芽孢杆菌表达系统的特点及研究进展
2017-10-16,,
,,
(中国农业大学食品科学与营养工程学院,北京 100083)
芽孢杆菌表达系统的特点及研究进展
苗苗,黄昆仑,梁志宏*
(中国农业大学食品科学与营养工程学院,北京100083)
芽孢杆菌表达系统作为基因工程表达系统,因具有外源蛋白易分离纯化、表达的外源蛋白不会形成包涵体、无致病性等多种优势而被广泛的研究和应用,很多种工业酶都在芽孢杆菌表达系统中获得成功表达。本文主要介绍了芽孢杆菌表达系统的研究进展,特点以及其在工业上的应用。对芽孢杆菌表达体系存在的缺陷提出了解决方法,并说明了芽孢杆菌今后发展的主要方向,为芽孢杆菌表达体系的研究提供参考。
芽孢杆菌,表达系统,枯草芽孢杆菌,研究进展
Abstract:Bacillusexpression system as gene engineering expression system has many advantages such as excellent secretion ability,successful heterologous protein expression system,not forming inclusion bodies,non-endotoxin,so it is widely studied and applied,many kinds of industrial enzymes were expressed inBacillussubtilisexpression system. In this review,it mainly talks about the advances,characters and application ofBacillusexpression system,and presents a solution to the defects in the expression system ofBacillus,offering the main research directions forBacillusexpression system.
Keywords:Bacillus;expression system;Bacillussubtilis;advances
芽孢杆菌是一种可以厌氧繁殖、能生成抗逆性孢子的菌,广泛存在于环境中[1]。如今,芽孢杆菌作为基因工程表达系统得到了越来越广泛的应用,该系统可表达耐热性酶制剂、多肽类药物和杀虫蛋白等外源蛋白,有的已经投入大规模生产,具有良好的应用前景[2]。特别是枯草芽孢杆菌,因其无内毒素产生,无致病性的优点,现已被开发成为食品级表达系统,在食物加工、医学药品、生物农药、生物饲料、生物降污等工业应用上都具有特殊的重要性。虽然芽孢杆菌表达系统有很多优势,但该系统存在着分泌蛋白酶和质粒不稳定的缺点,国内外研究的解决方法主要是使用蛋白酶缺陷菌株或添加强启动子来保证遗传的稳定性。芽孢杆菌中巨大芽孢杆菌(B.megaterium)、短芽孢杆菌(B.brevis)、解淀粉芽孢杆菌(B.amyloliquefaciens)、短小芽孢杆菌(B.pumilus)、地衣芽孢杆菌(B.licheniformis)、球形芽孢杆菌(B.sphaericus)、苏云金芽孢杆菌(B.thuringiensis)和嗜碱芽孢杆菌(B.alcalophilus)等都可用作表达宿主菌。本文介绍了枯草芽孢杆菌(B.subtilis)表达系统、巨大芽孢杆菌表达系统、短小芽孢杆菌表达系统、短芽孢杆菌表达系统、苏云金芽孢杆菌表达系统和地衣芽孢杆菌表达系统的研究进展、应用和特点,主要介绍了枯草芽孢杆菌表达系统。
1 构建高效表达的芽孢杆菌表达体系
芽孢杆菌表达体系是食用级安全的表达系统,表达的外源蛋白分离纯化。可通过提高表达载体的稳定性和提高芽孢杆菌表达体系的分泌表达效率,获得更加高效的芽孢杆菌表达系统[3-5]。
1.1 提高质粒的稳定性
自主复制质粒、整合质粒和噬菌体都可用作表达载体,自主复制的质粒应用较多。第一代主要来自金黄色葡萄球菌、革兰氏阴性菌,通过重组构成带有双抗性标志的嵌合质粒[6]。第二代质粒载体是穿梭质粒,可以在大肠杆菌表达系统和枯草芽孢杆菌表达系统中表达外源蛋白[7]。第三代质粒表达载体是由枯草芽孢杆菌的隐形质粒和大肠杆菌的质粒共同构成嵌合质粒[8]。除了质粒载体还可以使用噬菌体如sppl,Фl05噬菌体等噬菌体[9-10]。刘伟等人[11-12]构建了枯草芽孢杆菌-大肠杆菌穿梭表达载体,成功表达了绿色荧光蛋白和抗菌肽。目前常用的穿梭质粒载体有 pEB10、pEB60、pUB18和pWB980等,整合型载体,如pMutin4、pMutin-GFP+、pSG1151、pSG1156、pDG1662等。常见的大肠杆菌-枯草芽孢杆菌穿梭质粒载体和整合载体见表1。
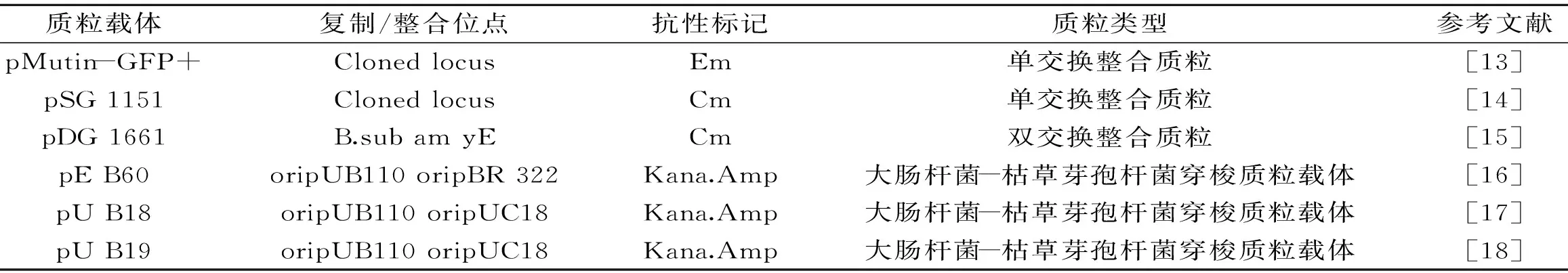
表1 芽孢杆菌整合和穿梭质粒载体Table 1 Bacillus integration and shuttle plasmid vector

表2 启动子的选择与优化Table 2 The selection and optimization of promoter
1.2 表达调控元件的选择

1.3 提高表达效率
芽孢杆菌自身会分泌多种蛋白酶,如枯草芽孢杆菌自身会分泌300多种蛋白酶[23],这些蛋白酶的分泌常常会导致外源蛋白被降解,对于这一问题可使用诱导系统,常用的有葡萄糖诱导系统和蔗糖诱导系统。使用较多的诱导系统有葡萄糖、木糖、IPTG诱导系统。Pxyl使用木糖诱导,但木糖较贵,还没有在工业上取得广泛应用,而IPTG本身对微生物有毒害作用,且本身成本也较高,也因此在工业上没有得到广泛使用[20-21]。另外提高表达效率还可使用蛋白酶突变型菌株作为宿主菌。以B.subtilis168为原始菌株的多种蛋白酶突变型菌株被广泛用于外源基因的表达,其蛋白酶突变菌株有DB104、DB105、DB431、WB600、WB700、LB700。对于表达载体、宿主菌及诱导因素和启动子等方面选择[24-25],整理了一些常见的表达体系见表3。

表3 芽孢杆菌表达系统的构建Table 3 The construction of the expression system of Bacillus

表4 枯草芽孢杆菌表达系统的应用 Table 4 The application of B.subtilis expression system

表5 芽孢杆菌表达系统的应用Table 5 The application of Bacillus expression system
2 芽孢杆菌表达系统的应用现状
2.1 B.subtilis芽孢杆菌表达系统的应用
枯草芽孢杆菌是一类好氧型杆状菌,广泛存在于自然界和动植物的体表中,其细胞外膜很薄,便于目的蛋白直接分泌到培养基中,易于分离和纯化[26]。Keith WY等人利用其简单的细胞壁,在一种工程枯草芽孢杆菌中表达了碱性成纤维细胞生长因子(bFGF),并在培养上清液中将其提取[27]。各种工业酶和饲用酶[28]都可在芽孢杆菌表达系统获得高效表达,如中性蛋白酶和淀粉酶等,结合国内外对芽孢杆菌表达系统的研究,将枯草芽孢杆菌表达系统在工业上的应用总结如下,见表4。
2.2 其他芽孢杆菌表达系统的应用
巨大芽孢杆菌具有诱导剂廉价、胞外蛋白酶活性低、质粒稳定性好的优点。是比大肠杆菌更具有优势的表达宿主,该表达系统作为外源蛋白的表达在国内外研究逐渐深入,并已经成功应用于多个基因和外源蛋白的分泌表达如β-半乳糖苷酶、水解酶、木糖等[29-30];苏云金芽孢杆菌(Bt)是来源较为广泛的土壤菌。该菌具有结晶内含物,具有杀虫的特性[33]。Bt杀虫晶体蛋白基因还含有双启动子,这种双启动子有加强基因表达的作用;短小芽孢杆菌开发成为重组体DNA分子的受体的研究受到越来越多的重视,因其还具有细胞壁蛋白会脱落的独特性质,使用携带细胞壁蛋白基因的启动子等表达元件,可使目的基因通过分泌方式得以高效表达;地衣芽孢杆菌细胞壁表面的蛋白基因也具有双启动子,该表达系统还可用于真核基因的表达,表达产物直接分泌到胞外,容易分离纯化。对于除枯草芽孢杆菌表达体系的其他芽孢杆菌表达体系的应用进行总结,见表5。
3 芽孢杆菌表达系统的特点及发展前景
随着分子生物学技术的发展和芽孢杆菌研究的深入,使用芽孢杆菌表达系统已经克隆和表达了大量基因,有些已进行大规模工业生产,多种酶和临床需要的化学药品或者工业产品都通过芽孢杆菌来表达生产。例如维生素B6、内切酶葡聚糖酶、碱性蛋白酶和脂肽[36-38],结合发酵技术,该系统还可用于工业上生产饲用酶和益生菌[41-42]。芽孢杆菌表达系统具有很强的蛋白质分泌功能,分泌的外源蛋白不易形成包涵体,无显著的密码子偏爱性,外源蛋白可直接分泌,易于分离纯化[39-40],另外枯草芽孢杆菌噬菌体和质粒都可以用作克隆载体,这是其他原核菌表达系统都不具备的优势。通过对表达调控元件的优化[54]、强启动子的使用[45-46]、发酵工艺调整[24]、筛选适合的蛋白酶缺陷菌株[49-50]等方法提高表达外源蛋白的表达效率,这对于芽孢杆菌表达系统的工业化应用具有重大意义。
[1]闫子祥,杨然 李秀婷.微生物表达系统研究进展[J]. 中国食品学报,2013,37(15):126-135.
[2]叶小兰,杨倩. 枯草芽孢杆菌在防御动物疾病中的研究进展[J]. 中国兽医科学,2011,41(9):958-988.
[3]杨明明.枯草芽孢杆菌关键遗传调控元件及表达系统的研究[D]. 咸阳:西北农林科技大学,2013:1-17.
[4]郭菁,田宝玉,蔡婉玲,等.侧孢短芽孢杆菌蛋白酶基因 BLG4 在枯草芽孢杆菌 WB600中的高效表达[J]. 福建农林大学学报:自然科学版,2011,40(2):165-171.
[5]Ameny Farhat-Khemakhem,Mounira Ben Farhat,Ines Boukhris,et al. Heterologous expression and optimization using experimental designs allowed highly efficient production of the PHY US417 phytase inBacillussubtilis168[J]. AMB Express,2012,2:2-11.
[6]Gryzczan T J.Molecular cloning inBacillussubtilis[J].The Molecular Biology of the Bacilli,1982:21-28.
[7]梁晓梅,黎明,成堏,等.大肠杆菌-枯草芽孢杆菌穿梭质粒的构建及碱性蛋白酶的的表达[J].生物技术通报,2011,4(6):165-169.
[8]夏雨.枯草芽孢杆菌食品级表达系统的构建和分泌表达研究[D].无锡:江南大学,2007:1-10.
[9]屈伸,刘志.分子生物学实验技术[M]. 北京:化学工业出版社,2008:201-204.
[10]徐子勤.功能基因组学[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2007:213-215.
[11]刘伟,林志伟,陈美霞,等. 枯草芽孢杆菌绿色荧光蛋白高效表达载体的构建[J]. 热带作物学报,2012,33(3):467-471.
[12]尚田田.枯草芽孢杆菌表达体系高效表达抗菌肽PNK-19方法的建立[D].新乡:河南科技学院,2014:8-10.
[13]Kaltwasser M,Wiegert T,Schumann W. Construction and application of epitope-and green fluorescent protein-tagging integration vect ors forBacillussubtilis[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2002,68(5):2624-2628.
[14]Feucht A,Lewis PJ. Improved plasmid vectors for the production of multiple fluorescent protein fu sions inBacillussubtilis[J]. Gene,2001,264(2):289-297.
[15]Guérout-Fleury AM,Frandsen N,Stragier P. Plasmids for ectopic integration inBacillussubtilis[J].Gene,1996,180(1):57-61.
[16]Nagarajan V,Albertson H,Chen M,et al. Modular expression and secretion vectors for Bacillus subtili[J]. Gene,1992,114(1):121-126.
[17]Wu SC,Wong SL. Development of improved pUB110-based vect ors for expression and secretion studies inBacillussubtilis[J].Journal of Biotechnology,1999,72(3):185-195.
[18]Wang LF,Wong SL,Lee SG,et al. Expres sion and secretion of human atrial natriureticα-factor inBacillussubtilisusing the subtilisin signal peptide[J]. Gene,1988,69(1):39-47.
[19]董晨,曹娟,张迹. 耐高温α-淀粉酶基因在枯草芽孢杆菌中的高效表达[J]. 应用与环境生物学报,2008,14(4):534-538.
[20]Long Liu,Yanfeng Liu,Hyun-dong Shin,et al. DevelopingBacillusspp. as a cell factory for production of microbial enzymes and industrially important biochemicals in the context of systems and synthetic biology[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,2013,97:6113-6127.
[21]Michel S,Dominique L C. The DNA sequence of the gene for the secretedBacillussubtilisenzyme levansucrase and its genetic control sites[J]. Molecular and General Genetics,1985,200:220-228.
[22]周勇,徐刚,杨立荣,等.信号肽优化在枯草芽孢杆菌体系中对脂肪酶分泌表达的影响[J].中国生物工程杂志,2015,35(9):42-49.
[23]Tjalsma H,Bolhuis A,Jongbloed JDH,et al. Signal peptide-dependent protein transport inBacillussubtilis:agenome-based survey of the secretome[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews,2000,64:515-547.
[24]李静静.高产α-乙酰乳酸脱羧酶重组枯草芽孢杆菌的构建及其发酵优化[D].无锡:江南大学,2013:25-44.
[25]丁伟,张明俐,史吉平,等.表达谷氨酸脱羧酶重组枯草芽孢杆菌的构建及其发酵条件的优化[J].生物工程,2015,36(23):194-198.
[26]郭苏. 芽胞杆菌属来源的普鲁兰酶基因的克隆表达及枯草芽孢杆菌表达体系的构建[D]. 上海:华东理工,2012:35-48.
[27]Keith WY Kwong,K L Ng,C C Lam Yule Y Wang,et al. Authentic human basic fibroblast growth factor produced by secretion inBacillussubtilis[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,2013,97:6803-6811.
[28]贾敏,万孟,张涛,等. D-阿洛酮糖 3-差向异构酶基因在枯草芽孢杆菌中的表达[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2014,33(11):1129-1135.
[29]郭德军,李岩松,王欣,等.巨大芽孢杆菌表达系统的特点及其研究进展[J].生物技术,2010,20(6):92-95.
[30]牟琳,王红宁,邹立扣.巨大芽孢杆菌表达外源蛋白的特点及其研究进展[J].中国生物工程杂志,2008,28(4):93-97.
[31]金辉,廖思明,王青艳.碱性α-淀粉酶基因在巨大芽孢杆菌中的表达及酶学性质研究[J]. 生物技术通报,2011(11):154-158.
[32]周海燕,饶力群,吴永尧.甘露聚糖酶man23基因的重组及其在短短芽孢杆菌中的表达[J].浙江大学学报,2008,34(4):389-394.
[33]张杰,宋福平,左雅慧,等.31株苏云金芽孢杆菌杀虫晶体蛋白基因型鉴定及表达产物研究[J]. 微生物学报,2000,40(7):372-377.
[34]陈启民,耿运琪,倪津.短小芽抱杆菌作为芽抱杆菌属基因工程受体菌的研究[J].遗传学报,1989,16(3):206-212.
[35]包怡红,刘伟丰,董志扬.耐碱性木聚糖酶在短小芽孢杆菌中高效分泌表达的研究[J].中国食品学报,2008,8(5):37-43.
[36]Commichau FM,Alzinger A,Sande R,et al. Overexpression of a non-native deoxyxylulose-dependent vitamin B6 pathway inBacillussubtilisfor the production of pyridoxine[J]. Metab Eng,2014,25:38-49.
[37]Zafar M,Ahmed S,Khan MI,et al. Recombinant expression and characterization of a novel endoglucanase fromBacillussubtilisinEscherichiacoli[J]. Molecular Biology Reports,2014,41:3295-302.
[38]Ju Jung,Kyung Ok Yu,Ahmad Bazli Ramzi,et al. Improvement of surfactin production inBacillussubtilisusing synthetic wastewater by overexpression of specific extracellular signaling peptides,comX and phrC[J]. Biotechnol Bioeng,2012,109:2349-2356.
[39]王金斌,陈大超,李文,等.食品级枯草芽孢杆菌表达系统的最新研究进展[J].上海农业学报,2014,30(1):115-120.
[40]Phan TTP,Nguyen HD,Schumann W. Development of a strong intracellular expression system forBacillussubtilisby optimizing promoter elements[J]. Biotechnol,2012,157:167-172.
[41]Zhang Xiao Zhou,Yan Xin,Cui Zhong Li,et al. Recombinant expression and secretion of mpd gene using the promoters of ytkA and ywoF gene fromBacillussubtilis[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology,2006,22(2):249-256.
[42]Shanshan Li,Xiaoqiang Jia,Jianping Wen. Improved 2-methyl-1-propanol production in an engineeredBacillussubtilisby constructing inducible pathways[J].Biotechnol Lett,2012,34:2253-2258.
[43]J Olmos-Soto,R Contreras-Flores.Genetic system constructed toover produce and secrete proinsulin inBacillussubtilis[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotech,2003,62:369-373.
[44]Mauriello,Ducb,Rachele Isticatoa,et al. Display of heterologous antigens on theBacillussubtilisspore coat using CotC as a fusion partner[J].Vaccine,2004,22:1177-1187.
[45]Chengran Guan,Wenjing Cui,Jintao Cheng,et al. Development of an efficient autoinducible expression system by promoter engineering inBacillussubtilis[J].Microbial Cell Factories,2016,15(66):2-12.
[46]Reza Panahi,Ebrahim Vasheghani-Farahani,Seyed Abbas Shojaosadati,et al. Induction ofBacillussubtilisexpression system using environmental stresses and glucose starvation[J]. Ann Microbiol,2014,64:879-882.
[47]毕台飞,胡雄斌,宋巍,等.枯草芽孢杆菌高效表达系统的构建[J].西北农林科技大学学报,2011,39(11):71-79.
[48]Prax M,Lee CY,Bertram R. An update on the molecular genetics toolbox for staphylococci[J]. Microbiol,2013,159:421-435.
[49]Sen-Lin Liu,Kun Du. Enhanced expression of an endoglucanase inBacillussubtilisby using the sucrose-inducible sacB promoter and improved properties of the recombinant enzyme[J]. Protein Expression and Purification,2012,83:164-168.
[50]Westers H,Dorenbos R,Dijl J M. Genome engineering reveals large dispensable regions inBacillussubtilis[J].Mol Biol Evol,2003,20(12):2076-2090.
[51]Cui W,Han L,Cheng J,et al. Engineering an inducible gene expression system forBacillussubtilisfrom a strong constitutive promoter and a theophylline-activated synthetic riboswitch[J]. Microbial Cell Factories,2016,15(1):199.
[52]Bambai RPEV-FSASB. Auto-inducible expression system based on the SigB-dependent ohrB promoter inBacillussubtilis[J]. Ann Microbiol,2014(64):879-82.
[53]Phan TT,Tran LT,Schumann W,et al. Development of Pgrac100-based expression vectors allowing high protein production levels inBacillussubtilisand relatively low basal expression inEscherichiacoli[J]. Microbial Cell Factories,2015:14-72.
[54]Toshitaka Minetoki HT,Akio Koda,Kenji Ozeki,et al. Development of high expression system with the improved promoter using the cis-acting element inAspergillusspecies[J]. J Biol Macromol,2003,3(3):89-96.
[55]Hernandez-Garcia CM,Finer JJ. A novel cis-acting element in the GmERF3 promoter contributes to inducible gene expression in soybean and tobacco after wounding[J]. Plant Cell Reports,2016,35(2):303-316.
[56]Guan C,Cui W,Cheng J,et al. Development of an efficient autoinducible expression system by promoter engineering inBacillussubtilis[J]. Microbial Cell Factories,2016,15:60-66.
[57]Liu B,Zhang J,Li B,et al. Expression and characterization of extreme alkaline,oxidation-resistant keratinase fromBacilluslicheniformisin recombinantBacillussubtilisWB600 expression system and its application in wool fiber processing[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology,2013,29(5):825-832.
[58]Cheng J,Guan C,Cui W,et al. Enhancement of a high efficient autoinducible expression system inBacillussubtilisby promoter engineering[J]. Protein Expression and Purification,2016,127:81-87.
[59]Bongers RS,Veening JW,Van Wieringen M,et al. Development and characterization of a subtilin-regulated expression system inBacillussubtilis:strict control of gene expression by addition of subtilin[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2005,71(12):8813-8826.
[60]Guan C,Cui W,Cheng J,et al. Construction and development of an auto-regulatory gene expression system in Bacillus subtilis[J]. Microbial Cell Factories,2015,14:8818-8824.
[61]Tobias Küppers1 VS,Hendrik Hellmuth1,Timothy O’Connell1,et al. Developing a new production host from a blueprint:Bacilluspumilusas an industrial enzyme producer[J]. Microbial Cell Factories,2014;44(13):2-15.
[62]Chen J,Zhu Y,Fu G,et al. High-level intra-and extra-cellular production of D-psicose 3-epimerase via a modified xylose-inducible expression system inBacillussubtilis[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology,2016,43(11):1577-1591.
[63]Guan C,Cui W,Cheng J,et al. Construction and development of an auto-regulatory gene expression system inBacillussubtilis[J]. Microbial Cell Factories,2015,14:150.
[64]Tobias Küppers,Victoria Steffen,Hendrik Hellmuth. Developing a new production host from a blueprint:Bacilluspumilusas an industrial enzyme producer[J]. Microbial Cell Factories,2014,44(13).
[65]Chen J,Jin Z,Gai Y,et al. A food-grade expression system for d-psicose 3-epimerase production inBacillussubtilisusing an alanine racemase-encoding selection marker[J]. Bioresources and Bioprocessing,2017,4(1):9.
[66]Thomas Rygus WH. Inducible high-level expression of heterologous genes inBacillusmegateriumusing the regulatory elements of the xylose-utilization operon[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,1991(35):594-599.
[67]T Rygus AS,R Allmansberger, W Hillen. Molecular cloning,structure,promoters and regulatory elements for transcription of theBacillusmegateriumencoded regulon for xylose utilization[J].Arch Microbiol,1991(155):535-542.
[68]Peng DH,Pang CY,Wu H. The expression and crystallization of Cry65Aa require two C-termini,revealing a novel evolutionary strategy ofBacillusthuringiensisCry proteins[J]. Scientific Reports,2015,5:8291.
ThecharactersandadvancesofBacillusexpressionsystem
MIAOMiao,HUANGKun-lun,LIANGZhi-hong*
(College of Food Science and Nutritional Engineering,China Agricultural University,Beijing 100083,China)
TS201
A
1002-0306(2017)18-0312-06
2017-02-13
苗苗(1995-),女,硕士研究生,研究方向:食品工程,E-mail:17801136541@163.com。
*通讯作者:梁志宏(1969-),女,博士,副教授,研究方向:微生物与食品安全,E-mail:lzh105@cau.edu.cn。
国家自然科学基金(31671947)。
10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2017.18.059
