上无损伤车轮的固有频率大于铰链组断裂损伤车轮对应的固有频率,大多数阻尼系数小于含有铰链组断裂损伤车轮对应的阻尼系数,节点的振型幅值大于相应的损伤车轮节点的振型幅值。该研究可为提高非充气弹性车轮的可靠性设计提供参考。
车辆;轮胎;车轮;局部损伤;负荷特性;接地特性;模态试验
0 引 言
轮胎作为轮式车辆行驶系的重要组成部分,主要作用为支撑整车质量、缓和路面冲击、产生驱动/制动力等,其性能对车辆的操纵稳定性、平顺性等影响显著[1-3]。装备充气轮胎的车辆存在刺破泄气、爆胎隐患,开发具有防爆胎、防刺破性能的安全轮胎对提高车辆行驶安全性、可靠性具有重要意义[4-6]。
目前,安全轮胎技术主要包括改进传统充气轮胎的性能和采用非充气轮胎(车轮)2种方案[4]。充气安全轮胎主要包括多腔式、自密封式、辅助支撑式等类型。由于多腔式充气安全轮胎制造工艺较复杂,成本较高;自密封式安全轮胎存在防爆能力有限、环境温度适应性差等关键技术需待解决;辅助支撑式安全轮胎存在生热严重、笨重等问题,性能仍需要进一步优化。非充气轮胎(车轮)采用非充气结构,从根本上解决爆胎、刺破等问题,为安全轮胎技术的研究提供了新的思路[7-12]。
课题组研究的非充气弹性车轮,采用非充气结构的輮轮及悬毂式承载方式实现支撑、缓冲减振等功能,从结构上有效地避免了爆胎、刺破泄气等潜在的安全隐患,并在越野车辆进行了装车验证。理论和试验研究表明,铰链组作为非充气弹性车轮重要的承载部件,受力十分复杂,其承载状况对弹性车轮的性能影响显著[13-16]。非充气弹性车轮从结构上避免了刺穿造成的失效,但是重要承载部件的疲劳等损伤形式仍然存在。尤其是在复杂越野路面行驶时,因冲击载荷导致的过载断裂失效、高应力应变承载部件的疲劳失效等是影响车轮安全性能的主要因素[17-20]。
铰链组断裂损伤的非充气弹性车轮在满足承载、缓冲减振等轮胎基本性能的前提下,还必须保证车辆行驶的安全性[21-24]。为探索重要承载部件失效后车轮的性能变化,有必要研究铰链组局部损伤对非充气弹性车轮性能的影响规律。本文采用拆除单组铰链组的方法模拟铰链组断裂损伤失效,基于台架试验对损伤前后车轮的负荷特性、接地压力分布特性及模态振型等进行了对比。
1 设备与方法
1.1 负荷特性及接地压力分布试验设备与方法
非充气弹性车轮负荷特性及接地压力分布试验在自行研制的试验台架上进行,如图1所示。通过液压缸2、压板4及侧板5在车轮轴处施加不同垂向力,模拟车轮承受的载荷。试验前,按照铰链组的位置将非充气弹性安全车轮沿圆周方向进行12等分并标记。在试验时记录车轮1-1′、2-2′等对点之间的长度数值,可得到变形后的车轮轨迹。首先对无损伤车轮进行试验,采用拆除单组铰链组的方法来模拟铰链组的断裂失效,然后对损伤前后的非充气弹性车轮负荷特性、接地压力分布特性进行对比分析,其中下沉量参照充气轮胎定义为车轮外半径与负荷作用下的静半径的差值。

1. 顶板 2. 液压缸 3. 电源控制器 4. 压板 5. 侧板 6. 车轮 7. 液压站 8. 导向柱 9. 底板
根据非充气弹性车轮的悬毂式承载结构分析可知,水平和竖直的位置是2个典型的极端工况,其余位置铰链组的受力是与转动位置相关的连续函数[13],分析上述2个典型工况能代表性地反应含有单组铰链组断裂损伤的非充气弹性车轮刚度的变化规律,因此针对上述2个工况分别进行加载试验。施加的负荷应小于车轮承受的最大承受,且负荷尽可能在分布整个负荷区间。
按照充气轮胎试验规程及要求[25-26],将车轮损伤位置分别布置在水平和竖直2个方向,进行径向加载试验。由导向柱的刻度可测量车轮的径向变形,然后再由测量工具测得标记的对点之间的数值。在车轮和底板之间放置复写纸,根据印迹颜色分布即可测得不同载荷下的接地压力分布。
1.2 模态试验设备与方法
模态试验是获取车轮模态参数的重要方法,也是研究车轮振动特性的基础[27-29]。为进一步研究含有单组铰链组断裂损伤的非充气弹性车轮的特性,对其进行自由模态试验,对比单组铰链组断裂损伤前后车轮的固有频率、阻尼系数和模态振型。参照充气轮胎的模态试验方法,一般有自由悬置法和固支法2种[30]。本文采用自由悬置法进行模态试验,试验原理如图2所示。

图2 自由悬置模态试验原理示意图
模态试验所用的主要设备有西门子公司的LMS SCM205多通道数据采集系统、PCB 333B30加速度传感器(灵敏度为100 mV/g)、PCB 086C03力传感器(灵敏度为2.25 mV/N)。进行试验时将车轮自由悬置,在胎面中心线上均匀12个测点,并进行编号,在编号①、③和⑤的位置布置3个单向加速度传感器,采用移动力锤依次敲击12个测点进行径向激振,试验如图3所示。

a. 车轮 b. 仪器
采用LMS Test.Lab中的多参考点最小二乘复频域(Poly MAX)方法可识别高度密集模态,且对每一阶模态参数都有较高的识别精度,因此本试验采用Poly MAX模态分析方法进行模态参数识别和试数据处理。
在轮胎旋转过程中的振动激励主要来自于路面不平度和由轮胎质量或者刚度不均匀带来的激励,其中路面不平度对轮胎的激励能量主要集中在低频段。一般情况下在400 Hz以内可识别出轮胎的前10阶模态参数[31-32]。实际行驶过程中,前几阶模态就能反映轮胎的动态特性,综合轮胎动力学关心的频率范围和计算效率等因素[33],本次试验在LMS Test Lab 13A模态试验分析系统中设置频带为512 Hz,设置频率分辨率为0.83 Hz。
2 结果与分析
2.1 负荷特性试验
由上述试验方法得到径向加载试验数据如表1所示。车轮加载变形前后轨迹对比如图4所示。

注:F为负荷,N;Fz为地面作用力,N。
由表1试验数据可知,在相同载荷作用下,铰链组断裂位置位于编号1水平位置时,比位于编号4竖直位置时车轮的下沉量要小,主要是由于在车轮无损伤情况下编号1处铰链组承受的拉力小于编号4处铰链组承受的拉力,因此径向变形也较小。

表1 铰链组断裂损伤前后非充气弹性车轮负荷特性试验
利用线性回归方法对铰链组断裂车轮的试验数据进行处理,得到静负荷特性曲线如图5所示。由图5可知在所施加负荷的范围内,无损伤车轮及不同方向铰链断裂的车轮静负荷特性曲线都近似为直线,直线斜率的倒数即为平均径向刚度。计算得到无损伤车轮的平均径向刚度为593.06 N/mm。编号1水平位置处铰链组断裂车轮的平均径向刚度值为443.2 N/mm,较无损伤车轮径向刚度值下降25%,编号4竖直位置处铰链组断裂车轮的平均径向刚度值为385.4 N/mm,较无损伤车轮径向刚度值下降35%。编号1处的铰链组断裂车轮的平均径向刚度值大于编号4处的铰链组断裂车轮的平均径向刚度值。
由上述结果分析可知,铰链组断裂损伤使车轮的径向刚度下降,且数值变化与损伤所在车轮的位置有关。含有单组铰链组断裂损伤的车轮在不同滚动位置时,径向刚度值一致性变差,进一步影响滚动过程中变形的均匀性。因此,在车轮设计中应尽可能的提高铰链组强度,或采用结构冗余技术提高车轮可靠性。

图5 铰链组断裂损伤前后非充气弹性车轮负荷特性曲线
2.2 接地压力分布试验
在台架上进行静态接地特性试验[25],得到4组不同垂向负荷作用下的无损伤非充气弹性车轮接地压力分布,如图6a-6d所示。由图6a-6d可知接地印迹形状近似为矩形,随着负荷的增加,接地宽度基保持不变,接地长度和接地面积均增加,且在輮轮的弹性环骨架处压力逐渐变大,如图6d圈注所示。
同样可得到铰链组断裂损伤在水平位置时车轮的接地压力分布,如图6e-6h所示。由图6e-6h可知此时的接地压力分布规律与6a-6d类似。测量图6a和图6e中接地印迹形状可知,在7 262 N的负荷作用下,无损伤车轮的接地印迹长度为120 mm,铰链组断裂损伤车轮的接地印迹长度增大至138 mm,增大15%,接地印迹宽度没有变化,均为285 mm;无损伤车轮的接地面积为34 200 mm2,铰链组断裂损伤车轮的接地面积增大至39 330 mm2。

a. F=7 262 N,无损伤车轮 a. F=7 262 N, Non-damage wheelb. F=13 492 N,无损伤车轮 b. F=13 492 N, Non-damage wheelc. F=19 722 N,无损伤车轮 c. F=19 722 N, Non-damage wheeld. F=26 201 N,无损伤车轮 d. F=26 201 N, Non-damage wheel e. F=7 262 N,损伤车轮 e. F=7 262 N, Damaged wheelf. F=13 554 N,损伤车轮 f. F=13 554 N, Damaged wheelg. F=16 607 N,损伤车轮 g. F=16 607 N, Damaged wheelh. F=22 993 N,损伤车轮 h. F=22 993 N, Damaged wheel
2.3 模态试验
分别对铰链组断裂损伤前后的非充气弹性车轮进行自由悬置模态试验,提取前8阶固有频率和阻尼系数如表2所示。由试验结果可知,除第1阶和第4阶外,无损伤非充气弹性安全车轮的固有频率均大于含有铰链组断裂损伤车轮对应的固有频率。这是由于车轮铰链组断裂损伤之后,车轮刚度变小,因此固有频率降低。对比阻尼系数可以看出,无损伤非充气车轮有5组阻尼系数小于含有铰链组断裂损伤车轮对应的阻尼系数。试验数据的不均匀分布主要是由于车轮的刚度和圆度的一致性误差、试验操作误差导致。
铰链组断裂损伤前后车轮前4阶模态振型图如图7所示。由图可知,排除个别节点,损伤前后车轮第一阶模态振型为“错动”,第二阶模态振型为“椭圆”,第三阶模态振型为“三瓣”,第四阶模态振型为“四瓣”,变化规律与充气轮胎类似[30]。对应阶数振型节点的幅值整体表现为:无损伤非充气弹性安全车轮节点的振型幅值大于相应的铰链组断裂损伤车轮节点振型幅值。
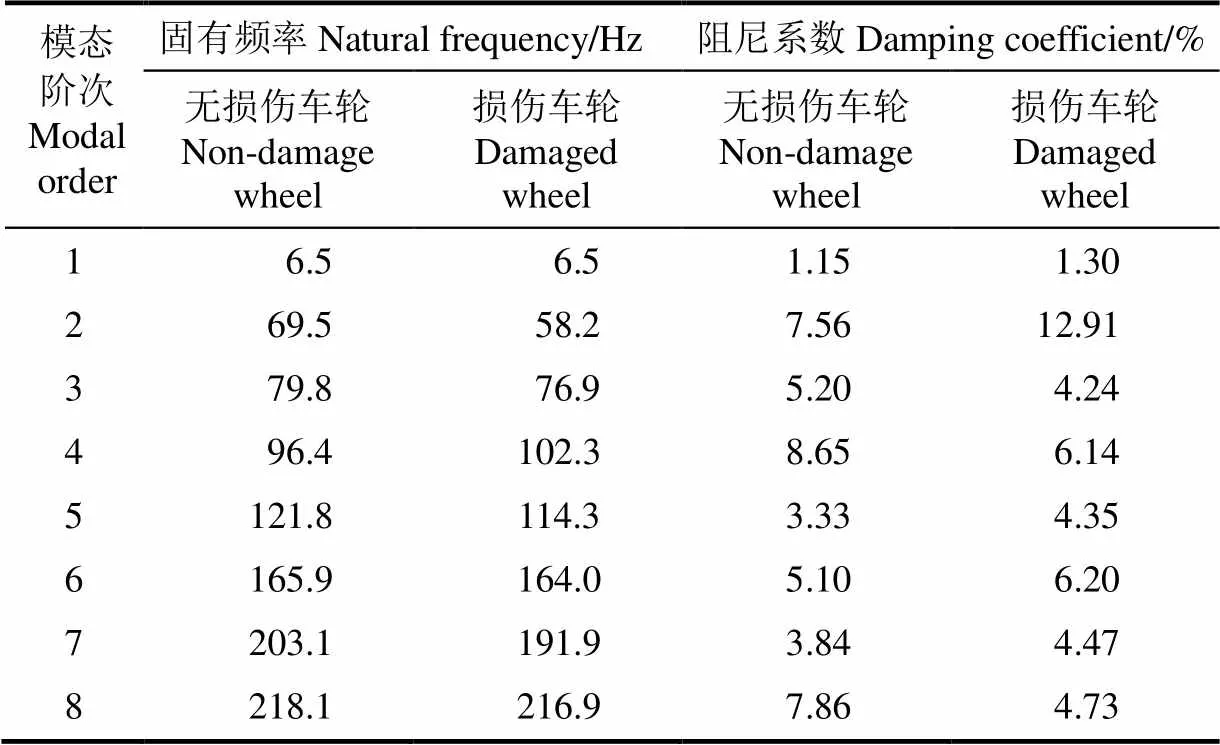
表2 铰链组断裂损伤前后车轮模态试验数据

a.无损伤车轮1阶振型 a. First-order mode of non-damage wheelb. 无损伤车轮2阶振型 b. Second-order mode of non-damage wheelc. 无损伤车轮3阶振型 c. Third-order mode of non-damage wheeld. 无损伤车轮4阶振型 d. Fourth-order mode of non-damage wheel e.损伤车轮1阶振型 e. First-order mode of damaged wheelf. 损伤车轮2阶振型 f. Second-order mode of damaged wheelg. 损伤车轮3阶振型 g. Third-order mode of damaged wheelh. 损伤车轮4阶振型 h. Fourth-order mode of damaged wheel
图7 铰链组断裂损伤前后非气充式弹性车轮1-4阶振型
Fig.7 Vibration modes of first-order to fourth-order of non-pneumatic elastic wheel before and after hinge group fracture
3 结 论
1)铰链组断裂损伤对车轮负荷特性的影响表现为径向刚度的变化,且与损伤所处车轮的位置有关。当损伤分别位于水平和竖直位置时,铰链组断裂损伤车轮的平均径向刚度较无损伤车轮的数值分别下降25%和35%。
2)铰链组断裂损伤对车轮接地压力分布特性的影响表现为接地印迹和接地面积的变化。在相同载荷作用下,铰链组断裂损伤车轮的接地印迹长度和接地面积增大。垂向载荷为7 262 N时,损伤车轮的接地印迹长度较无损伤车轮的数值增大15%,接地印迹宽度没有变化,接地面积增大。
3)除个别阶数,无损伤非充气弹性安全车轮的固有频率均大于损伤车轮对应的固有频率,且大多数无损伤非充气车轮的阻尼系数小于损伤车轮对应的阻尼系数;无损伤非充气弹性安全车轮节点的振型幅值大于相应损伤车轮节点的振型幅值。
[1] 庄继德. 现代汽车轮胎技术[M]. 北京:北京理工大学出版社,2001.
[2] Gent A N, Walter J D. The pneumatic tire[M]. Washington, D C: National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, 1985.
[3] 危银涛,李勇,冯希金,等.轮胎理论与技术[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2013.
[4] 佟金,杨欣,张伏,等. 零压续跑轮胎技术现状与发展[J]. 农业机械学报,2007,38(3):182-187.
Tong Jin, Yang Xin, Zhang Fu, et al. Development of run-flat tire technology[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2007, 38(3): 182-187. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 姜成,赵又群,阮米庆,等. 非充气安全轮胎技术现状与发展[J]. 机械设计与制造,2013(9):266-268.
Jiang Cheng, Zhao Youqun, Ruan Miqing, et al. The current situation and development of non- pneumatic safety tire[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2013(9): 266-268. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 解来卿,高树新,赵明,等. 自封式安全轮胎与普通轮胎装车对比道路试验[J].汽车技术,2008(8):52-54.
Xie Laiqing, Gao Shuxin, Zhao Ming, et al.Road test comparison of self-sealing safety tire and ordinary tire[J].Automobile Technology, 2008(8): 52-54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] Yoo S, Uddin M S, Heo H, et al. Thermoviscoelastic modeling of a non-pneumatic tire with a lattice spoke[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2017, 231(2): 241-252.
[8] Kumar A S, Kumar R K. Force and moment characteristics of a rhombi tessellated non-pneumatic tire[J]. Tire Science and Technology, 2016, 44(2): 130-148.
[9] Rhyne T B, Cron S M. Development of a non-pneumatic wheel[J]. Tire Science and Technology, 2006, 34(3): 150-169.
[10] Bras B, Cobert A. Life-cycle environmental impact of Michelin tweel tire for passenger vehicles[J]. SAE International Journal of Passenger Cars-Mechanical Systems, 2011, 4(1): 32-43.
[11] Kim K, Kim D M. Contact pressure of non-pneumatic tires with hexagonal lattice spokes[J]. SAE International Journal of Passenger Cars-Mechanical Systems, 2013, 6(3): 1518-1527.
[12] 臧利国,赵又群,李波,等. 机械弹性车轮提高轮胎耐磨性和抓地性分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(12):56-63.
Zang Liguo, Zhao Youqun, Li Bo, et al. Mechanical elastic wheel improving road holding and wear resistance of tire[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(12): 56-63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] Zhao Youqun, Zang Liguo, Chen Yueqiao, et al. Non-pneumatic mechanical elastic wheel natural dynamic characteristics and influencing factors[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2015, 22(5): 1707-1715.
[14] 臧利国,赵又群,李波,等.非充气机械弹性车轮接地特性试验研究[J]. 汽车工程,2016,38(3):350-355.
Zang Liguo, Zhao Youqun, Li Bo, et al. An experimental study on the ground contact characteristics of non-pneumatic mechanical elastic wheel[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2016,38(3): 350-355. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] Li Bo, Zhao Youqun, Zang Liguo. Closed-form solution of curved beam model of elastic mechanical wheel[J]. Journal of Vibroengineering, 2014, 16(8): 3951-3962.
[16] 何志刚,周孔亢,应世洲,等. 轮胎疲劳失效研究综述[J]. 机械工程学报,2009,45(3):76-83.
He Zhigang, Zhou Kongkang, Ying Shizhou, et al. Review of research approaches of fatigue failure of tyres[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 45(3): 76-83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 臧利国,赵又群,李波,等. 局部损伤的机械弹性车轮的静动态特性[J]. 振动、测试与诊断. 2016,36(3):478-483.
Zang Liguo, Zhao Youqun, Li Bo, et al. Static and dynamic state characteristics of local damage mechanical elastic wheel[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2016, 36(3): 478-483. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 张明杰,赵又群,杜现斌,等. 机械弹性车轮疲劳寿命及其影响因素研究[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报,2016,37(11):1560-1564.
Zhang Mingjie, Zhao Youqun,Du Xianbin, et al. Fatigue life and influencing factors of a mechanical elastic wheel[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2016, 37(11): 1560-1564. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 周长城,潘礼军,于曰伟,等. 车辆钢板弹簧悬架系统减振器最佳阻尼匹配[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(7):106-113.
Zhou Changcheng, Pan Lijun, Yu Yuewei, et al. Optimal damping matching for shock absorber of vehicle leaf spring suspension system[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(7): 106-113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 范政武,王铁,陈峙. 基于人工鱼群算法的车辆平顺性优化分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(6):107-114.
Fan Zhengwu, Wang Tie, Chen Zhi. Vehicle ride comfort analysis and optimization based on artificial fish swarm algorithm[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(6): 107-114. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 郭孔辉,邱恩超. 基于环模型的轮胎滚动接触有限元分析[J].吉林大学学报,2011,41(3):597-601.
Guo Konghui, Qiu Enchao. Finite element analysis of tire rolling contact based on ring supported on elastic foundation model[J]. Journal of Jilin University, 2011, 41(3): 597-601. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 左曙光,毛钰,吴旭东,等.基于柔性环轮胎模型的电动轮固有特性分析[J].振动与冲击,2016,35(3):41-47.
Zuo Shuguang, Mao Yu, Wu Xudong, et al. Inherent characteristic analysis of the electrical wheel based on a flexible ring model[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2016, 35(3): 41-47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 危银涛,刘哲,周福强,等. 考虑面外振动的轮胎三维环模型[J].振动工程学报,2016,29(5):765-803.
Wei Yintao, Liu Zhe, Zhou Fuqiang, et al. Three-dimensional REF model of tire including the out-of-plane vibration[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2016, 29(5): 765-803. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 梁晨,王国林,周海超,等. 子午线轮胎接地压力分布评价试验研究[J]. 汽车技术,2013(11):38-42.
Liang Chen, Wang Guolin, Zhou Haichao, et al. Experimental study of radial tire contact pressure distribution evaluation[J]. Automobile Technology, 2013(11): 38-42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 中国国家标准化管理委员会.GB/T 22038-2008 汽车轮胎静态接地压力分布试验方法[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2008.
[26] Shang Jin, Guan Dihua, Li Baojiang. Analysis and modelling of tyre in-plane time domain simulation with modal parameter tyre model[J]. International Journal of Vehicle Design, 2013, 63(1): 18-38.
[27] Wang Zhenfeng, Dong Mingming, Zhao Weipeng, et al. A novel tread model for tire modelling using experimental modal parameters[J]. Journal of Vibroengineering, 2017, 19(2): 1225-1240.
[28] Qiao Jianfeng, Du Yongchang, Zhao Peng. Three -dimensional modal parameters of tire[C]//Conference Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Mechanics Series.New York: Springer New York LLC, 2014: 225-230.
[29] Fan Chengjian, Guan Dihua. The quantitative analysis and experimental verification of the tire static enveloping model using experimental modal parameters[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2006, 44 (9): 675-688.
[30] 管迪华,彭会,范成建. 轮胎模态试验分析的研究[J].汽车工程, 2005,27(6):691-695.
Guan Dihua, Peng Hui, Fan Chengjian. A Research on tire modal testing analysis[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2005,27(6): 691-695. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 冯希金,危银涛,朱光苗,等. 子午线轮胎固有频率和阻尼辨识的数值与实验研究[J].弹性体,2015,25(4):26-30.
Feng Xijin, Wei Yintao, Zhu Guangmiao, et al. Numerical and test method on identifying natural frequency and damping ratio of a radial tire[J]. China Elastomerics, 2015, 25(4): 26-30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] Selig M, Lorenz B, Henrichmöller D, et al. Rubber friction and tire dynamics: A comparison of theory with experimental data[J]. Tire Science and Technology, 2014, 42(4): 216-262.
[33] Yamashita H, Matsutani Y, Sugiyama H. Longitudinal tire dynamics model for transient braking analysis: ANCF-LuGre tire model[J]. Journal of Computational and Nonlinear Dynamics, 2015, 10(3): 031003-1.
臧利国,赵又群,孙海燕,尹荣栋,林 棻. 铰链组局部损伤的非充气弹性车轮负荷接地及固有特性[J].农业工程学报,2017,33(19):102-107. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.19.013 http://www.tcsae.org
Zang Liguo, Zhao Youqun, Sun Haiyan, Yin Rongdong, Lin Fen. Load, contact behavior and natural characteristics of non-pneumatic elastic wheel with local damage hinge group[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(19): 102-107. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.19.013 http://www.tcsae.org
Load, contact behavior andnatural characteristics of non-pneumatic elastic wheel with local damage hinge group
Zang Liguo1,2, Zhao Youqun2※, Sun Haiyan1, Yin Rongdong1, Lin Fen2
(1.211167,; 2.210016,)
The conventional pneumatic tires have disadvantages in terms of puncture, blowout at high speed, pressure maintenance, and so on. Due to these structural inevitable weaknesses, non-pneumatic tires have been developed and are being investigated. A new non-pneumatic elastic wheel was proposed and studied to solve these problems. As an important bearing member of the non-pneumatic elastic wheel, the force of hinge group is very complex and it has a significant effect on the performance of the wheel. However, in the complex off-road driving, the hinge group has to withstand complex random load and impact load, and inevitably there will be damage failure. In order to explore the performance change of the wheel after the failure of the important bearing parts, it is necessary to study the influence of the hinge group with local damage on the performance of the non-inflated elastic wheel. In this paper, an experimental study on basic characteristics of non-pneumatic elastic wheel with local hinge group fracture damage was conducted in order to enhance the reliability. Based on tire characteristic test-bed, the tests on basic characteristics of static radical stiffness and contact behavior as well as the modal test were conducted. The wheel with local damage, one hinge group of which was disassembled, was used to simulate hinge group fracture condition in this paper. The results show that the effect of the hinge group fracture damage on the wheel load characteristics is the decrease of the radial stiffness, and it is also related to the damage position on the non-pneumatic elastic wheel. The radial stiffness of non-damaged non-pneumatic elastic wheel is 593.06 N/mm, and the corresponding values of the non-pneumatic elastic wheel with fractured hinge group on horizontal position and vertical position are 443.2 and 385.4 N/mm, respectively. Compared with non-damaged non-pneumatic elastic wheel, the numerical value of radial stiffness is reduced by 25% and 35% respectively on horizontal position and vertical position when the fractured hinge group is installed. That is to say the consistency of radial stiffness and deformation uniformity get worse for the wheel with local damage, so the poor performance of riding comfort of non-pneumatic elastic wheel appears. The influence of the hinge group fracture damage on the grounding pressure distribution is the change of grounded imprinting length and grounded area. Under the same vertical load, these 2 indicators of the non-pneumatic elastic wheel with fractured hinge group increase compared with non-damaged non-pneumatic elastic wheel. When the vertical load is 7 262 N, the imprinting length of the non-pneumatic elastic wheel with fractured hinge group on horizontal position is 138 mm, and the numerical value of non-damaged non-pneumatic elastic wheel is 120 mm. The ground imprinting length of the damaged wheel is increased by 15% compared with that of the non-damaged non-pneumatic elastic wheel. The grounded imprinting width does not change, and the value remains at 285 mm. As a result, the total grounded area of the damaged wheel also increases. The area of the non-damaged non-pneumatic elastic wheel is 34 200 mm2, and the area of damaged wheel increases to 39 330 mm2. The contact length and area of the wheel with local damage are greater than corresponding values of the non-damaged non-pneumatic elastic wheel under the same load. The influence of the hinge group fracture damage on the wheel modal test is the change of the natural frequency, the damping coefficient and the modal shape. In addition to a few orders, the natural frequency of non-damaged non-pneumatic elastic wheel is greater than that of non-pneumatic elastic wheel with local damage hinge group, and the damping coefficient of the most of non-damaged non-pneumatic elastic wheel is less than that of non-pneumatic elastic wheel with local damage hinge group. The value of the amplitude of modes gets smaller for the non-pneumatic elastic wheel with local damage hinge group.
vehicles; tires; wheels; local damage; load characteristic; contact behavior; modaltest
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.19.013
U463.341
A
1002-6819(2017)-19-0102-06
2017-05-25
2017-08-21
国家自然科学基金资助项目(51605215);总装探索研究项目(NHA13002);南京工程学院高层次引进人才科研启动基金资助项目(YKJ201516)
臧利国,山东菏泽人,讲师,博士,主要从事车辆系统动力学的研究。南京 南京工程学院汽车与轨道交通学院,211167。 Email:zangliguo1102503@ nuaa.edu.cn
※通信作者:赵又群,河北秦皇岛人,教授,博士生导师,主要从事车辆系统动力学的研究。南京 南京航空航天大学能源与动力学院,210016。Email:yqzhao@nuaa.edu.cn
